Losing Toby Keith at just 62 to stomach cancer has prompted many to ask, How Did Toby Keith Die? His passing highlights the need for greater awareness about this challenging disease. At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with leading specialists who can provide clarity on understanding, preventing, and treating stomach cancer. Our experts offer cutting-edge insights and personalized advice. Let’s delve into this topic, covering gastric cancer symptoms, forms, and treatments while exploring the importance of expert medical guidance.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Toby Keith’s Battle with Stomach Cancer
- What is Stomach Cancer? A Detailed Overview
- What are the Early Warning Signs and Symptoms of Stomach Cancer?
- Advanced Stage Symptoms: When to Seek Immediate Help
- What are the Different Types of Stomach Cancer?
- Adenocarcinoma: The Most Common Form of Stomach Cancer
- Lymphoma: Stomach Cancer of the Immune System
- Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST): A Rare Form
- Carcinoid Tumor: A Hormone-Related Stomach Cancer
- What are the Key Risk Factors for Developing Stomach Cancer?
- The Role of Diet and Lifestyle in Stomach Cancer Risk
- Genetic Predisposition: Is Stomach Cancer Hereditary?
- How is Stomach Cancer Diagnosed?
- Endoscopy and Biopsy: The Gold Standard for Diagnosis
- Imaging Techniques: CT Scans, MRIs, and PET Scans
- What are the Treatment Options for Stomach Cancer?
- Surgery: Different Surgical Procedures Explained
- Chemotherapy: How it Works and What to Expect
- Radiation Therapy: Targeting Cancer Cells with Precision
- Targeted Therapy: A Personalized Approach to Treatment
- Immunotherapy: Boosting Your Body’s Natural Defenses
- What is the Prognosis for Stomach Cancer?
- The Impact of Early Detection on Survival Rates
- Factors Influencing Prognosis: Stage, Type, and Treatment Response
- How Can I Reduce My Risk of Stomach Cancer?
- Dietary Recommendations for Stomach Cancer Prevention
- Lifestyle Changes: Exercise, Smoking Cessation, and Alcohol Consumption
- Regular Check-ups and Screenings: When to See a Doctor
- What Support Services are Available for Stomach Cancer Patients?
- Emotional Support: Counseling and Support Groups
- Nutritional Support: Working with a Dietitian
- Financial Assistance: Resources for Managing Costs
- How Can HOW.EDU.VN Help You?
- Connect with Top Experts
- Personalized Advice and Guidance
- Convenient and Confidential Consultations
- What are Some Frequently Asked Questions About Stomach Cancer?
- Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Health
1. Understanding Toby Keith’s Battle with Stomach Cancer
Toby Keith’s death from stomach cancer at the age of 62 underscores the severity and potential challenges in diagnosing and treating this disease. He publicly shared his diagnosis in the fall of 2021, revealing that he had undergone months of rigorous treatments, including chemotherapy, radiation, and surgery. According to a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine, early detection and comprehensive treatment approaches are critical in improving outcomes for patients with gastric cancer. Toby Keith’s experience highlights the need for increased awareness and proactive healthcare practices regarding stomach cancer.
 Toby Keith's public announcement of his stomach cancer diagnosis, raising awareness about the disease
Toby Keith's public announcement of his stomach cancer diagnosis, raising awareness about the disease
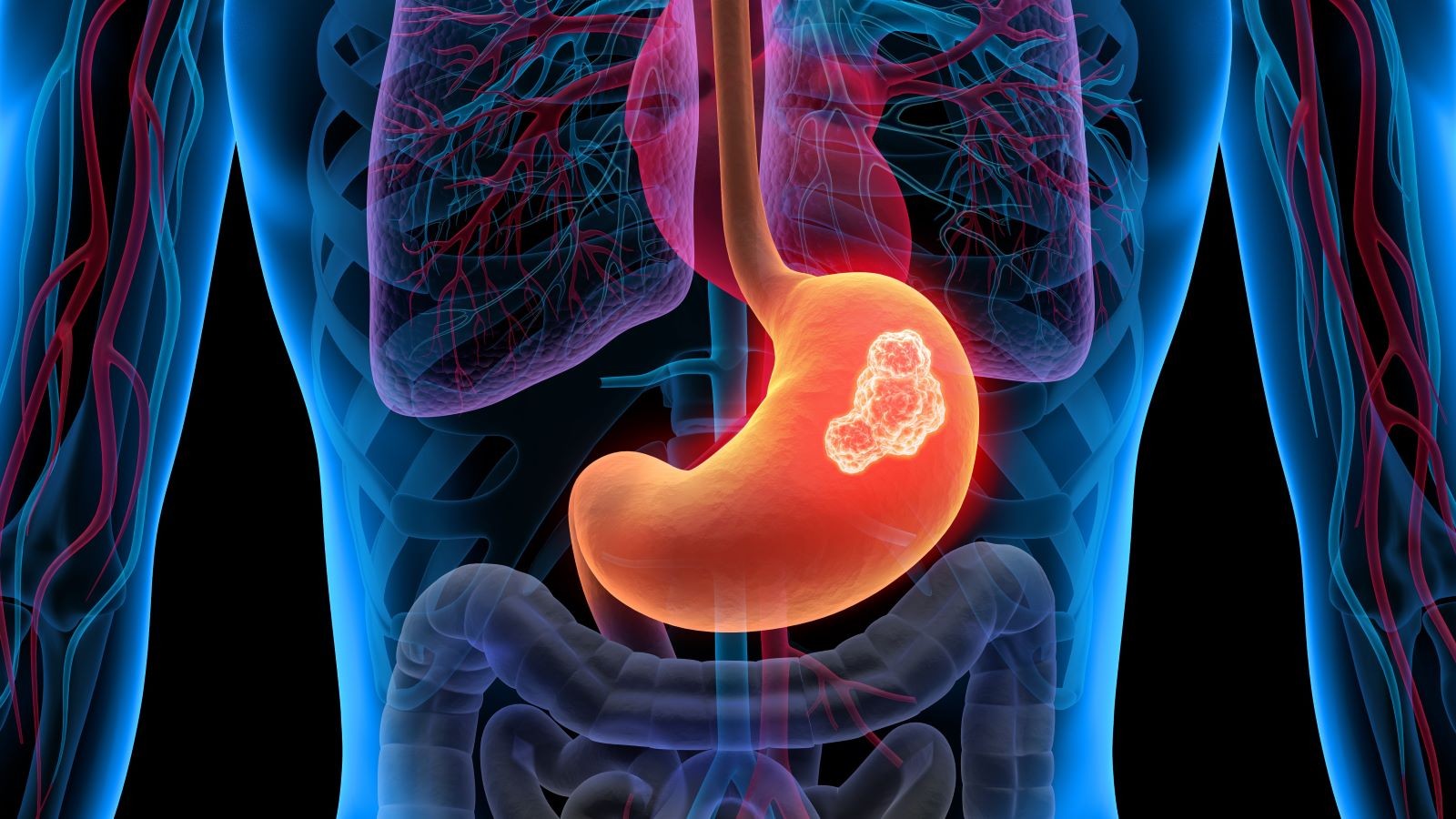
2. What is Stomach Cancer? A Detailed Overview
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a disease in which malignant cells form in the lining of the stomach. According to the American Cancer Society, stomach cancer accounts for approximately 1.5% of all new cancers diagnosed in the United States each year. The stomach, a J-shaped organ in the upper abdomen, plays a vital role in digesting food. Cancer can develop in any part of the stomach and spread to other organs, such as the liver, lungs, and lymph nodes. Understanding the basics of stomach cancer is the first step in recognizing its potential impact and seeking appropriate medical advice.
3. What are the Early Warning Signs and Symptoms of Stomach Cancer?
Early detection of stomach cancer is crucial for improving treatment outcomes. Unfortunately, the early signs of stomach cancer can be subtle and easily mistaken for other common ailments. According to a report by the Mayo Clinic, early symptoms may include:
- Persistent indigestion
- Unexplained stomach pain
- Feeling bloated after eating small meals
- Nausea
- Loss of appetite
- Frequent heartburn
These symptoms can often be attributed to minor digestive issues; however, if they persist or worsen, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional. Early diagnosis, facilitated by awareness of these subtle symptoms, can significantly increase the chances of successful treatment and improved life expectancy.
4. Advanced Stage Symptoms: When to Seek Immediate Help
As stomach cancer progresses, the symptoms become more pronounced and indicative of a serious underlying issue. Advanced stage symptoms, as outlined by the National Cancer Institute, may include:
- Blood in the stool
- Vomiting, potentially with blood
- Unexplained and rapid weight loss
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Ascites, or a build-up of fluid in the abdomen
- Difficulty swallowing
These advanced symptoms require immediate medical attention. If you experience any of these signs, it is critical to seek prompt medical evaluation to determine the cause and begin appropriate treatment. Timely intervention can help manage the disease and improve the quality of life for individuals with advanced stomach cancer.
5. What are the Different Types of Stomach Cancer?
Stomach cancer is not a single disease; it encompasses several different types, each with unique characteristics and treatment approaches. The four main types of stomach cancer include:
- Adenocarcinoma
- Lymphoma
- Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST)
- Carcinoid Tumor
Understanding these different types is essential for accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment planning. Each type originates from different cells within the stomach and behaves differently, influencing the course of the disease and the selection of the most effective therapies.
6. Adenocarcinoma: The Most Common Form of Stomach Cancer
Adenocarcinoma is the most prevalent type of stomach cancer, accounting for approximately 90-95% of all cases, as noted by the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO). This type of cancer develops in the inner lining of the stomach, known as the mucosa. Adenocarcinomas are further classified based on their appearance under a microscope, including intestinal and diffuse types. The intestinal type tends to form gland-like structures, while the diffuse type consists of individual cells that spread through the stomach wall. Understanding the specific subtype of adenocarcinoma is crucial for determining the prognosis and guiding treatment decisions.
7. Lymphoma: Stomach Cancer of the Immune System
Lymphoma is a type of cancer that originates in the cells of the immune system, specifically lymphocytes. When lymphoma occurs in the stomach, it is often referred to as gastric lymphoma. According to the Lymphoma Research Foundation, gastric lymphomas are relatively rare, accounting for only a small percentage of all stomach cancers. These lymphomas typically develop in the stomach wall and can be classified as either Hodgkin’s lymphoma or non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Treatment approaches for gastric lymphoma may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapy, depending on the specific type and stage of the lymphoma.
8. Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST): A Rare Form
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GISTs) are rare tumors that can develop anywhere in the digestive tract, but they most commonly occur in the stomach. According to the GIST Support International, GISTs originate from specialized cells in the stomach wall called interstitial cells of Cajal (ICCs), which play a role in controlling muscle contractions in the digestive system. GISTs are often treated with targeted therapy drugs that specifically inhibit the growth of these tumor cells. Surgical removal of the tumor may also be an option, depending on its size and location.
9. Carcinoid Tumor: A Hormone-Related Stomach Cancer
Carcinoid tumors are a type of neuroendocrine tumor that can develop in the hormone-producing cells of the stomach. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), these tumors are relatively rare and tend to grow slowly. Carcinoid tumors can produce various hormones, leading to symptoms such as flushing, diarrhea, and wheezing, known as carcinoid syndrome. Treatment options may include surgery, targeted therapy, and hormone-blocking medications to manage symptoms.
10. What are the Key Risk Factors for Developing Stomach Cancer?
Several factors can increase the risk of developing stomach cancer. According to the World Cancer Research Fund, these risk factors include:
- Infection with Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori)
- Chronic gastritis (inflammation of the stomach lining)
- A diet high in salty, smoked, or pickled foods
- Smoking
- Family history of stomach cancer
- Previous stomach surgery
- Certain genetic conditions, such as hereditary diffuse gastric cancer
Understanding these risk factors can help individuals make informed lifestyle choices and take proactive steps to reduce their risk of developing stomach cancer.
11. The Role of Diet and Lifestyle in Stomach Cancer Risk
Diet and lifestyle play a significant role in influencing the risk of stomach cancer. A diet high in salty, smoked, and pickled foods has been linked to an increased risk, while a diet rich in fruits and vegetables may offer some protection. According to a study published in the International Journal of Cancer, high consumption of processed meats and low intake of fresh produce are associated with a higher incidence of stomach cancer. Additionally, smoking and excessive alcohol consumption are known risk factors. Adopting a healthy diet and lifestyle can help reduce the risk of developing stomach cancer.
12. Genetic Predisposition: Is Stomach Cancer Hereditary?
While most cases of stomach cancer are not hereditary, a small percentage of cases can be attributed to genetic factors. Hereditary diffuse gastric cancer (HDGC) is a rare genetic condition caused by a mutation in the CDH1 gene, which significantly increases the risk of developing diffuse stomach cancer. According to the Gastric Cancer Foundation, individuals with a family history of stomach cancer, particularly diffuse-type, may consider genetic testing to assess their risk. Genetic counseling and screening can help families make informed decisions about their healthcare.
13. How is Stomach Cancer Diagnosed?
Diagnosing stomach cancer typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history review, and diagnostic tests. According to the American Gastroenterological Association, common diagnostic procedures include:
- Endoscopy
- Biopsy
- Imaging tests (CT scan, MRI, PET scan)
- Blood tests
These tests help healthcare professionals identify abnormalities in the stomach and determine the presence and extent of cancer. Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment planning and improved outcomes.
14. Endoscopy and Biopsy: The Gold Standard for Diagnosis
Endoscopy is a procedure in which a thin, flexible tube with a camera (endoscope) is inserted through the mouth and into the stomach to visualize the lining. According to the National Institute of Digestive Diseases and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), endoscopy allows doctors to examine the stomach for any abnormalities, such as ulcers, tumors, or inflammation. During the procedure, a biopsy may be performed, where a small tissue sample is taken for further examination under a microscope. Biopsy is the gold standard for confirming the presence of cancer cells and determining the type and grade of cancer.
15. Imaging Techniques: CT Scans, MRIs, and PET Scans
Imaging techniques play a crucial role in staging stomach cancer and determining whether it has spread to other organs. CT scans, MRIs, and PET scans are commonly used imaging modalities. According to the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA), CT scans use X-rays to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body, while MRIs use magnetic fields and radio waves. PET scans use a radioactive tracer to detect metabolically active cells, such as cancer cells. These imaging techniques provide valuable information for treatment planning and monitoring the response to therapy.
16. What are the Treatment Options for Stomach Cancer?
Treatment for stomach cancer depends on several factors, including the stage and type of cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health. According to the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN), common treatment options include:
- Surgery
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation therapy
- Targeted therapy
- Immunotherapy
These treatments may be used alone or in combination to achieve the best possible outcome. A multidisciplinary approach, involving surgeons, oncologists, and other specialists, is often recommended to develop an individualized treatment plan.
17. Surgery: Different Surgical Procedures Explained
Surgery is a primary treatment option for many cases of stomach cancer, particularly when the cancer is localized and has not spread to distant organs. According to the American College of Surgeons, surgical procedures for stomach cancer may include:
- Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR)
- Subtotal or Partial Gastrectomy
- Total Gastrectomy
EMR is used for early-stage cancers confined to the inner lining of the stomach. Partial gastrectomy involves removing a portion of the stomach, while total gastrectomy involves removing the entire stomach. The choice of surgical procedure depends on the location and extent of the cancer.
18. Chemotherapy: How it Works and What to Expect
Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing. According to the Chemotherapy Foundation, chemotherapy may be used before surgery (neoadjuvant chemotherapy) to shrink the tumor, after surgery (adjuvant chemotherapy) to kill any remaining cancer cells, or as the main treatment for advanced stomach cancer. Chemotherapy drugs are typically administered intravenously, and the treatment schedule depends on the specific drugs used and the patient’s response. Common side effects of chemotherapy may include nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and hair loss.
19. Radiation Therapy: Targeting Cancer Cells with Precision
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. According to the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO), radiation therapy may be used before surgery to shrink the tumor, after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells, or as the main treatment for patients who are not candidates for surgery. Radiation therapy can be delivered externally, using a machine that directs radiation beams at the cancer, or internally, using radioactive materials placed directly in or near the tumor. Side effects of radiation therapy depend on the area being treated and may include fatigue, skin irritation, and digestive issues.
20. Targeted Therapy: A Personalized Approach to Treatment
Targeted therapy involves the use of drugs that specifically target cancer cells while sparing normal cells. According to the National Cancer Institute (NCI), targeted therapy drugs work by interfering with specific molecules involved in cancer cell growth, such as growth factors or signaling pathways. Targeted therapy may be used for certain types of stomach cancer, such as GISTs or adenocarcinomas with specific genetic mutations. Before starting targeted therapy, patients may undergo genetic testing to determine whether their cancer cells have the specific targets that the drugs can act upon.
21. Immunotherapy: Boosting Your Body’s Natural Defenses
Immunotherapy is a type of treatment that helps your immune system fight cancer. According to the Cancer Research Institute (CRI), immunotherapy drugs work by blocking certain proteins that prevent the immune system from attacking cancer cells. Immunotherapy may be used for advanced stomach cancer that has not responded to other treatments. Side effects of immunotherapy can vary but may include fatigue, skin rash, and autoimmune reactions.
22. What is the Prognosis for Stomach Cancer?
The prognosis for stomach cancer depends on several factors, including the stage and type of cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health and response to treatment. According to the American Cancer Society, the overall 5-year survival rate for stomach cancer is around 32%. However, survival rates vary widely depending on the stage at diagnosis. Early-stage stomach cancer has a much higher survival rate than advanced-stage cancer.
23. The Impact of Early Detection on Survival Rates
Early detection of stomach cancer is crucial for improving survival rates. According to a study published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, patients diagnosed with early-stage stomach cancer have a 5-year survival rate of over 70%, compared to less than 5% for those diagnosed with advanced-stage cancer. Screening programs and increased awareness of early symptoms can help detect stomach cancer at an earlier stage, leading to more effective treatment and improved outcomes.
24. Factors Influencing Prognosis: Stage, Type, and Treatment Response
Several factors can influence the prognosis for stomach cancer. These factors include:
- Stage of cancer at diagnosis
- Type of cancer (e.g., adenocarcinoma, lymphoma)
- Location of the tumor in the stomach
- Overall health of the patient
- Response to treatment
- Presence of specific genetic mutations
Understanding these factors can help healthcare professionals develop an individualized treatment plan and provide patients with a more accurate prognosis.
25. How Can I Reduce My Risk of Stomach Cancer?
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent stomach cancer, there are several steps you can take to reduce your risk. According to the World Cancer Research Fund, these steps include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Eating a diet rich in fruits and vegetables
- Limiting intake of salty, smoked, and pickled foods
- Quitting smoking
- Limiting alcohol consumption
- Getting treated for H. pylori infection, if present
Adopting these lifestyle changes can help lower your risk of developing stomach cancer.
26. Dietary Recommendations for Stomach Cancer Prevention
Diet plays a significant role in stomach cancer prevention. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help protect against stomach cancer. According to the American Institute for Cancer Research (AICR), specific dietary recommendations include:
- Eating at least five servings of fruits and vegetables per day
- Choosing whole grains over refined grains
- Limiting intake of red and processed meats
- Avoiding salty, smoked, and pickled foods
- Drinking plenty of water
Following these dietary guidelines can help reduce your risk of developing stomach cancer.
27. Lifestyle Changes: Exercise, Smoking Cessation, and Alcohol Consumption
In addition to diet, lifestyle factors such as exercise, smoking, and alcohol consumption can also impact your risk of stomach cancer. Regular exercise can help maintain a healthy weight and boost your immune system, while quitting smoking can significantly reduce your risk of various cancers, including stomach cancer. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), limiting alcohol consumption to moderate levels (one drink per day for women, two drinks per day for men) is also recommended.
28. Regular Check-ups and Screenings: When to See a Doctor
Regular check-ups and screenings are essential for early detection of stomach cancer. According to the American Cancer Society, individuals with a family history of stomach cancer or other risk factors may benefit from regular screening, such as endoscopy. If you experience persistent symptoms such as indigestion, stomach pain, or unexplained weight loss, it is important to see a doctor for evaluation.
29. What Support Services are Available for Stomach Cancer Patients?
Coping with a diagnosis of stomach cancer can be challenging, both emotionally and physically. Fortunately, several support services are available to help patients and their families. These services may include:
- Counseling and support groups
- Nutritional support
- Financial assistance
- Palliative care
These resources can provide valuable assistance and support throughout the cancer journey.
30. Emotional Support: Counseling and Support Groups
Emotional support is crucial for stomach cancer patients and their families. Counseling and support groups can provide a safe and supportive environment to share experiences, learn coping strategies, and connect with others facing similar challenges. According to the Cancer Support Community, these resources can help reduce stress, improve quality of life, and enhance overall well-being.
31. Nutritional Support: Working with a Dietitian
Nutritional support is an essential part of stomach cancer care. Working with a registered dietitian can help patients manage side effects of treatment, maintain a healthy weight, and optimize their nutritional intake. According to the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, a dietitian can provide individualized meal plans, dietary recommendations, and strategies for managing digestive issues.
32. Financial Assistance: Resources for Managing Costs
The cost of cancer treatment can be substantial. Fortunately, several resources are available to help patients manage their financial burden. These resources may include:
- Government programs (e.g., Medicare, Medicaid)
- Nonprofit organizations (e.g., American Cancer Society, Cancer Research Institute)
- Pharmaceutical assistance programs
- Fundraising and crowdfunding
These programs can provide financial assistance for medical bills, medications, and other expenses.
33. How Can HOW.EDU.VN Help You?
At HOW.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges individuals face when dealing with complex health issues like stomach cancer. Our platform offers a unique opportunity to connect with leading medical experts who can provide personalized advice and guidance. We bridge the gap between you and the world’s top doctors and specialists, ensuring you receive the best possible information and support.
34. Connect with Top Experts
HOW.EDU.VN gives you direct access to a network of over 100 renowned Ph.D.s and specialists from various fields. These experts can offer insights into stomach cancer prevention, diagnosis, treatment options, and the latest research advancements. Whether you have questions about symptoms, risk factors, or treatment side effects, our specialists are here to provide clear and reliable answers.
35. Personalized Advice and Guidance
We recognize that every individual’s situation is unique. That’s why we emphasize personalized advice tailored to your specific needs and concerns. Our experts take the time to understand your medical history, lifestyle, and preferences to provide recommendations that align with your goals.
36. Convenient and Confidential Consultations
HOW.EDU.VN offers a convenient and confidential platform for seeking expert medical advice. You can connect with specialists from the comfort of your own home, eliminating the need for travel and long wait times. Our platform ensures the privacy and security of your personal information, so you can feel confident sharing your concerns.
For expert consultation and support, contact us today:
- Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
- Website: HOW.EDU.VN
37. What are Some Frequently Asked Questions About Stomach Cancer?
Q1: What are the early symptoms of stomach cancer?
Early symptoms include indigestion, stomach pain, feeling bloated after eating, nausea, loss of appetite, and heartburn.
Q2: What are the main risk factors for stomach cancer?
Risk factors include H. pylori infection, diet high in salty/smoked foods, smoking, family history, and certain genetic conditions.
Q3: How is stomach cancer diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves endoscopy, biopsy, imaging tests (CT, MRI, PET scans), and blood tests.
Q4: What are the primary treatment options for stomach cancer?
Treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy.
Q5: Can stomach cancer be prevented?
Risk can be reduced by maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, quitting smoking, and limiting alcohol.
Q6: Is stomach cancer hereditary?
While most cases aren’t hereditary, some genetic conditions like hereditary diffuse gastric cancer (HDGC) increase risk.
Q7: What support services are available for stomach cancer patients?
Support services include counseling, support groups, nutritional support, and financial assistance programs.
Q8: What is the survival rate for stomach cancer?
The 5-year survival rate varies by stage; early-stage has a higher rate than advanced-stage cancer.
Q9: How does diet impact stomach cancer risk?
A diet rich in fruits/vegetables may protect, while high intake of salty/smoked foods increases risk.
Q10: When should I see a doctor if I suspect stomach cancer?
See a doctor if you experience persistent symptoms like indigestion, stomach pain, or unexplained weight loss.
38. Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Health
Understanding stomach cancer is the first step in taking control of your health. With the right knowledge and support, you can make informed decisions about prevention, early detection, and treatment. At HOW.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing you with access to the best medical expertise and resources. Don’t face this challenge alone. Contact us today to connect with our team of specialists and receive the personalized guidance you deserve.
Remember, early detection and proactive management are key to improving outcomes and enhancing your quality of life. Reach out to how.edu.vn and let us help you navigate your path to better health.