How Long Is 1 Meter? Understanding this fundamental unit of length is crucial in various fields, from construction to scientific research. At HOW.EDU.VN, we provide expert insights and comprehensive conversions to help you visualize and utilize the meter effectively, and offering consultation by top-notch Ph.Ds.. Mastering meter conversions, real-world comparisons, and its significance in measurements are all very helpful.
1. Understanding the Meter: A Comprehensive Guide
The meter (m) is the base unit of length in the International System of Units (SI). It’s essential for everyday measurements and complex scientific calculations. This article delves into the meter’s definition, its relationship with other units, and practical examples to enhance your understanding.
1.1. Defining the Meter
A meter is defined as the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of 1/299,792,458 of a second. It is equivalent to 100 centimeters, or one-thousandth of a kilometer. Understanding this definition helps in appreciating the precision and universality of the metric system.
1.2. The Significance of the Meter in the Metric System
The metric system, with the meter as its foundation, simplifies measurements by using powers of 10. This makes conversions straightforward and intuitive, a significant advantage over other systems like the imperial system.
1.3. Brief History of the Meter
The concept of the meter originated during the French Revolution, aiming to create a universal measurement system. Initially, it was defined as one ten-millionth of the distance from the equator to the North Pole along a meridian. Over time, the definition has evolved to its current, more precise standard based on the speed of light.
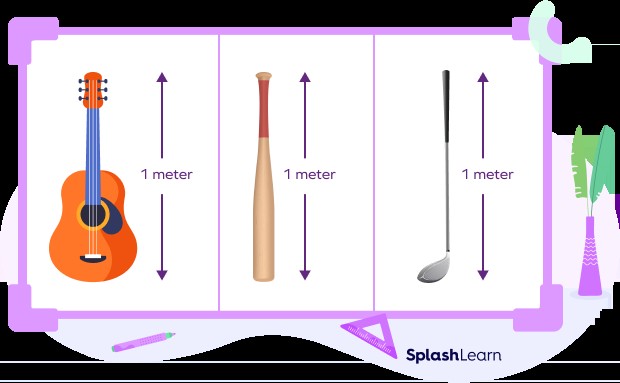
2. Visualizing a Meter: Real-World Examples
To truly grasp how long a meter is, comparing it to familiar objects can be incredibly helpful.
2.1. Common Objects Approximately One Meter Long
- Guitar: Most guitars are around 1 meter in length.
- Baseball Bat: A standard baseball bat is also approximately 1 meter long.
- Yardstick: A yardstick is very close to a meter (about 0.9144 meters).
2.2. Comparing a Meter to Human Height
An average five-year-old child is about 1 meter tall. Additionally, an adult’s step is roughly 1 meter long, providing a relatable comparison.
2.3. Meters in Construction and Everyday Life
In construction, meters are used to measure room dimensions, fabric lengths, and building materials. Understanding the meter’s length helps in planning and executing projects accurately.
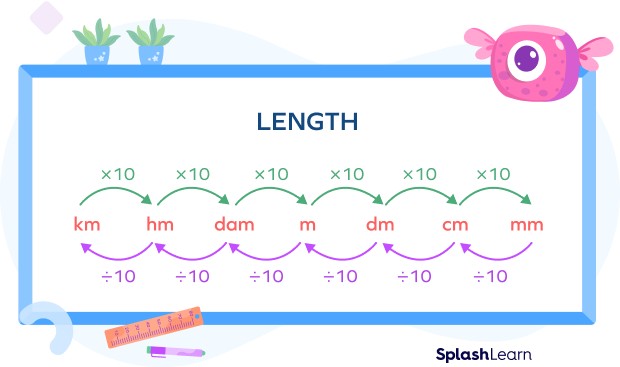
3. Meter Conversions: Metric and Imperial Units
Converting between meters and other units is essential for various applications. Here’s a detailed guide to converting meters to different units, both metric and imperial.
3.1. Converting Meters to Centimeters and Millimeters
- Meter to Centimeter: 1 meter = 100 centimeters
- Meter to Millimeter: 1 meter = 1000 millimeters
To convert meters to centimeters, multiply the meter value by 100. To convert meters to millimeters, multiply by 1000.
3.2. Converting Meters to Inches, Feet, and Yards
- Meter to Inches: 1 meter ≈ 39.37 inches
- Meter to Feet: 1 meter ≈ 3.28 feet
- Meter to Yards: 1 meter ≈ 1.094 yards
To convert meters to inches, multiply the meter value by 39.37. For feet, multiply by 3.28, and for yards, multiply by 1.094.
3.3. Converting Meters to Kilometers
- Meter to Kilometer: 1 meter = 0.001 kilometers
To convert meters to kilometers, divide the meter value by 1000.
3.4. Practical Conversion Examples
-
Example 1: Convert 5 meters to centimeters.
- 5 meters * 100 = 500 centimeters
-
Example 2: Convert 2.5 meters to inches.
-
- 5 meters * 39.37 = 98.425 inches
-
-
Example 3: Convert 1500 meters to kilometers.
- 1500 meters / 1000 = 1.5 kilometers
4. Why Accurate Measurements Matter
Accurate measurements are critical in science, engineering, and everyday life. Errors in measurement can lead to significant problems, highlighting the importance of precision.
4.1. The Role of Meters in Science and Engineering
In scientific experiments and engineering projects, precise measurements are essential for accuracy and reliability. The meter provides a standardized unit, ensuring consistency across different studies and projects.
4.2. Consequences of Measurement Errors
Measurement errors can have serious consequences. For instance, in construction, inaccurate measurements can lead to structural failures. In medicine, incorrect dosages can harm patients.
4.3. Tools for Accurate Measurement
Various tools are available for accurate measurement, including:
- Rulers: For measuring short lengths.
- Tape Measures: For measuring longer distances.
- Laser Distance Measurers: For highly accurate measurements over long distances.
Using the right tool and understanding its limitations is crucial for obtaining precise measurements.
5. Understanding Meter Conversions in Depth
To convert the length given in meters to other different units, we are required to know the relation or the conversion factor between the meter and the other units. Here’s an in-depth look at converting meters to other units, complete with examples and detailed explanations.
5.1. Meter to Centimeter
A centimeter (cm) is a unit, which is used to represent measurements that are smaller than the meter.
- 100 cm = 1 meter
- 1 cm = 1/100 m
Example: Convert 500 cm to meters.
1 cm = 1/100 meters
500 cm = 500 × (1/100) = 5 m
5.2. Meter to Millimeter
A millimeter (mm) is the smallest unit of length in the metric system.
- 1000 mm = 1 m
- 1 mm = 1/1000 m
Example: Convert 7000 mm to meters.
1 mm = 1/1000 m
7000 mm = 7000 × 1/1000 = 7 meters
5.3. Meter to Inches
An inch (in or ”) is a customary unit of length.
- 1 meter = 39.37007874 inches
- 1 inch = 0.0254 m
Example: Jason has a rope of length 58’’. Calculating how long the rope is in meters.
1 inch = 0.0254 meters
58 inches = 58 × 0.0254 meters = 1.4732 meters
5.4. Meter to Yards
A yard (yd) is a customary unit of length which is larger than an inch. 1 meter is longer than a yard since 1 m ≈ 3.28 feet but 1 yard = 3 feet.
Here are the conversion factors for the meters to yards conversion:
-
- 094 yard = 1 meter
- 1 yard = 1.914 m
Example: Convert 5 yards to meters.
1 yard = 1.914 of a meter.
5 yards = 5 × 1.914 meters = 4.572 meters
5.5. Meter to Feet
A foot, feet in plural, (ft) is a customary unit of length. Meter to feet (or feet to meter) conversions are based on the following conversion factors:
-
- 28084 feet = 1 meter
- 1 foot = 0.3048 meter
Example: Convert 8 ft into meters.
1 ft = 0.3048 meters
8 ft = 8 × 0.3048 meters = 2.4384 meters
6. Meter Conversions Chart
| 1 m = 1000 mm | 1 millimeter = 0.001 m |
|---|---|
| 1 m = 100 cm | 1 centimeter = 0.01 m |
| 1 m = 39.3701 in | 1 inch = 0.0254 m |
| 1 m = 1.09361 yards | 1 yard = 0.9144 m |
| 1 m = 3.28084 feet | 1 feet = 0.3048 m |
7. Advanced Applications of the Meter
Beyond everyday use, the meter plays a crucial role in advanced scientific and technological applications.
7.1. Meters in Physics and Astronomy
In physics, the meter is used to measure wavelengths of light, distances in particle accelerators, and more. In astronomy, it helps measure distances between celestial bodies, though larger units like light-years are more commonly used for interstellar distances.
7.2. Meters in GPS and Mapping Technologies
Global Positioning System (GPS) technology relies on precise distance measurements, often using meters, to determine locations accurately. Mapping technologies also use meters for creating detailed maps and geographic information systems.
7.3. The Meter in Sports
The meter is the standard unit for measuring distances in many sports, including track and field, swimming, and soccer. For example, the 100-meter dash is a prestigious event in athletics, showcasing speed and precision.
8. Common Mistakes in Meter Conversions and How to Avoid Them
Even with a clear understanding of conversion factors, mistakes can happen. Here are some common errors and tips to avoid them.
8.1. Incorrect Use of Conversion Factors
A common mistake is using the wrong conversion factor. Always double-check the factor before performing the calculation.
8.2. Rounding Errors
Rounding numbers too early in the calculation can lead to inaccuracies. Keep as many decimal places as possible until the final result, then round appropriately.
8.3. Unit Confusion
Mixing up units, especially when dealing with multiple conversions, can cause errors. Always label your units and ensure they are consistent throughout the calculation.
9. The Future of Measurement: Advanced Metrology
Metrology, the science of measurement, is constantly evolving. Advanced metrology techniques are pushing the boundaries of precision and accuracy.
9.1. Quantum Metrology
Quantum metrology uses quantum mechanics to achieve unprecedented levels of precision. This includes using atomic clocks for timekeeping and quantum sensors for measuring physical quantities with extreme accuracy.
9.2. The Redefinition of the Kilogram and its Impact on the Meter
In 2019, the kilogram was redefined based on fundamental constants of nature, rather than a physical artifact. This redefinition has implications for all units in the SI system, including the meter, by linking them to fundamental constants, ensuring long-term stability and accuracy.
9.3. Nanotechnology and the Meter
Nanotechnology involves manipulating materials at the nanometer scale. Accurate measurement at this level is crucial for developing new materials and devices. Advanced microscopy techniques and precision instruments are used to measure dimensions at the nanoscale.
10. Expert Insights on Measurement Best Practices
To ensure accurate and reliable measurements, follow these best practices recommended by experts at HOW.EDU.VN.
10.1. Calibrating Instruments Regularly
Calibration ensures that measurement instruments are accurate. Regular calibration, using certified standards, is essential for maintaining precision.
10.2. Using Multiple Measurements and Averaging
Taking multiple measurements and averaging the results can reduce random errors. This technique improves the reliability of your measurements.
10.3. Documenting Measurement Procedures
Documenting your measurement procedures ensures consistency and allows others to replicate your results. Include details such as the instruments used, the environmental conditions, and the steps taken.
11. Facts about “Meter”
- Growth differs from person to person, but an average 5 year old child is considered to be about 1 meter tall.
- An adult person takes about 1 meter long step.
- 1000 m = 1 km
- 1000 mm = 1 m
12. Solved Examples on “Meter”
1. The width of a door is 24 inches. How wide is the door in meters?
Solution:
The width of the door is 24 inches.
1 inch = 0.0254 meter
24 inches = 24 × 0.0254 = 0.6096 meters
Therefore, the width of the door = 0.6 meters approximately.
2. How many feet are in 15 meters?
Solution:
1 meter = 3.28 feet
Thus, 15 meter = 15 × 3.28 = 49.2126 feet
Therefore, there are just above 49 feet in 15 meters.
3. Is 1 meter longer than 1 yard?
Solution:
Let’s express 1 meter and 1 yard in terms of the same unit.
1 meter = 39.3701 inches
1 yard = 36 inches
Thus, 1 meter is a little longer than 1 yard (1 yard = 0.9144 m).
4. Convert 3 mm to meters.
Solution:
1 mm = 1/1000 m
Thus, 3 mm = 3 × 1/1000 = 0.003 m
Therefore, 3 mm = 0.003 m
13. Practice Problems on “Meter”
How Long Is a Meter? Definition, Conversions, Examples, FAQs
Attend this quiz & Test your knowledge.
-
1 meter = ____ cm
- 1000
- 100
- 10
- 1
Correct answer is: 100
1 m = 100 cm -
Convert 5 yards to meters.
-
- 572 m
-
- 989 m
- 12.55 m
- 11.565 m
Correct answer is: 4.572 m
1 yard = 0.9144 m We multiply the length value in yards by 0.9144 to convert it to meters. So, 5 × 0.9144 = 4.572 m -
-
How long is a meter compared to 1 mm?
- 1000 mm = 1 m
- 1000 m = 1 mm
- 100 m = 1m
- 10 m = 1 mm
Correct answer is: 1000 mm = 1 m
1000 mm = 1 meter -
Which of the following units are bigger than a meter?
- Centimeter
- Millimeter
- Inches
- Kilometer
Correct answer is: Kilometer
1 m = 100 cm
1 m = 1000 mm
1 m = 39.3701 in
1000 m = 1 km
14. Frequently Asked Questions about “Meter”
Is an inch smaller than 1 meter?
Yes, 1 inch is smaller than 1 meter.
1 m = 39.3701 in
What is a decimeter?
Decimeter is a unit for measuring the length that equals one-tenth of a meter.
10 m = 1 dm
How long is a meter compared to 1 mile?
1609.34 meters = 1 mile
How long is a meter stick? How long is a meter stick in inches?
A meter stick is exactly 1 meter long.
1 m = 39.3701 in = 3.28084 feet = 1.09361 yards = 0.000621371 miles
How long is a meter in feet?
1 m = 3.28084 feet
How long is a meter in inches?
1 m = 39.3701 in
How long is a meter in cm?
1 m = 100 cm
How long is a meter compared to a yard? How long is a meter in yards?
1 m = 1.09361 yards
15. Conclusion
Understanding how long a meter is, along with its conversions and applications, is fundamental in many fields. By grasping these concepts, you can improve accuracy in your measurements and gain a deeper appreciation for the metric system.
Navigating complex measurements can be challenging, but you don’t have to do it alone. At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with over 100 world-renowned Ph.Ds ready to provide expert guidance and personalized solutions tailored to your needs. Whether you’re tackling a scientific project, managing a business, or seeking personal advice, our experts offer the clarity and support you deserve.
Don’t let uncertainty hold you back. Contact HOW.EDU.VN today and experience the confidence that comes with having the world’s leading experts in your corner.
Ready to take the next step?
Reach out to us for a consultation and let our Ph.Ds provide the expert guidance you need.
Contact Information:
- Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
- Website: HOW.EDU.VN
Let how.edu.vn be your partner in achieving clarity and success.