How Much Caffeine In Mt Dew? The caffeine levels in Mountain Dew beverages vary, making it essential to understand the caffeine content of different varieties. HOW.EDU.VN offers expert insights into caffeine consumption and its effects, providing guidance for making informed choices about your beverage intake. Learn more about caffeine amounts, potential health impacts, and how to manage your caffeine intake effectively with our comprehensive resources.
1. Decoding Caffeine Levels in Mountain Dew Drinks
Mountain Dew, known for its citrus flavor and energizing kick, contains varying amounts of caffeine depending on the specific type and serving size. Understanding these levels is crucial for consumers who want to monitor their caffeine intake.
Here’s a detailed look at the caffeine content in different Mountain Dew drinks:
| Mountain Dew Drink | Caffeine Content (per 12 oz) |
|---|---|
| Regular Mountain Dew | 54 mg |
| Diet Mountain Dew | 54 mg |
| Mountain Dew Code Red | 54 mg |
| Mountain Dew Voltage | 69 mg |
| Mountain Dew White Out | 68 mg |
| Mountain Dew Kickstart | 68-92 mg |
| Mountain Dew Game Fuel | 90 mg |
| Mountain Dew Amp | 74 mg |
| Mountain Dew Energy | 180 mg |

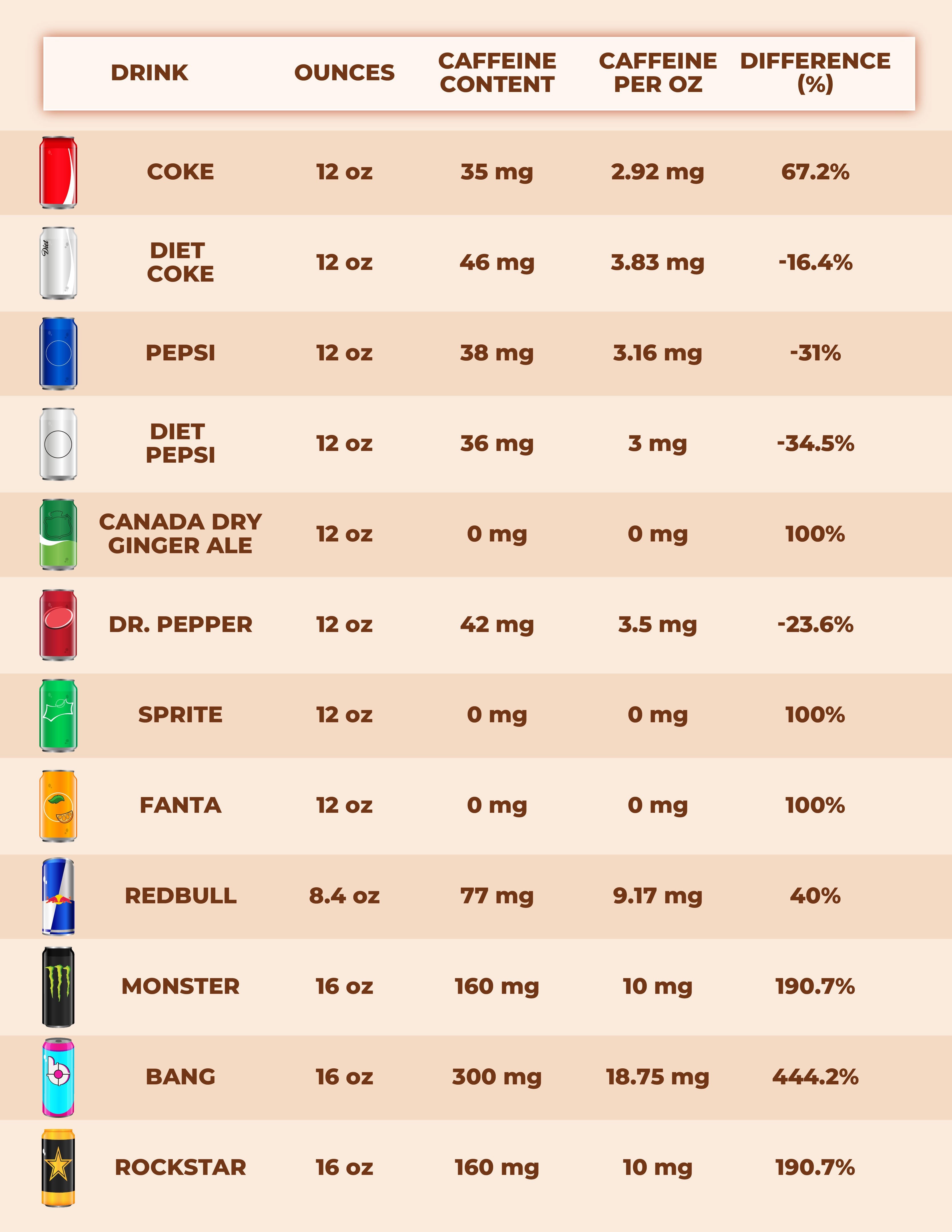
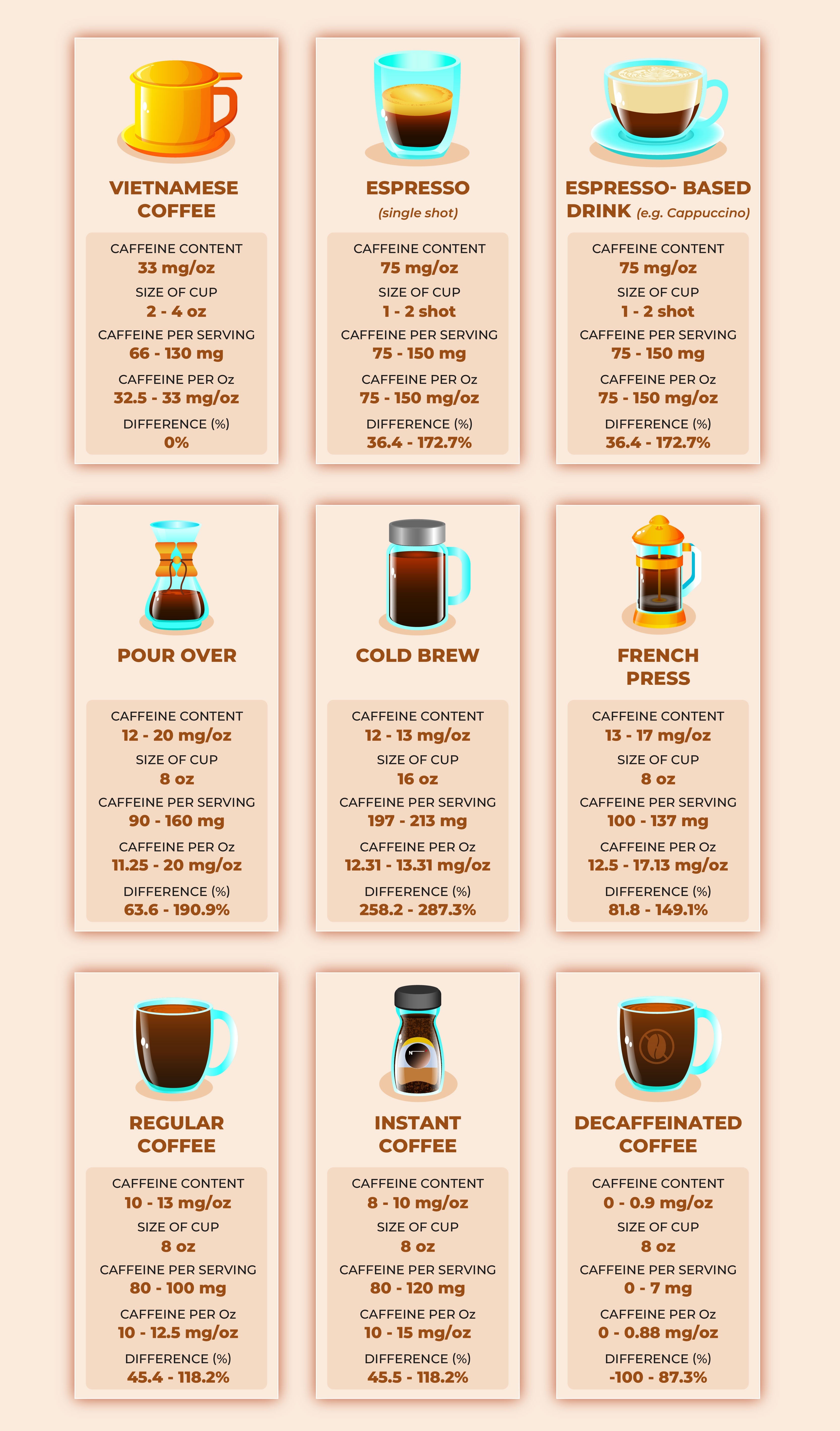
This table provides a clear overview, allowing consumers to quickly check the caffeine levels in their preferred Mountain Dew beverage. For personalized guidance on caffeine consumption, consult with the experts at HOW.EDU.VN.
2. Mountain Dew Caffeine vs. Other Energy Sources
When assessing the caffeine content in Mountain Dew, it’s helpful to compare it with other popular caffeinated drinks like coffee, tea, and other sodas. This comparison provides context for understanding where Mountain Dew falls in terms of caffeine strength.
2.1. Caffeine in Mountain Dew Compared to Sodas
Compared to other sodas, Mountain Dew generally has a higher caffeine content. For example:
| Soda Brand | Caffeine Content (per 12 oz) |
|---|---|
| Coca-Cola | 34 mg |
| Pepsi | 38 mg |
| Dr. Pepper | 41 mg |
| Mountain Dew | 54-69 mg |
As shown, Mountain Dew exceeds the caffeine levels found in many traditional sodas.
2.2. Mountain Dew Compared to Energy Drinks
Energy drinks typically contain significantly more caffeine than Mountain Dew. Common energy drinks and their caffeine levels include:
| Energy Drink | Caffeine Content (per 12 oz) |
|---|---|
| Red Bull | 111 mg |
| Monster | 120 mg |
| Rockstar | 160 mg |
Mountain Dew has a moderate caffeine level compared to these high-energy alternatives.
2.3. Mountain Dew Compared to Coffee
Coffee’s caffeine content varies greatly depending on the brewing method and type of coffee bean.
| Coffee Type | Caffeine Content (per 8 oz) |
|---|---|
| Brewed Coffee | 95-200 mg |
| Espresso | 63 mg |
| Instant Coffee | 30-90 mg |
In general, coffee contains a higher caffeine concentration than Mountain Dew. However, some smaller servings of coffee, like a single shot of espresso, may contain less caffeine than a 12 oz can of certain Mountain Dew flavors.
To make informed decisions about your caffeine consumption, consider consulting with a healthcare professional or the experienced experts at HOW.EDU.VN.
3. Exploring the Impact of Caffeine on Your Body
Caffeine, a stimulant found in Mountain Dew, affects the body in various ways. Understanding these effects can help you consume it responsibly.
3.1. Stimulant Effects
Caffeine primarily acts as a central nervous system stimulant. It increases alertness, reduces fatigue, and improves focus. These effects are why many people turn to caffeinated beverages for a mental boost.
3.2. Physical Effects
Caffeine can also impact physical functions, including:
- Increased Heart Rate: Caffeine can elevate heart rate and blood pressure.
- Diuretic Effect: It promotes urination, which can lead to dehydration if fluid intake is not adequately maintained.
- Enhanced Physical Performance: Caffeine can improve physical endurance and reduce perceived exertion during exercise.
3.3. Potential Side Effects
While caffeine offers several benefits, overconsumption can lead to side effects:
- Insomnia: Disrupts sleep patterns, making it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep.
- Anxiety: May exacerbate anxiety symptoms in susceptible individuals.
- Digestive Issues: Can cause stomach upset, heartburn, and diarrhea.
- Headaches: Both consumption and withdrawal can trigger headaches.
- Dependence: Regular consumption can lead to physical dependence, with withdrawal symptoms occurring upon cessation.
3.4. Recommended Intake
Health experts recommend that most adults limit their caffeine intake to no more than 400 milligrams per day. However, individual tolerance can vary based on factors like body weight, age, and overall health.
3.5. Identifying Symptoms of Overconsumption
Recognizing the symptoms of excessive caffeine intake is important. These symptoms include:
- Rapid heart rate
- Nervousness
- Irritability
- Tremors
- Dizziness
If you experience these symptoms, reducing or eliminating caffeine consumption is advisable.
For personalized advice on managing caffeine intake and understanding its effects on your body, consult the experts at HOW.EDU.VN. Our team of doctors and specialists can provide tailored recommendations based on your individual needs and health profile.
4. Risks and Side Effects of Over-Consuming Caffeine
While caffeine can offer alertness and enhanced performance, excessive intake carries potential health risks. Understanding these risks is crucial for making informed choices.
4.1. Cardiovascular Effects
Overconsumption of caffeine can lead to several cardiovascular issues:
- Increased Blood Pressure: Caffeine can elevate blood pressure, posing risks for individuals with hypertension.
- Heart Palpitations: Irregular heartbeats or palpitations may occur, leading to discomfort and anxiety.
- Arrhythmias: In sensitive individuals, high doses of caffeine may trigger abnormal heart rhythms.
4.2. Neurological Effects
The neurological side effects of excessive caffeine include:
- Insomnia: Disrupted sleep patterns, leading to chronic sleep deprivation.
- Anxiety and Nervousness: Worsening of anxiety symptoms and increased nervousness.
- Headaches: Both caffeine consumption and withdrawal can cause headaches.
- Tremors: Uncontrollable shaking or tremors, particularly in the hands.
4.3. Gastrointestinal Effects
Caffeine can also negatively affect the digestive system:
- Upset Stomach: Increased stomach acid production, leading to discomfort and heartburn.
- Diarrhea: Stimulation of bowel movements, potentially causing diarrhea.
- Nausea: Feelings of nausea, especially when consumed on an empty stomach.
4.4. Psychological Effects
Psychologically, excessive caffeine can lead to:
- Irritability: Increased feelings of irritability and mood swings.
- Anxiety Disorders: Exacerbation of existing anxiety disorders.
- Dependence: Physical and psychological dependence, resulting in withdrawal symptoms upon cessation.
4.5. Severe Health Risks
In extreme cases, caffeine overconsumption can lead to severe health issues:
- Caffeine Intoxication: Symptoms include confusion, agitation, rapid heart rate, and seizures.
- Rhabdomyolysis: Breakdown of muscle tissue, leading to kidney damage.
- Cardiac Arrest: In rare instances, excessive caffeine can cause cardiac arrest.
4.6. Vulnerable Populations
Certain populations are more susceptible to the adverse effects of caffeine:
- Pregnant Women: High caffeine intake is associated with increased risk of miscarriage and low birth weight.
- Children and Adolescents: May experience more pronounced anxiety and sleep disturbances.
- Individuals with Heart Conditions: Increased risk of arrhythmias and other cardiovascular complications.
- Individuals with Anxiety Disorders: Worsening of anxiety symptoms.
For personalized guidance on managing caffeine intake and understanding potential health risks, consult with the expert doctors at HOW.EDU.VN. Our specialists can provide tailored recommendations based on your individual health profile. Contact us at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States, or WhatsApp at +1 (310) 555-1212. Visit our website at HOW.EDU.VN for more information.
5. Exploring Caffeine-Free Alternatives
For those looking to reduce their caffeine intake, several caffeine-free alternatives can provide similar satisfactions without the stimulant effects.
5.1. Herbal Teas
Herbal teas offer a wide variety of flavors and health benefits without caffeine:
- Chamomile Tea: Known for its calming properties, making it an excellent choice for relaxation.
- Peppermint Tea: Refreshing and helps with digestion.
- Rooibos Tea: Rich in antioxidants and has a naturally sweet flavor.
- Ginger Tea: Soothes the stomach and reduces inflammation.
5.2. Decaffeinated Coffee
Decaffeinated coffee provides the taste and aroma of coffee with significantly reduced caffeine content:
- Swiss Water Process: A chemical-free method for removing caffeine from coffee beans.
- Methylene Chloride Process: A common method that uses a solvent to extract caffeine.
- CO2 Process: Uses carbon dioxide to remove caffeine, preserving the coffee’s flavor.
5.3. Sparkling Water
Sparkling water offers a refreshing and hydrating alternative to sugary sodas:
- Plain Sparkling Water: Provides a neutral base that can be flavored with fruits or herbs.
- Flavored Sparkling Water: Comes in various natural flavors like lemon, lime, and berry.
5.4. Fruit Infusions
Infusing water with fruits and herbs creates a flavorful and healthy beverage:
- Lemon and Cucumber Water: Refreshing and detoxifying.
- Strawberry and Mint Water: Sweet and aromatic.
- Raspberry and Lime Water: Tart and invigorating.
5.5. Chicory Root Coffee
Chicory root coffee is a caffeine-free alternative with a similar taste and texture to coffee:
- Roasted Chicory Root: Has a slightly bitter and woody flavor, often mixed with coffee.
- Chicory Root Tea: Can be brewed on its own for a caffeine-free hot beverage.
5.6. Golden Milk
Golden milk, or turmeric latte, is a warm and comforting beverage:
- Turmeric: Known for its anti-inflammatory properties.
- Ginger: Adds warmth and aids digestion.
- Cinnamon: Provides sweetness and aroma.
- Black Pepper: Enhances turmeric absorption.
5.7. Adaptogenic Drinks
Adaptogenic herbs help the body adapt to stress and can be added to beverages:
- Ashwagandha: Reduces anxiety and improves sleep.
- Rhodiola: Enhances energy and reduces fatigue.
- Holy Basil: Supports overall well-being and reduces stress.
These caffeine-free alternatives provide various options for those looking to reduce or eliminate caffeine from their diet without sacrificing flavor and enjoyment. For more personalized recommendations, consult with the experts at HOW.EDU.VN.
6. Mountain Dew and Pregnancy: What Expectant Mothers Need to Know
During pregnancy, monitoring caffeine intake is crucial for the health of both the mother and the developing fetus. Experts recommend that pregnant women limit their daily caffeine consumption to under 200 mg.
6.1. Risks of High Caffeine Intake During Pregnancy
Consuming more than 200 mg of caffeine per day during pregnancy can pose several risks:
- Miscarriage: Increased risk of pregnancy loss, particularly in the first trimester.
- Premature Birth: Higher likelihood of delivering the baby before 37 weeks of gestation.
- Low Birth Weight: Babies born with lower birth weights, which can lead to various health complications.
- Developmental Issues: Potential impact on the baby’s brain development.
6.2. Caffeine Content in Mountain Dew and Pregnancy
A 12-ounce can of Mountain Dew contains approximately 54 mg of caffeine. While this amount is lower than the recommended daily limit, it’s important to consider other sources of caffeine in the diet, such as coffee, tea, and chocolate.
6.3. Sugar and Artificial Additives
In addition to caffeine, Mountain Dew contains high levels of sugar and artificial additives, which can also pose risks during pregnancy:
- Gestational Diabetes: Increased risk of developing gestational diabetes due to high sugar content.
- Weight Gain: Excessive weight gain, which can lead to complications during pregnancy and delivery.
- Artificial Sweeteners: Potential health concerns associated with artificial sweeteners.
6.4. Recommended Alternatives
Expectant mothers can opt for healthier alternatives to Mountain Dew:
- Water: Staying hydrated with plain water is essential for overall health.
- Herbal Teas: Caffeine-free herbal teas like chamomile, peppermint, and rooibos are safe and beneficial.
- Fruit-Infused Water: Adding slices of fruits like lemon, cucumber, and berries to water can enhance flavor and hydration.
- Decaffeinated Beverages: Decaffeinated coffee and tea offer the taste without the caffeine.
6.5. Consulting Healthcare Professionals
It’s essential for pregnant women to consult with their healthcare providers for personalized advice on caffeine intake and dietary choices. Medical professionals can provide tailored recommendations based on individual health conditions and pregnancy progress.
For expert advice on pregnancy nutrition and managing caffeine intake, reach out to the doctors at HOW.EDU.VN. We offer specialized consultations to support a healthy pregnancy. Contact us at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States, or WhatsApp at +1 (310) 555-1212. Visit our website at HOW.EDU.VN for more information.
7. Interactions Between Mountain Dew, Caffeine, and Alcohol
Mixing Mountain Dew with alcohol can lead to several potential interactions and health risks. The combination of caffeine, sugar, and alcohol can have unpredictable effects on the body.
7.1. Masking Intoxication
Caffeine can mask the depressant effects of alcohol, making individuals feel more alert and less intoxicated than they actually are. This can lead to overconsumption and increased risk of alcohol poisoning.
7.2. Dehydration
Both caffeine and alcohol have diuretic properties, meaning they promote urination and can lead to dehydration. Dehydration can exacerbate the negative effects of alcohol, such as headaches and hangovers.
7.3. Increased Heart Rate
Caffeine can increase heart rate, and when combined with alcohol, this effect can be amplified, potentially leading to palpitations or arrhythmias.
7.4. Blood Sugar Imbalance
The high sugar content in Mountain Dew can cause rapid spikes and crashes in blood sugar levels, which can interfere with the body’s ability to metabolize alcohol properly.
7.5. Poor Decision-Making
The combination of caffeine and alcohol can impair judgment and decision-making abilities, increasing the risk of accidents and other risky behaviors.
7.6. Health Risks
Mixing caffeine and alcohol can pose serious health risks:
- Alcohol Poisoning: Increased risk of alcohol poisoning due to overconsumption.
- Liver Damage: Increased strain on the liver, which is responsible for metabolizing both alcohol and caffeine.
- Cardiovascular Problems: Potential for heart-related complications, especially in individuals with pre-existing conditions.
7.7. Safer Alternatives
If you choose to consume alcohol, it’s best to avoid mixing it with caffeinated beverages like Mountain Dew. Opt for non-caffeinated mixers such as water, juice, or club soda.
7.8. Seeking Medical Advice
If you have concerns about the interactions between alcohol, caffeine, and your health, consult with a healthcare professional. They can provide personalized advice based on your individual circumstances.
For expert guidance on managing alcohol and caffeine consumption, reach out to the specialists at HOW.EDU.VN. We offer consultations to help you make informed choices about your health. Contact us at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States, or WhatsApp at +1 (310) 555-1212. Visit our website at HOW.EDU.VN for more information.
8. The Potential for Caffeine Addiction from Mountain Dew
Regular consumption of Mountain Dew, due to its caffeine content, can potentially lead to caffeine dependence and addiction. Understanding the signs and symptoms of caffeine addiction is crucial for managing consumption habits.
8.1. How Caffeine Addiction Develops
Caffeine acts as a stimulant by blocking adenosine, a neurotransmitter that promotes relaxation and sleepiness. This leads to increased alertness and energy. Over time, the body adapts to the presence of caffeine, requiring more of it to achieve the same effects.
8.2. Symptoms of Caffeine Addiction
Recognizing the symptoms of caffeine addiction is the first step toward addressing the issue:
- Tolerance: Needing to consume increasing amounts of caffeine to achieve the desired effects.
- Withdrawal Symptoms: Experiencing negative symptoms when caffeine consumption is reduced or stopped abruptly.
- Continued Use Despite Negative Consequences: Continuing to consume caffeine despite experiencing adverse effects on health, sleep, or mood.
- Inability to Cut Back: Difficulty reducing or stopping caffeine consumption, even when wanting to do so.
- Cravings: Intense urges to consume caffeine.
8.3. Common Withdrawal Symptoms
Caffeine withdrawal can manifest in various ways:
- Headaches: One of the most common withdrawal symptoms.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired and lacking energy.
- Irritability: Increased feelings of frustration and moodiness.
- Difficulty Concentrating: Trouble focusing and staying on task.
- Depression: Feelings of sadness or hopelessness.
- Anxiety: Increased anxiety and nervousness.
8.4. Strategies for Reducing Caffeine Consumption
If you suspect you have a caffeine addiction, consider these strategies:
- Gradual Reduction: Slowly decrease your caffeine intake over several weeks to minimize withdrawal symptoms.
- Substitute with Decaf: Replace some caffeinated beverages with decaffeinated alternatives.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to help flush caffeine from your system.
- Get Enough Sleep: Prioritize sleep to combat fatigue and reduce cravings.
- Seek Support: Talk to a healthcare professional or join a support group for guidance and encouragement.
8.5. The Role of Balanced Diet and Lifestyle
Adopting a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle can support your efforts to reduce caffeine consumption:
- Nutrient-Rich Foods: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods to maintain energy levels.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to boost mood and reduce stress.
- Stress Management Techniques: Practice relaxation techniques like meditation or yoga to cope with stress.
8.6. Consulting Experts
If you struggle to manage your caffeine consumption on your own, consider seeking professional help. Healthcare providers and addiction specialists can offer personalized strategies and support.
For expert advice on managing caffeine addiction and adopting healthier habits, reach out to the doctors at HOW.EDU.VN. We offer consultations to help you make informed choices about your health. Contact us at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States, or WhatsApp at +1 (310) 555-1212. Visit our website at HOW.EDU.VN for more information.
9. FAQs: Unveiling the Caffeine Content in Mountain Dew
9.1. Are there any caffeine-free Mountain Dew flavors?
While most Mountain Dew formulas contain caffeine, Caffeine-Free Diet Mountain Dew is an exception. It offers the same flavor without the stimulant, making it a suitable choice for those looking to limit caffeine intake. However, its availability may be limited to certain regions.
9.2. How much Mountain Dew is too much?
Excessive consumption of Mountain Dew can lead to health issues due to its high sugar content and caffeine levels. Potential problems include diabetes, obesity, dental issues, heart disease, and fatty liver disease. Moderation is key to avoiding these risks. The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar intake to no more than 25 grams per day for women and 36 grams per day for men.
9.3. Is Mountain Dew safe for pregnant women?
Pregnant women should limit their daily caffeine intake to under 200 mg. High caffeine consumption during pregnancy can increase the risk of miscarriage, birth defects, premature labor, and reduced fertility. Additionally, Mountain Dew contains a lot of sugar and artificial additives that can pose health risks. It’s best to avoid making Mountain Dew a daily habit during pregnancy.
9.4. What happens when you mix Mountain Dew with alcohol?
Mixing Mountain Dew with alcohol can be dangerous because both sugar and caffeine can mask the intoxicating effects of alcohol. This can lead to overindulgence and an increased risk of alcohol poisoning. The combination can also contribute to dehydration and cause a more severe hangover.
9.5. Can Mountain Dew cause a caffeine addiction?
Yes, any drink high in caffeine can potentially lead to caffeine addiction. Caffeine is a stimulant that activates the reward centers in the brain, and regular consumption can lead to physical dependence. Symptoms of caffeine addiction include an inability to reduce or control caffeine consumption, withdrawal symptoms like headaches, depression, and anxiety, and severe cravings.
9.6. What is the caffeine content in Mountain Dew Energy?
Mountain Dew Energy contains a significantly higher caffeine level than regular Mountain Dew, with approximately 180 mg per 12 oz serving. This high caffeine content makes it a potent stimulant, and it should be consumed with caution, especially by those sensitive to caffeine.
9.7. Does Diet Mountain Dew have the same amount of caffeine as regular Mountain Dew?
Yes, Diet Mountain Dew generally has the same amount of caffeine as regular Mountain Dew, around 54 mg per 12 oz serving. The primary difference is the absence of sugar, with artificial sweeteners used instead.
9.8. What are some signs of caffeine overdose from Mountain Dew?
Signs of caffeine overdose can include rapid heart rate, nervousness, anxiety, insomnia, upset stomach, and dizziness. In severe cases, symptoms can include confusion, hallucinations, difficulty breathing, and uncontrollable movements. If you experience these symptoms, seek immediate medical attention.
9.9. How does the caffeine content in Mountain Dew compare to black tea?
The caffeine content in Mountain Dew (54 mg per 12 oz) is generally lower than that of black tea. An 8 oz cup of black tea typically contains between 40 and 70 mg of caffeine, depending on the brewing time and tea variety.
9.10. Can caffeine in Mountain Dew affect sleep patterns?
Yes, the caffeine in Mountain Dew can affect sleep patterns, especially if consumed close to bedtime. Caffeine can interfere with the onset and quality of sleep, leading to insomnia and daytime fatigue. It’s best to avoid caffeinated beverages several hours before going to bed.
10. Seeking Expert Advice on Caffeine Consumption
Navigating the complexities of caffeine consumption can be challenging. Whether you’re curious about the caffeine content in Mountain Dew or seeking personalized guidance, HOW.EDU.VN is here to help. Our team of experienced doctors and specialists offers expert consultations tailored to your individual needs.
10.1. Benefits of Consulting with Experts
- Personalized Recommendations: Receive tailored advice based on your health profile, lifestyle, and preferences.
- Comprehensive Information: Gain a deeper understanding of the effects of caffeine on your body.
- Management Strategies: Learn effective strategies for managing caffeine intake and addressing potential addiction.
- Addressing Health Concerns: Get expert guidance on specific health concerns related to caffeine, such as pregnancy, heart conditions, and anxiety disorders.
10.2. How HOW.EDU.VN Can Help
At HOW.EDU.VN, we provide a range of services to support your health and well-being:
- Individual Consultations: One-on-one consultations with our team of expert doctors and specialists.
- Nutritional Guidance: Personalized dietary recommendations to support healthy caffeine consumption.
- Addiction Support: Strategies and resources for overcoming caffeine addiction.
- Educational Resources: Access to articles, guides, and tools to enhance your understanding of caffeine and its effects.
10.3. Connect with Our Experts
Ready to take control of your caffeine consumption? Contact us today to schedule a consultation. Our team of over 100 renowned doctors and specialists is here to provide the support and guidance you need.
Contact Information:
- Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
- Website: HOW.EDU.VN
10.4. Take the First Step
Don’t let caffeine control your life. Contact HOW.EDU.VN today and embark on a journey towards a healthier, more balanced lifestyle. Our team is ready to answer your questions, address your concerns, and provide the expert guidance you deserve.
Call to Action:
Are you concerned about your caffeine intake? Do you want to learn more about the effects of caffeine on your body? Contact HOW.EDU.VN today and schedule a consultation with our expert doctors. Let us help you make informed choices and achieve optimal health. Visit our website at how.edu.vn or contact us via WhatsApp at +1 (310) 555-1212. We are here to support you every step of the way.
