Princess Diana’s death on August 31, 1997, sent shockwaves across the globe, plunging millions into mourning and sparking intense public and media scrutiny. Understanding How Did Princess Diana Die requires delving into the details of the tragic car crash in Paris and the factors that contributed to this devastating event. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the circumstances surrounding her death, the official findings, and the broader implications that arose from this tragedy.
The fateful night began in Paris, where Princess Diana and her companion, Dodi Fayed, along with their driver Henri Paul and bodyguard Trevor Rees-Jones, were attempting to evade paparazzi. In the early hours of August 31st, their Mercedes-Benz W140 S-Class crashed in the Pont de l’Alma tunnel. The crash resulted in the deaths of Diana, Fayed, and Paul. Rees-Jones, the only survivor, sustained severe injuries.
Initial reports and subsequent investigations pointed to a combination of factors leading to the crash. A primary cause was the reckless driving of Henri Paul, the chauffeur, who was later found to be heavily intoxicated, exceeding the legal alcohol limit in France by three times. Excessive speed was another significant factor, as the vehicle was traveling at a high speed in an attempt to outrun pursuing paparazzi on motorcycles.
The presence of paparazzi also played a crucial role. While not directly causing the crash, their relentless pursuit created a high-pressure situation, contributing to the driver’s loss of control. The inquests also highlighted the fact that Princess Diana and Dodi Fayed were not wearing seatbelts, which significantly worsened the severity of their injuries in the high-impact collision.
Official investigations conducted by the French authorities concluded that the crash was an accident caused by the driver’s intoxication and excessive speed. The French Supreme Court upheld these findings, dismissing any conspiracy theories that emerged in the aftermath of the tragedy. These conspiracy theories, though widely circulated, lacked credible evidence and were ultimately debunked by official inquiries.
The death of Princess Diana triggered an unprecedented outpouring of grief worldwide. Her funeral was watched by an estimated 2.5 billion people globally, reflecting her immense popularity and the deep impact she had on people’s lives. Beyond the immediate emotional response, Diana’s death also brought about broader societal reflections, particularly concerning media intrusion, privacy, and road safety.
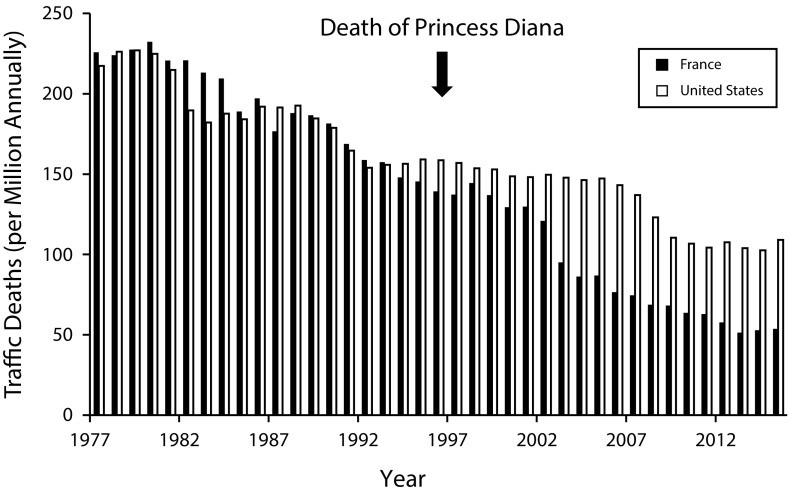
Interestingly, as highlighted in the original article, Princess Diana’s death inadvertently brought traffic safety into sharper focus, especially in France. Prior to her death, traffic fatality trends in France and the United States were relatively similar. However, in the years following 1997, France witnessed a more significant reduction in traffic fatalities compared to the US.
While direct causality is difficult to establish, some experts suggest that the public attention drawn to road safety following Diana’s death may have contributed to policy changes and increased awareness in France. France implemented stricter traffic laws and enforcement measures, including widespread use of photo-radar speed enforcement and traffic light radar systems. Furthermore, public discourse around drunk driving and seatbelt usage may have been amplified in the wake of the tragedy.
Comparing traffic safety measures between France and the US reveals notable differences that could explain the divergent trends in traffic fatalities. France has stricter urban speed limits, widespread photo-radar enforcement, and stricter impaired driving laws compared to the United States. Additionally, France mandates helmet use for motorcyclists and seatbelt use for all vehicle occupants, while regulations in the US vary by state and are often less stringent.
In conclusion, Princess Diana died as a result of injuries sustained in a car crash in Paris. The primary causes were the drunk driving and excessive speed of her chauffeur, compounded by the pursuit of paparazzi and the non-use of seatbelts. While a tragic accident, her death had far-reaching consequences, prompting global mourning and potentially influencing traffic safety policies, particularly in France. The legacy of how did Princess Diana die extends beyond the immediate tragedy, serving as a somber reminder of the importance of responsible driving, media ethics, and the fragility of life.