Navigating the nuances of caffeine content in chocolate can be perplexing, with levels varying based on cacao origin and chocolate type; however, understanding these variations is key. At HOW.EDU.VN, we decode these complexities, offering clarity on caffeine levels, the influence of theobromine, and the entourage effect, ensuring you’re well-informed about your favorite treat. Delve into the factors influencing caffeine levels, explore the entourage effect, and uncover the caffeine content in various chocolate types.
1. Understanding Caffeine and Other Stimulants in Chocolate
Chocolate contains three naturally occurring stimulants: theobromine, caffeine, and theophylline. These compounds, known as xanthines, are produced by plants like cacao trees to ward off insects. Xanthines can paralyze or kill insects, but in humans, they offer benefits such as improved cognitive function, reduced risk of Alzheimer’s and cardiovascular disease, and protection against tooth decay.
1.1 The Role of Xanthines
Xanthines play a crucial role in the stimulating effects of chocolate. They affect our bodies by:
- Improving Cognitive Function: Enhancing alertness and mental performance.
- Reducing Health Risks: Providing protection against neurodegenerative and cardiovascular diseases.
- Protecting Tooth Enamel: Helping to prevent tooth decay.
1.2 Different Types of Xanthines
Each xanthine has a unique effect on the body:
- Theobromine: A milder stimulant than caffeine, providing a longer-lasting, gentler energy boost.
- Caffeine: A well-known stimulant that increases alertness and reduces fatigue.
- Theophylline: A less potent stimulant found in smaller amounts in chocolate.
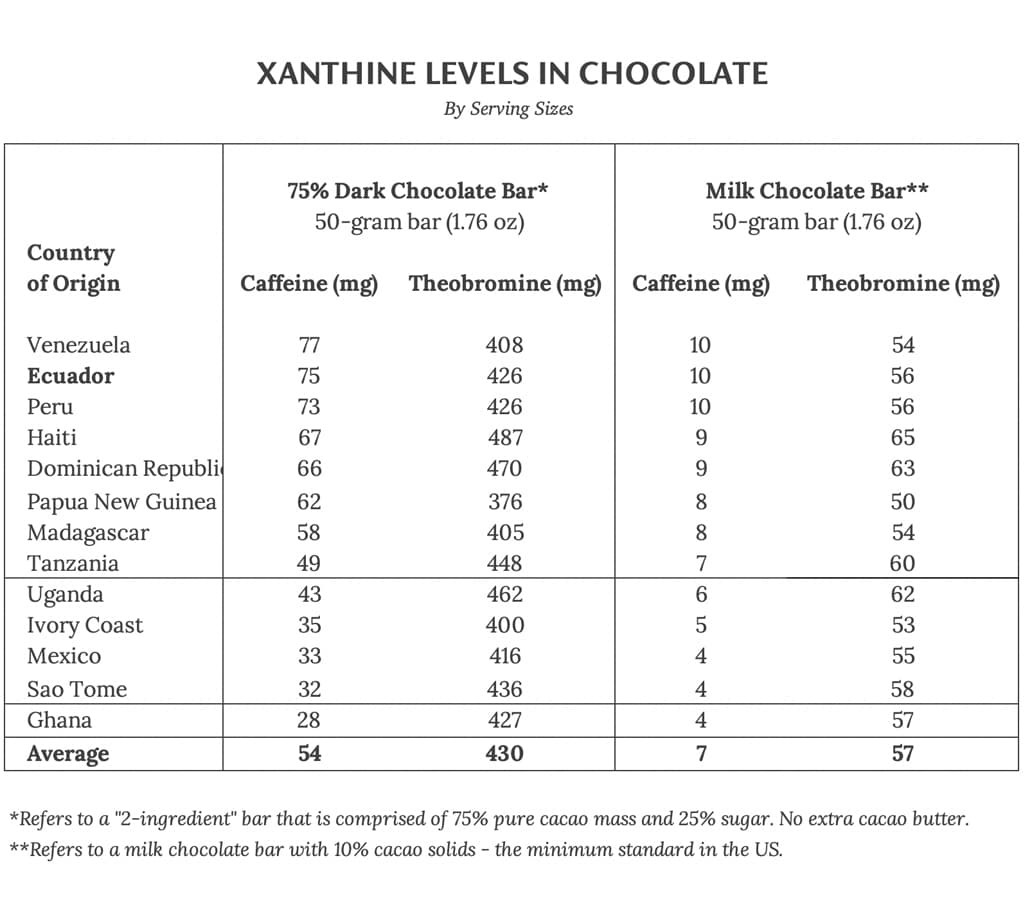
2. How Caffeine Levels Vary by Cacao Origin
Caffeine levels in cacao vary significantly depending on where the cacao is grown. A comprehensive research report, “Measurement of theobromine content in cocoa for determining cocoa solids content in chocolate,” tested over 200 cacao samples from 26 countries and revealed significant differences.
2.1 Key Findings from the Research Report
The research report highlighted several key differences in caffeine levels:
- Geographical Variation: Cacao from South America and the Caribbean generally has more caffeine than African cacao.
- Specific Countries: The most caffeinated cacao comes from Ecuador, Venezuela, and Peru.
- Least Caffeinated: The least caffeinated cacao comes from West African countries and Mexico.
- Significant Differences: Cacao from Ecuador, Venezuela, and Peru has more than twice as much caffeine as cacao from West African countries.
- Theobromine-to-Caffeine Ratio: The average theobromine-to-caffeine ratio is 9 to 1.
2.2 Table of Caffeine Content by Country
| Country | Caffeine Content (mg per 50g of 100% Dark Chocolate) |
|---|---|
| Ecuador | 75-150 mg |
| Venezuela | 70-140 mg |
| Peru | 65-130 mg |
| Dominican Republic | 40-80 mg |
| Ghana | 30-60 mg |
| Ivory Coast | 25-50 mg |
| Mexico | 20-40 mg |

2.3 Factors Influencing Xanthine Levels
Country of origin isn’t the only factor. Studies in Ecuador show that cacao harvested in the dry season has 15–23% more caffeine and 8–12% more theobromine than cacao harvested in the rainy season. Roasting does not alter caffeine levels.
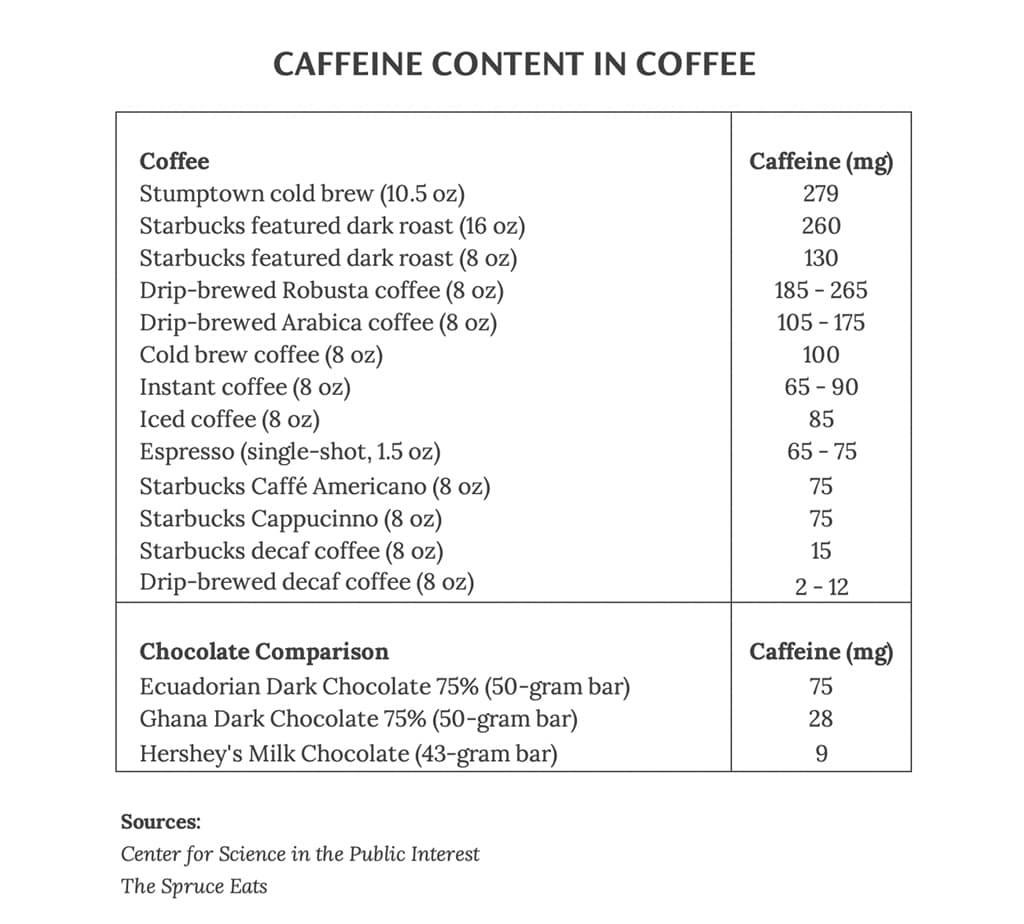
3. Caffeine Content Compared to Coffee
A 50-gram bar of 75% Ecuadorian dark chocolate has roughly the same amount of caffeine (75 mg) as a single shot of espresso or a Starbucks cappuccino. However, the effect is different due to the “entourage effect” between caffeine, theobromine, and other psychoactive compounds.
3.1 Caffeine in Coffee
The amount of caffeine in coffee varies significantly depending on the preparation method. Key parameters affecting caffeine content are time and volume.
- Ristretto and Cold Brew: These have the highest amount of caffeine.
- Preparation Method: affects the caffeine content in coffee
- Time and Volume: are the most important parameters
3.2 Table of Caffeine Content in Different Coffee Drinks
| Coffee Drink | Caffeine Content (mg) |
|---|---|
| Espresso (Single) | 75 mg |
| Cappuccino | 75 mg |
| Brewed Coffee (8 oz) | 95-200 mg |
| Cold Brew (8 oz) | 200-300 mg |
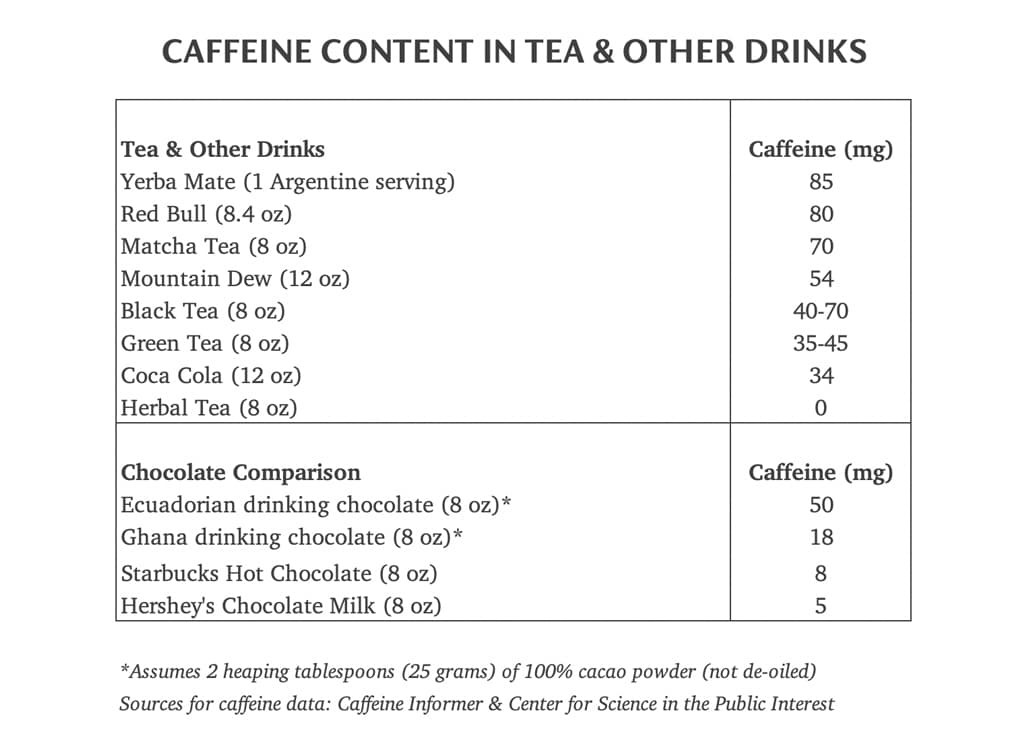
4. Comparing Caffeine Content: Chocolate vs. Tea, Matcha, and Energy Drinks
Understanding how chocolate’s caffeine content stacks up against other popular beverages and products can help you make informed choices about your stimulant intake. Here’s a detailed comparison:
4.1 Caffeine in Tea and Matcha
- Tea: The caffeine content in tea varies widely depending on the type and brewing method. Black tea generally has more caffeine than green or white tea.
- Matcha: Matcha, a powdered green tea, contains a significant amount of caffeine due to the consumption of the entire tea leaf.
4.2 Caffeine in Energy Drinks
- Red Bull: A popular energy drink, Red Bull, contains a moderate amount of caffeine, comparable to a cup of coffee.
4.3 Table Comparing Caffeine Content
| Product | Caffeine Content (mg) |
|---|---|
| Dark Chocolate (50g) | 35-150 mg |
| Black Tea (8 oz) | 40-70 mg |
| Green Tea (8 oz) | 28-38 mg |
| Matcha (1 tsp) | 70 mg |
| Red Bull (8.4 oz) | 80 mg |
5. The Entourage Effect in Chocolate
The “entourage effect” refers to the synergistic interaction between compounds, enhancing their overall impact. In chocolate, this effect involves caffeine, theobromine, terpenes, polyphenols, and endogenous cannabinoids.
5.1 How the Entourage Effect Works
The entourage effect suggests that these compounds, when consumed together, have a greater effect than when consumed alone. A recent psychopharmacology publication, “More than just caffeine: psychopharmacology of methylxanthine interactions with plant-derived phytochemicals,” found that:
Specific sets of constituent compounds such as polyphenols, theobromine and L-theanine appear to enhance mood and cognition effects of caffeine and alleviate negative psychophysiological effects of caffeines.
5.2 Benefits of the Entourage Effect in Chocolate
- Enhanced Mood and Cognition: Polyphenols, theobromine, and L-theanine enhance the mood and cognitive effects of caffeine.
- Reduced Negative Effects: The entourage effect helps alleviate negative effects of caffeine, such as jitters and the midday crash.
- Better Sleep: Consuming caffeine in the form of dark chocolate may lead to better sleep compared to other caffeine sources.
5.3 User-Friendly Experience
Cacao is often considered more user-friendly than coffee due to its overall physiological effects. The entourage effect makes the caffeine in chocolate more manageable, providing a smoother, more sustained energy boost without the harsh side effects.
6. Different Types of Chocolate and Caffeine Levels
The caffeine content in chocolate varies depending on the type of chocolate. Dark chocolate generally has more caffeine than milk chocolate or white chocolate.
6.1 Dark Chocolate
Dark chocolate has the highest caffeine content due to its higher percentage of cacao. The darker the chocolate, the more caffeine it contains.
6.2 Milk Chocolate
Milk chocolate has less caffeine than dark chocolate because it contains milk solids, which dilute the cacao content.
6.3 White Chocolate
White chocolate contains no cacao solids and therefore has no caffeine. It is made from cocoa butter, sugar, and milk solids.
6.4 Table of Caffeine Content by Chocolate Type (per 50g serving)
| Chocolate Type | Caffeine Content (mg) |
|---|---|
| Dark Chocolate (70-85% Cacao) | 50-80 mg |
| Milk Chocolate | 10-20 mg |
| White Chocolate | 0 mg |
7. Deciphering Chocolate Labels for Caffeine Content
Understanding how to read and interpret chocolate labels is essential for managing your caffeine intake. Labels can provide valuable information about the composition of the chocolate, including the percentage of cacao and other ingredients that influence caffeine levels.
7.1 Key Information on Chocolate Labels
- Cacao Percentage: This indicates the amount of cacao solids in the chocolate. A higher percentage generally means more caffeine.
- Ingredients List: Look for ingredients like cacao, cocoa, or cocoa mass, which contribute to the caffeine content.
- Nutritional Information: Some labels provide specific caffeine content per serving, although this is not always mandatory.
7.2 Factors Influencing Caffeine Levels
Several factors can affect the accuracy and reliability of caffeine information on chocolate labels:
- Variability: Caffeine levels can vary due to the origin of the cacao beans and the manufacturing process.
- Label Accuracy: Not all labels provide precise caffeine content, and some may only offer general estimates.
7.3 Tips for Reading Chocolate Labels
- Compare Products: Look at multiple chocolate products to compare caffeine content and make informed choices.
- Check Serving Size: Pay attention to the serving size listed on the label to accurately assess caffeine intake.
- Research Brands: Research chocolate brands known for transparency and accurate labeling practices.
8. Health Benefits and Considerations of Caffeine in Chocolate
Caffeine in chocolate can offer several health benefits, but it’s important to consider potential drawbacks and individual sensitivities.
8.1 Potential Health Benefits
- Improved Alertness: Caffeine can enhance alertness and cognitive function.
- Mood Enhancement: Theobromine and other compounds in chocolate can improve mood.
- Antioxidant Properties: Cacao is rich in antioxidants, which can protect against cell damage.
8.2 Potential Drawbacks
- Insomnia: Caffeine can interfere with sleep if consumed close to bedtime.
- Anxiety: Some people may experience anxiety or jitters from caffeine.
- Dependence: Regular caffeine consumption can lead to dependence.
8.3 Recommendations for Consumption
- Moderate Intake: Consume chocolate in moderation to avoid excessive caffeine intake.
- Timing: Avoid eating chocolate close to bedtime to prevent sleep disturbances.
- Individual Sensitivity: Be mindful of your individual sensitivity to caffeine and adjust consumption accordingly.
9. How Much Caffeine is Too Much? Understanding Safe Limits
Determining a safe amount of caffeine to consume from chocolate involves considering several factors, including individual tolerance, overall health, and the presence of other stimulants in your diet.
9.1 Recommended Daily Caffeine Intake
- General Guidelines: Health authorities generally recommend limiting caffeine intake to 400 milligrams per day for adults.
- Individual Factors: Factors such as body weight, metabolism, and sensitivity to caffeine can influence individual tolerance levels.
9.2 Risks of Excessive Caffeine Consumption
Consuming too much caffeine can lead to various adverse effects:
- Common Symptoms: These include insomnia, anxiety, irritability, and digestive issues.
- Severe Reactions: In rare cases, excessive caffeine intake can result in more severe reactions such as heart palpitations or panic attacks.
9.3 Strategies for Monitoring Caffeine Intake
- Track Consumption: Keep a record of caffeine sources, including chocolate, coffee, tea, and energy drinks, to monitor overall intake.
- Read Labels: Check labels for caffeine content to accurately assess the amount in different products.
- Adjust Intake: Adjust caffeine consumption based on individual responses and tolerance levels to minimize potential adverse effects.
10. Consulting Experts for Personalized Advice
Navigating the complexities of caffeine intake, especially in relation to specific health conditions or concerns, often requires personalized advice from qualified experts. Consulting with professionals can provide tailored guidance and ensure informed decision-making.
10.1 Benefits of Expert Consultation
- Personalized Guidance: Experts can assess individual health profiles and provide tailored recommendations based on specific needs and concerns.
- Informed Decisions: Professional advice can help individuals make informed decisions about caffeine consumption and lifestyle adjustments.
10.2 How HOW.EDU.VN Can Help
At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with leading experts who can address your specific questions and concerns about caffeine intake and its effects on your health. Our team of over 100 Ph.D.s offers personalized consultations to help you make informed decisions.
10.3 Connect with Our Experts
- Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
- Website: HOW.EDU.VN
For those seeking clarity and personalized advice, HOW.EDU.VN is your trusted resource.
FAQ Section
1. How much caffeine is in dark chocolate compared to milk chocolate?
Dark chocolate generally has more caffeine than milk chocolate due to its higher cacao content. A 50g serving of dark chocolate can contain between 50-80 mg of caffeine, while the same amount of milk chocolate has around 10-20 mg.
2. Does the origin of cacao beans affect the caffeine content in chocolate?
Yes, the origin of cacao beans significantly impacts caffeine content. Cacao from South America and the Caribbean tends to have more caffeine than cacao from West African countries.
3. Is there caffeine in white chocolate?
No, white chocolate does not contain caffeine as it is made from cocoa butter, sugar, and milk solids, without any cacao solids.
4. How does caffeine in chocolate compare to caffeine in coffee?
A 50-gram bar of 75% Ecuadorian dark chocolate has roughly the same amount of caffeine (75 mg) as a single shot of espresso or a Starbucks cappuccino.
5. What is the “entourage effect” in relation to chocolate?
The “entourage effect” refers to the synergistic interaction between caffeine, theobromine, terpenes, polyphenols, and endogenous cannabinoids in chocolate, enhancing their overall impact and reducing negative side effects.
6. What are the health benefits of caffeine in chocolate?
Caffeine in chocolate can improve alertness, enhance mood, and provide antioxidant benefits due to the presence of cacao.
7. What are the potential drawbacks of consuming caffeine in chocolate?
Potential drawbacks include insomnia, anxiety, and dependence, especially with excessive consumption.
8. How can I monitor my caffeine intake from chocolate?
Track your chocolate consumption, read labels for caffeine content, and be mindful of your individual sensitivity to caffeine.
9. What is a safe amount of caffeine to consume daily?
Health authorities generally recommend limiting caffeine intake to 400 milligrams per day for adults.
10. Can consulting an expert help with managing caffeine intake?
Yes, consulting experts can provide personalized guidance based on individual health profiles and specific needs.
Are you finding it challenging to navigate the nuances of caffeine in chocolate and its impact on your health? Do you seek personalized advice tailored to your unique needs and concerns? Don’t let uncertainty hold you back. Connect with our team of over 100 Ph.D.s at HOW.EDU.VN today and receive expert guidance to make informed decisions about your dietary choices. Contact us at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States, WhatsApp us at +1 (310) 555-1212, or visit our website at how.edu.vn for personalized consultations that prioritize your well-being.