Melatonin supplements have surged in popularity as a go-to sleep aid for those battling sleepless nights. If you’re considering joining the millions who use melatonin to catch some Z’s, you’re likely wondering: How Long Does Melatonin Last? This seemingly simple question has layers of complexity, as the duration of melatonin’s effects is influenced by various factors, from the specific formulation you choose to your individual body chemistry.
Melatonin is naturally produced by your brain to regulate your sleep-wake cycle, acting as a key player in your body’s internal clock. Supplementing with melatonin aims to bolster this natural process, particularly when sleep patterns are disrupted by issues like jet lag, shift work, or insomnia. While generally considered safe for short-term use and available over-the-counter in many countries, understanding how long melatonin remains active in your system is crucial for maximizing its benefits and minimizing potential side effects.
This article delves into the science behind melatonin, exploring how long its effects typically last, the factors that can influence its duration, and how to use melatonin supplements effectively for better sleep.
Melatonin’s Role in Your Sleep Cycle
To grasp how long supplemental melatonin lasts, it’s helpful to first understand the role of naturally produced melatonin. Your brain’s pineal gland releases melatonin in response to darkness, signaling to your body that it’s time to prepare for sleep. This hormone interacts with receptors in your brain to reduce alertness and promote drowsiness. This intricate process is part of your circadian rhythm, the 24-hour internal clock that governs sleep and wakefulness.
Environmental cues, primarily light and darkness, synchronize your circadian rhythm. As daylight fades, melatonin levels naturally rise, peaking in the evening and then gradually decreasing as morning approaches and light exposure increases. This natural ebb and flow of melatonin helps you feel awake and alert during the day and sleepy at night.
Onset of Action: How Quickly Does Melatonin Work?
Melatonin supplements are known for their relatively rapid onset of action. Generally, you can expect to feel the effects of melatonin within 30 to 60 minutes of taking a fast-release formulation. This quick action is why it’s often recommended to take melatonin shortly before your desired bedtime.
However, the speed at which melatonin takes effect can be influenced by several variables:
- Formulation: Fast-release tablets are designed for quick absorption, leading to a faster onset. Extended-release versions, on the other hand, are designed to release melatonin gradually, which may result in a slightly delayed initial effect but a longer duration overall.
- Dosage: While higher doses might seem like they would work faster, this isn’t necessarily the case. The optimal dose for sleep is often lower than what is commonly available, and excessive doses may not lead to a quicker onset and could increase the risk of next-day grogginess.
- Individual Metabolism: Just like with any supplement or medication, individual differences in metabolism can affect how quickly your body absorbs and processes melatonin. Factors like age, overall health, and even what you’ve eaten can play a role.
Decoding Melatonin Duration: How Long Does It Stay in Your System?
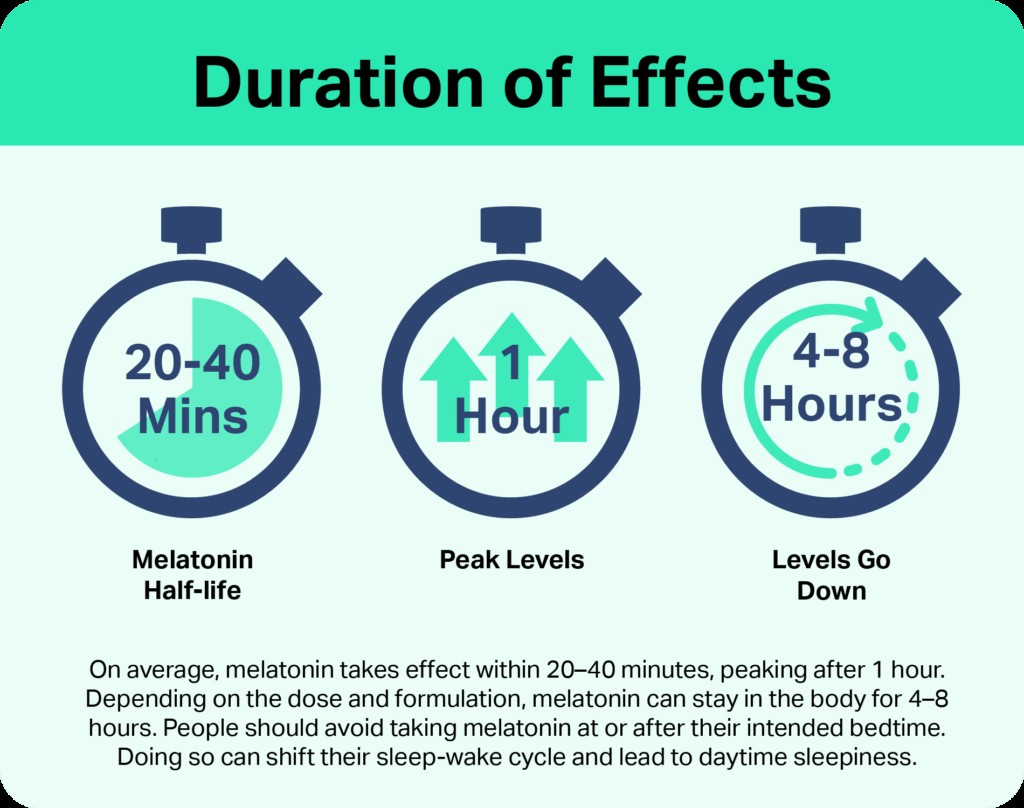
Now, to the core question: how long does melatonin last in your system? The answer isn’t a fixed number, but a general guideline is that melatonin’s effects typically last for approximately 4 to 5 hours. This duration is closely linked to melatonin’s half-life, which is the time it takes for your body to eliminate half of the initial dose. Melatonin has a relatively short half-life, ranging from 20 to 40 minutes.
This short half-life explains why melatonin is generally considered effective for initiating sleep but less so for maintaining sleep throughout the night, unless you are using an extended-release formulation. After about 4-5 hours, melatonin levels in your body will have significantly decreased, reducing its sleep-promoting effects.
However, it’s crucial to understand that this 4-5 hour timeframe is an average. Several factors can extend or shorten the duration of melatonin’s effects:
- Formulation Type: As mentioned earlier, extended-release melatonin is specifically designed to last longer. These formulations release melatonin slowly over several hours, aiming to mimic the natural sustained release of melatonin by the pineal gland. This can be beneficial for individuals who struggle with staying asleep.
- Dosage Size: While the duration isn’t directly proportional to the dose, higher doses of melatonin might take slightly longer for the body to fully metabolize and eliminate, potentially extending the effects marginally. However, exceeding recommended dosages is generally not advised due to the increased risk of side effects.
- Individual Factors: Individual characteristics play a significant role in how long melatonin persists in your system.
- Age: Studies suggest that older adults may metabolize melatonin more slowly than younger individuals. This means melatonin might stay in their system and exert its effects for a longer duration, potentially increasing the risk of daytime drowsiness.
- Liver Function: The liver is primarily responsible for metabolizing melatonin. Individuals with impaired liver function may process melatonin more slowly, leading to a longer duration of action.
- Medications: Certain medications can interact with melatonin metabolism, either prolonging or shortening its duration in the body. It’s essential to discuss melatonin use with your doctor, especially if you are taking other medications.
- Smoking: Smoking can accelerate the metabolism of melatonin, potentially reducing its duration of effect.
- Caffeine and Alcohol: While research is ongoing, caffeine and alcohol might influence melatonin metabolism, although the exact nature of these interactions is complex and not fully understood.
Melatonin and Wakefulness: Will it Make You Groggy?
One common concern with sleep aids is the potential for next-day grogginess. With fast-release melatonin at typical doses (e.g., 1-5mg), the risk of morning grogginess is generally low because it is largely cleared from your system within a few hours, aligning with a normal sleep cycle.
However, the likelihood of experiencing grogginess increases with:
- Higher Doses: Taking excessively high doses of melatonin, especially fast-release formulations, can lead to residual melatonin effects in the morning, causing drowsiness.
- Extended-Release Formulations: While beneficial for staying asleep, extended-release melatonin may increase the risk of next-day sleepiness, particularly if taken too late in the evening or if your body is particularly sensitive to its effects.
- Individual Sensitivity and Age: As mentioned, older adults may be more susceptible to prolonged melatonin effects, increasing the chance of daytime drowsiness. Some individuals may simply be more sensitive to melatonin’s sedative effects than others.
To minimize the risk of morning grogginess, it’s crucial to:
- Start with a Low Dose: Begin with the lowest effective dose of melatonin and gradually increase if needed, under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
- Time it Right: Take melatonin at the appropriate time before bed, generally 30-60 minutes for fast-release and potentially a bit earlier for extended-release, allowing sufficient time for it to clear your system before you need to wake up.
- Avoid Driving or Operating Machinery: It’s generally recommended to avoid driving or operating heavy machinery for at least 4-5 hours after taking melatonin, especially when first starting to use it or if you are unsure of your individual response.
Optimizing Melatonin Use: When and How to Take It
Melatonin can be a valuable tool for improving sleep, but like any supplement, it’s most effective when used appropriately. Here are some key considerations for optimizing melatonin use:
When to Take Melatonin:
- For Sleep Onset Insomnia: If you have trouble falling asleep, fast-release melatonin taken 30-60 minutes before bedtime can be helpful.
- For Jet Lag: Melatonin can assist in resetting your sleep-wake cycle when traveling across time zones. Timing will depend on the direction of travel, but generally, taking melatonin in the evening at your destination’s bedtime for a few days can be beneficial.
- For Shift Work: Individuals working irregular shifts can use melatonin to promote sleep during their desired sleep times.
- For Children with Sleep Onset Difficulties: In some cases, pediatricians may recommend melatonin for children with specific sleep onset issues. Dosage and timing should always be determined by a doctor.
When to Avoid Melatonin or Exercise Caution:
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Due to limited research on safety during pregnancy and breastfeeding, melatonin is generally not recommended unless advised by a healthcare professional.
- Certain Medical Conditions: Individuals with certain medical conditions, such as autoimmune diseases or seizure disorders, should consult their doctor before using melatonin.
- Dementia: Melatonin is not typically recommended for individuals with dementia.
- Driving or Operating Machinery Soon: Avoid melatonin if you need to be fully alert and perform tasks requiring concentration within 4-5 hours.
- Interactions with Medications: Melatonin can interact with various medications, including anticoagulants, antidepressants, and immunosuppressants. Always discuss melatonin use with your doctor if you are taking any medications.
General Recommendations:
- Consult a Healthcare Professional: Before starting melatonin, especially for chronic sleep problems, it’s advisable to consult with a doctor to rule out underlying sleep disorders and determine if melatonin is appropriate for you.
- Start Low and Go Slow: Begin with a low dose (e.g., 0.5mg to 1mg) and gradually increase if needed, up to a maximum of 5mg for adults, unless otherwise directed by a doctor.
- Prioritize Sleep Hygiene: Melatonin is most effective when combined with good sleep hygiene practices, such as maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and ensuring a dark, quiet, and cool sleep environment.
- Short-Term Use: Melatonin is generally considered safe for short-term use. If you find yourself needing it long-term, it’s crucial to revisit your sleep issues with a healthcare professional to explore underlying causes and long-term solutions.
The Takeaway: Melatonin Duration and Responsible Use
So, how long does melatonin last? The effects of a standard dose of fast-release melatonin typically last for around 4 to 5 hours, making it a relatively short-acting sleep aid primarily useful for initiating sleep. Extended-release formulations can prolong this duration, which may be beneficial for those who struggle with sleep maintenance.
Understanding the factors that influence melatonin’s duration, such as formulation, dosage, and individual characteristics, empowers you to use it more effectively and responsibly. By starting with a low dose, timing it appropriately, and consulting with a healthcare professional when needed, you can harness the potential benefits of melatonin for improved sleep while minimizing the risk of unwanted side effects. Remember, melatonin is a tool to support healthy sleep, and integrating it with good sleep habits is key to achieving restful nights andWakeful days.