How much cobalt does Apple get from DRC is a crucial question, given the ethical concerns surrounding cobalt mining in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC). At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with leading experts who can shed light on this complex issue, offering comprehensive analysis and potential solutions for responsible sourcing. This article explores Apple’s cobalt supply chain, the challenges of ethical sourcing, and how consumers and companies can promote responsible practices, including due diligence and supply chain transparency.
1. Understanding Cobalt and Its Importance
Cobalt is a hard, lustrous, silver-gray metal used primarily in lithium-ion batteries, which power smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles. Its unique properties make it essential for battery stability, energy density, and longevity. Cobalt is also used in various other industrial applications, including superalloys, magnetic materials, and pigments.
1.1. Properties and Applications of Cobalt
- High-Temperature Strength: Cobalt-based alloys maintain their strength at high temperatures, making them ideal for jet engines and gas turbines.
- Magnetic Properties: Cobalt is a key component in powerful magnets used in electric motors, generators, and data storage devices.
- Chemical Stability: Cobalt compounds are used as catalysts in various chemical reactions and as pigments in ceramics, paints, and plastics.
- Battery Technology: Cobalt enhances the performance and lifespan of lithium-ion batteries, crucial for electric vehicles and portable electronics.
1.2. The Global Demand for Cobalt
The demand for cobalt has surged in recent years due to the rapid growth of the electric vehicle (EV) market and the increasing popularity of portable electronic devices. As governments and consumers worldwide embrace EVs to reduce carbon emissions, the demand for cobalt is expected to continue to rise significantly in the coming years. This surge in demand has put pressure on cobalt supply chains, particularly those originating in the DRC.
1.3. Why the DRC Is Crucial for Cobalt Supply
The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) is the world’s leading producer of cobalt, accounting for over 70% of global production. The DRC’s vast cobalt reserves make it a critical source for meeting the growing demand for this essential metal. However, the DRC’s cobalt mining sector is plagued by serious human rights abuses, including child labor, dangerous working conditions, and environmental degradation.
2. Apple’s Cobalt Supply Chain: An Overview
Apple, as a major consumer electronics company, relies heavily on cobalt for its lithium-ion batteries. Understanding Apple’s cobalt supply chain is essential for assessing the company’s commitment to ethical sourcing and responsible business practices.
2.1. Apple’s Reliance on Cobalt for Batteries
Apple uses cobalt in the batteries of its iPhones, iPads, MacBooks, and other products. The company’s high production volumes mean that it requires a significant amount of cobalt annually. The specific amount of cobalt used varies depending on the battery size and composition of each product.
2.2. Tracing Apple’s Cobalt Sources Back to the DRC
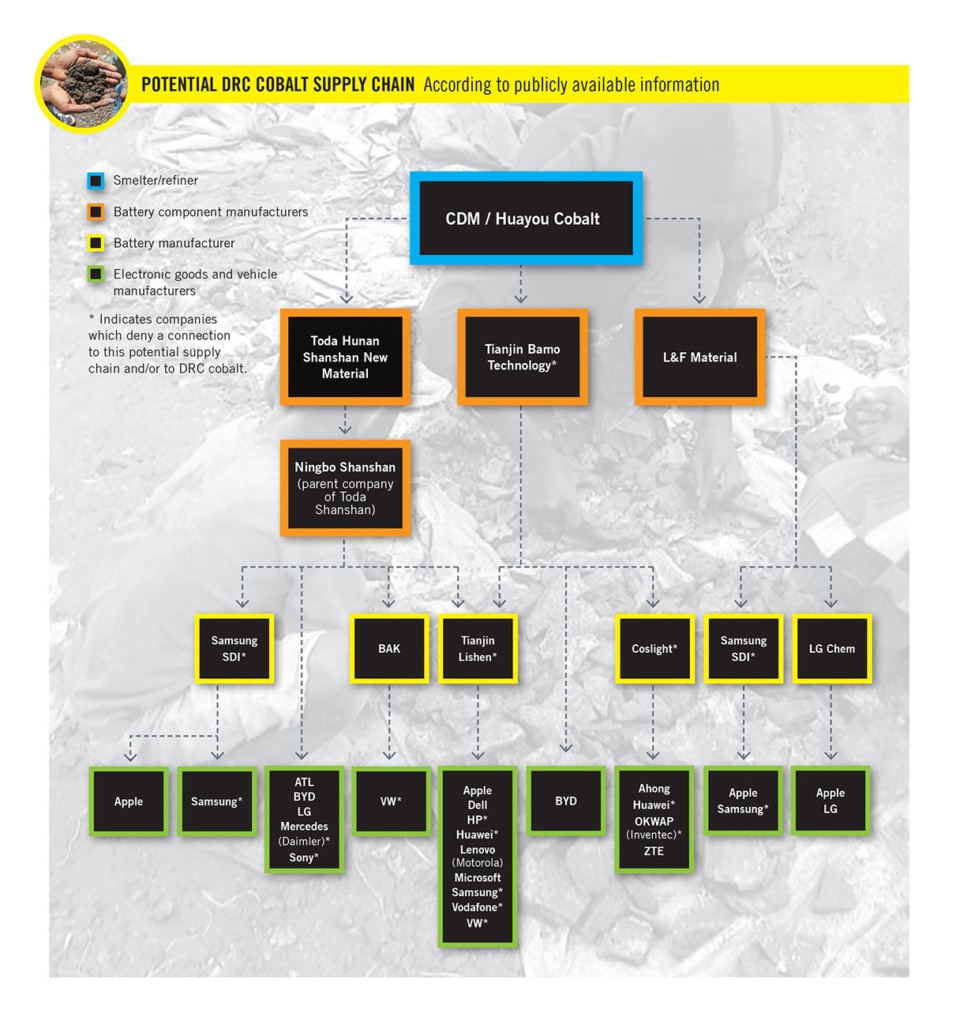
While Apple does not directly mine cobalt in the DRC, its suppliers source cobalt from the region. The cobalt typically passes through multiple intermediaries, including mining companies, traders, and battery component manufacturers, before reaching Apple’s battery suppliers. Tracing the exact origin of cobalt in Apple’s products is a complex and challenging task due to the lack of transparency in the supply chain.
2.3. Apple’s Stated Commitment to Ethical Sourcing
Apple has publicly stated its commitment to ethical sourcing and responsible business practices. The company has implemented policies and programs aimed at ensuring that its suppliers adhere to strict labor and environmental standards. Apple also conducts audits and assessments of its suppliers to monitor compliance with these standards. However, despite these efforts, challenges remain in ensuring that all cobalt in Apple’s supply chain is sourced ethically and responsibly.
3. The Dark Side of Cobalt Mining in the DRC
Cobalt mining in the DRC is associated with a range of serious human rights abuses and environmental problems. Understanding these issues is crucial for evaluating the ethical implications of cobalt sourcing and for identifying opportunities for improvement.
3.1. Prevalence of Child Labor in Cobalt Mines
One of the most pressing concerns is the widespread use of child labor in cobalt mines in the DRC. Children as young as seven years old work in dangerous conditions, often without protective equipment, to extract cobalt ore. These children face significant health risks, including respiratory problems, skin diseases, and injuries from mine collapses. The use of child labor is a clear violation of international human rights standards and raises serious ethical concerns for companies that source cobalt from the DRC.
3.2. Hazardous Working Conditions for Miners
Adult miners in the DRC also face hazardous working conditions. Artisanal miners, who extract cobalt using hand tools, work in unstable tunnels with a high risk of collapse. Miners are exposed to dust and toxic chemicals, which can cause long-term health problems. Accidents are common, and many miners die or are seriously injured each year.
3.3. Environmental Degradation and Health Impacts
Cobalt mining in the DRC has significant environmental impacts. Mining operations can lead to deforestation, soil erosion, and water pollution. The release of toxic chemicals from mining activities can contaminate water sources and harm aquatic life. Local communities are often exposed to these pollutants, leading to health problems such as respiratory illnesses and skin diseases.
4. How Much Cobalt Does Apple Get From DRC?
Determining the exact amount of cobalt that Apple sources from the DRC is difficult due to the complexity and lack of transparency in the supply chain. However, estimates and reports can provide some insight into Apple’s reliance on DRC cobalt.
4.1. Estimates of Apple’s Cobalt Consumption
Industry analysts estimate that Apple consumes a significant portion of the world’s cobalt supply. While the exact amount varies from year to year, it is estimated that Apple uses several thousand metric tons of cobalt annually for its battery production.
4.2. Percentage of Apple’s Cobalt Sourced From the DRC
Given that the DRC produces over 70% of the world’s cobalt, it is likely that a significant percentage of Apple’s cobalt is sourced from the region. However, Apple does not publicly disclose the exact percentage of its cobalt that comes from the DRC.
4.3. Challenges in Tracking Cobalt Supply Chains
Tracking cobalt supply chains is a complex and challenging task. Cobalt ore often passes through multiple intermediaries, making it difficult to trace the exact origin of the metal. The lack of transparency in the supply chain makes it easier for unethical practices, such as child labor and environmental degradation, to go undetected.
5. Apple’s Efforts to Address Ethical Concerns
Apple has taken steps to address the ethical concerns associated with cobalt mining in the DRC. These efforts include supply chain audits, responsible sourcing initiatives, and support for industry-wide solutions.
5.1. Supply Chain Audits and Assessments
Apple conducts regular audits and assessments of its suppliers to ensure compliance with its labor and environmental standards. These audits include visits to mining sites and battery component manufacturing facilities. Apple’s auditors look for evidence of child labor, unsafe working conditions, and environmental violations.
5.2. Responsible Sourcing Initiatives
Apple participates in responsible sourcing initiatives aimed at promoting ethical practices in the cobalt mining sector. These initiatives include partnerships with organizations such as the Responsible Minerals Initiative (RMI) and the Cobalt Institute. Through these collaborations, Apple works to develop and implement industry-wide standards for responsible cobalt sourcing.
5.3. Support for Industry-Wide Solutions
Apple supports the development of industry-wide solutions to address the challenges of ethical cobalt sourcing. This includes advocating for greater transparency in the supply chain, supporting efforts to formalize artisanal mining operations, and investing in technologies to trace the origin of cobalt.
6. Criticisms and Controversies Surrounding Apple’s Cobalt Sourcing
Despite Apple’s efforts, the company has faced criticism and controversies regarding its cobalt sourcing practices. Critics argue that Apple’s efforts are not sufficient to eliminate the risk of child labor and human rights abuses in its supply chain.
6.1. Reports of Child Labor Persisting in Apple’s Supply Chain
Despite Apple’s audits and assessments, reports of child labor in cobalt mines linked to Apple’s supply chain continue to surface. These reports raise questions about the effectiveness of Apple’s monitoring efforts and the company’s ability to ensure that its cobalt is sourced ethically.
6.2. Lack of Transparency in Apple’s Sourcing Practices
Critics also point to the lack of transparency in Apple’s sourcing practices. Apple does not publicly disclose the names and locations of all of its cobalt suppliers, making it difficult for independent observers to verify the company’s claims about ethical sourcing.
6.3. Lawsuits and Legal Challenges
Apple has faced lawsuits and legal challenges related to its cobalt sourcing practices. These lawsuits allege that Apple has benefited from the use of child labor in its cobalt supply chain and has failed to take adequate steps to prevent human rights abuses.
7. Alternative Sources of Cobalt and Future Trends
To reduce its reliance on DRC cobalt and mitigate ethical concerns, Apple and other companies are exploring alternative sources of cobalt and investing in research and development of battery technologies that require less or no cobalt.
7.1. Exploring Cobalt Mining in Other Countries
Companies are exploring cobalt mining in other countries, such as Australia, Canada, and the United States. These countries have stricter environmental and labor regulations, which could help to ensure more responsible cobalt sourcing.
7.2. Recycling Cobalt From Old Batteries
Recycling cobalt from old lithium-ion batteries is another promising alternative. Battery recycling can reduce the need for newly mined cobalt and help to minimize the environmental impacts of battery production. Companies are investing in technologies to improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of battery recycling.
7.3. Research and Development of Cobalt-Free Batteries
Researchers are working on developing battery technologies that do not require cobalt. These include lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries and solid-state batteries. Cobalt-free batteries could significantly reduce the demand for cobalt and eliminate the ethical concerns associated with cobalt mining.
8. The Role of Consumers in Promoting Ethical Sourcing
Consumers can play a vital role in promoting ethical sourcing by making informed purchasing decisions and demanding greater transparency from companies.
8.1. Making Informed Purchasing Decisions
Consumers can research the cobalt sourcing practices of companies before making purchasing decisions. By choosing products from companies that are committed to ethical sourcing, consumers can send a strong message that they value human rights and environmental responsibility.
8.2. Demanding Transparency From Companies
Consumers can demand greater transparency from companies about their cobalt sourcing practices. This includes asking companies to disclose the names and locations of their cobalt suppliers and to provide information about their efforts to prevent child labor and human rights abuses.
8.3. Supporting Advocacy Groups and NGOs
Consumers can support advocacy groups and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) that are working to promote ethical cobalt sourcing. These organizations play a critical role in monitoring companies, raising awareness about human rights abuses, and advocating for policy changes.
9. The Importance of Due Diligence and Supply Chain Transparency
Due diligence and supply chain transparency are essential for ensuring ethical cobalt sourcing and preventing human rights abuses.
9.1. Implementing Robust Due Diligence Processes
Companies should implement robust due diligence processes to identify and mitigate the risks of child labor, unsafe working conditions, and environmental degradation in their cobalt supply chains. This includes conducting regular audits, engaging with suppliers, and implementing corrective action plans.
9.2. Promoting Supply Chain Transparency
Companies should promote supply chain transparency by disclosing information about their cobalt suppliers and their sourcing practices. This can help to build trust with consumers and stakeholders and to ensure that companies are held accountable for their actions.
9.3. Collaborating With Industry Stakeholders
Companies should collaborate with industry stakeholders, including suppliers, NGOs, and government agencies, to develop and implement solutions to the challenges of ethical cobalt sourcing. This includes sharing best practices, developing industry-wide standards, and supporting efforts to formalize artisanal mining operations.
10. Expert Advice From HOW.EDU.VN’s Network of Professionals
At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with leading experts who can provide insights and guidance on ethical cobalt sourcing and responsible business practices. Our network of professionals includes supply chain experts, human rights advocates, and environmental consultants who can help you navigate the complexities of the cobalt supply chain and implement effective solutions.
10.1. Connecting With Supply Chain Experts
Our supply chain experts can help you assess the risks in your cobalt supply chain, develop due diligence processes, and implement responsible sourcing initiatives. They can also provide training and support to your suppliers to help them improve their environmental and labor practices.
10.2. Consulting With Human Rights Advocates
Our human rights advocates can provide guidance on how to prevent and address human rights abuses in your cobalt supply chain. They can help you develop policies and procedures to protect the rights of workers and communities affected by cobalt mining.
10.3. Engaging With Environmental Consultants
Our environmental consultants can help you assess the environmental impacts of your cobalt sourcing practices and develop strategies to minimize your environmental footprint. They can also help you comply with environmental regulations and promote sustainable mining practices.
The information provided in this article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute professional advice. Consult with qualified experts for specific guidance on ethical cobalt sourcing and responsible business practices.
FAQ: Ethical Cobalt Sourcing and Apple’s Supply Chain
Here are some frequently asked questions about ethical cobalt sourcing and Apple’s supply chain:
1. What is cobalt and why is it important?
Cobalt is a hard, lustrous, silver-gray metal used primarily in lithium-ion batteries, which power smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles. It is essential for battery stability, energy density, and longevity.
2. Where does cobalt come from?
The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) is the world’s leading producer of cobalt, accounting for over 70% of global production.
3. What are the ethical concerns associated with cobalt mining in the DRC?
Cobalt mining in the DRC is associated with serious human rights abuses, including child labor, dangerous working conditions, and environmental degradation.
4. How much cobalt does Apple use in its products?
Industry analysts estimate that Apple consumes a significant portion of the world’s cobalt supply, using several thousand metric tons annually for its battery production.
5. What steps has Apple taken to address ethical concerns in its cobalt supply chain?
Apple conducts supply chain audits, participates in responsible sourcing initiatives, and supports industry-wide solutions to address ethical concerns in its cobalt supply chain.
6. What are some alternative sources of cobalt?
Alternative sources of cobalt include mining in other countries with stricter regulations, recycling cobalt from old batteries, and developing cobalt-free battery technologies.
7. How can consumers promote ethical cobalt sourcing?
Consumers can make informed purchasing decisions, demand transparency from companies, and support advocacy groups working to promote ethical cobalt sourcing.
8. What is due diligence and why is it important?
Due diligence is the process of identifying and mitigating the risks of child labor, unsafe working conditions, and environmental degradation in a company’s cobalt supply chain. It is essential for ensuring ethical cobalt sourcing and preventing human rights abuses.
9. How can HOW.EDU.VN help companies with ethical cobalt sourcing?
HOW.EDU.VN connects companies with leading experts who can provide insights and guidance on ethical cobalt sourcing, including supply chain experts, human rights advocates, and environmental consultants.
10. What should companies do if they find evidence of child labor in their cobalt supply chain?
Companies should immediately take steps to remove children from the workforce, provide them with appropriate support and rehabilitation, and work with suppliers to prevent future incidents of child labor.
Conclusion: Towards a More Ethical Future for Cobalt Sourcing
Addressing the ethical challenges associated with cobalt mining in the DRC requires a multi-faceted approach involving companies, governments, consumers, and civil society organizations. By implementing robust due diligence processes, promoting supply chain transparency, and investing in alternative sources of cobalt, we can work towards a more ethical and sustainable future for cobalt sourcing.
At HOW.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing you with the expertise and resources you need to navigate the complexities of ethical cobalt sourcing and responsible business practices. Contact us today to connect with our network of professionals and learn how we can help you make a positive impact.
Contact Information:
- Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
- Website: HOW.EDU.VN
Let how.edu.vn connect you with the expertise you need to make informed decisions and drive positive change in the world.