Are you curious about how much dentists earn annually in their private practices? At HOW.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of this information for those considering dental practice ownership or seeking to understand the financial landscape of dentistry. We provide expert insights to guide you. Discover the factors influencing dentist earnings, including practice profitability, location, and specialization, as well as strategies for boosting your income potential in the dental field.
1. Understanding the Average Dentist Salary
What is the average annual income for a dentist? The average annual income for a dentist in private practice in the U.S. is approximately $414,000. However, this figure is just a starting point. Several factors influence a dentist’s earning potential, including location, specialization, years of experience, and practice management skills. Understanding these variables can provide a more accurate picture of what you can expect to earn as a dentist.
Dentists can increase their earning potential through various strategies. These include specializing in high-demand areas such as orthodontics or oral surgery, improving practice efficiency through technology adoption, expanding service offerings to include cosmetic dentistry, and focusing on patient retention and referrals.
2. Key Factors Influencing a Dentist’s Yearly Income
What factors affect a dentist’s annual salary? Several key factors can significantly influence a dentist’s yearly income. These include the practice’s location, specialization, overhead costs, patient volume, and the dentist’s experience and skills. A dentist’s ability to manage and optimize these factors directly impacts their earning potential.
2.1. Location, Location, Location
How does geographical location impact a dentist’s income? The geographical location of a dental practice plays a crucial role in determining income. Areas with higher living costs and greater demand for dental services often correlate with higher earnings for dentists. Metropolitan areas and affluent suburbs may offer more lucrative opportunities compared to rural or underserved regions.
2.2. Specialization Matters
Which dental specialties command higher salaries? Dental specialties such as orthodontics, oral and maxillofacial surgery, and periodontics typically command higher salaries than general dentistry. These specialties require additional years of training and expertise, allowing specialists to charge higher fees for their specialized services. General dentists can also increase their income by offering specialized services like implant dentistry or cosmetic procedures.
2.3. Overhead Costs and Profit Margins
How do overhead costs affect a dentist’s take-home pay? Managing overhead costs is essential for maximizing a dentist’s take-home pay. Overhead expenses, including rent, staff salaries, supplies, and marketing, can significantly impact a practice’s profitability. Efficient practice management and cost-control strategies are crucial for maintaining healthy profit margins.
2.4. Patient Volume and Retention
Why is patient volume important for dentist income? Patient volume directly impacts a dentist’s income. Attracting and retaining a steady stream of patients is vital for maintaining a profitable practice. Effective marketing strategies, excellent patient care, and convenient scheduling options can help increase patient volume and loyalty.
2.5. Experience and Skill Set
How does experience influence a dentist’s earning potential? A dentist’s experience and skill set significantly contribute to their earning potential. Experienced dentists who have honed their clinical skills and built a strong reputation often attract more patients and command higher fees for their services. Continuous professional development and training in advanced techniques can further enhance a dentist’s earning capacity.
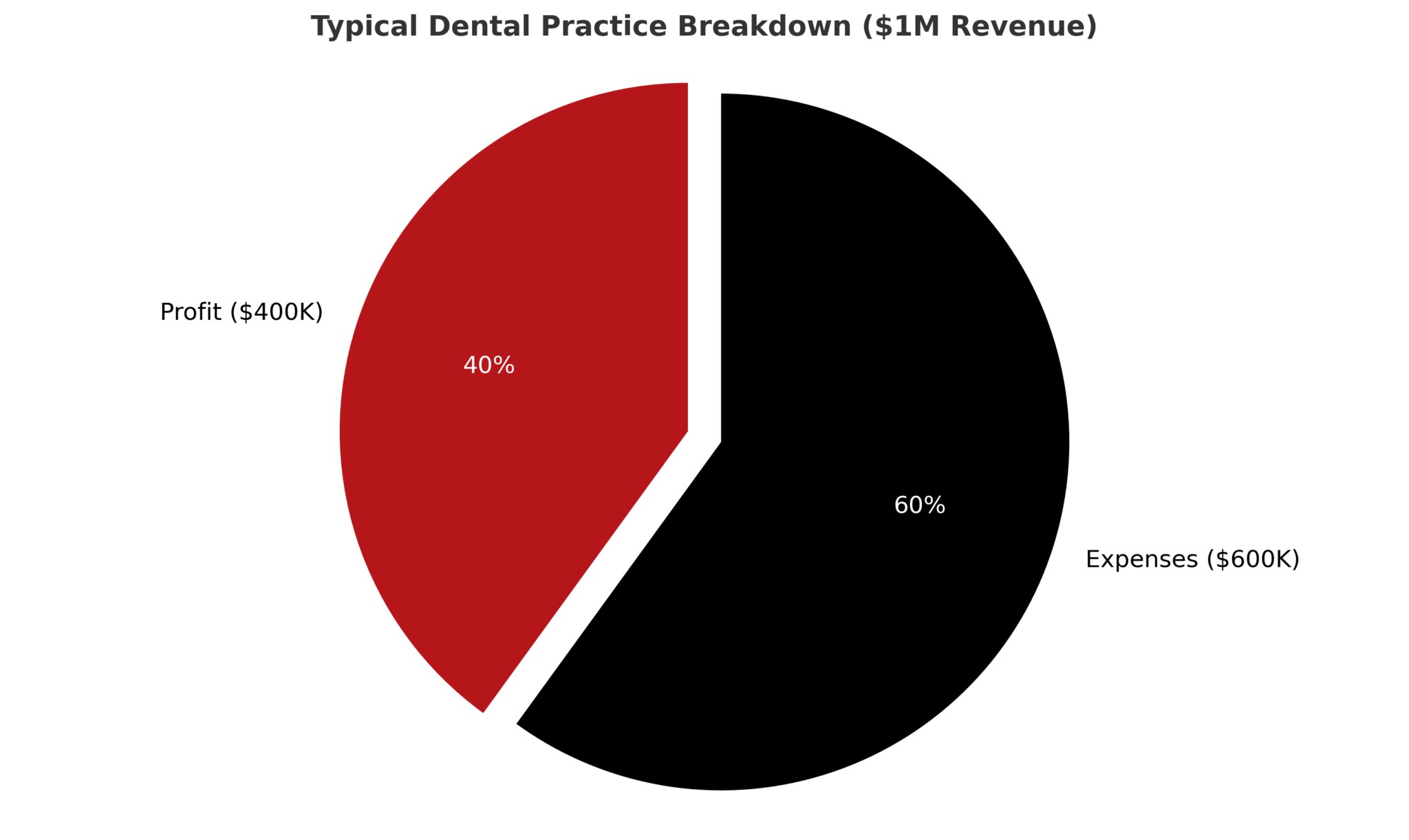
3. Breaking Down the Numbers: Revenue, Expenses, and Profit
How does a dental practice’s revenue translate into a dentist’s salary? Understanding the relationship between revenue, expenses, and profit is crucial for dentists to assess their financial performance and optimize their income. By analyzing these key metrics, dentists can identify areas for improvement and implement strategies to increase their profitability.
3.1. Calculating Gross Revenue
What constitutes a dental practice’s gross revenue? Gross revenue represents the total income generated by a dental practice before deducting any expenses. This includes revenue from patient services, insurance reimbursements, and other sources. Tracking gross revenue provides a baseline for evaluating the practice’s overall financial performance.
3.2. Identifying and Managing Expenses
What are the typical expenses for a dental practice? Dental practices incur various expenses, including:
- Staff salaries: Compensation for dental hygienists, assistants, and administrative staff.
- Rent or mortgage: Costs associated with the practice’s physical space.
- Supplies and equipment: Expenses for dental instruments, materials, and technology.
- Marketing and advertising: Costs for attracting new patients.
- Insurance: Professional liability, property, and worker’s compensation insurance.
- Continuing education: Expenses for professional development and training.
Managing these expenses effectively is crucial for maximizing profitability.
3.3. Determining Net Profit
How is net profit calculated for a dental practice? Net profit is calculated by subtracting total expenses from gross revenue. This figure represents the actual profit earned by the dental practice and directly impacts the dentist’s salary. A higher net profit translates into a higher income for the dentist.
4. Comparing Employed Dentists vs. Practice Owners
What are the financial differences between being an employed dentist and owning a practice? The financial landscape differs significantly between employed dentists and practice owners. Understanding these differences is essential for dentists to make informed decisions about their career paths and financial goals. Practice owners typically have the potential to earn more but also bear the risks and responsibilities of managing a business.
4.1. The Employed Dentist’s Perspective
What is the typical salary and benefits package for an employed dentist? Employed dentists typically receive a fixed salary or a percentage of their production. They may also receive benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off. While their income potential may be limited compared to practice owners, they enjoy greater job security and less administrative burden.
4.2. The Practice Owner’s Perspective
What are the potential financial rewards and risks of owning a dental practice? Practice owners have the potential to earn significantly more than employed dentists, as their income is directly tied to the practice’s profitability. However, they also bear the risks and responsibilities of managing a business, including financial liabilities, staffing issues, and regulatory compliance. Successful practice owners are typically entrepreneurial, skilled managers, and dedicated clinicians.
4.3. Financial Considerations
How do taxes and business expenses differ between employed dentists and practice owners? Employed dentists pay income taxes on their salary, while practice owners are responsible for paying self-employment taxes and managing business expenses. Practice owners can deduct legitimate business expenses from their income, which can reduce their overall tax liability. Consulting with a qualified accountant or financial advisor is essential for navigating the complexities of dental practice finances.
5. Strategies to Increase Your Dental Practice Income
What steps can dentists take to boost their yearly earnings? Dentists can implement various strategies to increase their yearly earnings, including improving practice efficiency, expanding service offerings, focusing on marketing and patient retention, and negotiating better insurance contracts. By proactively managing these aspects of their practice, dentists can significantly enhance their income potential.
5.1. Improving Practice Efficiency
How can streamlining operations improve a dentist’s income? Improving practice efficiency can significantly impact a dentist’s income by reducing overhead costs and increasing patient throughput. Implementing technology solutions such as electronic health records, digital imaging, and online scheduling can streamline operations and improve productivity.
5.2. Expanding Service Offerings
What new services can dentists offer to increase revenue? Dentists can increase revenue by expanding their service offerings to include high-demand procedures such as cosmetic dentistry, implant dentistry, and orthodontics. These services often command higher fees and can attract new patients to the practice.
5.3. Marketing and Patient Retention
How does marketing affect a dental practice’s profitability? Effective marketing strategies are essential for attracting new patients and retaining existing ones. Utilizing online marketing channels such as social media, search engine optimization (SEO), and email marketing can help dentists reach a wider audience and build their brand. Providing excellent patient care and fostering strong relationships can also improve patient retention and referrals.
5.4. Negotiating Insurance Contracts
Why is it important to negotiate favorable insurance contracts? Negotiating favorable insurance contracts can significantly impact a dentist’s income by increasing reimbursement rates and reducing claim denials. Dentists should carefully review their insurance contracts and negotiate for fair and competitive terms.
6. The Role of Practice Management in Dentist Earnings
How does effective practice management contribute to a higher dentist salary? Effective practice management is crucial for maximizing dentist earnings. A well-managed practice operates efficiently, controls costs, and delivers excellent patient care, leading to increased profitability and higher income for the dentist. Key aspects of practice management include financial management, staff management, marketing, and regulatory compliance.
6.1. Financial Management
How can dentists improve their practice’s financial health? Sound financial management is essential for maintaining a healthy dental practice. This includes budgeting, financial planning, and monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) such as revenue, expenses, and profit margins. Utilizing accounting software and seeking advice from financial professionals can help dentists make informed decisions about their practice’s finances.
6.2. Staff Management
Why is it important to have a well-trained and motivated dental team? A well-trained and motivated dental team is essential for providing excellent patient care and maintaining a smooth-running practice. Investing in staff training and development can improve productivity, reduce errors, and enhance patient satisfaction. Effective communication, delegation, and conflict resolution skills are also crucial for successful staff management.
6.3. Marketing Strategies
How can dentists use marketing to attract and retain patients? Marketing strategies play a vital role in attracting new patients and retaining existing ones. Dentists can utilize a variety of marketing channels, including online advertising, social media, email marketing, and traditional advertising, to reach their target audience. Building a strong brand and providing exceptional patient experiences can also enhance patient loyalty and referrals.
6.4. Regulatory Compliance
Why is compliance with regulations important for dental practices? Compliance with regulatory requirements is essential for avoiding legal and financial penalties. Dental practices must adhere to regulations related to patient privacy, infection control, and workplace safety. Staying informed about changes in regulations and implementing appropriate policies and procedures can help dentists maintain compliance and protect their practice.
7. Long-Term Financial Planning for Dentists
How can dentists plan for their financial future? Long-term financial planning is essential for dentists to achieve their financial goals and secure their future. This includes retirement planning, investment strategies, and estate planning. Consulting with a qualified financial advisor can help dentists develop a comprehensive financial plan tailored to their individual needs and circumstances.
7.1. Retirement Planning
What are the best retirement savings options for dentists? Dentists have several retirement savings options to choose from, including 401(k) plans, Roth IRAs, and defined benefit plans. The best option depends on the dentist’s income, tax situation, and retirement goals. Starting early and contributing consistently to a retirement plan can help dentists accumulate a substantial nest egg for their future.
7.2. Investment Strategies
How should dentists invest their money to achieve financial security? Diversifying investments across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, can help dentists reduce risk and maximize returns. Working with a financial advisor can help dentists develop an investment strategy that aligns with their risk tolerance and financial goals.
7.3. Estate Planning
Why is estate planning important for dentists? Estate planning is essential for ensuring that a dentist’s assets are distributed according to their wishes and minimizing estate taxes. This includes creating a will, establishing trusts, and designating beneficiaries for retirement accounts and insurance policies. Consulting with an estate planning attorney can help dentists create a comprehensive estate plan that protects their assets and provides for their loved ones.
8. Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Can you provide examples of how dentists have increased their income through strategic decisions? Real-world examples and case studies can provide valuable insights into how dentists have successfully increased their income through strategic decisions. These examples may involve implementing new technologies, expanding service offerings, improving marketing strategies, or enhancing practice efficiency.
8.1. Case Study 1: Implementing Technology
How did one dentist increase their income by adopting new technology? One dentist increased their income by implementing digital imaging and CAD/CAM technology in their practice. This allowed them to offer same-day crowns and other restorative procedures, which attracted new patients and increased revenue. The technology also improved practice efficiency, reducing chair time and increasing patient throughput.
8.2. Case Study 2: Expanding Service Offerings
How did adding new services boost a dental practice’s revenue? Another dentist increased their revenue by expanding their service offerings to include implant dentistry. They invested in training and equipment to offer implant placement and restoration services, which attracted patients seeking comprehensive dental care. This new service offering significantly increased the practice’s profitability.
8.3. Case Study 3: Improving Marketing Strategies
How can a dentist use marketing to attract more high-value patients? One dentist improved their marketing strategies by focusing on online advertising and social media. They created targeted ads to attract patients interested in cosmetic dentistry and used social media to showcase their expertise and build their brand. This resulted in a significant increase in new patient inquiries and revenue.
9. Common Myths About Dentist Salaries
What are some common misconceptions about how much dentists earn? There are several common myths about dentist salaries that can lead to unrealistic expectations and poor financial decisions. These myths include the belief that all dentists earn high incomes, that specialization is a guaranteed path to wealth, and that owning a practice is always more profitable than being employed.
9.1. Myth 1: All Dentists Are Rich
Is it true that all dentists make a lot of money? While some dentists earn high incomes, not all dentists are rich. Income varies widely depending on factors such as location, specialization, experience, and practice management skills. Many dentists face financial challenges such as student loan debt, high overhead costs, and competitive market conditions.
9.2. Myth 2: Specialization Guarantees Wealth
Does specializing always lead to a higher salary? Specialization does not guarantee wealth. While specialists typically earn more than general dentists, they also incur additional costs for training and equipment. Success as a specialist depends on factors such as demand for the specialty, competition in the market, and the dentist’s clinical and business skills.
9.3. Myth 3: Owning a Practice Is Always More Profitable
Is owning a dental practice always the most profitable option? Owning a practice is not always more profitable than being employed. Practice owners bear the risks and responsibilities of managing a business, including financial liabilities, staffing issues, and regulatory compliance. Success as a practice owner requires entrepreneurial skills, business acumen, and a commitment to providing excellent patient care.
10. Navigating the Challenges and Maximizing Your Potential
What are the biggest challenges dentists face in maximizing their earnings, and how can they overcome them? Dentists face several challenges in maximizing their earnings, including student loan debt, high overhead costs, competitive market conditions, and regulatory compliance. Overcoming these challenges requires proactive financial planning, efficient practice management, and a commitment to continuous learning and improvement.
10.1. Student Loan Debt
How can dentists manage their student loan debt effectively? Managing student loan debt effectively is essential for dentists to achieve financial stability. This includes exploring options such as income-driven repayment plans, loan consolidation, and loan forgiveness programs. Creating a budget and prioritizing debt repayment can help dentists reduce their debt burden and improve their financial outlook.
10.2. High Overhead Costs
What are some strategies for reducing overhead expenses in a dental practice? Reducing overhead expenses can significantly improve a dental practice’s profitability. Strategies for reducing overhead costs include negotiating lower rent or supply costs, implementing energy-efficient technologies, and streamlining administrative processes.
10.3. Competitive Market Conditions
How can dentists differentiate themselves in a competitive market? Differentiating themselves in a competitive market requires dentists to offer unique services, provide exceptional patient care, and build a strong brand. Utilizing online marketing channels, such as social media and search engine optimization (SEO), can help dentists reach a wider audience and attract new patients.
10.4. Regulatory Compliance
How can dentists stay compliant with changing regulations? Staying compliant with changing regulations requires dentists to stay informed about new laws and guidelines and implement appropriate policies and procedures. Joining professional organizations and attending continuing education courses can help dentists stay up-to-date on regulatory requirements and best practices.
Navigating the financial landscape of dentistry requires careful planning, sound management, and a commitment to continuous improvement. By understanding the factors that influence dentist earnings and implementing effective strategies to maximize their potential, dentists can achieve financial success and secure their future.
Are you looking for expert advice on how to maximize your dental practice income? Contact the team of experienced Doctors at HOW.EDU.VN today for personalized guidance and support.
Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
Whatsapp: +1 (310) 555-1212
Website: how.edu.vn
FAQ: Private Practice Dentist Salary
1. What kind of dentist gets paid the most?
Specialists like orthodontists, oral surgeons, and periodontists typically earn the highest incomes due to their advanced training and specialized skills.
2. At what age do most dentists retire?
Many dentists consider retirement around age 65, but this varies based on personal, financial, and health factors.
3. What percent of dental practices fail?
Dental practices have a low failure rate, with only about 1% failing within the first five years, significantly lower than other businesses.
4. What is the average career length for a dentist?
The average career length for a dentist can span 30 years or more, with many continuing to practice well into their 60s and beyond.
5. What dental procedures have the highest profit margin?
Cosmetic dentistry treatments like teeth whitening, veneers, and dental implants typically have higher profit margins due to specialized skills and equipment required.
6. What is the average dental patient worth?
The value of a dental patient can be calculated using the formula: Average Annual Value x Lifelong Relationship + Client Referral Value = Lifetime Value. For example, with an average annual value of $800, a lifelong relationship of 10 years, and a client referral value of $100, the lifetime value is $8,800.
7. How can a dentist increase their annual income?
Dentists can increase their annual income by improving practice efficiency, expanding service offerings, focusing on marketing and patient retention, and negotiating better insurance contracts.
8. What is the role of a dental practice manager?
A dental practice manager oversees the daily operations of a dental office, ensuring efficient workflow, managing staff, handling finances, and maintaining patient satisfaction.
9. How does the location of a dental practice impact income?
The location of a dental practice significantly impacts income, with metropolitan areas and affluent suburbs often offering more lucrative opportunities due to higher living costs and greater demand for dental services.
10. Is it better to be an employed dentist or a practice owner financially?
Practice owners typically have the potential to earn more than employed dentists, as their income is directly tied to the practice’s profitability, but they also bear more risks and responsibilities.