Are you curious about executive compensation and its impact on the economy? This article, brought to you by HOW.EDU.VN, explores CEO salaries, their growth, and their relation to worker compensation, offering insights and potential solutions to address income inequality. Discover how CEO pay has evolved and what it means for the future of economic equity.
1. Understanding CEO Compensation Trends
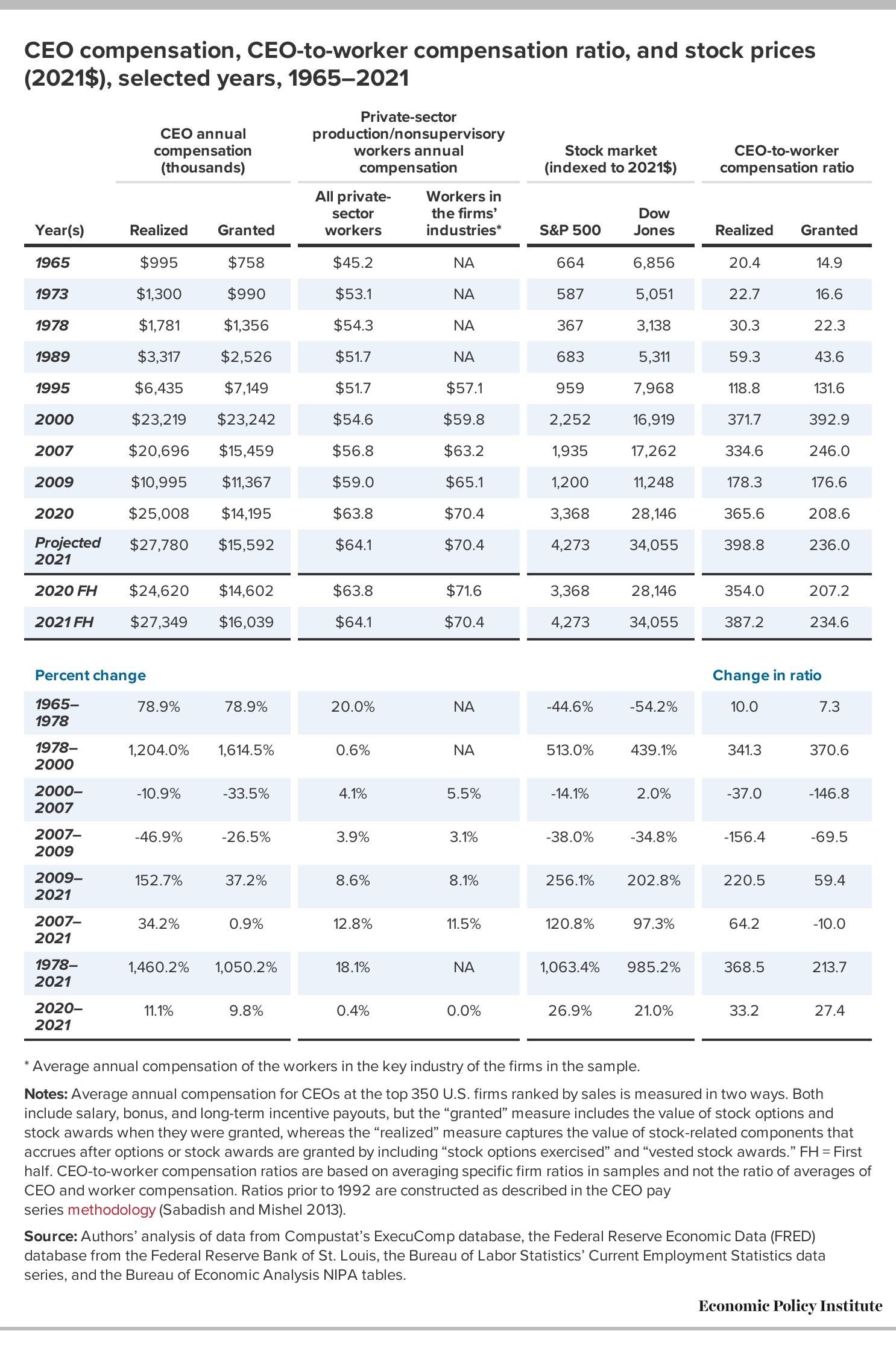
Executive compensation has experienced significant growth in recent decades. From 1978 to 2021, the compensation for top CEOs increased by an astounding 1,460.2%, far outpacing the growth of the stock market (1,063%) and typical worker compensation (18.1%). This disparity raises questions about the factors driving executive pay and its broader economic implications.
2. Decoding CEO Pay Metrics: Realized vs. Granted
Two primary methods are used to measure CEO compensation: realized and granted. The realized measure includes stock options when exercised and stock awards when vested, reflecting the actual value executives receive. Conversely, the granted measure values stock options and awards at their fair value when initially granted. Both metrics offer valuable insights into executive pay trends and the evolving composition of compensation packages.
3. The Unequal Impact: CEO Pay vs. Worker Wages
The gap between CEO compensation and worker wages has widened dramatically. In 2021, the CEO-to-worker compensation ratio reached an all-time high of 399-to-1, a stark contrast to the 20-to-1 ratio in 1965. This growing disparity underscores the increasing income inequality and raises concerns about the distribution of economic gains.
4. Pandemic Pay Disparities: Executive Gains Amidst Economic Hardship
During the COVID-19 pandemic, CEO compensation surged while millions faced job losses and wage declines. From 2019 to 2021, CEO realized compensation jumped by 30.3%, while typical worker compensation rose by only 3.9%. This divergence highlights the disconnect between executive gains and the economic realities faced by many workers during times of crisis.
5. Analyzing the Composition of CEO Compensation
Stock-related components, such as stock awards and stock options, constitute a significant and increasing share of CEO compensation. In 2021, these components accounted for 82.0% of total CEO compensation. This shift towards stock-based pay raises questions about incentives, risk-taking, and alignment with shareholder interests.
6. The Role of Stock Awards vs. Stock Options
Companies have increasingly shifted from stock options to stock awards in CEO compensation packages. Stock awards promote better alignment of a CEO’s goals with those of shareholders by incentivizing long-term stock price appreciation while mitigating excessive risk-taking. This shift reflects a growing recognition of the need for balanced incentives in executive compensation.
7. Examining Long-Term Trends in CEO Compensation
Analyzing historical data reveals significant long-term trends in CEO compensation. Realized CEO compensation has generally risen and fallen with the S&P 500 Index over the past five decades. However, since 1978, CEO compensation growth has far exceeded the growth in worker compensation, highlighting the increasing income inequality.
8. Comparing CEO-to-Worker Compensation Ratios Over Time
The CEO-to-worker compensation ratio provides a clear illustration of the growing divergence between executive and worker pay. In 1965, CEOs earned 20 times as much as the typical worker, while in 2021, this ratio reached 399-to-1. This exponential growth underscores the widening income gap and raises concerns about economic fairness.
9. Unpacking the “Market for Skills” Argument
Some argue that rising CEO compensation is driven by the demand for skills, reflecting a competitive market for talent. However, data suggests that CEO compensation has grown far faster than that of other highly paid workers, casting doubt on the notion that the market for skills is solely responsible for the rapid growth in executive pay.
10. Challenging the Correlation Between CEO Pay and Market Trends
While there is a correlation between stock prices and CEO compensation, this relationship does not necessarily imply that CEOs are being paid solely for their performance. CEO compensation often rises with the overall stock market, regardless of individual firm performance, suggesting that market-wide factors play a significant role.
11. Analyzing the CEO-to-Top-0.1% Compensation Ratio
Comparing CEO compensation to the earnings of the top 0.1% of wage earners reveals a striking disparity. In 2020, CEO compensation was 6.88 times the pay of the top 0.1%, significantly higher than the historical average. This suggests that factors beyond skills drive the compensation levels of CEOs.
12. The Role of CEO Pay in Overall Income Inequality
Exorbitant CEO compensation contributes to the growth of top 1% and top 0.1% incomes, fueling widespread inequality. Income growth among executives is a significant factor leading to increased incomes for the top 0.1% and top 1% of households, highlighting the impact of executive pay on overall income distribution.
13. Policy Recommendations for Reversing the Trend
To address excessive executive pay and promote broader wage growth, several policy options can be considered. Implementing higher marginal income tax rates at the top, setting corporate tax rates higher for firms with high CEO-to-worker ratios, and enhancing corporate governance practices can help reverse the trend of excessive executive compensation.
14. Examining the Stock Market and Executive Pay
The relationship between the stock market and executive pay is a critical factor in understanding compensation trends. While rising stock values often lead to increased executive pay, it is essential to differentiate between company-specific performance and market-wide trends to accurately assess the fairness and justification of executive compensation.
15. Exploring the Impact of Economic Rents on CEO Compensation
High CEO pay reflects economic rents, which are concessions CEOs can extract from the economy due to their positions of power. If CEOs were paid less, the economy would not necessarily suffer any loss of output, suggesting that a portion of executive compensation is not directly tied to productivity.
16. Connecting CEO Pay and Overall Inequality
The connection between CEO pay and overall inequality is undeniable. Rising pay for CEOs and other executives reflects income that could have accrued to other workers, impacting broader-based wage growth. Addressing excessive executive compensation is crucial for promoting economic equity and fairness.
17. The Impact of Rising Pay on the Bottom 90%
Rising pay for CEOs and other executives has a direct impact on the bottom 90% of wage earners. Wage growth for the bottom 90% would have been significantly faster over the past decades had wage inequality not grown. This underscores the importance of addressing executive compensation to promote wage growth for all workers.
18. Policy Solutions for Excessive Executive Pay
To reverse the trend of excessive executive pay, policymakers can consider several solutions, including higher marginal income tax rates, corporate tax rates tied to CEO-to-worker ratios, and enhanced corporate governance practices. These measures can help restrain executive pay and promote more equitable income distribution.
19. The Importance of Corporate Governance
Corporate governance plays a crucial role in regulating executive pay. Greater use of “say on pay,” which allows shareholders to vote on top executives’ compensation, can help restrain excessive pay. Additionally, providing worker representation on corporate boards can further enhance the power of shareholders to oversee executive compensation.
20. Exploring the Link Between CEO Pay and Market Power
The large firms headed by highly compensated CEOs often enjoy significant market power. Restraining these firms’ market power through antitrust enforcement and regulation can not only promote economic efficiency and competition but also help restrain executive pay.
21. The Impact of Wages in The Top 1%
Studies of tax returns from 1979 to 2005 show that increases in income among the top 1% and top 0.1% of households were driven by those in executive positions and financial-sector workers. This means that CEO compensation is the largest driver of top incomes and contributes to the rising income inequality.
22. The Lake Wobegon World of CEO Compensation
The “Lake Wobegon” effect in CEO compensation refers to the tendency for every firm to believe its CEO is above average and therefore needs to be correspondingly remunerated. This belief fuels the growth of CEO compensation, as each firm seeks to outdo the others in rewarding its executives.
23. Real-World Examples: Case Studies in Executive Compensation
Examining real-world case studies can provide valuable insights into executive compensation practices. By analyzing specific examples of CEO pay packages and their impact on firm performance, stakeholders can gain a better understanding of the complexities and consequences of executive compensation decisions.
24. Understanding the SEC’s Regulations for Executive Compensation
The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) now requires publicly owned firms to provide a metric for the ratio of CEO compensation to that of the median worker in a firm. Understanding these regulations and their implications is crucial for stakeholders seeking to promote transparency and accountability in executive compensation.
25. Why is Understanding CEO Salaries Important?
Understanding CEO salaries is vital for several reasons. It sheds light on income inequality, helps inform policy decisions, and promotes corporate transparency. By examining executive compensation, we can better understand the economic forces shaping our society and work towards a more equitable future.
Are you facing challenges related to executive compensation or seeking expert advice? At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with over 100 renowned PhDs who can provide personalized solutions and guidance. Contact us today for a consultation and unlock your potential with expert insights.
Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
Website: HOW.EDU.VN
FAQ: Understanding CEO Compensation
1. What is CEO compensation?
CEO compensation includes salary, bonuses, stock options, and other benefits paid to the chief executive officer of a company.
2. How is CEO compensation measured?
CEO compensation is measured using two primary methods: realized compensation (stock options exercised and stock awards vested) and granted compensation (value of stock options and awards when granted).
3. Why has CEO compensation increased so much?
CEO compensation has increased due to factors such as market forces, corporate governance issues, and the structure of executive pay packages, which often include significant stock-based incentives.
4. What is the CEO-to-worker compensation ratio?
The CEO-to-worker compensation ratio is the ratio of CEO compensation to the average compensation of workers in the same industry.
5. How does CEO compensation compare to other high earners?
CEO compensation has grown faster than the earnings of other high earners, such as those in the top 0.1% of wage earners.
6. What are the implications of high CEO pay?
High CEO pay contributes to income inequality and may reflect economic rents, which are not tied to productivity.
7. How does the stock market affect CEO pay?
CEO pay is often linked to the stock market, with rising stock values leading to increased executive compensation.
8. What can be done to address excessive CEO pay?
Policy solutions include higher marginal income tax rates, corporate tax rates tied to CEO-to-worker ratios, and enhanced corporate governance practices.
9. What role does corporate governance play in regulating CEO pay?
Corporate governance practices, such as “say on pay,” can help restrain excessive CEO compensation by giving shareholders more power to oversee executive pay.
10. How can I learn more about executive compensation?
You can learn more about executive compensation through academic research, government reports, and expert consultations. Visit how.edu.vn to connect with renowned PhDs for personalized advice.