The academic year has commenced in most parts of the United States, and a recent Pew Research Center analysis of data from the Education Commission of the States indicates that K-12 public schools will, on average, be in session for approximately 180 days this year. However, variations exist from state to state regarding the duration of schooling and even what qualifies as a school day. Let’s delve into the details of how states regulate instructional time and explore the differences across the nation.
Each state establishes regulations specifying the minimum duration of school sessions, typically a combination of days and hours per year, as well as hours per day. State policies also determine the extent to which non-instructional time, such as lunch breaks, recess, and class transitions, can contribute to these minimum requirements. School districts then create their own calendars based on these statewide regulations, unless they receive a waiver.
The most prevalent approach for states to govern instructional time involves setting a minimum number of days for the school year. Currently, 38 states and the District of Columbia employ this method. Among these, 27 states, along with D.C., mandate 180 instructional days, effectively establishing a quasi-national standard.
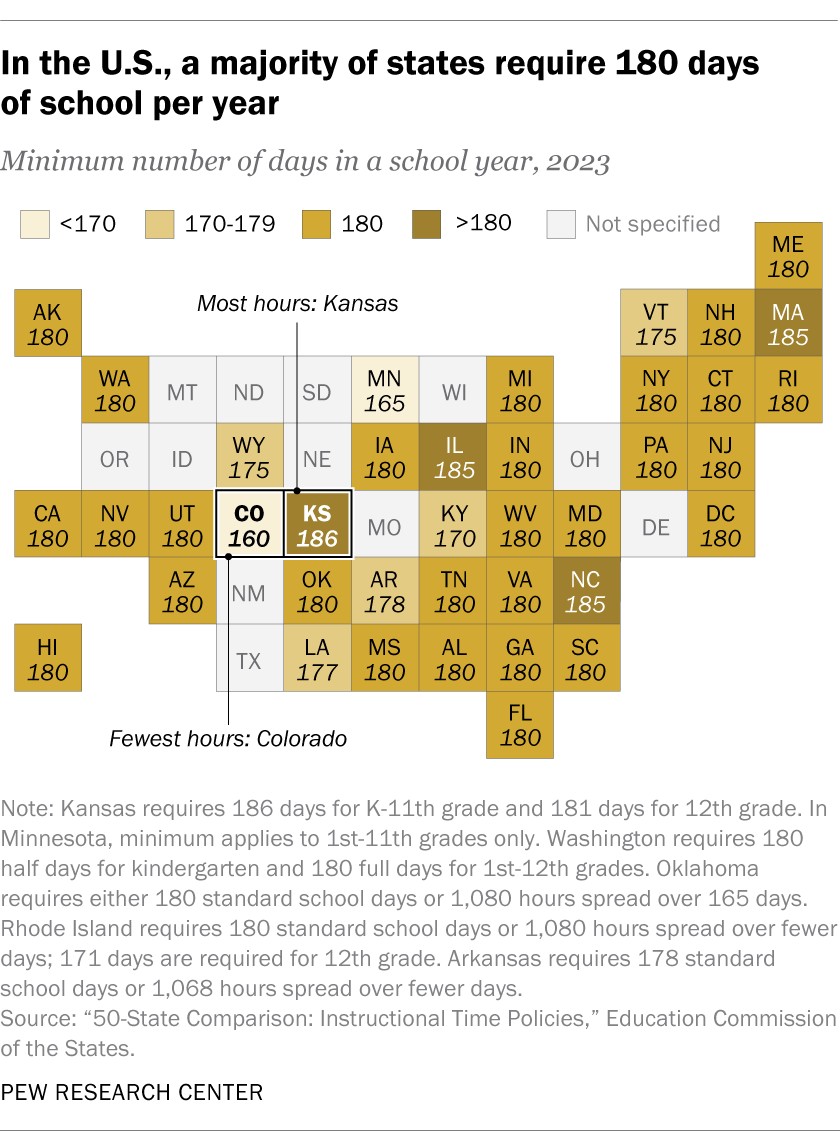 A map showing that, in the U.S., a majority of states require 180 days of school per year, highlighting instructional time policies and the average number of school days.
A map showing that, in the U.S., a majority of states require 180 days of school per year, highlighting instructional time policies and the average number of school days.
State Variations in School Days
While 180 days is the norm, some states deviate. Seven states have minimums below 180 days, with Colorado requiring the fewest at 160 days. On the other end, four states mandate more than 180 days, with Kansas leading the way at 186 days for kindergarten through 11th grade and 181 days for 12th grade. Across all states with a minimum requirement, the average is 179 days.
This 180-day standard has been in place for a while. A 1989 report by the National Center for Education Statistics revealed that 33 states and D.C. had 180-day requirements. Only one state, Ohio, required more days at 182, while 12 states required fewer. The remaining states either had no minimum or set a range of 175 to 180 days.
Hours in a School Day and Year
In addition to setting a minimum number of days, states may also regulate school time by mandating a specific number of hours or minutes per school year. According to the Education Commission of the States, 39 states have laws or policies of this kind. Some states allow districts to meet either a minimum number of days or a minimum number of hours per year. For example, Oklahoma allows districts to schedule either 180 standard school days or 1,080 hours spread across 165 days.
In most of these states (26 of 39), annual time minimums vary by grade level. South Dakota, for instance, requires 875 hours per year for fourth graders and 962.5 hours for eighth graders.
The average annual time minimum for fourth graders across states is 997.8 hours. For 11th graders, the required number of hours ranges from 720 in Arizona (including lunch) to 1,260 in Texas, which expresses its requirements in minutes. The average requirement for 11th graders among the 39 states with one is 1,034.8 hours per year.
States can also require a certain number of hours or minutes per school day, which 29 states and D.C. do. In 16 of these states, requirements differ by grade level. For example, Pennsylvania mandates a minimum school day length of 2.5 hours for kindergarten, 5 hours for first through eighth grades, and 5.5 hours for ninth through 12th grades.
For eighth graders, the school day ranges from 3 hours in Maryland and Missouri to 6.5 hours in Tennessee. Interestingly, New Hampshire and Oregon set maximums for the school day length: 6 hours for eighth graders in New Hampshire and 8 hours in Oregon. States also vary on whether and how to count lunch, recess, and other non-classroom time.
Texas stands out by setting only a minimum number of minutes in the school year—75,600, or 1,260 hours, including intermissions and recess. Districts can distribute these minutes as they choose. Previously, Texas mandated 7 hours per school day, including intermissions, recesses, and other non-instructional time. Following this older convention would result in a school year of 180 days.
Conclusion
The question of “How Much Days In A Year” students attend school varies across the United States, influenced by state regulations and local policies. While the average school year hovers around 180 days, the specific number of days and hours can differ significantly. Understanding these variations is essential for educators, policymakers, and parents alike, as they shape the educational experiences of students nationwide.