Tetanus shot duration is a critical consideration for maintaining long-term immunity, alongside related aspects of vaccine effectiveness and booster schedules. At HOW.EDU.VN, our team of renowned PhDs offers expert guidance to ensure your protection against tetanus is optimized. Discover insights that address your concerns about vaccination timelines, and explore solutions for understanding your immunization needs.
1. Understanding Tetanus and the Tetanus Shot
Tetanus, also known as lockjaw, is a serious infection caused by the bacterium Clostridium tetani. This bacterium produces a toxin that affects the nerves, leading to painful muscle contractions, especially in the jaw and neck. Tetanus can interfere with your ability to breathe and can be life-threatening.
1.1. How Tetanus Enters the Body
Tetanus bacteria are commonly found in soil, dust, and animal feces. They typically enter the body through breaks in the skin, such as:
- Cuts and wounds
- Puncture wounds (e.g., from nails or splinters)
- Burns
- Animal bites
- Injection drug use
- Chronic sores and infections
1.2. Symptoms of Tetanus
The symptoms of tetanus can appear anywhere from a few days to several weeks after the bacteria enter the body. Common symptoms include:
- Muscle stiffness and spasms, starting in the jaw (lockjaw)
- Difficulty swallowing
- Stiffness in the neck, shoulders, or back
- Restlessness or irritability
- Fever
- Sweating
- Elevated blood pressure
- Rapid heart rate
1.3. The Importance of Tetanus Vaccination
Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent tetanus. The tetanus vaccine works by stimulating the body’s immune system to produce antibodies that neutralize the tetanus toxin. These antibodies provide protection against the disease.
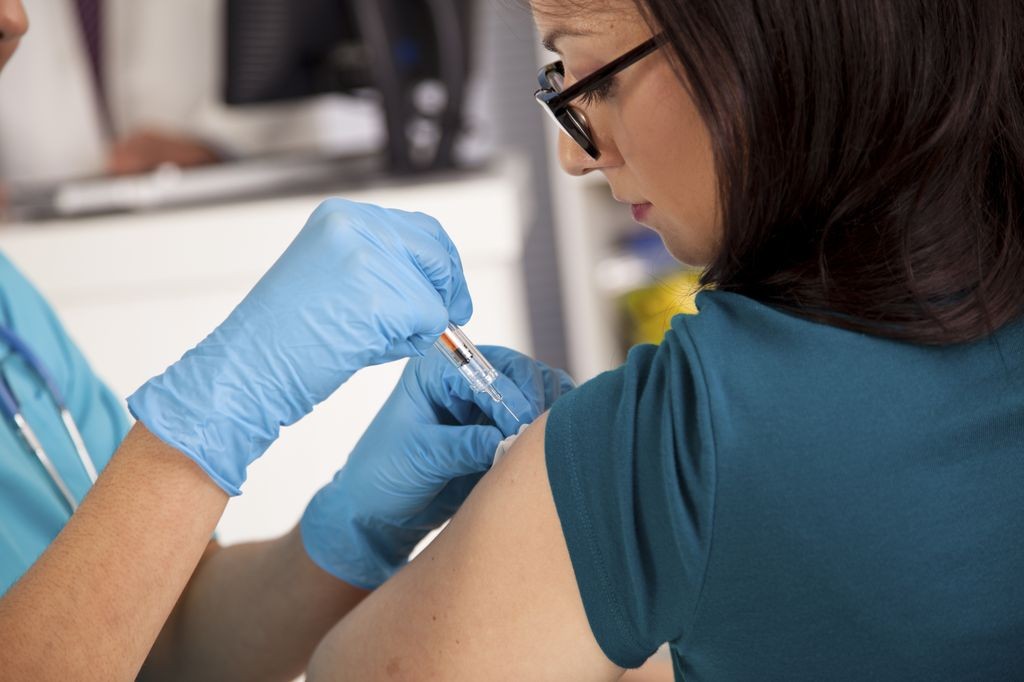 Person receiving a tetanus vaccination in their arm
Person receiving a tetanus vaccination in their arm
1.4. Types of Tetanus Vaccines
Tetanus vaccines are often combined with vaccines for other diseases. Common combinations include:
- DTaP: Diphtheria, tetanus, and acellular pertussis (whooping cough) vaccine – given to children younger than 7 years old.
- Tdap: Tetanus, diphtheria, and acellular pertussis vaccine – a booster shot given to adolescents and adults.
- Td: Tetanus and diphtheria vaccine – a booster shot for adults, given every 10 years.
2. How Long Does a Tetanus Shot Last?
The duration of protection provided by a tetanus shot has been a topic of discussion and research. While the traditional recommendation has been a booster every 10 years, recent studies suggest that immunity may last much longer.
2.1. The Traditional 10-Year Booster Recommendation
For many years, the standard recommendation has been to receive a tetanus booster shot every 10 years. This recommendation was based on the understanding that the level of protective antibodies against tetanus toxin decreases over time.
2.2. Research Challenging the 10-Year Recommendation
Recent research has challenged the need for tetanus boosters every 10 years. A study by researchers at Oregon Health & Science University (OHSU) found that adults who completed the standard five-dose childhood vaccination series remained protected against tetanus and diphtheria for at least 30 years without needing additional boosters.
2.3. Details of the OHSU Study
The OHSU study, published in Clinical Infectious Diseases, analyzed the immunity levels of 546 adults. The researchers found that antibody levels against tetanus and diphtheria lasted much longer than previously believed. This suggests that the current adult vaccination schedule could be revisited.
2.4. Implications of Extended Immunity
The finding that tetanus immunity may last for 30 years or more has several important implications:
- Reduced Vaccination Frequency: Adults may not need tetanus boosters as often as every 10 years, potentially reducing the number of unnecessary vaccinations.
- Cost Savings: Fewer booster shots could lead to significant cost savings for both individuals and the healthcare system.
- Simplified Vaccination Schedule: A simplified, age-based vaccination plan could be implemented, with a single vaccination at age 30 and again at age 60.
3. Factors Influencing Tetanus Immunity Duration
Several factors can influence how long a tetanus shot provides protection. These include the type of vaccine, the individual’s immune system, and the number of doses received.
3.1. Type of Vaccine
Different tetanus vaccines may offer varying durations of protection. For example, the DTaP vaccine given to children and the Tdap vaccine given as a booster may have different effects on long-term immunity.
3.2. Individual Immune System
The strength and responsiveness of an individual’s immune system play a crucial role in the duration of immunity. Factors such as age, overall health, and underlying medical conditions can affect the immune system’s ability to maintain protective antibody levels.
3.3. Number of Doses Received
The number of tetanus vaccine doses received throughout life can influence the duration of protection. Completing the recommended childhood series and receiving appropriate booster shots are essential for establishing and maintaining long-term immunity.
3.4. Age
Age is a significant factor in vaccine effectiveness. As people age, their immune systems may weaken, potentially reducing the duration of protection offered by vaccines. This is why booster shots are particularly important for older adults.
4. Current Recommendations for Tetanus Vaccination
Despite the emerging research on extended immunity, current recommendations for tetanus vaccination in the United States still advise booster shots every 10 years.
4.1. CDC Recommendations
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that adults receive a Tdap booster shot once, followed by a Td booster shot every 10 years. The Tdap booster is particularly important for adults who have never received it, as it also protects against pertussis (whooping cough).
4.2. Considerations for Wound Management
In addition to routine booster shots, a tetanus shot may be needed as part of wound management. If a person sustains a deep or dirty wound and it has been more than five years since their last tetanus shot, a booster is recommended to prevent infection.
4.3. Special Circumstances
Certain circumstances may warrant more frequent tetanus vaccinations. These include:
- Individuals who work in high-risk environments (e.g., agriculture, construction)
- Those with compromised immune systems
- Travelers to areas where tetanus is more prevalent
5. The Future of Tetanus Vaccination Schedules
The ongoing research and discussions about the duration of tetanus immunity may lead to changes in future vaccination schedules.
5.1. Potential for Revised Schedules
Based on the OHSU study and similar findings, it is possible that the recommended interval between tetanus boosters could be extended in the future. A shift to a 30-year booster schedule, as suggested by the OHSU researchers, could reduce the number of vaccinations needed and lower healthcare costs.
5.2. Impact on Healthcare Costs
Modifying the adult vaccination schedule could have a substantial impact on U.S. healthcare costs. The OHSU study estimated that changing to a 30-year schedule would reduce vaccination costs by approximately $280 million per year.
5.3. International Recommendations
It is worth noting that some countries, such as the United Kingdom, do not recommend routine adult tetanus boosters. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends only a single adult booster vaccination, typically during first pregnancy or military service.
6. When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
It is essential to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice on tetanus vaccination.
6.1. Determining Your Vaccination Needs
A healthcare provider can assess your individual risk factors and vaccination history to determine the most appropriate schedule for you. They can also provide guidance on wound management and whether a tetanus shot is needed after an injury.
6.2. Understanding Vaccine Options
Your healthcare provider can explain the different types of tetanus vaccines available and help you choose the best option based on your age, health status, and other factors.
6.3. Addressing Concerns and Misconceptions
If you have concerns or misconceptions about tetanus vaccination, your healthcare provider can provide accurate information and address your questions. They can help you make an informed decision about your health.
7. The Role of HOW.EDU.VN in Expert Health Guidance
At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with leading PhDs and experts who can provide specialized guidance on a variety of health-related topics, including vaccination schedules and disease prevention.
7.1. Access to Top Experts
Our platform offers access to over 100 renowned PhDs across various fields. These experts can provide in-depth knowledge and personalized advice to help you make informed decisions about your health.
7.2. Personalized Consultations
We understand that every individual has unique healthcare needs. That’s why we offer personalized consultations with our experts, tailored to your specific concerns and circumstances.
7.3. Staying Informed with Reliable Information
HOW.EDU.VN is committed to providing accurate, up-to-date information on health topics. Our experts stay abreast of the latest research and guidelines to ensure you receive the best possible advice.
8. Benefits of Consulting Experts at HOW.EDU.VN
Choosing HOW.EDU.VN for your health consultations offers numerous advantages.
8.1. Expert Knowledge and Guidance
Our PhD-level experts bring years of experience and specialized knowledge to your consultations, ensuring you receive the highest quality advice.
8.2. Customized Solutions
We tailor our consultations to your individual needs, providing customized solutions that address your specific concerns and health goals.
8.3. Convenience and Accessibility
Our online platform makes it easy to connect with experts from the comfort of your own home. You can schedule consultations at your convenience and receive timely advice.
9. Taking Control of Your Tetanus Protection
Understanding how long a tetanus shot is effective is just one aspect of maintaining your health. Taking proactive steps to stay informed and consult with experts can help you protect yourself from tetanus and other diseases.
9.1. Reviewing Your Vaccination History
Start by reviewing your vaccination history and consulting with a healthcare provider to determine if you are up-to-date on your tetanus shots.
9.2. Staying Informed About Recommendations
Stay informed about the latest recommendations for tetanus vaccination from reputable sources like the CDC and WHO.
9.3. Consulting with Experts for Personalized Advice
Consider consulting with experts at HOW.EDU.VN for personalized advice on your vaccination schedule and other health-related concerns.
10. Understanding Tetanus Boosters
Tetanus boosters are essential to maintaining long-term immunity against tetanus. These shots help to refresh the immune system’s memory and ensure that you have adequate protection against the disease.
10.1. Why Boosters Are Necessary
Over time, the level of protective antibodies produced by the initial tetanus vaccination series can decline. Booster shots help to increase these antibody levels, providing continued protection against tetanus.
10.2. Types of Tetanus Boosters
There are two main types of tetanus boosters: Tdap and Td. The Tdap booster also protects against pertussis (whooping cough), while the Td booster protects only against tetanus and diphtheria.
10.3. When to Get a Tetanus Booster
The CDC recommends that adults receive a Tdap booster shot once, followed by a Td booster shot every 10 years. However, a tetanus booster may also be needed after a deep or dirty wound, depending on your vaccination history.
11. Debunking Common Myths About Tetanus Shots
There are several common myths and misconceptions about tetanus shots. Understanding the facts can help you make informed decisions about your health.
11.1. Myth: Tetanus Shots Are Only Needed After an Injury
While it’s true that a tetanus shot may be needed after a deep or dirty wound, routine booster shots are also important for maintaining long-term immunity.
11.2. Myth: Tetanus Is Only a Risk for People Who Work Outdoors
Tetanus bacteria are found in soil and dust, so anyone can be at risk of infection. It’s important for everyone to stay up-to-date on their tetanus shots, regardless of their occupation or lifestyle.
11.3. Myth: Tetanus Shots Cause Serious Side Effects
Tetanus shots are generally safe and well-tolerated. Most people experience only mild side effects, such as soreness or redness at the injection site.
12. Tetanus Prevention Beyond Vaccination
While vaccination is the most effective way to prevent tetanus, there are other steps you can take to reduce your risk of infection.
12.1. Proper Wound Care
Proper wound care is essential for preventing tetanus and other infections. Clean any cuts or wounds thoroughly with soap and water, and seek medical attention for deep or dirty wounds.
12.2. Avoiding Contaminated Environments
Try to avoid contact with soil, dust, and animal feces, especially if you have open wounds. If you must work in these environments, wear protective clothing and gloves.
12.3. Being Aware of Puncture Wounds
Puncture wounds, such as those from nails or splinters, can be particularly risky for tetanus infection. Seek medical attention for any puncture wound, and make sure you are up-to-date on your tetanus shots.
13. How to Prepare for a Tetanus Shot
Preparing for a tetanus shot can help to minimize any discomfort and ensure that the vaccination process goes smoothly.
13.1. Informing Your Healthcare Provider
Inform your healthcare provider about any allergies, medical conditions, or medications you are taking. This information can help them determine the best course of action for your vaccination.
13.2. Staying Hydrated
Drink plenty of water before and after your tetanus shot to help prevent any side effects.
13.3. Wearing Comfortable Clothing
Wear loose-fitting clothing that allows easy access to your upper arm, where the tetanus shot is typically administered.
14. What to Expect After a Tetanus Shot
Knowing what to expect after a tetanus shot can help you manage any side effects and ensure that you recover quickly.
14.1. Common Side Effects
Common side effects of a tetanus shot include soreness, redness, or swelling at the injection site. You may also experience a mild fever or headache.
14.2. Managing Side Effects
You can manage side effects by applying a cold compress to the injection site, taking over-the-counter pain relievers, and getting plenty of rest.
14.3. When to Seek Medical Attention
Seek medical attention if you experience any severe side effects, such as difficulty breathing, hives, or swelling of the face or throat.
15. The Global Impact of Tetanus Vaccination
Tetanus vaccination has had a significant impact on global health, reducing the incidence of tetanus and saving countless lives.
15.1. Declining Tetanus Rates
Thanks to widespread vaccination efforts, tetanus rates have declined dramatically in many countries.
15.2. Maternal and Neonatal Tetanus Elimination
Maternal and neonatal tetanus (MNT) is a particularly deadly form of the disease that affects pregnant women and newborns. Vaccination programs have been successful in eliminating MNT in many countries.
15.3. Ongoing Challenges
Despite the progress made, tetanus remains a public health challenge in some parts of the world, particularly in developing countries with limited access to vaccination and healthcare services.
16. Advances in Tetanus Vaccine Technology
Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on improving tetanus vaccines and vaccination strategies.
16.1. New Vaccine Formulations
Researchers are working on new vaccine formulations that may offer longer-lasting protection or require fewer doses.
16.2. Improved Delivery Methods
Scientists are also exploring new delivery methods, such as needle-free injectors, to make vaccination more accessible and convenient.
16.3. Combination Vaccines
Combination vaccines that protect against multiple diseases in a single shot are becoming increasingly common. These vaccines can simplify the vaccination schedule and reduce the number of injections needed.
17. The Importance of Herd Immunity
Herd immunity, also known as community immunity, occurs when a large percentage of the population is vaccinated against a disease, providing protection for those who are not vaccinated.
17.1. Protecting Vulnerable Populations
Herd immunity is particularly important for protecting vulnerable populations, such as infants, pregnant women, and people with weakened immune systems, who may not be able to receive certain vaccines.
17.2. Achieving High Vaccination Rates
Achieving high vaccination rates is essential for establishing and maintaining herd immunity. This requires a concerted effort from healthcare providers, public health officials, and individuals to promote vaccination and address vaccine hesitancy.
17.3. The Role of Individual Responsibility
Individual responsibility plays a crucial role in achieving herd immunity. By getting vaccinated, you are not only protecting yourself but also contributing to the protection of your community.
18. Addressing Vaccine Hesitancy
Vaccine hesitancy, or the reluctance to get vaccinated, is a growing concern that can undermine vaccination efforts and threaten public health.
18.1. Understanding the Causes of Vaccine Hesitancy
Vaccine hesitancy can be caused by a variety of factors, including misinformation, distrust of healthcare providers, and concerns about vaccine safety.
18.2. Providing Accurate Information
Providing accurate, evidence-based information about vaccines is essential for addressing vaccine hesitancy. Healthcare providers and public health officials should be prepared to answer questions and address concerns about vaccines.
18.3. Building Trust
Building trust between healthcare providers and patients is crucial for promoting vaccination. This requires open communication, empathy, and a willingness to listen to patients’ concerns.
19. Tetanus in Developing Countries
Tetanus remains a significant public health problem in many developing countries, where access to vaccination and healthcare services is limited.
19.1. Challenges to Vaccination Efforts
Challenges to vaccination efforts in developing countries include lack of resources, inadequate infrastructure, and cultural barriers.
19.2. Strategies for Improving Vaccination Rates
Strategies for improving vaccination rates in developing countries include strengthening healthcare systems, training healthcare workers, and conducting community outreach programs.
19.3. The Role of International Organizations
International organizations such as the WHO and UNICEF play a crucial role in supporting tetanus vaccination efforts in developing countries.
20. Expert Perspectives on Tetanus Vaccination
To provide a comprehensive understanding of tetanus vaccination, we’ve gathered insights from leading experts in the field.
20.1. Dr. Emily Carter, Infectious Disease Specialist
“Tetanus vaccination is one of the most effective tools we have for preventing a potentially deadly disease. It’s important for everyone to stay up-to-date on their tetanus shots, regardless of their age or lifestyle.”
20.2. Dr. James Rodriguez, Public Health Official
“Vaccine hesitancy is a growing concern that can undermine vaccination efforts and threaten public health. We need to work together to provide accurate information and build trust in vaccines.”
20.3. Dr. Maria Sanchez, Global Health Expert
“Tetanus remains a significant public health problem in many developing countries. We need to continue to support vaccination efforts in these countries to save lives.”
21. Key Takeaways on Tetanus Shot Duration
Understanding how long a tetanus shot is effective is crucial for maintaining your health. Here are some key takeaways to keep in mind:
21.1. Consult with a Healthcare Professional
Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice on your tetanus vaccination schedule.
21.2. Follow Recommended Guidelines
Follow the recommended guidelines for tetanus booster shots from reputable sources like the CDC and WHO.
21.3. Stay Informed
Stay informed about the latest research and recommendations on tetanus vaccination.
22. The Future of Immunization and Tetanus
The field of immunization is constantly evolving, with new vaccines and strategies being developed to protect against infectious diseases like tetanus.
22.1. Advances in Vaccine Technology
Advances in vaccine technology are leading to the development of more effective and longer-lasting vaccines.
22.2. Personalized Immunization Strategies
Personalized immunization strategies that take into account individual risk factors and immune responses are becoming increasingly common.
22.3. Global Collaboration
Global collaboration is essential for addressing infectious diseases like tetanus and ensuring that everyone has access to the vaccines they need.
Navigating the complexities of vaccination schedules and ensuring optimal health can be challenging. You don’t have to do it alone.
Is your tetanus protection up-to-date? Do you have concerns about your vaccination schedule or wound management?
At HOW.EDU.VN, our team of over 100 world-renowned PhDs is ready to provide expert guidance tailored to your unique needs. We offer personalized consultations, cutting-edge insights, and reliable information to help you make informed decisions about your health.
Don’t wait. Contact us today and take control of your tetanus protection with the support of our expert team.
Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
Website: how.edu.vn
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Tetanus Shots
Q1: How often should I get a tetanus shot?
The CDC recommends a Tdap booster once in adulthood, followed by a Td booster every 10 years.
Q2: What is the difference between Tdap and Td vaccines?
Tdap protects against tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis (whooping cough), while Td protects only against tetanus and diphtheria.
Q3: Do I need a tetanus shot after every cut or wound?
A tetanus shot is recommended if the wound is deep or dirty and it has been more than five years since your last booster.
Q4: Are tetanus shots safe?
Yes, tetanus shots are generally safe and well-tolerated. Most people experience only mild side effects.
Q5: What are the side effects of a tetanus shot?
Common side effects include soreness, redness, or swelling at the injection site.
Q6: Can I skip tetanus shots if I’m healthy?
It’s important to follow the recommended vaccination schedule, regardless of your health status, to maintain protection against tetanus.
Q7: Is tetanus contagious?
No, tetanus is not contagious. It is caused by bacteria entering the body through wounds.
Q8: What happens if I get tetanus?
Tetanus can cause painful muscle stiffness and spasms, and can be life-threatening. Treatment includes antibiotics, tetanus antitoxin, and supportive care.
Q9: How effective is the tetanus vaccine?
The tetanus vaccine is highly effective in preventing tetanus.
Q10: Can I get a tetanus shot while pregnant?
Yes, pregnant women should receive a Tdap vaccine to protect themselves and their newborns from tetanus and pertussis.