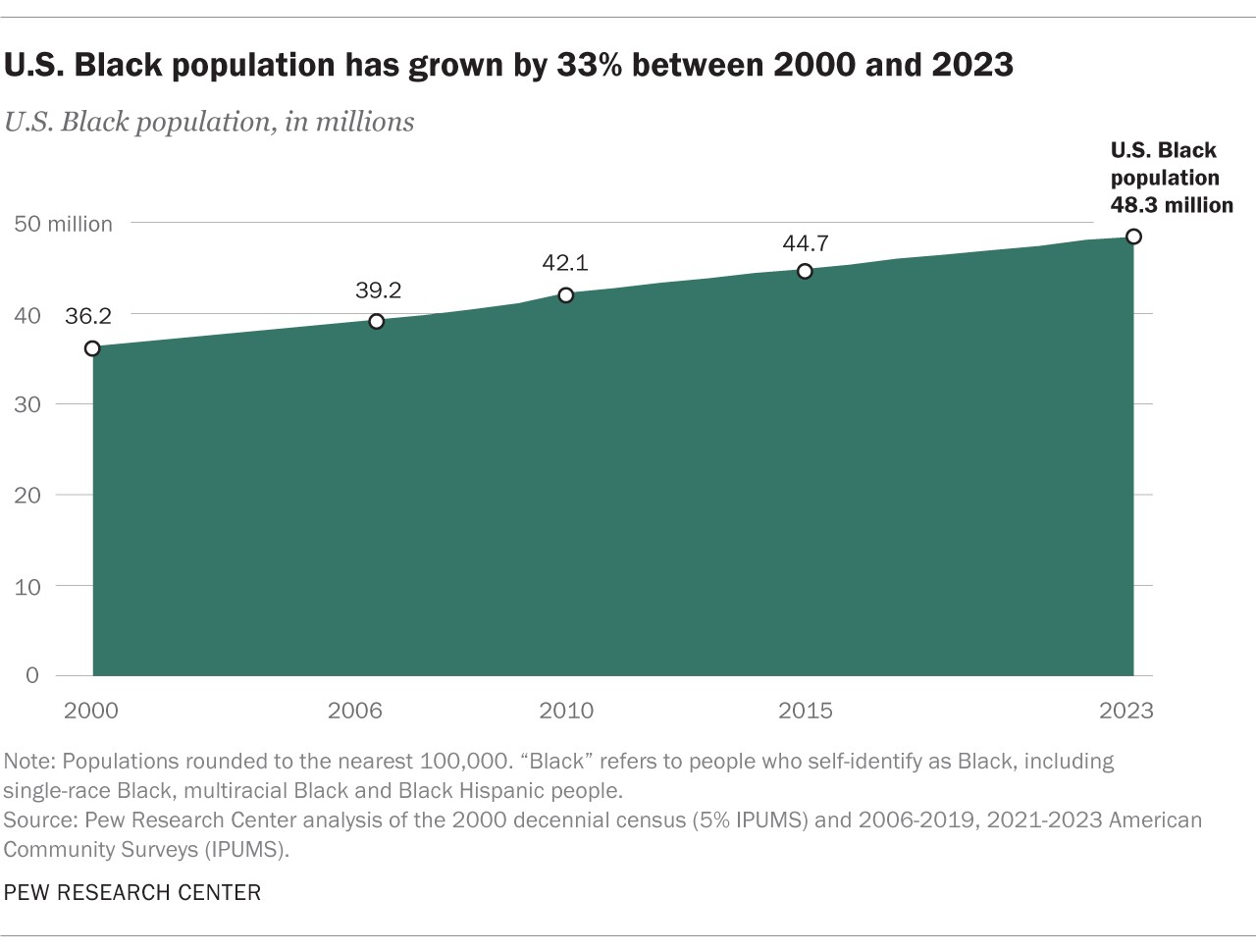
The Black population in the United States is a vibrant and growing demographic group, central to the nation’s history and culture. In 2023, approximately 48.3 million people in the U.S. identified as Black, representing 14.4% of the total U.S. population. This figure, drawn from the Census Bureau’s 2023 American Community Survey (ACS), highlights a significant 33% increase since 2000, when the Black population stood at 36.2 million. This article delves into the composition, characteristics, and key facts about the Black population in the United States, providing a comprehensive overview for anyone seeking to understand this diverse community.
It is important to note that the data presented here relies on self-identification of race and ethnicity, a methodology used by the Census Bureau. Definitions and categorizations have evolved over time, influencing how individuals identify themselves. Furthermore, personal identity can be fluid, changing across a person’s lifetime and influenced by societal perceptions of race.
Understanding the Terminology
To accurately discuss the Black population, it’s crucial to understand the terminology used:
- U.S. Black population or total Black population: This encompasses all individuals in the United States who self-identify as Black. This includes those who identify as Black alone, those who identify as Black in combination with other races, and those who identify as Black and Hispanic. The terms “Black population” and “Black people” are used interchangeably.
- Single-race, non-Hispanic Black; single-race Black; Black alone, non-Hispanic: These terms refer to individuals who exclusively identify as Black and do not identify as Hispanic or Latino.
- Multiracial, non-Hispanic Black or multiracial Black: This group includes individuals who identify with two or more races and do not identify as Hispanic or Latino.
- Black Hispanic: This refers to individuals who identify as both Hispanic or Latino and as Black, either alone or in combination with other races. It’s important to distinguish this group from the broader Afro-Latino population, as these categories are not entirely overlapping.
- Foreign born or immigrant: These terms are used interchangeably to describe individuals born outside of the United States to parents who were not U.S. citizens.
Population Growth Trends
The Black population in the U.S. has experienced substantial growth in recent decades.
- Overall Growth: As mentioned, the Black population reached an estimated 48.3 million in 2023, a 33% increase since 2000. This growth underscores the increasing demographic significance of Black Americans in the U.S.
- Immigrant Contribution: A notable aspect of this growth is the rising number of foreign-born Black individuals. In 2023, over 5 million Black Americans were born outside the U.S., accounting for about 11% of the total Black population. This is a significant increase from 2000, when foreign-born individuals represented 7% of the Black population.
Breakdown by Subgroups
Within the Black population, there are distinct subgroups with varying growth rates and characteristics:
- Single-Race, Non-Hispanic Black Population: This remains the largest subgroup, comprising 39.6 million people in 2023, or 82% of the total Black population. This group has grown by 17% since 2000. Immigration also plays a role here, with over 4 million single-race Black individuals being foreign-born in 2023, representing 11% of this subgroup.
- Multiracial, Non-Hispanic Black Population: This subgroup has experienced the most dramatic growth, increasing by 269% since 2000 to reach 5.6 million in 2023. Multiracial Black individuals now constitute 12% of the overall Black population. While the number of foreign-born individuals in this group has increased, their share of the multiracial Black population has slightly decreased since 2000.
- Black Hispanic Population: The smallest subgroup, Black Hispanics numbered 3.0 million in 2023, accounting for 6% of the total Black population. However, this group has also seen significant growth, increasing by 210% since 2000. Approximately 19% of Black Hispanics are foreign-born. It’s crucial to remember that this group is distinct from the broader Afro-Latino population.
Age Structure: A Young Population
The Black population in the United States is notably younger compared to the overall U.S. population.
- Median Age: In 2023, the median age of Black people was 32.6 years, about six years younger than the U.S. median age of 38.2. Approximately 30% of the Black population was under 20 years old, while 12% were 65 or older.
- Age Distribution: Nearly half (44%) of Black Americans were under 30 in 2023, and over a quarter (27%) were under 18. This youthful age structure has implications for future demographic trends and societal needs.
- Fertility Rate: The general fertility rate among Black females aged 15 to 44 was 5.8% in 2023.
This young age structure is even more pronounced within specific subgroups:
- Single-Race, Non-Hispanic Black: Median age of 35.4 years.
- Multiracial, Non-Hispanic Black: The youngest subgroup with a median age of just 19.5 years.
- Black Hispanic: Median age of 21.7 years, the second-youngest subgroup.
Language Diversity
English is the predominant language within the Black community, but linguistic diversity exists.
- English Proficiency: The vast majority (96%) of the Black population primarily speaks English, with 88% speaking only English and another 8% speaking another language at home but also speaking English very well.
- Other Languages: Besides English, other languages spoken at home include Spanish (4%), French or Haitian Creole (3%), Niger-Congo languages (1%), and Amharic and other Ethiopian languages (1%).
Language patterns vary slightly across subgroups:
- Single-Race, Non-Hispanic Black: 97% are proficient in English.
- Multiracial, Non-Hispanic Black: 98% are proficient in English.
- Black Hispanic: While still largely English-speaking (82% proficient), Spanish is spoken by a significant portion (46%).
Geographic Distribution
The geographic distribution of the Black population is concentrated in certain regions of the United States.
- Regional Concentration: Over half (56%) of the Black population resides in the South. The Midwest and Northeast each account for 17%, and the West for 10%.
- State and Metro Areas: Texas, Florida, and Georgia have the largest Black populations among states. The New York City metropolitan area has the highest number of Black residents, followed by Atlanta and Washington, D.C.
This regional concentration varies slightly across subgroups:
- Single-Race, Non-Hispanic Black: Even more concentrated in the South (59%).
- Multiracial, Non-Hispanic Black: While the South is still prominent (42%), there is a more even distribution across other regions.
- Black Hispanic: Heavily concentrated in the Northeast and South (71% combined).
Household Income
Household income provides insights into the economic status of the Black population.
- Median Household Income: In 2023, the median household income for households headed by a Black person was $54,000. Over a third (37%) of Black households earned $75,000 or more.
Income levels vary across subgroups:
- Single-Race, Non-Hispanic Black: Median household income of $52,800.
- Multiracial, Non-Hispanic Black: Higher median household income of $65,800.
- Black Hispanic: Median household income of $60,000.
Household Type
Household structures within the Black population reflect diverse living arrangements.
- Married-Couple Households: About 39% of Black people live in households headed by married couples.
- Female-Headed Households: Three-in-ten live in female-headed households.
- Nonfamily Households: 17% live in nonfamily households (householders living alone or with nonrelatives).
Household types vary slightly across subgroups:
- Single-Race, Non-Hispanic Black: Similar to the total Black population in household types.
- Multiracial, Non-Hispanic Black: Higher percentage living in married-couple households (45%).
- Black Hispanic: Also a higher percentage in married-couple households (43%).
Educational Attainment
Educational attainment is a key indicator of socioeconomic progress.
- Bachelor’s Degree or Higher: About 27% of Black adults aged 25 and older have a bachelor’s degree or more. This includes 16% with a bachelor’s degree and 11% with an advanced degree.
Educational attainment levels vary across subgroups:
- Single-Race, Non-Hispanic Black: 26% have a bachelor’s degree or higher.
- Multiracial, Non-Hispanic Black: Higher educational attainment, with 35% holding a bachelor’s degree or higher.
- Black Hispanic: 28% have a bachelor’s degree or higher.
Conclusion
The Black population in the United States is a dynamic and diverse group, experiencing significant growth and diversification. Understanding the demographic characteristics, geographic distribution, and socioeconomic indicators of this population is crucial for informed discussions about American society. This analysis, based on the latest data from the U.S. Census Bureau, provides a detailed snapshot of “How Many Black People In The United States” and offers valuable insights into the multifaceted nature of this vital segment of the nation.