Hemorrhoids, while generally not a severe health concern, can significantly disrupt your daily life and cause considerable discomfort if left unaddressed. Characterized by symptoms such as anal pain, swelling, itching, rectal bleeding, and pain during bowel movements, these issues warrant attention from experienced gastroenterologists. At how.edu.vn, we aim to provide expert insights into understanding hemorrhoids, specifically addressing the common question: “How Long Do Hemorrhoids Last?”. This comprehensive guide will delve into the duration of hemorrhoids, explore effective treatment options, and offer practical home remedies to manage symptoms and prevent recurrence, ensuring you can tackle this condition with confidence and minimize discomfort.
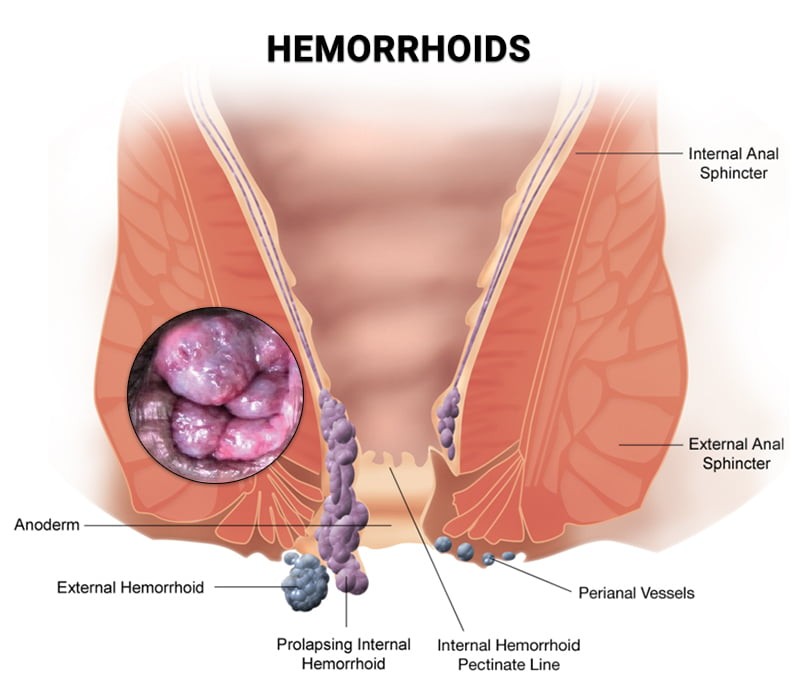 Diagram illustrating Hemorrhoids, a common anorectal condition, for educational purposes.
Diagram illustrating Hemorrhoids, a common anorectal condition, for educational purposes.
Hemorrhoids, also known as piles, are a prevalent condition affecting a large portion of the population due to various lifestyle and health factors. While they can affect anyone across all age groups and genders, certain demographics are more susceptible, including older adults, pregnant individuals, those with gastrointestinal conditions, and individuals with a family history of hemorrhoids.
Essentially, hemorrhoids are enlarged and swollen veins located either outside the anus or in the lower rectum. The rectum is the final section of the large intestine leading to the anus, the body’s opening for waste elimination. Gaining a clear understanding of hemorrhoids, including their expected duration and the nature of the condition, is crucial for effective self-care and preventing potential complications.
Types of Hemorrhoids: Internal vs. External
Hemorrhoids are broadly classified into two main types, based on their location:
- Internal Hemorrhoids: These develop within the lower rectum and are typically not visible externally. Often, internal hemorrhoids are painless, but their presence can be indicated by other symptoms.
- External Hemorrhoids: Located under the skin around the anus, external hemorrhoids are often more painful and noticeable, causing significant discomfort.
Consulting a healthcare professional is paramount for accurate diagnosis and personalized advice, especially when dealing with anorectal discomfort. Expert guidance can provide answers to your specific questions and offer relief from what can be a distressing condition.
Recognizing Hemorrhoid Symptoms
Identifying hemorrhoid symptoms is the crucial first step toward effective management and treatment. Common symptoms associated with hemorrhoids include:
- Anal Pain: Discomfort or pain in the anal region, which can range from mild to severe.
- Pain During Bowel Movements: Increased pain or discomfort experienced while passing stool.
- Rectal Bleeding: The presence of bright red blood on toilet paper or in the toilet bowl after a bowel movement.
- Anal Itching: Irritation and itchiness in the anal area.
- Swelling Around the Anus: Noticeable lumps or swelling in the anal region.
It’s important to note that these symptoms can overlap with other, more serious conditions such as anal cancer or polyps. Hemorrhoids also share symptoms with anal fissures, which are tears in the lining of the anus and often characterized by more intense pain. If you are uncertain about the cause of your symptoms, particularly if you are over 50, seeking medical advice is essential to rule out any underlying medical issues and ensure timely and appropriate treatment.
How Long Do Hemorrhoids Typically Last?
The duration of hemorrhoids is not fixed and varies significantly from person to person. Several factors influence how long hemorrhoids last:
- Severity and Size: Smaller hemorrhoids often resolve spontaneously within a few days, often with minimal intervention and home care.
- Larger or Thrombosed Hemorrhoids: Larger hemorrhoids, especially those that are thrombosed (containing a blood clot) and cause intense pain, swelling, and itching, are less likely to disappear on their own. These typically require medical treatment and may persist for several weeks without intervention.
- Pregnancy-Related Hemorrhoids: Hemorrhoids that develop during pregnancy often improve and resolve after childbirth as hormonal and physical pressures change.
- Recurrent Hemorrhoids: Even after successful treatment, hemorrhoids can recur. This is a common concern, and long-term management often involves lifestyle and dietary adjustments recommended by a gastroenterologist to manage symptoms and prevent future episodes.
Factors that can influence the duration and recurrence of hemorrhoids include:
- Low-Fiber Diet: Insufficient dietary fiber can lead to constipation and straining during bowel movements, exacerbating hemorrhoids and hindering healing.
- Obesity and Overweight: Excess weight can increase pressure on the veins in the rectum and anus, contributing to hemorrhoid development and prolonged symptoms.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and increased pressure in the abdomen during pregnancy can trigger or worsen hemorrhoids.
- Chronic Constipation and Diarrhea: Both constipation and diarrhea can strain the anorectal area, irritating existing hemorrhoids or leading to new ones.
- Aging: As we age, the tissues supporting the veins in the rectum and anus can weaken, increasing susceptibility to hemorrhoids.
- Prolonged Toilet Sitting: Spending extended periods on the toilet can increase pressure on the veins in the anus and rectum.
- Straining During Bowel Movements: Excessive straining puts pressure on these veins, contributing to hemorrhoid formation and prolonged duration.
- Anal Intercourse: Frequent anal intercourse can increase the risk of hemorrhoids.
- Overuse of Laxatives or Enemas: Excessive use can disrupt natural bowel function and potentially worsen hemorrhoids over time.
Addressing these risk factors is crucial not only for preventing hemorrhoids but also for promoting healing and reducing the duration of existing hemorrhoids.
Preventing Hemorrhoids: Lifestyle and Dietary Adjustments
While it’s not always possible to completely prevent hemorrhoids, adopting certain lifestyle modifications and preventive strategies can significantly reduce your risk:
- Increase Fiber Intake: A diet rich in fiber softens stool, making it easier to pass and reducing straining. Incorporate plenty of fresh fruits, vegetables, and whole grains into your daily meals. If dietary changes are challenging, consult your doctor about fiber supplements.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking ample water is essential for overall health and helps maintain soft stools, preventing constipation and easing bowel movements.
- Limit Toilet Time: Avoid prolonged sitting on the toilet, as it increases pressure on the anorectal veins. Minimize distractions like phones or reading material in the bathroom.
- Address Constipation Promptly: If you experience frequent constipation, seek medical advice to manage it effectively and prevent straining that can lead to hemorrhoids.
- Heed the Urge to Defecate: Don’t delay bowel movements. Responding to the urge promptly can prevent stool from becoming dry and hard, reducing strain.
- Maintain Physical Activity: Regular exercise promotes bowel regularity and can help with weight management, reducing pressure on veins. Avoid prolonged periods of sitting or reclining.
- Use Laxatives Judiciously: Avoid self-medicating with laxatives or enemas. Use them only as recommended by your doctor to avoid disrupting your digestive system’s natural rhythm.
Hemorrhoid Treatment: Finding Relief and Medical Options
Various treatment options are available to alleviate hemorrhoid discomfort. Smaller hemorrhoids often respond well to home treatments and over-the-counter (OTC) medications.
Home Remedies for Symptom Relief:
- Sitz Baths: Soaking in a warm, shallow bath for 10-15 minutes several times a day can improve blood flow, soothe irritation, and keep the anal area clean. Sitz bath kits are available that fit over a toilet seat, or a regular bathtub can be used.
- Cold Compresses: Applying ice packs to the anal area can help reduce swelling, pain, and itching, particularly with external hemorrhoids.
- Donut Cushions: These cushions, also called tailbone cushions, reduce pressure on the anal area when sitting, providing relief for those who sit for extended periods.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relief: Oral pain relievers like ibuprofen, acetaminophen, or aspirin can help manage pain.
- Topical Creams and Ointments: OTC hemorrhoid creams and ointments containing ingredients like hydrocortisone or witch hazel can reduce itching, swelling, and pain.
When to Consult a Doctor for Hemorrhoids
While home remedies can be effective for mild cases, it’s crucial to know when to seek professional medical advice. Consult a doctor if you experience:
- Persistent or Worsening Pain: Hemorrhoids that become increasingly painful or do not improve with home care require medical evaluation.
- Rectal Bleeding: Any rectal bleeding, especially if significant or persistent, needs medical attention to rule out other conditions.
- Changes in Stool Color: Black or maroon-colored stool can indicate more serious gastrointestinal bleeding and warrants immediate medical evaluation.
- Symptoms Unresponsive to Home Treatment: If hemorrhoid symptoms persist for more than a week despite home remedies, it’s time to see a doctor.
Bleeding from hemorrhoids, if significant, can lead to complications like anemia, dizziness, or faintness. Seeking timely medical help is essential to prevent complications and ensure appropriate management.
Doctor-Recommended Hemorrhoid Treatments
For hemorrhoids that don’t resolve with home care, doctors can recommend various treatments and procedures:
- Prescription Medications: If OTC creams are insufficient, doctors may prescribe stronger medicated creams or suppositories to reduce inflammation and pain.
- External Hemorrhoid Thrombectomy: For painful thrombosed external hemorrhoids, a doctor can surgically remove the clot under local anesthesia, providing rapid relief if done within 72 hours of clot formation.
- Rubber Band Ligation: A common office procedure for internal hemorrhoids, rubber band ligation involves placing small rubber bands at the base of the hemorrhoid to cut off circulation. The hemorrhoid shrinks and falls off within a week.
- Sclerotherapy: This involves injecting a chemical solution into the hemorrhoid to shrink it. It’s generally less painful than rubber band ligation but may be less effective.
- Coagulation Therapies: Techniques using infrared light, laser, or bipolar coagulation use heat to harden and shrivel small, bleeding internal hemorrhoids. These methods usually have minimal side effects and discomfort.
When less invasive treatments are not effective, or in cases of large or prolapsed hemorrhoids, surgery may be recommended.
Surgical Removal of Hemorrhoids
Surgical options for hemorrhoid removal include:
- Hemorrhoidectomy: This surgical procedure involves removing the hemorrhoid and surrounding tissue through a small incision. It’s typically performed under local or general anesthesia and has a high success rate in eliminating hemorrhoids.
- Hemorrhoidopexy (Stapled Hemorrhoidectomy): This procedure, often called stapling, is used for internal hemorrhoids. It either removes the hemorrhoidal tissue or repositions a prolapsed hemorrhoid back inside the anus.
Post-surgery, pain and itching typically resolve. Some post-operative discomfort is expected but can be managed with medication. Recovery usually takes about 1 to 2 weeks with adherence to the doctor’s post-operative instructions.
Untreated hemorrhoids can lead to significant pain and distress, impacting quality of life. However, with proper management, including lifestyle adjustments, home care, and medical interventions when necessary, hemorrhoids can be effectively treated and prevented from recurring. If you are concerned about hemorrhoids or if they are not improving with self-care, consult the experienced gastroenterologists at how.edu.vn for expert evaluation and personalized treatment plans to achieve lasting relief. Our commitment is to provide you with the most up-to-date and effective solutions for your gastrointestinal health concerns.
