Menstrual bleeding can vary from person to person, but understanding what’s considered normal is crucial for your health. At HOW.EDU.VN, we provide expert insights into menstrual health, helping you distinguish between typical blood loss and when to seek professional advice. This article will cover average blood loss, symptoms of heavy bleeding, and potential underlying causes. For personalized guidance and in-depth consultations, connect with our experienced doctors.
1. Understanding Menstrual Blood Loss: What’s Normal?
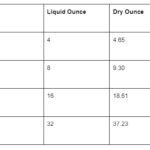
The volume of blood lost during a menstrual period varies greatly from person to person, but generally falls within a specific range. Most women lose less than 80ml (about 2.7 ounces) of blood during their period, which typically lasts between 2 to 7 days. This amount can be hard to visualize, so it’s often described in terms of how many pads or tampons are soaked through.
1.1 Average Blood Loss Measurement
The average menstrual flow is around 30 to 50 milliliters (mL), which is about 1 to 1.7 ounces. This might seem like a small amount, but it’s enough to soak several pads or tampons over the course of a period. Here’s a simple breakdown:
- Light Flow: Less than 30 mL (1 ounce)
- Moderate Flow: 30-50 mL (1-1.7 ounces)
- Heavy Flow: More than 80 mL (2.7 ounces)
While tracking the exact volume can be difficult, paying attention to how frequently you need to change your menstrual products and the presence of large blood clots can help you gauge whether your bleeding is within the normal range.
1.2 Factors Influencing Menstrual Flow
Several factors can influence the amount of blood lost during menstruation. These include:
- Age: Menstrual flow can change as you age, often becoming heavier as you approach perimenopause.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone levels can affect the thickness of the uterine lining, which in turn affects menstrual flow.
- Uterine Conditions: Conditions like fibroids or polyps can lead to heavier bleeding.
- Contraception: Certain types of birth control, such as IUDs, can increase or decrease menstrual flow.
- Overall Health: Medical conditions like bleeding disorders or thyroid issues can also affect menstrual bleeding.
1.3 How to Track Your Menstrual Blood Loss
Tracking menstrual blood loss can help you determine if your periods are within the normal range. Here are a few methods you can use:
-
Pad/Tampon Count: Keep a record of how many pads or tampons you use each day. If you’re soaking through a pad or tampon every hour for several hours, this could indicate heavy bleeding.
-
Menstrual Cups: These collect menstrual fluid, allowing you to measure the volume more accurately.
-
Symptom Tracking Apps: Several apps can help you track your period, including the heaviness of your flow and any related symptoms.
-
Better You Know Menstrual Chart: The Better You Know Menstrual Chart and Scoring System is a helpful tool for tracking your period. You can download the chart and use it to record the dates of your period and how heavy you think your flow is by counting how many pads or tampons you use. Bring this information with you when you visit your healthcare provider so that you can give them as much information as possible.
Better You Know Menstrual Chart and Scoring System
2. Identifying Heavy Menstrual Bleeding (Menorrhagia)
Heavy menstrual bleeding, also known as menorrhagia, is a common concern among women. It’s characterized by prolonged or excessively heavy periods that can interfere with daily life. Recognizing the signs of menorrhagia is essential for seeking timely medical advice and appropriate management.
2.1 Defining Menorrhagia
Menorrhagia is defined as menstrual bleeding that lasts longer than seven days or involves losing more than 80 mL of blood per period. However, since it can be challenging to measure blood loss precisely, other indicators can help identify the condition.
2.2 Key Symptoms of Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
Common symptoms of menorrhagia include:
- Soaking Through Pads or Tampons Quickly: Needing to change your pad or tampon every hour for several consecutive hours.
- Needing to Double Up on Pads: Using two pads at once to manage the flow.
- Nighttime Interruptions: Waking up during the night to change pads or tampons.
- Large Blood Clots: Passing blood clots that are the size of a quarter or larger.
- Prolonged Bleeding: Bleeding for more than seven days.
- Impact on Daily Activities: Feeling restricted from usual activities due to heavy flow.
- Symptoms of Anemia: Experiencing fatigue, weakness, or shortness of breath, which can indicate iron deficiency due to excessive blood loss.
- Constant pain: Experiencing constant pain in the lower part of the stomach during your periods.
If you experience several of these symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and discuss appropriate treatment options.
2.3 When to Seek Medical Attention
It’s advisable to seek medical attention if:
- You suddenly experience a significant increase in menstrual flow.
- Your periods are interfering with your daily activities.
- You develop symptoms of anemia, such as persistent fatigue or shortness of breath.
- You have concerns about changes in your menstrual cycle.
2.4 Seeking Professional Help
Navigating menstrual health can be challenging, but you’re not alone. At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with experienced doctors who can provide personalized guidance and support. Whether you’re concerned about heavy bleeding, irregular cycles, or any other menstrual issues, our team is here to help.
Contact us today for a consultation and take control of your menstrual health. Our experts are dedicated to providing the highest quality care and empowering you to make informed decisions about your health.
3. Causes of Excessive Menstrual Blood Loss
Identifying the causes of excessive menstrual blood loss is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. Several factors can contribute to heavy periods, ranging from hormonal imbalances to structural issues within the uterus.
3.1 Common Underlying Causes
Some of the most common causes of heavy menstrual bleeding include:
- Hormonal Imbalances:
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): PCOS can lead to irregular and prolonged periods due to hormonal imbalances.
- Thyroid Disorders: Both hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) can affect menstrual bleeding.
- Uterine Issues:
- Uterine Fibroids: These non-cancerous growths in the uterus can cause heavy and prolonged bleeding.
- Uterine Polyps: Small growths in the uterine lining can also lead to heavier periods.
- Adenomyosis: This condition occurs when the uterine lining grows into the muscular wall of the uterus, causing heavy and painful bleeding.
- Bleeding Disorders:
- Von Willebrand Disease (VWD): This genetic disorder affects the blood’s ability to clot, leading to prolonged and heavy bleeding.
- Platelet Function Disorders: Problems with platelets can also impair blood clotting and result in menorrhagia.
- Contraception:
- Intrauterine Devices (IUDs): Non-hormonal IUDs can sometimes cause heavier periods, especially in the initial months after insertion.
- Other Medical Conditions:
- Endometrial Hyperplasia: Thickening of the uterine lining can result in heavy bleeding.
- Cancer: In rare cases, uterine or cervical cancer can cause abnormal bleeding.
- Medications:
- Certain medications, such as anti-inflammatory drugs or blood thinners, can increase menstrual bleeding.
3.2 Diagnostic Tests to Identify Causes
To determine the cause of heavy menstrual bleeding, healthcare providers may recommend various diagnostic tests, including:
-
Blood Tests: These tests can check for anemia, thyroid disorders, and bleeding disorders.
-
Pelvic Exam: A physical examination to assess the uterus, ovaries, and other reproductive organs.
-
Ultrasound: This imaging technique can help identify fibroids, polyps, or other structural abnormalities in the uterus.
-
Endometrial Biopsy: A small sample of the uterine lining is taken and examined under a microscope to check for abnormal cells or endometrial hyperplasia.
-
Hysteroscopy: A thin, lighted scope is inserted into the uterus to visualize the uterine lining and identify any abnormalities.
-
Sonohysterogram: An ultrasound performed after fluid is injected into the uterus to better visualize the uterine lining.
The female reproductive tract
3.3 Expertise at HOW.EDU.VN
At HOW.EDU.VN, our team of experienced doctors specializes in diagnosing and treating the causes of heavy menstrual bleeding. We provide comprehensive evaluations and personalized treatment plans to address your specific needs.
4. Treatment Options for Managing Heavy Menstrual Flow
Managing heavy menstrual flow involves various treatment options tailored to the underlying cause and the individual’s needs. These options range from medical therapies to surgical interventions, each with its own benefits and considerations.
4.1 Medical Treatments
Medical treatments are often the first line of defense in managing heavy menstrual bleeding. These include:
- Hormonal Birth Control:
- Oral Contraceptives (Birth Control Pills): These pills can help regulate periods, reduce bleeding, and alleviate menstrual cramps.
- Hormonal IUDs: These intrauterine devices release progestin, which can thin the uterine lining and reduce menstrual flow.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs):
- Medications like ibuprofen and naproxen can help reduce pain and inflammation, and may also decrease menstrual bleeding to some extent.
- Tranexamic Acid:
- This medication helps reduce bleeding by preventing blood clots from breaking down too quickly.
- Iron Supplements:
- If heavy bleeding has led to anemia, iron supplements can help replenish iron levels in the body.
- Hormone Therapy:
- Hormone therapy involves drugs that contain estrogen and/or progesterone to reduce the amount of bleeding.
- Desmopressin Nasal Spray (Stimate®):
- This spray is used to stop bleeding in people with certain bleeding disorders, such as von Willebrand disease and mild hemophilia.
4.2 Surgical Procedures
If medical treatments are not effective, surgical procedures may be considered:
- Dilation and Curettage (D&C):
- A procedure in which the top layer of the uterus lining is removed to reduce menstrual bleeding.
- Operative Hysteroscopy:
- A surgical procedure to view the inside of the uterus and remove polyps and fibroids, correct abnormalities of the uterus, and remove the lining of the uterus to manage heavy menstrual flow.
- Endometrial Ablation:
- This procedure involves removing or destroying the uterine lining to reduce or stop menstrual bleeding.
- Uterine Artery Embolization:
- A minimally invasive procedure to block blood flow to fibroids, causing them to shrink.
- Myomectomy:
- Surgical removal of fibroids while leaving the uterus intact, which may be an option for women who wish to preserve fertility.
- Hysterectomy:
- Surgical removal of the entire uterus, which is a permanent solution for heavy menstrual bleeding but results in infertility.
4.3 Tailored Treatment Plans at HOW.EDU.VN
At HOW.EDU.VN, our expert doctors create tailored treatment plans based on your individual needs and medical history. We consider factors such as the cause of your heavy bleeding, your age, and your desire for future pregnancies.
5. The Impact of Heavy Bleeding on Daily Life and Health
Heavy menstrual bleeding can significantly impact a woman’s daily life and overall health. Understanding these effects can help women seek timely and appropriate medical care.
5.1 Physical Impacts
The physical impacts of heavy menstrual bleeding can be substantial:
- Anemia: Prolonged heavy bleeding can lead to iron deficiency anemia, causing fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, and pale skin.
- Pain and Discomfort: Heavy periods are often accompanied by severe menstrual cramps (dysmenorrhea), which can be debilitating.
- Frequent Bathroom Trips: The need to change pads or tampons frequently can disrupt daily activities and lead to anxiety.
- Sleep Disturbances: Waking up at night to change menstrual products can lead to sleep deprivation and fatigue.
5.2 Emotional and Psychological Impacts
In addition to the physical challenges, heavy menstrual bleeding can also have significant emotional and psychological effects:
- Anxiety and Stress: Worrying about bleeding through clothing or being caught without adequate supplies can cause anxiety and stress.
- Social Isolation: Some women may avoid social activities or work due to concerns about managing their periods.
- Depression: Chronic pain and fatigue associated with heavy bleeding can contribute to feelings of depression.
- Reduced Self-Esteem: The inconvenience and embarrassment of heavy periods can negatively impact self-esteem.
5.3 Long-Term Health Risks
Untreated heavy menstrual bleeding can lead to long-term health risks:
- Chronic Anemia: Persistent iron deficiency can affect various bodily functions and lead to chronic fatigue and weakness.
- Increased Risk of Infections: Frequent use of tampons can increase the risk of vaginal infections.
- Impact on Fertility: Certain causes of heavy bleeding, such as fibroids or PCOS, can affect fertility.
5.4 Expert Support at HOW.EDU.VN
At HOW.EDU.VN, we understand the profound impact that heavy menstrual bleeding can have on your life. Our team of dedicated doctors is here to provide compassionate care and effective solutions to help you regain control of your health and well-being.
6. Debunking Myths About Menstrual Blood Loss
There are many misconceptions surrounding menstrual blood loss. Separating fact from fiction can help women better understand their bodies and make informed decisions about their health.
6.1 Common Myths and Misconceptions
- Myth: Passing large blood clots is always normal.
- Fact: While small blood clots are common during menstruation, consistently passing large clots (the size of a quarter or larger) may indicate heavy bleeding and should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
- Myth: Heavy periods are just a normal part of being a woman.
- Fact: While menstrual cycles vary, excessively heavy bleeding that disrupts daily life is not normal and may indicate an underlying health issue.
- Myth: You can get pregnant during your period.
- Fact: While it’s less likely, it is still possible to get pregnant during your period, especially if you have a shorter cycle or if your period lasts longer.
- Myth: Exercise can make your period heavier.
- Fact: Exercise generally does not make periods heavier. In some cases, intense exercise can lead to irregular periods or even amenorrhea (absence of menstruation).
- Myth: You can “store up” menstrual blood if you delay your period with birth control pills.
- Fact: Birth control pills prevent the uterine lining from thickening as much, so there’s less to shed when you do have a period. You’re not storing up blood; there’s simply less to eliminate.
6.2 Expert Insights from HOW.EDU.VN
At HOW.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing accurate, evidence-based information about menstrual health. Our team of experienced doctors can help you navigate the complexities of menstrual cycles and address any concerns you may have.
7. Lifestyle Adjustments to Manage Menstrual Blood Loss
In addition to medical treatments, certain lifestyle adjustments can help manage menstrual blood loss and alleviate associated symptoms.
7.1 Dietary Changes
- Iron-Rich Foods: Consuming foods rich in iron, such as lean meats, poultry, fish, beans, and leafy green vegetables, can help prevent or treat anemia.
- Vitamin C: Pairing iron-rich foods with vitamin C-rich foods, such as citrus fruits, strawberries, and bell peppers, can enhance iron absorption.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated can help alleviate bloating and cramping.
- Limit Caffeine and Alcohol: These substances can sometimes worsen menstrual symptoms.
7.2 Exercise and Physical Activity
- Regular Exercise: Moderate exercise can improve overall health, reduce stress, and alleviate menstrual cramps.
- Yoga and Stretching: Gentle exercises like yoga and stretching can help relax muscles and ease discomfort.
7.3 Stress Management Techniques
- Relaxation Techniques: Practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and mindfulness can help reduce stress and improve overall well-being.
- Adequate Sleep: Getting enough sleep is essential for managing stress and maintaining a healthy immune system.
7.4 Comprehensive Support at HOW.EDU.VN
At HOW.EDU.VN, we offer comprehensive support to help you manage menstrual blood loss and improve your quality of life. Our expert doctors can provide personalized recommendations for lifestyle adjustments and medical treatments tailored to your specific needs.
8. Understanding Menstrual Products and Their Impact on Tracking Blood Loss
Choosing the right menstrual products can significantly impact your ability to track blood loss and manage your period effectively. Each type of product has its own advantages and considerations.
8.1 Types of Menstrual Products
- Pads:
- Pads are external products that adhere to underwear and absorb menstrual flow. They come in various sizes and absorbencies.
- Pros: Easy to use, good for tracking flow, readily available.
- Cons: Can feel bulky, may cause skin irritation, need frequent changing.
- Tampons:
- Tampons are inserted into the vagina to absorb menstrual flow internally. They also come in various sizes and absorbencies.
- Pros: Discreet, allow for swimming and other activities.
- Cons: Require proper insertion technique, need frequent changing, risk of Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS) if not used correctly.
- Menstrual Cups:
- Menstrual cups are reusable, bell-shaped cups made of silicone or rubber that are inserted into the vagina to collect menstrual blood.
- Pros: Reusable and eco-friendly, can be worn for up to 12 hours, allow for accurate measurement of blood loss.
- Cons: Require practice to insert and remove, need to be cleaned regularly.
- Menstrual Discs:
- Menstrual discs are similar to cups but sit higher in the vaginal canal, near the cervix.
- Pros: Can be worn for up to 12 hours, less likely to cause cramping.
- Cons: Require practice to insert and remove, may be messy to empty.
- Period Underwear:
- Period underwear is designed with absorbent layers to soak up menstrual flow.
- Pros: Comfortable, reusable, eco-friendly.
- Cons: Can be expensive, need to be washed after each use, may not be suitable for very heavy flow.
8.2 Tracking Blood Loss with Different Products
- Pads and Tampons:
- Keep track of how many pads or tampons you use each day, noting the size and absorbency. If you’re soaking through a pad or tampon every hour for several consecutive hours, this could indicate heavy bleeding.
- Menstrual Cups and Discs:
- These products allow you to measure the volume of blood collected. Empty the cup or disc into a measuring cup to track your blood loss accurately.
- Period Underwear:
- While it’s difficult to measure blood loss with period underwear, you can gauge the heaviness of your flow based on how quickly the underwear becomes saturated.
8.3 Personalized Recommendations at HOW.EDU.VN
At HOW.EDU.VN, our expert doctors can provide personalized recommendations for menstrual products based on your individual needs and preferences. We can help you choose the right products to manage your period effectively and track your blood loss accurately.
9. Menstrual Irregularities Beyond Blood Loss: What to Watch For
While heavy menstrual bleeding is a common concern, other menstrual irregularities can also indicate underlying health issues. Understanding these irregularities is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being.
9.1 Types of Menstrual Irregularities
- Amenorrhea: Absence of menstruation for three or more consecutive months.
- Oligomenorrhea: Infrequent periods, with cycles longer than 35 days.
- Dysmenorrhea: Painful periods with severe menstrual cramps.
- Irregular Periods: Cycles that vary in length by more than a few days each month.
- Spotting: Light bleeding between periods.
9.2 Potential Causes of Menstrual Irregularities
Various factors can contribute to menstrual irregularities:
- Hormonal Imbalances: Fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone levels can disrupt the menstrual cycle.
- Stress: High levels of stress can affect hormone production and lead to irregular periods.
- Weight Changes: Significant weight gain or loss can impact hormone levels and menstrual cycles.
- Thyroid Disorders: Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can cause menstrual irregularities.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): This hormonal disorder can lead to irregular periods, ovarian cysts, and other health issues.
- Premature Ovarian Insufficiency (POI): This condition occurs when the ovaries stop functioning normally before age 40, leading to irregular or absent periods.
- Uterine Issues: Fibroids, polyps, and other uterine abnormalities can cause irregular bleeding.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as antidepressants and corticosteroids, can affect menstrual cycles.
9.3 When to Seek Medical Attention
It’s advisable to seek medical attention if you experience any of the following:
- Sudden changes in your menstrual cycle.
- Periods that become significantly more painful or heavy.
- Bleeding between periods.
- Absence of menstruation for three or more months.
- Concerns about your menstrual health.
9.4 Expert Guidance at HOW.EDU.VN
At HOW.EDU.VN, our team of experienced doctors can provide expert guidance and comprehensive evaluations to address your menstrual health concerns. We offer personalized treatment plans to help you manage menstrual irregularities and improve your overall well-being.
10. Seeking Expert Consultation and Support
Navigating menstrual health can be complex, and seeking expert consultation and support is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective management.
10.1 Benefits of Consulting a Specialist
- Accurate Diagnosis: A specialist can perform thorough evaluations and diagnostic tests to identify the underlying cause of your menstrual issues.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: A specialist can develop a tailored treatment plan based on your individual needs and medical history.
- Effective Management: A specialist can provide ongoing support and guidance to help you manage your menstrual health effectively.
- Improved Quality of Life: By addressing your menstrual concerns, a specialist can help you improve your overall quality of life.
10.2 How HOW.EDU.VN Can Help
At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with experienced doctors who specialize in women’s health. Our team is dedicated to providing compassionate care and expert guidance to help you manage your menstrual health.
10.3 Call to Action
Don’t let menstrual issues disrupt your life. Contact HOW.EDU.VN today for a consultation with our experienced doctors. We’re here to provide the support and expertise you need to regain control of your health and well-being.
For expert advice and personalized solutions, reach out to HOW.EDU.VN. Connect with our leading doctors at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States. Contact us via Whatsapp at +1 (310) 555-1212 or visit our website at how.edu.vn. Let us help you navigate your health concerns with confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is considered a normal amount of blood loss during a menstrual period?
A normal amount of blood loss is generally less than 80 mL (about 2.7 ounces), typically lasting 2-7 days.
2. What are the signs of heavy menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia)?
Signs include soaking through pads or tampons every hour, needing to double up on pads, waking up at night to change pads, passing large blood clots, and prolonged bleeding lasting more than seven days.
3. What are some common causes of heavy menstrual bleeding?
Common causes include hormonal imbalances, uterine fibroids or polyps, bleeding disorders like Von Willebrand disease, and certain types of contraception like non-hormonal IUDs.
4. When should I seek medical attention for heavy menstrual bleeding?
Seek medical attention if you experience a significant increase in menstrual flow, periods interfering with daily activities, symptoms of anemia, or concerns about changes in your menstrual cycle.
5. What diagnostic tests are used to identify the cause of heavy menstrual bleeding?
Diagnostic tests may include blood tests, pelvic exams, ultrasounds, endometrial biopsies, hysteroscopies, and sonohysterograms.
6. What are some medical treatments for managing heavy menstrual flow?
Medical treatments include hormonal birth control (pills or IUDs), NSAIDs, tranexamic acid, iron supplements, and hormone therapy.
7. What are some surgical procedures for managing heavy menstrual flow?
Surgical procedures include dilation and curettage (D&C), operative hysteroscopy, endometrial ablation, uterine artery embolization, myomectomy, and hysterectomy.
8. How can lifestyle adjustments help manage menstrual blood loss?
Lifestyle adjustments include dietary changes (iron-rich foods, vitamin C), regular exercise, and stress management techniques like relaxation and adequate sleep.
9. How do different menstrual products impact tracking blood loss?
Pads and tampons allow for tracking frequency of changes, while menstrual cups and discs allow for measuring the volume of blood collected.
10. What other menstrual irregularities should I watch for besides heavy bleeding?
Other irregularities include amenorrhea (absence of menstruation), oligomenorrhea (infrequent periods), dysmenorrhea (painful periods), irregular cycles, and spotting between periods.