How much should a 6’3″ man weigh to maintain optimal health and well-being? Generally, a 6’3″ man should weigh between 176 to 216 pounds for a healthy weight range, according to the ideal body weight charts, but numerous factors contribute to a healthy weight, which HOW.EDU.VN can help you navigate through expert guidance. This article delves into the various factors influencing ideal weight, methods to determine it, and expert insights for maintaining a healthy lifestyle, ensuring you receive the best advice and support for your wellness journey.
1. Understanding Ideal Body Weight for a 6’3″ Man
Ideal body weight (IBW) is an estimated weight range considered optimal for health based on height, sex, and body frame size. For a 6’3″ man, the ideal weight typically falls between 176 and 216 pounds. However, this range is a general guideline, and other factors play a crucial role in determining what is healthy for an individual. These factors include body composition, muscle mass, age, activity level, and overall health status. It’s essential to consider these elements to get a more accurate and personalized understanding of your ideal weight.
1.1. Factors Influencing Ideal Body Weight
Several factors can influence what is considered a healthy weight for a 6’3″ man:
- Body Composition: Muscle weighs more than fat. A man with more muscle mass may weigh more but still be healthy.
- Age: As people age, their body composition changes. Muscle mass tends to decrease, while body fat can increase.
- Activity Level: Active individuals often have more muscle mass and a lower body fat percentage.
- Overall Health: Certain health conditions can affect weight, making it necessary to adjust weight goals accordingly.
1.2. Limitations of Ideal Body Weight Charts
While ideal body weight charts offer a quick reference, they have limitations. They do not account for body composition, muscle mass, or individual health conditions. As such, relying solely on these charts may not provide an accurate assessment of a healthy weight. It’s important to use these charts as a starting point and consider other methods for a more comprehensive evaluation.
2. Methods to Calculate Ideal Weight
Several methods can help determine a healthy weight range, each with its own advantages and considerations.
2.1. Body Mass Index (BMI)
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a commonly used measure that estimates body fat based on height and weight. It is calculated using the formula:
BMI = weight (kg) / height (m^2)Or, in pounds and inches:
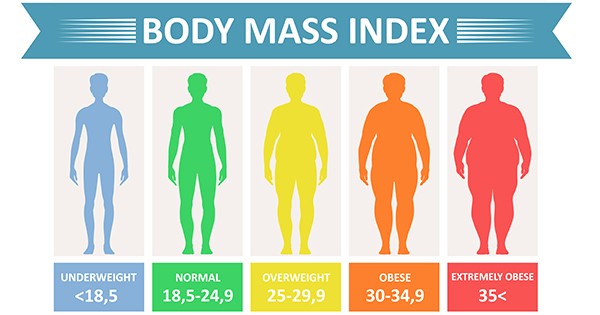
BMI = [weight (lb) / height (in^2)] x 703BMI Categories:
- Underweight: BMI less than 18.5
- Normal weight: BMI between 18.5 and 24.9
- Overweight: BMI between 25 and 29.9
- Obese: BMI of 30 or greater
For a 6’3″ man (1.905 meters), a healthy BMI range of 18.5 to 24.9 corresponds to a weight range of approximately 133 to 180 pounds. However, BMI does not account for body composition. A muscular individual may have a high BMI but still be healthy.
2.2. Hamwi Method
The Hamwi method is another way to estimate ideal body weight:
- For men: IBW = 106 pounds for the first 5 feet + 6 pounds for each inch over 5 feet
- For women: IBW = 100 pounds for the first 5 feet + 5 pounds for each inch over 5 feet
For a 6’3″ man, the Hamwi method calculates as follows:
- IBW = 106 pounds + (15 inches x 6 pounds)
- IBW = 106 + 90 = 196 pounds
This method provides a single weight estimate rather than a range.
 Measuring BMI on digital device
Measuring BMI on digital device
2.3. Devine Formula
The Devine formula is often used in clinical settings to calculate ideal body weight, particularly when dosing medications:
- For men: IBW = 50 kg + 2.3 kg for each inch over 5 feet
- For women: IBW = 45.5 kg + 2.3 kg for each inch over 5 feet
For a 6’3″ man:
- IBW = 50 kg + (15 inches x 2.3 kg)
- IBW = 50 + 34.5 = 84.5 kg
- Converting to pounds: 84.5 kg x 2.205 = 186.32 pounds
2.4. Body Fat Percentage
Body fat percentage is a more accurate measure of health than weight alone. It represents the proportion of your body weight that is fat. Healthy body fat percentages for men typically fall within the following ranges:
- Essential Fat: 2-5%
- Athletes: 6-13%
- Fitness: 14-17%
- Acceptable: 18-24%
- Obese: 25% or higher
Measuring body fat percentage can be done using various methods, including:
- Skinfold Calipers: Measures the thickness of skinfolds at different body locations.
- Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA): Sends a small electrical current through the body to estimate body composition.
- Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA): A medical imaging technique that provides a detailed breakdown of body composition.
- Hydrostatic Weighing: Measures body density by submerging a person in water.
3. Health Implications of Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for overall health and well-being. Being underweight or overweight can lead to various health problems.
3.1. Health Risks of Being Underweight
Being underweight can result in:
- Weakened Immune System: Increased susceptibility to infections.
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Lack of essential vitamins and minerals.
- Osteoporosis: Decreased bone density, increasing the risk of fractures.
- Fertility Problems: Irregular menstrual cycles in women.
- Muscle Weakness: Loss of strength and endurance.
3.2. Health Risks of Being Overweight
Being overweight can lead to:
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Increased risk of heart disease, high blood pressure, and stroke.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Impaired insulin sensitivity and high blood sugar levels.
- Certain Cancers: Increased risk of breast, colon, and endometrial cancers.
- Sleep Apnea: Disrupted sleep patterns due to breathing difficulties.
- Osteoarthritis: Joint pain and stiffness due to increased stress on joints.
3.3. The Importance of a Balanced Approach
Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight requires a balanced approach that includes a healthy diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep. It’s also important to manage stress levels and seek support from healthcare professionals when needed.
4. Nutritional Guidelines for Maintaining a Healthy Weight
A well-balanced diet is essential for maintaining a healthy weight. Focus on consuming whole, unprocessed foods and limiting your intake of sugary drinks, processed snacks, and unhealthy fats.
4.1. Macronutrient Balance
The three main macronutrients are carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Aim for a balanced intake of these nutrients to support overall health:
- Carbohydrates: 45-65% of total calories
- Proteins: 10-35% of total calories
- Fats: 20-35% of total calories
Choose complex carbohydrates like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. Opt for lean protein sources like chicken, fish, beans, and lentils. Include healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil.
4.2. Micronutrient Intake
Micronutrients, including vitamins and minerals, are essential for various bodily functions. Ensure you consume a variety of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to meet your micronutrient needs. Consider taking a multivitamin if you have specific deficiencies or dietary restrictions.
4.3. Hydration
Drinking enough water is crucial for overall health and weight management. Water helps regulate appetite, boost metabolism, and support various bodily functions. Aim to drink at least 8 glasses of water per day.
4.4. Portion Control
Practicing portion control can help you manage your calorie intake and maintain a healthy weight. Use smaller plates, measure your food, and avoid eating directly from large containers.
4.5. Mindful Eating
Mindful eating involves paying attention to your hunger and fullness cues and eating without distractions. This can help you avoid overeating and develop a healthier relationship with food.
5. Exercise Recommendations for a 6’3″ Man
Regular exercise is vital for maintaining a healthy weight, improving cardiovascular health, and boosting overall well-being.
5.1. Cardiovascular Exercise
Cardiovascular exercise, also known as aerobic exercise, involves activities that increase your heart rate and breathing. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week. Examples include:
- Brisk Walking: A simple and accessible form of exercise.
- Running: A high-impact activity that burns a lot of calories.
- Cycling: A low-impact exercise that’s easy on the joints.
- Swimming: A full-body workout that’s gentle on the body.
- Dancing: A fun and engaging way to get your heart rate up.
5.2. Strength Training
Strength training involves exercises that strengthen your muscles and bones. Aim for at least two strength training sessions per week, targeting all major muscle groups. Examples include:
- Weightlifting: Using dumbbells, barbells, or weight machines.
- Bodyweight Exercises: Using your own body weight for resistance, such as push-ups, squats, and lunges.
- Resistance Bands: Using elastic bands to provide resistance during exercises.
5.3. Flexibility and Balance Exercises
Flexibility and balance exercises can improve your range of motion, prevent injuries, and enhance overall physical function. Examples include:
- Stretching: Holding stretches for 30 seconds to improve muscle flexibility.
- Yoga: A mind-body practice that combines physical postures, breathing techniques, and meditation.
- Pilates: A system of exercises that focuses on core strength, flexibility, and body awareness.
- Tai Chi: A gentle form of exercise that involves slow, flowing movements.
5.4. Creating a Workout Plan
Develop a workout plan that incorporates a variety of exercises to target different aspects of fitness. Be sure to warm up before each workout and cool down afterward. Consult with a fitness professional to create a personalized workout plan that meets your individual needs and goals.
6. Lifestyle Adjustments for Weight Management
In addition to diet and exercise, several lifestyle adjustments can support weight management.
6.1. Sleep Hygiene
Getting enough sleep is crucial for overall health and weight management. Lack of sleep can disrupt hormones that regulate appetite, leading to increased cravings and weight gain. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
6.2. Stress Management
Chronic stress can lead to increased cortisol levels, which can promote fat storage and weight gain. Practice stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
6.3. Limiting Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol is high in calories and can contribute to weight gain. Limit your alcohol intake or avoid it altogether if you’re trying to lose weight.
6.4. Quitting Smoking
Smoking can negatively impact your health and make it more difficult to maintain a healthy weight. Quitting smoking can improve your overall health and support weight management efforts.
6.5. Regular Check-ups
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider can help you monitor your health and identify any potential issues that may affect your weight.
7. Expert Insights on Weight Management
Seeking advice from healthcare professionals and experts in weight management can provide valuable guidance and support.
7.1. Consulting with a Doctor
Your doctor can assess your overall health, identify any underlying conditions that may be affecting your weight, and provide personalized recommendations for weight management.
7.2. Working with a Registered Dietitian
A registered dietitian can help you develop a healthy eating plan that meets your individual needs and goals. They can provide guidance on portion control, meal planning, and making healthy food choices.
7.3. Partnering with a Certified Personal Trainer
A certified personal trainer can help you develop an exercise program that’s tailored to your fitness level and goals. They can provide guidance on proper form, exercise technique, and progression.
7.4. Seeking Support from a Therapist
A therapist can help you address emotional eating, body image issues, and other psychological factors that may be contributing to weight gain or difficulty maintaining a healthy weight.
8. Real-Life Examples and Case Studies
Understanding how others have successfully managed their weight can provide inspiration and practical tips.
8.1. Case Study 1: John’s Weight Loss Journey
John, a 6’3″ man, weighed 240 pounds and had a BMI of 30, classifying him as obese. He consulted with a registered dietitian and a certified personal trainer to develop a comprehensive weight loss plan. John followed a balanced diet, incorporating lean protein, whole grains, and plenty of fruits and vegetables. He also engaged in regular cardiovascular and strength training exercises. Over the course of a year, John lost 60 pounds and achieved a healthy weight of 180 pounds.
8.2. Case Study 2: Sarah’s Muscle Gain
Sarah, a 6’3″ woman, weighed 150 pounds and wanted to increase her muscle mass. She worked with a personal trainer to develop a strength training program. Sarah focused on compound exercises like squats, deadlifts, and bench presses. She also increased her protein intake to support muscle growth. Over time, Sarah gained 15 pounds of muscle and improved her overall body composition.
8.3. Anonymized Client Success at HOW.EDU.VN
One of our clients, we’ll call him Mark, a 6’3” professional in his late 40s, came to HOW.EDU.VN seeking guidance on weight management. Weighing in at 230 pounds, Mark was concerned about his increasing BMI and potential health risks. Through personalized consultations with our expert nutritionists and fitness specialists, Mark adopted a tailored diet and exercise plan. He focused on portion control, mindful eating, and incorporated a mix of cardio and strength training into his routine. Over six months, Mark successfully lost 45 pounds, achieving a healthier weight and significantly improving his overall well-being. Mark’s journey exemplifies the effectiveness of personalized expert guidance in achieving sustainable weight management goals.
9. Common Myths About Weight Management
It’s important to debunk common myths about weight management to make informed decisions.
9.1. Myth: Fad Diets Work
Fad diets may promise quick weight loss, but they are often unsustainable and can be harmful to your health. Focus on making long-term lifestyle changes rather than following short-term diet trends.
9.2. Myth: Skipping Meals Helps You Lose Weight
Skipping meals can lead to overeating later in the day and can disrupt your metabolism. Eating regular, balanced meals is more effective for weight management.
9.3. Myth: Cardio Is the Only Way to Lose Weight
Cardio is important for burning calories, but strength training is also essential for building muscle and boosting metabolism. A combination of both types of exercise is ideal for weight loss.
9.4. Myth: You Have to Cut Out All Your Favorite Foods
You don’t have to completely eliminate your favorite foods to lose weight. Enjoy them in moderation as part of a balanced diet.
9.5. Myth: Weight Loss Is All About Willpower
Weight loss is influenced by a variety of factors, including genetics, hormones, and environment. It’s important to be kind to yourself and seek support when needed.
10. Tools and Resources for Tracking Weight and Progress
Utilizing tools and resources can help you track your weight, monitor your progress, and stay motivated.
10.1. Weight Scales
A reliable weight scale is essential for tracking your weight. Consider investing in a digital scale that provides accurate measurements.
10.2. Fitness Trackers
Fitness trackers can monitor your activity levels, track your sleep, and provide valuable insights into your daily habits.
10.3. Calorie Tracking Apps
Calorie tracking apps can help you monitor your calorie intake and macronutrient balance. Popular apps include MyFitnessPal, Lose It!, and Fitbit.
10.4. Body Measurement Trackers
Tracking your body measurements, such as waist circumference and hip circumference, can provide additional insights into your progress.
10.5. Online Support Groups
Online support groups can provide a sense of community and support as you work toward your weight management goals.
11. The Role of Genetics in Weight
Genetics can play a significant role in determining your weight and body composition. However, genetics do not determine your destiny. Lifestyle factors, such as diet and exercise, can still have a powerful impact on your weight.
11.1. Genetic Predisposition
Certain genes can increase your risk of obesity or make it more difficult to lose weight. However, these genes do not guarantee that you will be overweight.
11.2. Epigenetics
Epigenetics refers to changes in gene expression that are not caused by changes in the DNA sequence. Lifestyle factors, such as diet and exercise, can influence epigenetic changes that affect your weight.
11.3. Gene-Environment Interactions
The interaction between your genes and your environment plays a crucial role in determining your weight. Even if you have a genetic predisposition to obesity, you can still maintain a healthy weight through healthy lifestyle choices.
12. Psychological Aspects of Weight Management
Weight management is not just about diet and exercise. Psychological factors also play a crucial role.
12.1. Emotional Eating
Emotional eating involves using food to cope with negative emotions. Addressing emotional eating requires identifying triggers, developing coping strategies, and seeking support from a therapist if needed.
12.2. Body Image Issues
Negative body image can lead to unhealthy eating behaviors and difficulty maintaining a healthy weight. Cultivating a positive body image requires focusing on self-acceptance, challenging negative thoughts, and practicing self-care.
12.3. Motivation and Goal Setting
Setting realistic goals and staying motivated are essential for successful weight management. Break down large goals into smaller, more manageable steps, and reward yourself for your progress.
12.4. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a type of therapy that can help you identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that are contributing to weight gain or difficulty maintaining a healthy weight.
13. Weight Management for Specific Populations
Weight management strategies may need to be tailored for specific populations, such as athletes, older adults, and individuals with certain health conditions.
13.1. Weight Management for Athletes
Athletes may have different weight goals than the general population. They may need to focus on optimizing body composition for performance, rather than simply losing weight.
13.2. Weight Management for Older Adults
Older adults may need to focus on maintaining muscle mass and bone density, rather than simply losing weight. They may also need to adjust their diet and exercise plan to accommodate age-related changes in their bodies.
13.3. Weight Management for Individuals with Health Conditions
Individuals with health conditions, such as diabetes or heart disease, may need to follow specific dietary and exercise guidelines to manage their weight and improve their health.
14. Long-Term Strategies for Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight is a lifelong journey. Focus on making sustainable lifestyle changes rather than following short-term diet trends.
14.1. Consistency
Consistency is key to long-term weight management. Stick to your healthy eating and exercise plan as much as possible, even when you’re busy or stressed.
14.2. Flexibility
Allow yourself some flexibility in your diet and exercise plan. It’s okay to indulge in your favorite foods occasionally or take a day off from exercise.
14.3. Self-Monitoring
Continue to monitor your weight and body composition regularly to track your progress and make adjustments to your plan as needed.
14.4. Seeking Support
Continue to seek support from healthcare professionals, registered dietitians, personal trainers, and support groups to help you stay on track with your weight management goals.
14.5. Celebrating Successes
Celebrate your successes along the way to stay motivated and reinforce your healthy habits.
15. How HOW.EDU.VN Can Help
At HOW.EDU.VN, we understand the complexities of achieving and maintaining a healthy weight. Our team of expert doctors and specialists is dedicated to providing personalized guidance and support to help you reach your wellness goals. We offer a range of services tailored to your individual needs, including:
15.1. Personalized Consultations
Connect with our experienced doctors for in-depth consultations. We assess your current health status, lifestyle, and goals to create a customized weight management plan.
15.2. Customized Nutrition Plans
Our registered dietitians develop personalized nutrition plans that align with your dietary preferences and health requirements. We focus on balanced eating, portion control, and mindful eating practices to support sustainable weight management.
15.3. Tailored Exercise Programs
Our certified personal trainers design customized exercise programs that fit your fitness level and preferences. We incorporate a mix of cardiovascular, strength training, and flexibility exercises to optimize your overall health and well-being.
15.4. Psychological Support
Our licensed therapists offer psychological support to address emotional eating, body image issues, and other psychological factors that may be contributing to weight gain or difficulty maintaining a healthy weight.
15.5. Continuous Monitoring and Support
We provide continuous monitoring and support to track your progress and make adjustments to your plan as needed. Our team is always available to answer your questions and provide guidance along the way.
15.6. Access to Cutting-Edge Research
Our team stays up-to-date with the latest research in weight management to provide you with the most effective and evidence-based strategies.
15.7. A Holistic Approach
We believe in a holistic approach to weight management, addressing all aspects of your health and well-being to support long-term success.
16. Conclusion: Achieving a Healthy Weight is a Journey, Not a Destination
Determining how much a 6’3″ man should weigh involves considering various factors, including body composition, age, activity level, and overall health. While ideal body weight charts and BMI can provide a general guideline, they should not be the sole determinant of a healthy weight. A balanced approach that includes a healthy diet, regular exercise, and lifestyle adjustments is essential for achieving and maintaining a healthy weight. Seeking guidance from healthcare professionals and experts in weight management can provide valuable support and personalized recommendations.
Maintaining a healthy weight is a lifelong journey, not a destination. Embrace the process, be patient with yourself, and celebrate your successes along the way. With the right tools, resources, and support, you can achieve your weight management goals and live a healthier, happier life.
Are you ready to take the next step in your weight management journey? Contact us at HOW.EDU.VN today to schedule a personalized consultation with our expert team. Let us help you achieve your wellness goals and live your best life.
Contact Information:
- Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
- Website: HOW.EDU.VN
17. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
17.1. What is the ideal BMI for a 6’3″ man?
A healthy BMI range is between 18.5 and 24.9. For a 6’3″ man, this corresponds to a weight range of approximately 180 to 215 pounds.
17.2. How can I calculate my ideal body weight?
You can use methods like BMI, the Hamwi method, or the Devine formula. However, consider body composition and consult a healthcare professional for a personalized assessment.
17.3. Is muscle heavier than fat?
Yes, muscle is denser than fat. A muscular person may weigh more but have a lower body fat percentage and be healthier.
17.4. How often should I exercise to maintain a healthy weight?
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week, plus two strength training sessions.
17.5. What are some healthy eating habits for weight management?
Focus on whole, unprocessed foods, balanced macronutrient intake, portion control, and mindful eating. Limit sugary drinks, processed snacks, and unhealthy fats.
17.6. How important is sleep for weight management?
Getting enough sleep is crucial as it regulates hormones that control appetite. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
17.7. Can genetics affect my weight?
Yes, genetics can play a role, but lifestyle factors like diet and exercise have a powerful impact on your weight.
17.8. What is emotional eating, and how can I manage it?
Emotional eating is using food to cope with negative emotions. Identify triggers, develop coping strategies, and seek therapy if needed.
17.9. How can HOW.EDU.VN help me with weight management?
how.edu.vn offers personalized consultations, customized nutrition plans, tailored exercise programs, psychological support, and continuous monitoring to help you achieve your weight management goals.
17.10. What should I do if I’m struggling to lose weight?
Consult with a healthcare professional, registered dietitian, or personal trainer for personalized guidance and support. Consider seeking therapy to address emotional or psychological barriers.
18. Glossary of Terms
18.1. Body Mass Index (BMI)
A measure of body fat based on height and weight.
18.2. Ideal Body Weight (IBW)
An estimated weight range considered optimal for health based on height, sex, and body frame size.
18.3. Body Composition
The proportion of fat, muscle, bone, and other tissues in the body.
18.4. Macronutrients
The three main nutrients that provide energy: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
18.5. Micronutrients
Vitamins and minerals that are essential for various bodily functions.
18.6. Cardiovascular Exercise
Activities that increase your heart rate and breathing.
18.7. Strength Training
Exercises that strengthen your muscles and bones.
18.8. Flexibility Exercises
Exercises that improve your range of motion.
18.9. Balance Exercises
Exercises that improve your stability and coordination.
18.10. Emotional Eating
Using food to cope with negative emotions.
18.11. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
A type of therapy that helps identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors.
18.12. Epigenetics
Changes in gene expression that are not caused by changes in the DNA sequence.
18.13. Hydrostatic Weighing
Measuring body density by submerging a person in water.
18.14. Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA)
A medical imaging technique that provides a detailed breakdown of body composition.
18.15. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA)
Sends a small electrical current through the body to estimate body composition.