The salary of a medical coder is a common point of interest for those considering a career in healthcare. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual wage for medical records and health information specialists, including medical coders, was $48,780 per year or $23.45 per hour as of 2023. However, this figure can vary significantly based on factors like location, experience, certification, and the type of employer. This guide provides an in-depth look at what impacts “How Much Does A Medical Coder Make” and helps you understand your earning potential in this field.
According to the AAPC, certified medical coders earn significantly more, approximately 17.7%, than their non-certified counterparts. Let’s explore the various factors that influence medical coding salaries.
Factors Influencing Medical Coder Salaries
Several elements influence how much a medical coder can earn. These include:
- Location: Salaries vary significantly by state and city due to differences in cost of living and demand.
- Experience: As with most professions, experience plays a crucial role in determining salary.
- Certification: Certified coders consistently earn more than non-certified coders.
- Workplace: The type of healthcare facility can affect compensation.
- Education: While not always required, additional education can increase earning potential.
Certification: A Key to Higher Earnings
One of the most significant factors influencing medical coder salaries is certification. The AAPC reports a considerable difference in earnings between certified and non-certified coders. Earning professional certifications demonstrates expertise and commitment to the profession.
Medical Billing and Coding Salary by State
Location plays a significant role in determining a medical coder’s salary. The following table shows the average salary and hourly rate for medical billers and coders in each state:
| State | Average Salary | Average Hourly Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Alabama | $49,481 | $23.79 |
| Alaska | $60,531 | $29.10 |
| Arizona | $58,065 | $27.92 |
| Arkansas | $52,868 | $25.42 |
| California | $67,660 | $32.53 |
| Colorado | $60,615 | $29.14 |
| Connecticut | $62,659 | $30.12 |
| Delaware | $56,845 | $27.33 |
| District of Columbia | $65,000 | $31.25 |
| Florida | $58,020 | $27.89 |
| Georgia | $56,600 | $27.21 |
| Hawaii | $55,000 | $26.44 |
| Idaho | $56,190 | $27.01 |
| Illinois | $58,476 | $28.11 |
| Illinois | $46,286 | $22.25 |
| Indiana | $47,176 | $22.68 |
| Iowa | $55,463 | $26.66 |
| Kansas | $55,427 | $26.65 |
| Kentucky | $53,286 | $25.62 |
| Louisiana | $50,917 | $24.48 |
| Maine | $57,348 | $27.57 |
| Maryland | $63,068 | $30.32 |
| Massachusetts | $66,222 | $31.84 |
| Michigan | $55,273 | $26.57 |
| Minnesota | $60,462 | $29.07 |
| Mississippi | $48,908 | $23.51 |
| Missouri | $54,604 | $26.25 |
| Montana | $53,591 | $25.77 |
| Nebraska | $54,909 | $26.40 |
| Nevada | $57,191 | $27.50 |
| New Hampshire | $60,959 | $29.31 |
| New Jersey | $65,568 | $31.52 |
| New Mexico | $55,273 | $26.57 |
| New York | $62,369 | $29.99 |
| North Carolina | $56,166 | $27.00 |
| North Dakota | $53,929 | $25.93 |
| Ohio | $55,086 | $26.48 |
| Oklahoma | $53,094 | $25.53 |
| Pennsylvania | $56,964 | $27.39 |
| Rhode Island | $65,110 | $31.30 |
| South Carolina | $54,433 | $26.17 |
| South Dakota | $56,360 | $27.10 |
| Tennessee | $57,159 | $27.48 |
| Texas | $59,393 | $28.55 |
| Utah | $54,171 | $26.04 |
| Vermont | $62,500 | $30.05 |
| Virginia | $56,680 | $27.25 |
| Washington | $61,920 | $29.77 |
| West Virginia | $51,240 | $24.63 |
| Wisconsin | $60,204 | $28.94 |
| Wyoming | $57,917 | $27.84 |
Data Extracted from AAPC 2023 Medical Coding and Billing Salary Report
Top Paying States
According to the BLS, certain states offer higher average salaries for medical billers and coders. These states often have a higher demand for skilled professionals or a higher cost of living.
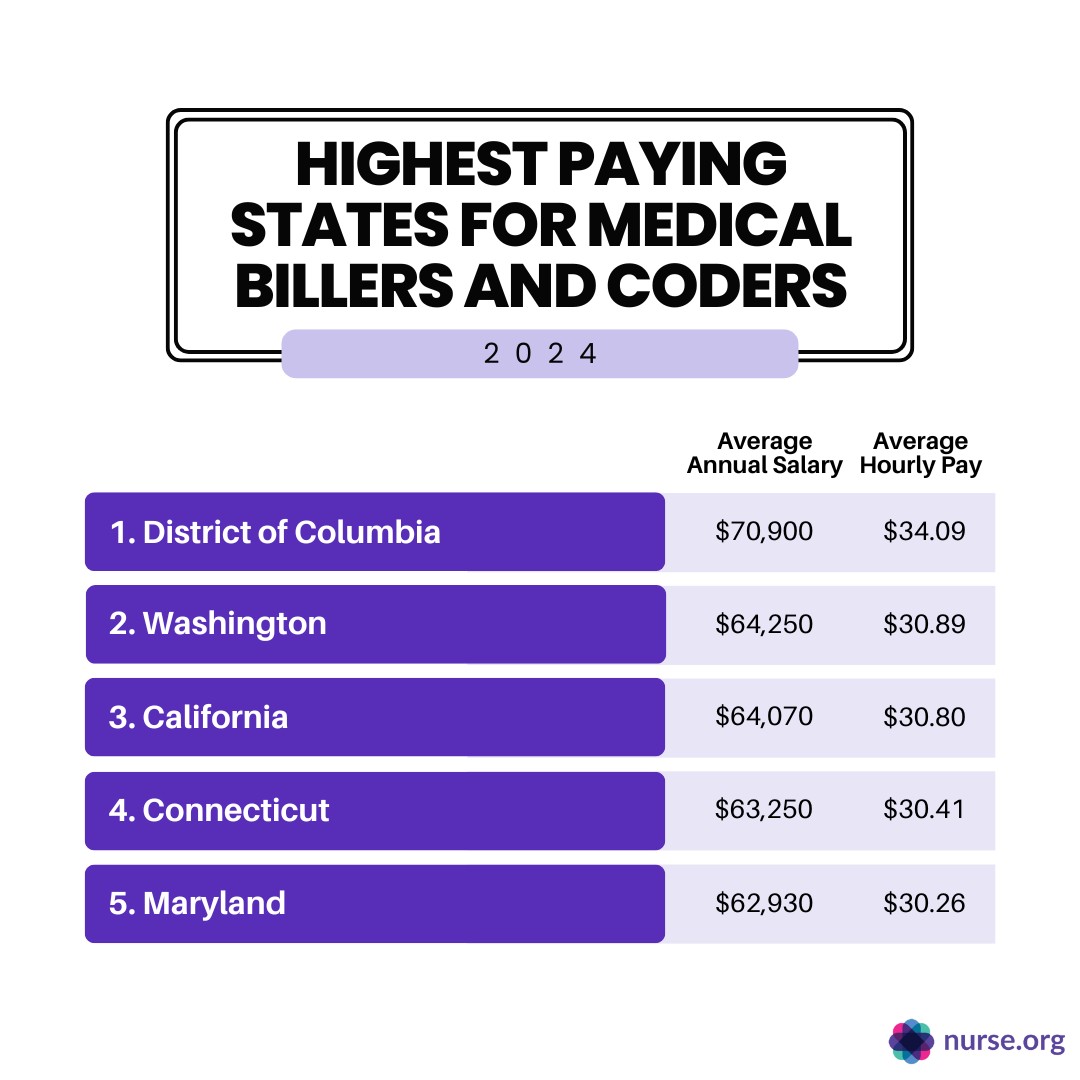 highest paying states for medical billers and coders
highest paying states for medical billers and coders
Top Paying Metropolitan Areas
Salaries can also vary significantly within a state, depending on the metropolitan area. The following table highlights the metropolitan areas with the highest annual mean salaries for medical coding and billing, according to the BLS:
| Metropolitan Area | Hourly Wage | Annual Salary |
|---|---|---|
| San Jose-Sunnyvale-Santa Clara, CA | $39.98 | $83,150 |
| San Francisco-Oakland-Hayward, CA | $36.53 | $75,980 |
| Stockton-Lodi, CA | $35.06 | $72,920 |
| Sacramento–Roseville–Arden-Arcade, CA | $34.11 | $70,950 |
| Seattle-Tacoma-Bellevue, WA | $34.02 | $70,760 |
Salary Variations by Workplace
The type of healthcare facility where a medical coder works also impacts their salary. Larger healthcare systems and hospitals often offer higher compensation and more comprehensive benefits packages compared to smaller practices. According to the AAPC’s latest salary survey results:
- Health System – $59,129
- Large Group Practice (50+ physicians) – $56,548
- Hospital Inpatient and Outpatient – $56,477
- Medium Group Practice (11-49 physicians) – $50,896
- Solo Practice/Small Group Practice (1-10 physicians) – $50,709
Additionally, the option to telecommute or work remotely can also influence salary negotiations.
Increasing Your Earning Potential
Besides location and workplace, medical coders can take proactive steps to increase their salaries:
Gain Experience
Experience is a significant factor in salary progression. Payscale data indicates the following salary ranges based on experience:
- Less than 1 year: $40,589 annually
- 1 to 4 years: $45,903 annually
- 5 to 9 years: $53,591 annually
- 10 to 19 years: $55,872 annually
- 20+ years: $58,019 annually
Further Education
While not always a strict requirement, additional education can positively impact your earning potential. According to the AAPC, a college education, whether an associate degree or some college-level classes, can add approximately 2.7% to your annual salary. Graduate education can increase your earning potential by up to 10%.
Add Certifications and Credentials
Pursuing advanced credentials demonstrates expertise and proficiency, leading to higher salaries. The AAPC reports that the average coder’s salary boost from increased credentials is about 3%. Coding specialists with the Certified Inpatient Coder (CIC) credential may earn over 7.67% more.
Getting Started in Medical Coding
The quickest way to enter this career field is by attending a 4-week online course for medical coding and billing. The next shortest program is still quite speedy at just 16 weeks.
Follow these basic steps to start a career in medical billing and coding:
- Earn a high school diploma or equivalent
- Gain experience
- Pursue continuing education
- Pursue certifications
Education and Certification
Consider enrolling in in-person and online programs to gain the necessary skills and knowledge. These programs can often be completed full-time or part-time.
After completing coursework, consider pursuing certifications like the Certified Professional Coder (CPC) exam.
Is a Career in Medical Coding Worth It?
For many, a career in medical coding offers a good balance of job security, earning potential, and flexibility. While the cost of education and certification can range from $5,000 to $21,000, the median annual salary allows most professionals to recoup their investment within the first year of work. The AAPC reports that medical billing and coding professionals often earn above their state’s median annual income.
Key Takeaways
Understanding “how much does a medical coder make” requires considering several factors, including location, experience, certification, and workplace. By investing in education, pursuing certifications, and gaining experience, medical coders can significantly increase their earning potential and enjoy a rewarding career in the healthcare industry.
Medical Billing & Coding FAQs
- How much does a medical biller and coder make per hour?
According to the BLS, medical billers and coders make $47,180 per year or $22.69 per hour. - Do medical coders work from home?
Medical coders can work from home, in doctor’s offices, or in healthcare facilities. - What pays more – medical billing or coding?
Medical coders may earn slightly more than medical billers. - How long does it take to become a medical biller or coder?
The shortest accredited medical billing and coding program lasts 16 weeks, and even the longest programs last less than a year, offering extremely quick entry into this career field. - Is it worth going to school for medical billing and coding?
Medical billers and coders can earn a decent salary for an entry-level position and have the option to work from home.