Creatine, a well-researched supplement, offers numerous benefits for women, but understanding the right dosage is key. This article, brought to you by HOW.EDU.VN, provides a comprehensive guide on how much creatine a woman should take, exploring its impact on performance, body composition, mood, and overall health. Discover the optimal creatine dosage for women to maximize its effectiveness and safety. Delve into creatine supplementation, muscle growth, and athletic performance.
1. What is the Appropriate Creatine Dosage for Women?
The appropriate creatine dosage for women varies depending on their goals and stage of life. Generally, a loading phase of 0.3g/kg of body weight per day for 5-7 days, followed by a maintenance dose of 3-5g per day, is effective for increasing muscle creatine stores. Understanding creatine supplementation, athletic performance, and muscle strength are key.
Creatine is a naturally occurring compound found in muscle cells, and it plays a vital role in energy production during high-intensity activities. While the body produces some creatine on its own, supplementation can help increase muscle creatine stores, leading to improved performance and other health benefits.
1.1 Creatine Loading Phase: Is it Necessary?
The loading phase is a common strategy to rapidly increase muscle creatine levels. It involves taking a higher dose of creatine for a short period, typically 5-7 days. For women, this usually means consuming about 0.3 grams of creatine per kilogram of body weight each day, divided into several doses throughout the day.
For example, a 60kg woman would take 18 grams of creatine per day (60 kg x 0.3g/kg = 18g). This could be divided into four doses of 4.5 grams each, taken at different times of the day.
The primary benefit of the loading phase is that it saturates the muscles with creatine more quickly than a lower, consistent dose. This can lead to faster improvements in strength, power, and muscle size. Some studies suggest that creatine loading can increase total muscle creatine concentrations by as much as 19%.
However, a loading phase is not strictly necessary. Consistent daily supplementation with a lower dose of creatine, such as 3-5 grams per day, will also increase muscle creatine stores over time. It just takes longer, typically around 3-4 weeks, to achieve the same level of saturation.
The choice between loading and consistent dosing depends on individual preferences and goals. If rapid results are desired, a loading phase may be beneficial. If there’s no rush, a lower, consistent dose may be more comfortable and easier to manage.
1.2 Creatine Maintenance Dose: Sustaining Muscle Creatine Levels
Once muscle creatine stores are saturated, a maintenance dose is needed to sustain those levels. For women, the recommended maintenance dose is typically 3-5 grams of creatine per day. This dose helps to offset the natural breakdown of creatine and keeps the muscles fully loaded.
The maintenance dose is crucial for long-term benefits, such as continued improvements in strength, power, and muscle size. It also helps to maintain the positive effects of creatine on mood and cognition.
Some women may choose to cycle creatine, meaning they take it for a period of time, then stop for a period before resuming again. However, there is no strong evidence to support cycling creatine, and it may actually reduce its effectiveness. Consistent daily supplementation with a maintenance dose is generally recommended for sustained benefits.
1.3 Creatine Dosage for Specific Goals: Strength, Performance, Mood
The optimal creatine dosage may vary depending on specific goals, such as improving strength, enhancing athletic performance, or boosting mood.
For strength and power gains, the standard loading and maintenance doses are usually effective. However, some studies suggest that higher doses of creatine, such as 0.1g/kg of body weight per day, may be beneficial for maximizing strength gains.
For athletic performance, the timing of creatine supplementation may also be important. Taking creatine before or after exercise may help to improve performance and recovery. Some athletes also use creatine loading before competitions to quickly boost their performance.
For mood and cognitive benefits, higher doses of creatine may be needed. Studies have shown that doses of 5-20 grams per day can improve mood and reduce symptoms of depression, particularly in women. This may be due to creatine’s ability to increase energy levels in the brain and improve neurotransmitter function.
It’s important to note that individual responses to creatine can vary, so it’s best to start with the standard doses and adjust as needed based on individual results and tolerance.
2. Why Should Women Consider Taking Creatine?
Women should consider taking creatine for its potential benefits in enhancing muscle strength, improving exercise performance, supporting bone health, and boosting mood and cognitive function. Benefits include improved athletic performance, muscle recovery, and overall well-being.
Creatine is not just for men; it offers several unique advantages for women as well. Understanding these benefits can help women make informed decisions about whether or not to include creatine in their supplementation routine.
2.1 Enhanced Muscle Strength and Power: Breaking the Myths
One of the primary reasons women should consider taking creatine is its ability to enhance muscle strength and power. Contrary to popular belief, creatine does not cause women to bulk up or develop a masculine physique. Instead, it helps to increase muscle creatine stores, which can lead to improved strength and power output during high-intensity activities.
Studies have shown that creatine supplementation can significantly increase strength in women, particularly during resistance training. For example, one study found that women who took creatine while participating in a resistance training program experienced greater increases in leg press and squat strength compared to those who took a placebo.
Creatine also helps to improve muscle power, which is the ability to exert force quickly. This can be particularly beneficial for athletes who need to perform explosive movements, such as sprinting, jumping, or weightlifting.
The increased strength and power from creatine supplementation can help women to push harder during workouts, leading to greater gains in muscle mass and overall fitness.
2.2 Improved Exercise Performance: Beyond Strength Training
In addition to enhancing muscle strength and power, creatine can also improve exercise performance in other ways. Creatine helps to increase the availability of ATP, the primary energy source for muscle contractions. This can lead to improved endurance, reduced fatigue, and faster recovery times.
Creatine has been shown to improve performance in a variety of activities, including:
- High-intensity interval training (HIIT): Creatine can help women to perform more repetitions and sets during HIIT workouts, leading to greater gains in cardiovascular fitness and fat loss.
- Sprinting: Creatine can improve sprint speed and power, making it beneficial for athletes in sports like track and field, soccer, and basketball.
- Swimming: Creatine can enhance swim performance, particularly during repeated sprints, by improving power output and reducing fatigue.
- Endurance exercise: While creatine is not typically associated with endurance exercise, some studies suggest that it can help to reduce fatigue and improve performance during prolonged activities.
By improving exercise performance across a range of activities, creatine can help women to achieve their fitness goals more quickly and effectively.
2.3 Supporting Bone Health: A Benefit for Post-Menopausal Women
As women age, they are at an increased risk of osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weakened bones and an increased risk of fractures. Creatine may help to support bone health by increasing bone mineral density and reducing bone loss.
Studies have shown that creatine supplementation, particularly when combined with resistance training, can improve bone health in post-menopausal women. For example, one study found that women who took creatine while participating in a resistance training program experienced greater increases in bone mineral density in the hip region compared to those who took a placebo.
The mechanisms by which creatine supports bone health are not fully understood, but it may involve increasing the activity of osteoblasts, the cells responsible for bone formation, and reducing the activity of osteoclasts, the cells responsible for bone breakdown.
By supporting bone health, creatine can help women to maintain their mobility and independence as they age.
2.4 Mood and Cognitive Function: The Brain-Boosting Effects
In addition to its physical benefits, creatine may also have positive effects on mood and cognitive function. Creatine helps to increase energy levels in the brain and improve neurotransmitter function, which can lead to improved mood, reduced symptoms of depression, and enhanced cognitive performance.
Studies have shown that creatine supplementation can improve mood and reduce symptoms of depression in women. For example, one study found that women who took creatine while taking antidepressant medication experienced greater improvements in mood compared to those who took antidepressant medication alone.
Creatine has also been shown to improve cognitive function, particularly in tasks that require attention, memory, and mental processing speed. This may be due to creatine’s ability to increase energy levels in the brain and improve the efficiency of neural communication.
By boosting mood and cognitive function, creatine can help women to feel more energized, focused, and mentally sharp.
3. Addressing Concerns and Dispelling Myths About Creatine for Women
Many women have concerns about taking creatine, often based on misinformation and myths. Addressing these concerns and dispelling these myths is crucial to understanding the true potential of creatine for women’s health and fitness. Discover the truth about water retention, bloating, and safety.
Despite the numerous benefits of creatine for women, many still hesitate to try it due to common misconceptions and concerns. Addressing these concerns and dispelling these myths is essential to help women make informed decisions about whether or not to include creatine in their supplementation routine.
3.1 Will Creatine Cause Me to Bulk Up? The Truth About Muscle Growth
One of the biggest concerns women have about creatine is that it will cause them to bulk up and develop a masculine physique. This is simply not true. Creatine does not cause women to gain large amounts of muscle mass.
Creatine helps to increase muscle strength and power, which can lead to increased muscle growth over time. However, the amount of muscle growth that women experience from creatine is typically much less than what men experience. This is because women have lower levels of testosterone, the hormone responsible for muscle growth.
Creatine is a tool that enhances muscle function, not a magic potion for instant bulk. Women can use creatine to boost their strength and performance without fear of unwanted muscle mass.
3.2 Water Retention and Bloating: Separating Fact from Fiction
Another common concern about creatine is that it causes water retention and bloating. While it’s true that creatine can cause a temporary increase in water weight, this is not the same as bloating.
Creatine draws water into muscle cells, which can lead to a slight increase in body weight. However, this water is stored inside the muscles, not in the stomach or other areas of the body, so it does not cause bloating.
The water retention associated with creatine is typically temporary and subsides within a few weeks of starting supplementation. It’s also important to note that not everyone experiences water retention from creatine.
For women who are concerned about water retention, it’s best to start with a low dose of creatine and gradually increase it over time. This can help to minimize any potential water retention and bloating.
3.3 Creatine and Kidney Health: Is It Safe?
Some people believe that creatine is harmful to the kidneys. However, numerous studies have shown that creatine is safe for healthy individuals to take, even in high doses.
There is no evidence to suggest that creatine causes kidney damage in people with healthy kidneys. However, people with pre-existing kidney conditions should talk to their doctor before taking creatine.
Creatine is one of the most well-researched supplements on the market, and it has been shown to be safe and effective for a wide range of people, including women.
3.4 Creatine and Hair Loss: Debunking the Link
There is a myth circulating that creatine causes hair loss. This claim is based on a single study that found a link between creatine supplementation and an increase in dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone associated with hair loss.
However, this study has been widely criticized for its small sample size and methodological flaws. There is no other evidence to support the claim that creatine causes hair loss.
The vast majority of studies on creatine have found no link between creatine supplementation and hair loss. Creatine is considered to be safe for hair health.
4. How to Choose the Right Creatine Supplement
Choosing the right creatine supplement can be overwhelming. Learn about different forms of creatine, including creatine monohydrate, creatine ethyl ester, and creatine hydrochloride, and understand the factors to consider when selecting a product. Also explore third-party testing, quality, and purity.
Not all creatine supplements are created equal. With so many different products on the market, it’s important to know how to choose the right creatine supplement for your needs.
4.1 Creatine Monohydrate: The Gold Standard
Creatine monohydrate is the most well-researched and widely used form of creatine. It’s also the most affordable. Numerous studies have shown that creatine monohydrate is safe and effective for increasing muscle strength, power, and size.
Creatine monohydrate is considered the gold standard of creatine supplements because it has been extensively studied and proven to be effective. It’s also readily available and affordable.
4.2 Other Forms of Creatine: Ethyl Ester, Hydrochloride, and More
In addition to creatine monohydrate, there are other forms of creatine available, such as creatine ethyl ester, creatine hydrochloride, and buffered creatine. These forms of creatine are often marketed as being superior to creatine monohydrate, but there is little evidence to support these claims.
Creatine ethyl ester is a form of creatine that is claimed to be more easily absorbed than creatine monohydrate. However, studies have shown that creatine ethyl ester is actually less effective than creatine monohydrate at increasing muscle creatine stores.
Creatine hydrochloride is a form of creatine that is claimed to be more soluble than creatine monohydrate. However, there is no evidence to suggest that creatine hydrochloride is more effective than creatine monohydrate.
Buffered creatine is a form of creatine that is claimed to be more stable than creatine monohydrate. However, there is no evidence to suggest that buffered creatine is more effective than creatine monohydrate.
4.3 Third-Party Testing: Ensuring Quality and Purity
When choosing a creatine supplement, it’s important to look for products that have been third-party tested. Third-party testing ensures that the product has been tested by an independent laboratory for quality, purity, and potency.
Third-party testing can help to ensure that you are getting a safe and effective creatine supplement. Look for products that have been tested by organizations such as NSF International, Informed-Sport, or USP.
4.4 Considerations for Women: Vegan Options and Allergies
Women who are vegan or have allergies should take extra care when choosing a creatine supplement.
Creatine is naturally found in animal products, so many creatine supplements are not vegan. However, there are vegan creatine supplements available that are made from synthetic creatine.
Women with allergies should carefully read the label of creatine supplements to ensure that they do not contain any allergens.
5. Timing and Combining Creatine with Other Supplements
Timing and combining creatine with other supplements can enhance its effects. Explore whether to take creatine before or after workouts, and learn about synergistic supplements like protein, carbohydrates, and beta-alanine.
To maximize the benefits of creatine supplementation, it’s important to consider the timing of your doses and whether or not to combine creatine with other supplements.
5.1 Creatine Before or After Workout? Optimizing Timing
There is some debate over whether it’s better to take creatine before or after workouts. Some people believe that taking creatine before workouts can help to improve performance, while others believe that taking creatine after workouts can help to improve recovery.
Studies have shown that both pre-workout and post-workout creatine supplementation can be effective. However, some studies suggest that taking creatine after workouts may be slightly more beneficial for muscle growth and recovery.
Ultimately, the best time to take creatine is the time that works best for you. Consistency is key, so choose a time that you can stick to on a regular basis.
5.2 Synergistic Supplements: Protein, Carbohydrates, and Beta-Alanine
Creatine can be combined with other supplements to enhance its effects. Some of the most synergistic supplements for creatine include protein, carbohydrates, and beta-alanine.
Protein is essential for muscle growth and repair. Combining creatine with protein can help to maximize muscle growth and strength gains.
Carbohydrates can help to increase insulin levels, which can improve creatine uptake into muscle cells. Combining creatine with carbohydrates can help to improve creatine absorption and effectiveness.
Beta-alanine is an amino acid that helps to buffer muscle acidity. Combining creatine with beta-alanine can help to improve endurance and reduce fatigue.
6. Creatine Use During Different Life Stages for Women
Creatine’s benefits extend across different life stages for women. Understand how creatine can support women during menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause, addressing specific needs and hormonal changes. Creatine supplementation can be tailored to support women’s health and fitness.
Creatine can be a valuable supplement for women at different stages of life, each with its unique physiological demands and hormonal changes.
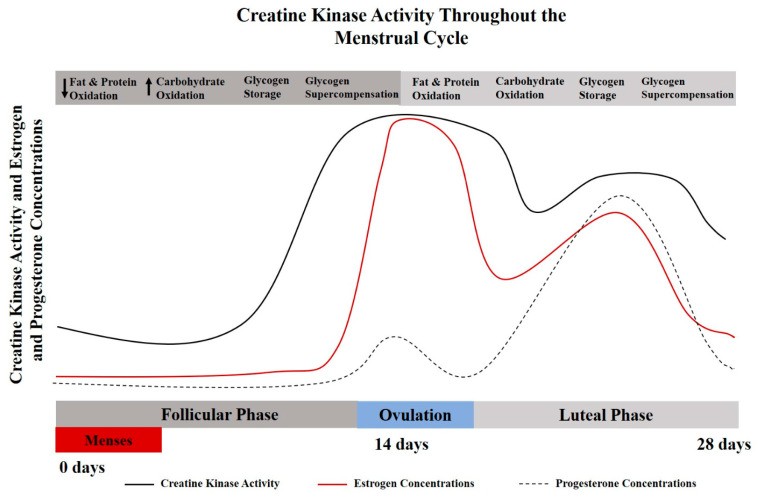
6.1 Menstruation: Counteracting Protein Turnover
During menstruation, women experience hormonal fluctuations that can affect muscle protein turnover. Estrogen levels are at their peak during the luteal phase, which can lead to elevated protein catabolism and reduced carbohydrate storage.
Creatine supplementation may help to counteract these effects by supporting muscle protein preservation. By increasing muscle creatine stores, creatine can help to improve muscle strength and power, even during menstruation.
6.2 Pregnancy: Supporting Maternal and Fetal Health
During pregnancy, the metabolic demands of both the mother and the developing fetus increase significantly. This can lead to a reduced creatine pool, which may be associated with low birth weight and pre-term birth.
Creatine supplementation during pregnancy may help to support maternal and fetal health by increasing creatine stores and improving energy availability. Animal studies have shown that creatine supplementation during pregnancy can enhance neuronal cell uptake of creatine and support mitochondrial integrity in offspring, reducing brain injury induced by intrapartum asphyxia.
However, there are currently no human studies on the effects of creatine supplementation during pregnancy. Women who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant should talk to their doctor before taking creatine.
6.3 Menopause: Combating Muscle and Bone Loss
Menopause is associated with a decline in estrogen levels, which can lead to muscle and bone loss. Creatine supplementation may help to counteract these effects by reducing inflammation, oxidative stress, and serum markers of bone resorption, while also increasing osteoblast cell activity.
Studies have shown that creatine supplementation, particularly when combined with resistance training, can improve muscle mass, strength, and bone mineral density in post-menopausal women.
7. Expert Recommendations and Guidelines for Creatine Use
Consulting experts and following guidelines ensures safe and effective creatine use. Review recommendations from sports nutritionists and healthcare professionals, and understand the importance of individualizing dosage based on body weight, activity level, and health status.
To ensure the safe and effective use of creatine, it’s important to consult with experts and follow established guidelines.
7.1 Recommendations from Sports Nutritionists
Sports nutritionists generally recommend a creatine loading phase of 0.3g/kg of body weight per day for 5-7 days, followed by a maintenance dose of 3-5g per day. They also recommend taking creatine with carbohydrates or protein to improve absorption.
Sports nutritionists emphasize the importance of individualizing creatine dosage based on body weight, activity level, and health status. They also recommend choosing a creatine supplement that has been third-party tested for quality and purity.
7.2 Consulting Healthcare Professionals: When to Seek Advice
People with pre-existing health conditions should talk to their doctor before taking creatine. This is especially important for people with kidney conditions, liver conditions, or diabetes.
Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should also talk to their doctor before taking creatine.
7.3 Individualizing Dosage: Body Weight, Activity Level, and Health Status
The optimal creatine dosage can vary depending on individual factors such as body weight, activity level, and health status.
Women who are smaller in size may need a lower creatine dose than women who are larger in size. Women who are more active may need a higher creatine dose than women who are less active.
People with pre-existing health conditions may need to adjust their creatine dosage based on their individual needs.
Creatine is a safe and effective supplement for women, but it’s important to use it responsibly and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
8. Potential Side Effects and How to Manage Them
While creatine is generally safe, understanding potential side effects and how to manage them is important. Learn about common side effects, such as gastrointestinal issues and dehydration, and how to mitigate them.
Although creatine is generally safe, it’s important to be aware of potential side effects and how to manage them.
8.1 Common Side Effects: Gastrointestinal Issues and Dehydration
The most common side effects of creatine supplementation are gastrointestinal issues, such as stomach cramps, diarrhea, and nausea. These side effects are usually mild and temporary and can be managed by reducing the creatine dosage or taking creatine with food.
Another potential side effect of creatine supplementation is dehydration. Creatine draws water into muscle cells, which can lead to dehydration if you don’t drink enough water. To prevent dehydration, it’s important to drink plenty of water throughout the day when taking creatine.
8.2 Rare Side Effects: Muscle Cramps and Interactions with Medications
Rarely, creatine supplementation can cause muscle cramps. This is more likely to occur if you are dehydrated or if you are taking high doses of creatine. If you experience muscle cramps while taking creatine, reduce your dosage and make sure to drink plenty of water.
Creatine can interact with certain medications, such as diuretics and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). If you are taking any medications, talk to your doctor before taking creatine.
8.3 Managing Side Effects: Dosage Adjustments and Hydration Strategies
To manage potential side effects of creatine supplementation, start with a low dose and gradually increase it over time. Drink plenty of water throughout the day, and take creatine with food to reduce the risk of gastrointestinal issues.
If you experience any side effects while taking creatine, reduce your dosage or stop taking it altogether. Talk to your doctor if you have any concerns.
9. Real-Life Examples: Women Who Have Benefited from Creatine
Hearing from real women who have benefited from creatine can be inspiring. Read personal stories and testimonials about improved athletic performance, increased strength, and enhanced well-being.
To illustrate the benefits of creatine for women, here are some real-life examples of women who have benefited from creatine supplementation:
- Sarah, a marathon runner: “I started taking creatine to improve my endurance and reduce fatigue during long runs. I’ve noticed a significant improvement in my performance, and I’m able to run faster and longer without getting as tired.”
- Jessica, a weightlifter: “I was hesitant to try creatine because I didn’t want to bulk up. But after doing some research, I decided to give it a try. I’ve been amazed at how much stronger I’ve become. I’m able to lift heavier weights and build more muscle without getting bulky.”
- Emily, a busy mom: “I was feeling tired and run down all the time. A friend recommended that I try creatine, and I’m so glad I did. I have more energy, I’m more focused, and I’m able to keep up with my kids.”
These are just a few examples of the many women who have benefited from creatine supplementation. Creatine can be a valuable tool for women of all ages and fitness levels.
10. Maximizing the Benefits of Creatine with HOW.EDU.VN
Maximize the benefits of creatine supplementation with expert guidance from HOW.EDU.VN. Access personalized advice, expert consultations, and comprehensive resources to optimize your health and fitness journey.
HOW.EDU.VN connects you with leading experts and resources to help you optimize your creatine supplementation and achieve your health and fitness goals.
Navigating the world of supplements can be challenging, but with the right information and support, you can make informed decisions and achieve remarkable results. Whether you’re aiming to enhance athletic performance, improve muscle strength, support bone health, or boost mood and cognitive function, HOW.EDU.VN is here to guide you every step of the way.
10.1 Connect with Experts for Personalized Advice
At HOW.EDU.VN, we understand that every woman’s body is unique. That’s why we offer personalized consultations with our team of experienced PhDs and specialists. These experts can provide tailored guidance based on your specific needs, goals, and health status.
During a consultation, you can discuss your current diet, exercise routine, and any health concerns you may have. Our experts will then develop a customized creatine supplementation plan that aligns with your individual requirements.
10.2 Access Comprehensive Resources and Guides
HOW.EDU.VN is your go-to source for comprehensive resources and guides on creatine supplementation. Our team of experts has curated a wealth of information to help you understand the science behind creatine and how it can benefit your health and fitness journey.
Whether you’re a seasoned athlete or just starting out, our resources can provide valuable insights and practical tips. Learn about:
- The different forms of creatine and their effectiveness
- The optimal dosage for your body weight and activity level
- The best time to take creatine for maximum results
- How to combine creatine with other supplements for synergistic effects
- Potential side effects and how to manage them
10.3 Stay Updated with the Latest Research and Insights
The field of sports nutrition is constantly evolving, and new research is emerging all the time. At HOW.EDU.VN, we stay on top of the latest scientific findings and insights to ensure that our recommendations are always up-to-date and evidence-based.
We regularly publish articles, blog posts, and videos that cover the latest developments in creatine research. By staying informed, you can make the best possible decisions for your health and fitness.
10.4 Join Our Community of Empowered Women
At HOW.EDU.VN, we believe that women are stronger together. That’s why we’ve created a supportive community where you can connect with other women who are passionate about health and fitness.
Share your experiences, ask questions, and get encouragement from like-minded individuals. Our community is a safe and welcoming space where you can feel empowered to take control of your health and achieve your goals.
Achieve Your Health and Fitness Goals with HOW.EDU.VN
Ready to unlock the full potential of creatine supplementation and take your health and fitness to the next level? Contact HOW.EDU.VN today. Our team of experts is here to provide personalized advice, comprehensive resources, and ongoing support.
Visit our website at HOW.EDU.VN to learn more about our services and connect with a PhD specialist. Let us help you optimize your health and fitness journey with creatine!
Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
Website: how.edu.vn
FAQ: Common Questions About Creatine for Women
Still have questions about creatine? Here are some frequently asked questions to help you better understand its benefits, safety, and usage for women.
1. Is creatine safe for women?
Yes, creatine is generally safe for women when taken as directed. Numerous studies have shown that creatine supplementation is safe for healthy individuals.
2. Will creatine make me bulk up?
No, creatine will not make you bulk up. Creatine helps to increase muscle strength and power, which can lead to increased muscle growth over time. However, the amount of muscle growth that women experience from creatine is typically much less than what men experience.
3. Does creatine cause water retention?
Creatine can cause a temporary increase in water weight, but this is not the same as bloating. Creatine draws water into muscle cells, which can lead to a slight increase in body weight. However, this water is stored inside the muscles, not in the stomach or other areas of the body.
4. How much creatine should I take?
The recommended creatine dosage is a loading phase of 0.3g/kg of body weight per day for 5-7 days, followed by a maintenance dose of 3-5g per day.
5. When should I take creatine?
You can take creatine before or after workouts. Some studies suggest that taking creatine after workouts may be slightly more beneficial for muscle growth and recovery.
6. Can I combine creatine with other supplements?
Yes, creatine can be combined with other supplements to enhance its effects. Some of the most synergistic supplements for creatine include protein, carbohydrates, and beta-alanine.
7. Is creatine safe for my kidneys?
Creatine is safe for healthy individuals to take, even in high doses. However, people with pre-existing kidney conditions should talk to their doctor before taking creatine.
8. Can I take creatine during menstruation?
Yes, creatine can be beneficial during menstruation by supporting muscle protein preservation.
9. Is creatine safe during pregnancy?
There are currently no human studies on the effects of creatine supplementation during pregnancy. Women who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant should talk to their doctor before taking creatine.
10. Is creatine safe during menopause?
Yes, creatine can be beneficial during menopause by improving muscle mass, strength, and bone mineral density.