How to see how much RAM you have is crucial for optimizing your computer’s performance. Knowing your RAM capacity and usage helps you identify potential bottlenecks and make informed decisions about upgrades. At HOW.EDU.VN, we provide expert guidance to help you understand your system’s memory and improve its efficiency.
1. Understanding RAM and Its Importance
Random Access Memory (RAM) is a vital component of your computer. It temporarily stores data that your CPU needs to access quickly. Unlike your hard drive or SSD, which stores data long-term, RAM provides rapid access to information, significantly impacting your system’s responsiveness and multitasking capabilities.
1.1. What is RAM?
RAM is volatile memory, meaning it loses its data when the power is turned off. It acts as a short-term storage space for the operating system, applications, and data currently in use. The more RAM you have, the more data your computer can keep readily available, reducing the need to access slower storage devices.
1.2. Why is Knowing Your RAM Important?
Knowing how much RAM you have is essential for several reasons:
- Performance Optimization: Insufficient RAM can cause your computer to slow down, especially when running multiple applications or handling large files.
- Upgrade Decisions: Understanding your RAM usage helps you determine if you need to upgrade to improve performance.
- Troubleshooting: Identifying RAM issues can help you diagnose and fix system problems like crashes or freezes.
- Software Compatibility: Some applications and games require a specific amount of RAM to run smoothly.
1.3. RAM vs. Storage (HDD/SSD)
It’s crucial to differentiate between RAM and storage devices like Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) or Solid State Drives (SSDs). RAM is for short-term data access, while HDDs and SSDs are for long-term storage.
| Feature | RAM | HDD/SSD |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Short-term data access | Long-term data storage |
| Volatility | Volatile (data lost when power is off) | Non-volatile (data persists) |
| Speed | Very fast | Slower than RAM |
| Capacity | Typically smaller (e.g., 8GB, 16GB) | Typically larger (e.g., 500GB, 1TB) |
| Cost | More expensive per gigabyte | Less expensive per gigabyte |
| Data Access | Random | Sequential (HDD) or Random (SSD) |
| Common Use | Running applications, caching data | Storing files, operating system |
| Impact on Speed | High impact on system responsiveness | Impact on boot times and file loading |

1.4. Common RAM Terminology
Understanding RAM terminology can help you better grasp its specifications and performance capabilities:
- Capacity: The total amount of RAM available, usually measured in gigabytes (GB).
- Speed: The rate at which RAM can transfer data, measured in megahertz (MHz).
- Type: The generation of RAM technology, such as DDR3, DDR4, or DDR5.
- Latency: The delay between a command and the availability of data, measured in clock cycles or nanoseconds (ns).
- Dual/Quad Channel: Configurations that allow the CPU to access multiple RAM modules simultaneously, increasing bandwidth.
- SODIMM: Small Outline Dual Inline Memory Module, used in laptops and small form-factor PCs.
- DIMM: Dual Inline Memory Module, used in desktop computers.
2. How to Check RAM on Windows
Checking your RAM on Windows is a straightforward process. The steps vary slightly depending on the version of Windows you are using.
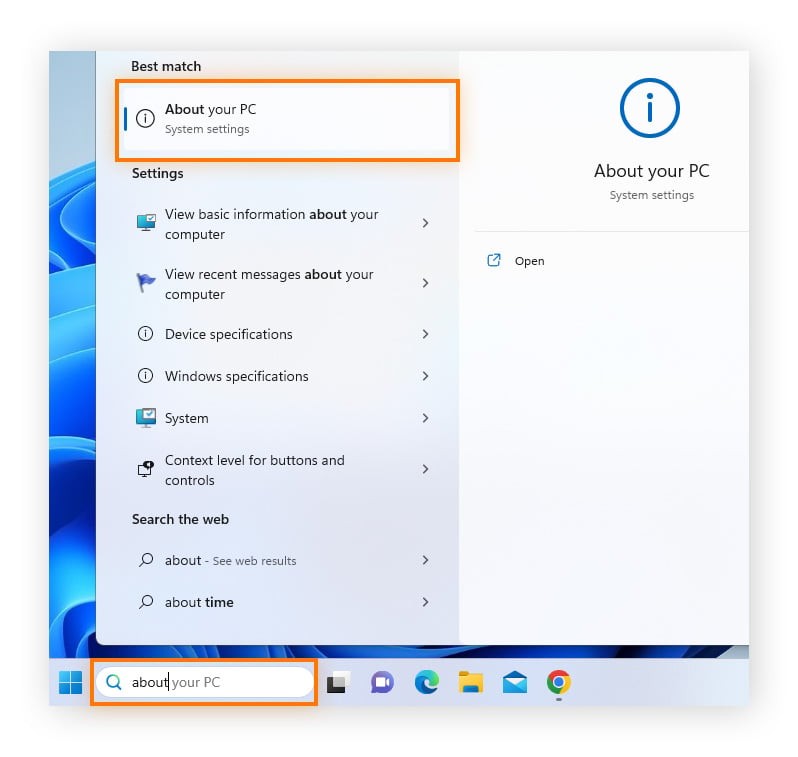
2.1. Checking RAM on Windows 11
Windows 11 provides a simple way to check your RAM:
- Open Settings: Click on the Start menu and select the Settings icon (gear icon).
- Navigate to System: In the Settings window, click on “System.”
- Select About: Scroll down and click on “About.”
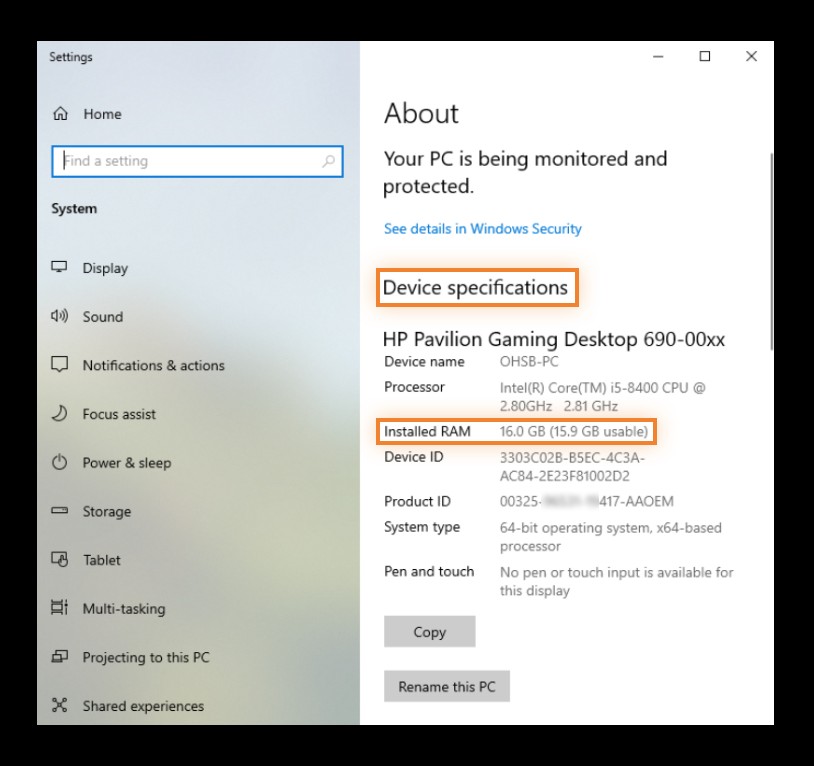
- View Installed RAM: Under the “Device specifications” section, you will find “Installed RAM,” which shows the total amount of RAM installed on your system.
2.2. Checking RAM on Windows 10
The process is similar on Windows 10:
- Open Settings: Click on the Start menu and select the Settings icon.
- Navigate to System: In the Settings window, click on “System.”
- Select About: In the left sidebar, click on “About.”
- View Installed RAM: Under the “Device specifications” section, you will find “Installed RAM,” indicating the total RAM capacity.
2.3. Checking RAM on Windows 7
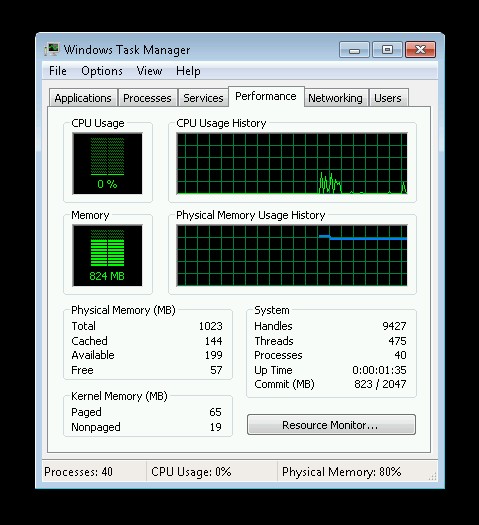
For those still using Windows 7, you can use Task Manager:
- Open Task Manager: Press
Ctrl + Shift + Escto open Task Manager. Alternatively, right-click on the Taskbar and select “Task Manager.” - Select Performance Tab: In Task Manager, click on the “Performance” tab.
- View Memory Information: In the “Memory” section, you will see the total RAM capacity listed under “Physical Memory.”
3. How to Check RAM Type on PC
Knowing the type of RAM your computer uses is important when considering upgrades, as different RAM types are not compatible with each other.
3.1. Why Check RAM Type?
- Compatibility: Ensuring that new RAM is compatible with your motherboard.
- Performance: Different RAM types offer varying levels of performance.
- Upgradability: Understanding the maximum RAM type supported by your system.
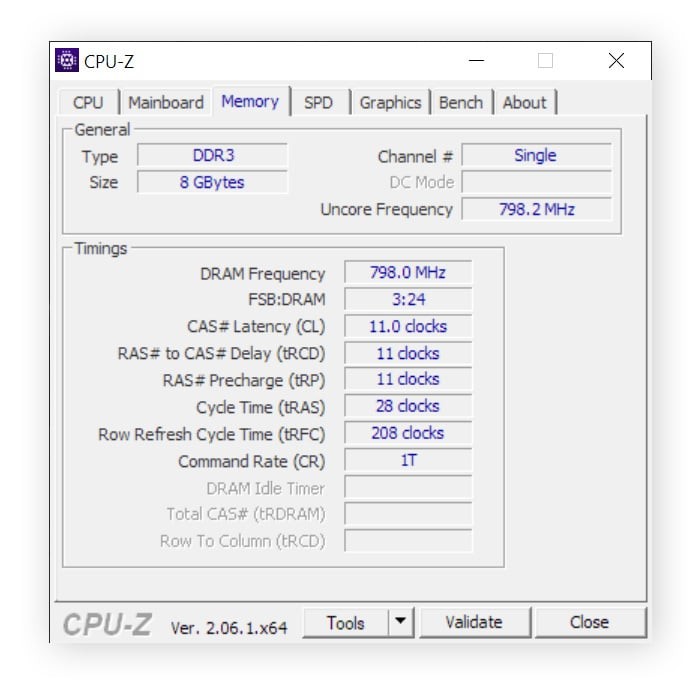
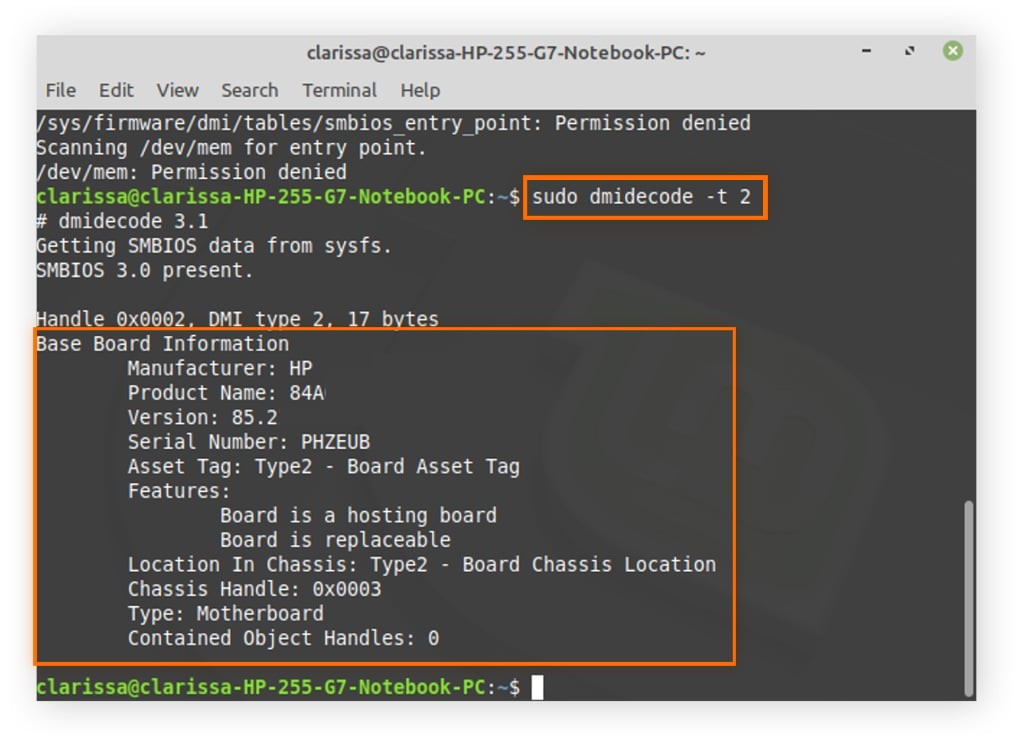
3.2. Using CPU-Z to Check RAM Type
CPU-Z is a free, third-party tool that provides detailed information about your system’s hardware, including the RAM type:
- Download CPU-Z: Download CPU-Z from the official website: CPU-Z.
- Install CPU-Z: Run the downloaded file and follow the installation instructions.
- Launch CPU-Z: Open the CPU-Z application.
- Navigate to Memory Tab: Click on the “Memory” tab.
- View Memory Type: Under the “General” section, you will find the “Type” field, which displays the RAM type (e.g., DDR3, DDR4, DDR5).
3.3. Understanding DDR Generations
DDR (Double Data Rate) RAM has evolved through several generations, each offering improved speed and efficiency:
| DDR Generation | Peak Transfer Rate (MT/s) | Voltage (V) | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| DDR3 | 800 – 2133 | 1.5 | Lower power consumption than DDR2 |
| DDR4 | 2133 – 4800 | 1.2 | Higher density and lower voltage than DDR3 |
| DDR5 | 4800 – 8400+ | 1.1 | Increased bandwidth and efficiency over DDR4 |
4. How to Check RAM Usage on Windows
Monitoring your RAM usage helps you understand how your computer is utilizing its memory resources and identify potential bottlenecks.
4.1. Using Task Manager
Task Manager provides real-time information about RAM usage:
- Open Task Manager: Press
Ctrl + Shift + Escto open Task Manager. - Select Performance Tab: Click on the “Performance” tab.
- Click Memory: In the left sidebar, click on “Memory.”
- View RAM Usage: The right pane displays detailed information about RAM usage, including:
- Total Physical Memory: The total amount of RAM installed.
- Available Memory: The amount of RAM currently available.
- Cached Memory: The amount of RAM used for caching frequently accessed data.
- Commit Charge: The total amount of virtual memory in use.
- Memory Composition: Graphical representation of memory usage.
4.2. Identifying Memory-Intensive Processes
The “Processes” tab in Task Manager allows you to see which applications are using the most RAM:
- Open Task Manager: Press
Ctrl + Shift + Escto open Task Manager. - Select Processes Tab: Click on the “Processes” tab.
- Sort by Memory: Click on the “Memory” column header to sort processes by RAM usage.
- Identify Resource-Intensive Apps: Identify which applications are consuming the most RAM.
4.3. Freeing Up RAM
If your computer is running low on RAM, you can free up memory by:
- Closing Unused Applications: Close any applications that you are not currently using.
- Ending Unnecessary Processes: In Task Manager, end any processes that are consuming significant RAM but are not essential.
- Disabling Startup Programs: Disable programs that automatically start when your computer boots up.
- Using Optimization Tools: Use system optimization tools like Avast Cleanup to free up RAM and improve performance.
5. How to Check RAM on macOS
Checking RAM information on macOS is also a simple process, allowing you to monitor your system’s memory usage and performance.
5.1. Checking Total RAM Capacity
To find out how much RAM is installed on your Mac:
- Open Apple Menu: Click on the Apple icon in the top-left corner of the screen.
- Select About This Mac: Click on “About This Mac.”
- View Memory Information: In the “Overview” tab, you will see the amount of RAM listed next to “Memory.”
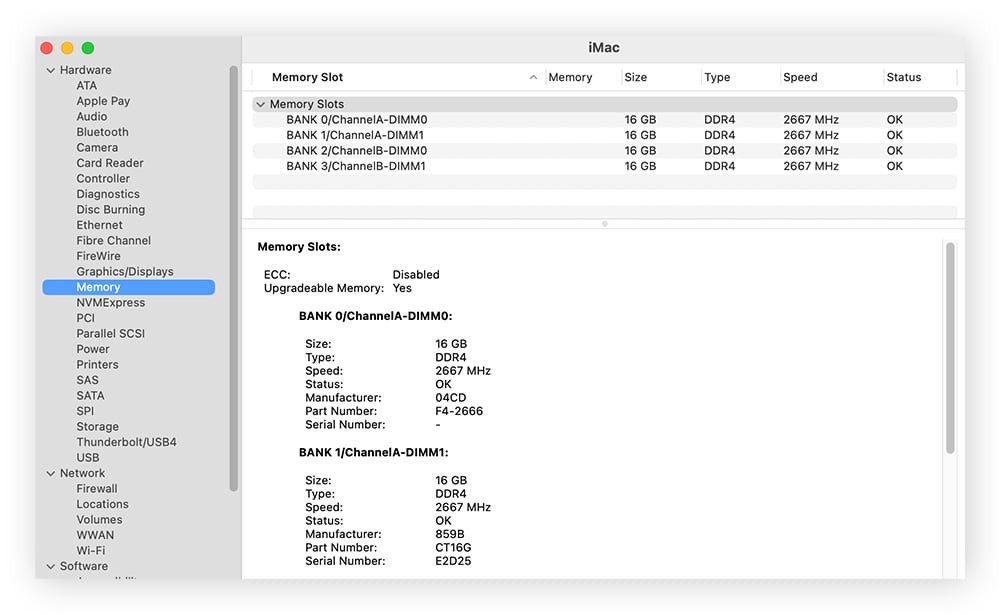
5.2. Checking RAM Type on macOS
To check the RAM type on your Mac:
- Open Spotlight Search: Press
Cmd + Spaceto open Spotlight search. - Type System Information: Type “System Information” and press Enter.
- Select Memory: In the left sidebar, click on “Memory.”
- View Memory Details: The right pane displays detailed information about your RAM, including the type, speed, and size of each module.
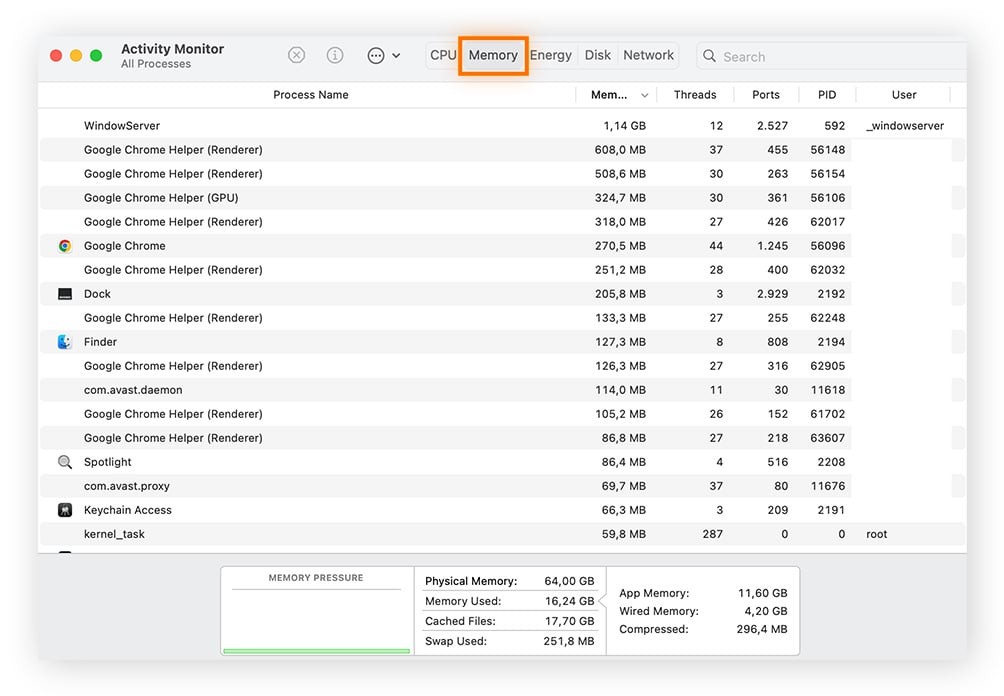
5.3. Checking RAM Usage on macOS
To monitor RAM usage on your Mac:
- Open Finder: Click on the Finder icon in the Dock.
- Navigate to Utilities: Click on “Go” in the menu bar, then select “Utilities.”
- Open Activity Monitor: Double-click on “Activity Monitor.”
- Select Memory Tab: Click on the “Memory” tab.
- View RAM Usage: The Memory tab displays real-time information about RAM usage, including:
- Memory Used: The total amount of RAM being used.
- Cached Files: The amount of RAM used for caching files.
- Swap Used: The amount of disk space being used as virtual memory.
- App Memory: The amount of RAM being used by applications.
- Wired Memory: The amount of RAM being used by the system kernel and drivers.
- Free Memory: The amount of RAM available.
5.4. Interpreting macOS Memory Usage
Understanding the different categories of memory usage in Activity Monitor can help you identify potential issues:
- High Memory Used: Indicates that your system is using a significant portion of its RAM, which could lead to slowdowns.
- High Swap Used: Indicates that your system is relying heavily on virtual memory, which can significantly impact performance.
- High App Memory: Indicates that specific applications are consuming a large amount of RAM.
- Low Free Memory: Indicates that your system has little RAM available for new tasks.
6. Determining If You Need to Upgrade Your RAM
Deciding whether to upgrade your RAM depends on your computer usage and performance needs.
6.1. Signs You Need More RAM
- Slow Performance: Your computer takes a long time to open applications or switch between tasks.
- Frequent Freezing: Your computer freezes or becomes unresponsive frequently.
- Error Messages: You receive error messages indicating that you are running out of memory.
- High Disk Activity: Your hard drive is constantly working, indicating that your system is using virtual memory excessively.
- Struggling with Multitasking: Your computer slows down significantly when running multiple applications simultaneously.
6.2. How Much RAM Do You Need?
The amount of RAM you need depends on your typical usage:
| Use Case | Recommended RAM |
|---|---|
| Basic Tasks (Web Browsing, Word Processing) | 8 GB |
| General Use (Multitasking, Light Gaming) | 16 GB |
| Gaming and Content Creation | 32 GB |
| Professional Workstations | 64 GB or more |
6.3. Impact of Upgrading RAM
Upgrading RAM can significantly improve your computer’s performance by:
- Reducing Lag: Providing more memory for applications to run smoothly.
- Improving Multitasking: Allowing you to run more applications simultaneously without slowdowns.
- Enhancing Gaming Performance: Enabling smoother gameplay and faster load times.
- Supporting Resource-Intensive Tasks: Making it easier to handle tasks like video editing, 3D rendering, and software development.
7. Checking Your Memory for Errors
Memory errors can cause system instability, crashes, and data corruption. It’s important to periodically check your RAM for errors.
7.1. Using Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool
Windows includes a built-in memory diagnostic tool:
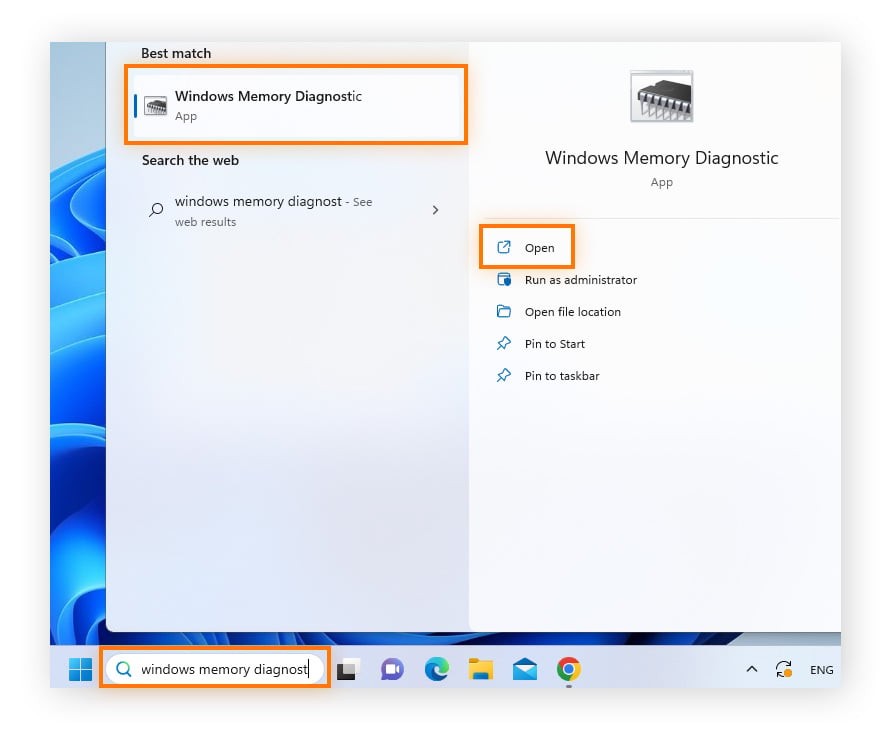
- Open Windows Memory Diagnostic: Type “Windows Memory Diagnostic” in the search bar and select the “Windows Memory Diagnostic” option.
- Restart and Check: Choose the option to “Restart now and check for problems.”
- Wait for the Test: Your computer will restart and perform a memory test.
- View Results: After the test is complete, your computer will restart again, and the results will be displayed in the notification area or Event Viewer.
7.2. Interpreting Memory Diagnostic Results
If the memory diagnostic tool detects errors, it indicates that there is a problem with your RAM. You should consider replacing the faulty RAM module to prevent further issues.
8. Optimizing RAM Usage
Even with sufficient RAM, optimizing its usage can improve your computer’s performance.
8.1. Closing Unnecessary Programs
Close any programs that you are not currently using to free up RAM.
8.2. Disabling Startup Programs
Disable programs that automatically start when your computer boots up to reduce RAM usage at startup.
8.3. Managing Browser Tabs
Having too many browser tabs open can consume a significant amount of RAM. Close unnecessary tabs to free up memory.
8.4. Using System Optimization Tools
System optimization tools like Avast Cleanup can help you identify and remove junk files, disable unnecessary startup programs, and optimize RAM usage.
8.5. Monitoring Performance Regularly
Regularly monitor your RAM usage and performance to identify potential issues and optimize your system.
9. Expert Consultation at HOW.EDU.VN
At HOW.EDU.VN, we understand the complexities of computer hardware and performance optimization. Our team of expert doctors and specialists is available to provide personalized guidance and support to help you maximize your system’s potential.
9.1. Connecting with Experts
If you are experiencing performance issues or need advice on upgrading your RAM, we encourage you to connect with our experts. Our team can provide tailored recommendations based on your specific needs and usage patterns.
9.2. Personalized Guidance
We offer personalized guidance on:
- Assessing Your RAM Needs: Determining the optimal amount of RAM for your specific usage.
- Choosing Compatible RAM: Selecting RAM modules that are compatible with your motherboard and system.
- Optimizing RAM Usage: Providing tips and tools to optimize your RAM usage and improve performance.
- Troubleshooting Memory Issues: Diagnosing and resolving memory-related problems.
9.3. Benefits of Expert Consultation
- Expert Advice: Receive advice from experienced professionals with in-depth knowledge of computer hardware.
- Tailored Recommendations: Get personalized recommendations based on your specific needs and budget.
- Time Savings: Save time and effort by getting the right advice from the start.
- Improved Performance: Maximize your computer’s performance and efficiency.
10. Success Stories and Case Studies
To illustrate the benefits of expert consultation, consider the following success stories:
10.1. Case Study 1: Gaming Enthusiast
A gaming enthusiast was experiencing poor performance and frequent crashes while playing the latest games. After consulting with our experts at HOW.EDU.VN, they discovered that their system had only 8 GB of RAM, which was insufficient for modern gaming. We recommended upgrading to 16 GB of RAM, which significantly improved their gaming performance and eliminated the crashes.
10.2. Case Study 2: Video Editor
A video editor was struggling with slow performance and frequent delays while editing large video files. Our experts at HOW.EDU.VN determined that their system’s RAM was insufficient for the demands of video editing. We recommended upgrading to 32 GB of RAM, which dramatically improved their editing workflow and reduced rendering times.
10.3. Case Study 3: Business Professional
A business professional was experiencing slowdowns and delays while multitasking between multiple applications. Our experts at HOW.EDU.VN found that their system’s RAM was being heavily utilized, leading to performance issues. We recommended upgrading to 16 GB of RAM, which improved their multitasking capabilities and increased their productivity.
11. Call to Action
Don’t let insufficient or poorly optimized RAM hinder your computer’s performance. Contact the experts at HOW.EDU.VN today for personalized guidance and support. Whether you need help assessing your RAM needs, choosing compatible RAM modules, optimizing RAM usage, or troubleshooting memory issues, our team is here to help.
- Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
- Website: HOW.EDU.VN
Take control of your computer’s performance and unlock its full potential with HOW.EDU.VN.
12. FAQs
12.1. Do I need 8 GB or 16 GB RAM?
Whether you need 8 GB or 16 GB of RAM depends on your usage. 8 GB is sufficient for basic tasks like web browsing and word processing, while 16 GB is recommended for multitasking, light gaming, and content creation.
12.2. How much RAM can my PC take?
The maximum amount of RAM your PC can take depends on the motherboard. Consult your motherboard’s documentation or manufacturer’s website for specifications.
12.3. Will 32 GB RAM be faster than 16 GB?
In most cases, 32 GB of RAM will not be noticeably faster than 16 GB for general tasks. However, if you use memory-intensive applications like video editing software, you may see a performance improvement.
12.4. Can too much RAM slow down my computer?
No, too much RAM will not slow down your computer. However, it may be unnecessary if you don’t use applications that require it.
12.5. Will upgrading to 32 GB of RAM make a difference?
Upgrading to 32 GB of RAM can make a difference if you use memory-intensive applications like video editing or 3D rendering software. If you primarily use your computer for basic tasks, you may not see a significant performance improvement.
12.6. What is the best way to check RAM usage on Windows?
The best way to check RAM usage on Windows is to use Task Manager. Open Task Manager by pressing Ctrl + Shift + Esc, then click on the “Performance” tab and select “Memory.”
12.7. How can I free up RAM on my computer?
You can free up RAM by closing unused applications, disabling startup programs, managing browser tabs, and using system optimization tools like Avast Cleanup.
12.8. What does “swap used” mean on macOS Activity Monitor?
“Swap used” refers to the amount of disk space being used as virtual memory. When your system runs out of RAM, it uses the hard drive or SSD as temporary memory. High swap usage indicates that your system is relying heavily on virtual memory, which can significantly impact performance.
12.9. How often should I check my RAM for errors?
You should check your RAM for errors periodically, especially if you are experiencing system instability, crashes, or data corruption. A good practice is to run the Windows Memory Diagnostic tool or other memory testing software every few months.
12.10. What should I do if the memory diagnostic tool detects errors?
If the memory diagnostic tool detects errors, it indicates that there is a problem with your RAM. You should consider replacing the faulty RAM module to prevent further issues. Consult with our experts at how.edu.vn for personalized guidance and support.