Have you ever stopped to observe the shapes around you? From the square tiles on the floor to the round face of a clock, geometry is everywhere. Among these shapes, the pentagon stands out with its distinctive five sides. But beyond simply counting sides, what truly defines a pentagon, and what are its unique characteristics? Let’s delve into the world of pentagons and explore everything about this fascinating polygon.
[](alt=Close-up of hands using digital tablet for online tutoring, emphasizing personalized learning)
Decoding the Pentagon: Sides, Angles, and Corners
The very name “pentagon” holds the answer to our primary question. Originating from the Greek word “pente,” meaning five, a pentagon is fundamentally defined by its five sides. This isn’t just about sides, though. A pentagon is a polygon, a closed, two-dimensional shape with straight sides. Therefore, by definition, a pentagon has:
- Five Sides: The defining characteristic.
- Five Angles: Formed at each vertex where two sides meet.
- Five Vertices (or Corners): The points where the sides intersect.
Imagine drawing five straight lines on a piece of paper and connecting them end-to-end to form a closed shape. If you’ve done it correctly, you’ve created a pentagon. These sides are all straight, and the shape is completely enclosed, distinguishing it from open or curved shapes.
[](alt=Banner showcasing academy courses, illustrating educational resources and opportunities)
Regular vs. Irregular Pentagons: Not All Pentagons Are Created Equal
While all pentagons have five sides, they aren’t all identical. The distinction lies in the regularity of their sides and angles. This leads us to two main categories:
Regular Pentagons: The Epitome of Symmetry
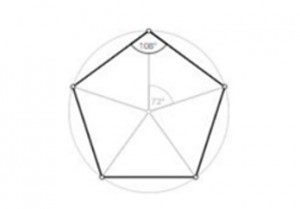
A regular pentagon is a special type where all sides are of equal length, and all interior angles are of equal measure. This perfect symmetry gives regular pentagons unique properties:
- Equal Sides: All five sides are congruent.
- Equal Angles: Each interior angle measures 108 degrees.
- Rotational Symmetry: It looks the same after rotations of 72°, 144°, 216°, and 288°.
- Reflectional Symmetry: It has five lines of symmetry.
Think of a stop sign – it’s a classic example of a regular octagon, but if it were five-sided and regular, it would exemplify a regular pentagon’s balanced and symmetrical form.
[](alt=Robotics and engineering concept banner, highlighting technological advancements and learning)
Irregular Pentagons: Variety in Five Sides
In contrast, an irregular pentagon is any pentagon that doesn’t meet the criteria of a regular pentagon. This means that its sides are not all the same length, or its angles are not all the same measure, or both. Irregular pentagons come in many forms, showcasing the versatility of five-sided shapes.
Diving Deeper: Types of Irregular Pentagons
The world of irregular pentagons is diverse. Within it, we find further classifications based on angle properties:
Convex and Concave Pentagons: Angles Pointing Inward or Outward
- Convex Pentagon: In a convex pentagon, all interior angles are less than 180 degrees, and all vertices “point outwards.” Imagine stretching a rubber band around a convex pentagon; it will perfectly hug the shape.
- Concave Pentagon (or Re-entrant Pentagon): A concave pentagon has at least one interior angle greater than 180 degrees. This creates a “dent” or a vertex that “points inwards.” If you were to stretch a rubber band around a concave pentagon, it wouldn’t touch the dented part.
Equilateral and Cyclic Pentagons: Side and Circle Relationships
- Equilateral Pentagon: As the name suggests, an equilateral pentagon has all five sides of equal length. However, unlike a regular pentagon, its angles can be unequal.
- Cyclic Pentagon: A cyclic pentagon is special because all its vertices lie on a single circle. This means you can draw a circle that passes through all five corners of the pentagon. Regular pentagons are always cyclic, but irregular pentagons can be cyclic too.
[](alt=Coding and computer science banner, promoting digital literacy and programming skills)
[](alt=Graduation cap banner, symbolizing academic achievement and higher education)
Beyond Pentagons: Exploring Other Polygons
Pentagons are just one member of the vast family of polygons. Polygons are classified and named based on their number of sides. Here’s a quick look at some common polygons:
| Polygon | Number of Sides |
|---|---|
| Triangle | 3 |
| Quadrilateral | 4 |
| Pentagon | 5 |
| Hexagon | 6 |
| Heptagon | 7 |
| Octagon | 8 |
| Nonagon | 9 |
| Decagon | 10 |







And the list goes on, with polygons having even more sides, each with its own unique properties and name!
[](alt=Study abroad program banner, encouraging international education and global experiences)
Pentagons in the Real World: Nature and Beyond
Pentagons aren’t just abstract geometric shapes; they appear surprisingly often in nature and human creations:
- Nature: Look closely at the cross-section of an okra, morning glory flowers, apple cores (gynoecium), and star fruit – you’ll find pentagonal shapes. Starfish and sea urchins exhibit pentagonal symmetry. Even some crystal structures show pentagonal faces.
- Architecture: The most famous example is the Pentagon building in Arlington, Virginia, USA, which houses the U.S. Department of Defense.
- Everyday Objects: While less common than squares or rectangles, pentagonal shapes can be found in tile designs, logos, and decorative patterns.
[](alt=Banner comparing undergraduate studies in India and abroad, assisting students in choosing education path)
Calculating Pentagon Properties: Area and Perimeter
Understanding pentagons also involves knowing how to calculate their area and perimeter.
Area of a Pentagon: Measuring the Enclosed Space
The area of a pentagon is the amount of space it encloses. For a regular pentagon, the area can be calculated using the formula:
A = ¼√5(5+2√5)s²
Where ‘s’ is the length of a side.
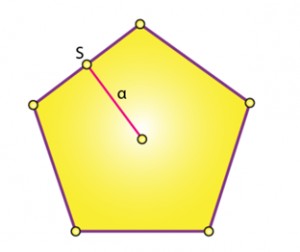
For irregular pentagons, the area calculation is more complex and often involves dividing the pentagon into triangles and summing their areas. A more general formula using the apothem (the perpendicular distance from the center to a side) applicable to regular pentagons is:
A = 5/2 x s x a
Where ‘s’ is the side length, and ‘a’ is the apothem.
Perimeter of a Pentagon: Measuring the Boundary
The perimeter of any polygon, including a pentagon, is simply the sum of the lengths of all its sides.
Perimeter = Side 1 + Side 2 + Side 3 + Side 4 + Side 5
For a regular pentagon, since all sides are equal, the perimeter is:
Perimeter = 5 x s
Where ‘s’ is the length of one side.
Putting it into Practice: Pentagon Examples
Let’s solidify our understanding with a few examples:
| Example 1: Finding a Missing Angle
Problem: A pentagon has angles measuring 160°, 55°, 130°, and 145°. What is the measure of the fifth angle?
Solution: The sum of interior angles in a pentagon is always 540 degrees (using the formula (n-2) * 180°, where n=5). Adding the known angles: 160° + 55° + 130° + 145° = 490°. Subtracting from the total sum: 540° – 490° = 50°. Therefore, the fifth angle is 50°.
| Example 2: Area with Side and Apothem
Problem: Calculate the area of a regular pentagon with a side length of 5 cm and an apothem of 2 cm.
Solution: Using the formula A = 5/2 x s x a, we get A = 5/2 x 5 cm x 2 cm = 25 cm². The area is 25 square centimeters.
| Example 3: Area of a Regular Pentagon with Side
Problem: What is the area of a regular pentagon with a side length of 10 cm?
Solution: Using the formula A = ¼√5(5+2√5)s², with s = 10 cm, we get A = ¼√5(5+2√5)(10 cm)² ≈ 172.04 cm².
| Example 4: Perimeter of an Irregular Pentagon
Problem: An irregular pentagon has sides measuring 4 cm, 5 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm, and 8 cm. What is its perimeter?
Solution: Perimeter = 4 cm + 5 cm + 4 cm + 5 cm + 8 cm = 26 cm. The perimeter is 26 centimeters.
Conclusion: The Five-Sided Wonder
So, How Many Sides Does A Pentagon Have? The answer is definitively five. But as we’ve explored, a pentagon is much more than just a five-sided shape. It’s a polygon with diverse forms, from perfectly symmetrical regular pentagons to varied irregular pentagons, each with unique properties and appearances in nature and our world. Understanding the pentagon is a fundamental step in appreciating the broader world of geometry and the shapes that surround us every day.
