How Much Does Electricity Cost? Understanding electricity costs is crucial for effective budgeting and energy management. At HOW.EDU.VN, we provide expert insights into energy pricing, helping you navigate the complexities of kilowatt-hour rates and explore cost-saving strategies. Discover the factors influencing your power bill and learn how to optimize your energy consumption for significant savings with our cost of electricity guide.
1. Understanding Electricity Rates by State
Electricity rates can vary significantly from state to state due to various factors such as the cost of fuel, power plant efficiency, and regulations. To give you a clear picture, here’s a breakdown of average electricity rates across the U.S.
Here’s a map of the U.S. with a breakdown of average electricity rates by state — the darker the state is shaded, the more expensive the electricity:
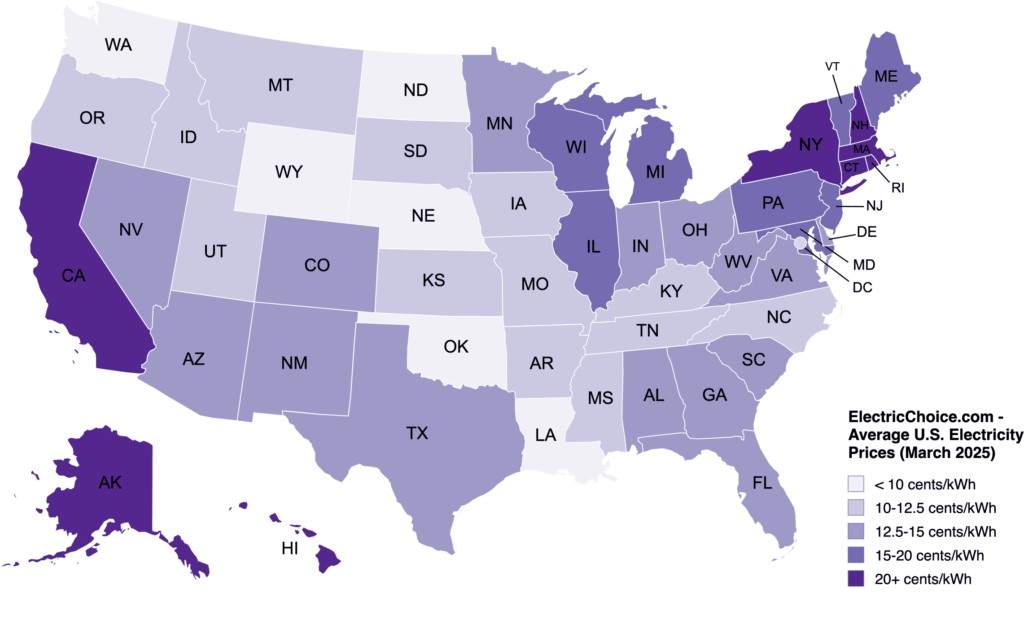 US Map of Electricity Rates by State
US Map of Electricity Rates by State
This map is updated monthly. Please feel free to use/show this map on your site or publication but provide us with accreditation.
1.1. Factors Influencing Electricity Prices
Several elements contribute to the final cost of electricity that consumers see on their bills. These factors can be broadly categorized into:
- Fuel Costs: The price of natural gas, coal, and other fuels used to generate electricity significantly impacts rates. Fluctuations in these markets directly affect the cost of production.
- Infrastructure and Maintenance: Maintaining power plants, transmission lines, and distribution networks requires substantial investment. These costs are passed on to consumers.
- Regulations and Policies: State and federal regulations, including environmental mandates and renewable energy standards, can add to the cost of electricity.
- Demand and Supply: Peak demand periods, such as during summer heatwaves or winter cold snaps, can drive up prices due to increased strain on the grid.
- Regional Differences: Geographic factors, such as access to resources and population density, also play a role in determining electricity rates.
1.2. Average Electricity Rates Table
Here’s a detailed table outlining the average residential and commercial electricity rates for each state:
| State | Residential (¢ per kWh) | Commercial (¢ per kWh) | Average (¢ per kWh) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | 14.91 | 13.83 | 14.37 |
| Alaska | 22.38 | 18.43 | 20.41 |
| Arizona | 15.20 | 11.92 | 13.56 |
| Arkansas | 11.74 | 10.11 | 10.93 |
| California | 30.55 | 23.13 | 26.84 |
| Colorado | 15.16 | 11.12 | 13.14 |
| Connecticut | 28.16 | 23.40 | 25.78 |
| Delaware | 16.68 | 12.83 | 14.76 |
| District of Columbia | 18.83 | 17.53 | 18.18 |
| Florida | 14.20 | 11.20 | 12.70 |
| Georgia | 13.49 | 11.31 | 12.40 |
| Hawaii | 42.34 | 38.29 | 40.32 |
| Idaho | 10.97 | 8.34 | 9.66 |
| Illinois | 15.99 | 11.64 | 13.82 |
| Indiana | 14.42 | 12.45 | 13.44 |
| Iowa | 12.43 | 10.19 | 11.31 |
| Kansas | 13.85 | 10.74 | 12.30 |
| Kentucky | 13.28 | 11.91 | 12.60 |
| Louisiana | 11.70 | 10.73 | 11.22 |
| Maine | 26.29 | 19.57 | 22.93 |
| Maryland | 18.15 | 13.55 | 15.85 |
| Massachusetts | 31.22 | 22.46 | 26.84 |
| Michigan | 18.41 | 13.73 | 16.07 |
| Minnesota | 14.05 | 10.98 | 12.52 |
| Mississippi | 13.44 | 12.34 | 12.89 |
| Missouri | 11.57 | 9.45 | 10.51 |
| Montana | 11.87 | 10.95 | 11.41 |
| Nebraska | 10.78 | 8.20 | 9.49 |
| Nevada | 14.88 | 9.85 | 12.37 |
| New Hampshire | 23.62 | 19.91 | 21.77 |
| New Jersey | 19.49 | 14.76 | 17.13 |
| New Mexico | 14.26 | 10.49 | 12.38 |
| New York | 24.37 | 18.77 | 21.57 |
| North Carolina | 13.49 | 10.92 | 12.21 |
| North Dakota | 10.21 | 7.18 | 8.70 |
| Ohio | 15.98 | 10.68 | 13.33 |
| Oklahoma | 11.52 | 8.48 | 10.00 |
| Oregon | 14.12 | 10.58 | 12.35 |
| Pennsylvania | 17.60 | 11.12 | 14.36 |
| Rhode Island | 25.31 | 24.08 | 24.70 |
| South Carolina | 13.87 | 10.62 | 12.25 |
| South Dakota | 12.42 | 10.61 | 11.52 |
| Tennessee | 13.04 | 12.73 | 12.89 |
| Texas | 15.32 | 8.85 | 12.09 |
| Utah | 11.02 | 7.77 | 9.40 |
| Vermont | 22.29 | 19.58 | 20.94 |
| Virginia | 14.46 | 9.05 | 11.76 |
| Washington | 11.83 | 10.59 | 11.21 |
| West Virginia | 14.51 | 11.77 | 13.14 |
| Wisconsin | 16.31 | 11.76 | 14.04 |
| Wyoming | 11.78 | 9.07 | 10.43 |
| U.S. Average | 16.26 | 12.76 | 12.89 |
Source: Internal/proprietary data gathered from utilities and energy providers across the United States
This table provides a comprehensive overview of electricity rates, allowing you to compare costs across different states. Understanding these variations can help inform decisions about relocation or business expansion.
2. States with the Cheapest Electricity Rates
For those looking to minimize their energy expenses, certain states offer significantly lower electricity rates. These states often benefit from access to abundant natural resources or favorable regulatory environments. Here are the states with the lowest electricity rates in the U.S.:
| State | Residential (¢ per kWh) | Commercial (¢ per kWh) | Average (¢ per kWh) |
|---|---|---|---|
| North Dakota | 10.21 | 7.18 | 8.70 |
| Utah | 11.02 | 7.77 | 9.40 |
| Nebraska | 10.78 | 8.20 | 9.49 |
| Idaho | 10.97 | 8.34 | 9.66 |
| Oklahoma | 11.52 | 8.48 | 10.00 |
These states offer a cost-effective environment for both residential and commercial electricity consumption.
3. Key Takeaways on Electricity Costs
Analyzing the data presented, several key insights emerge regarding electricity rates in the United States:
- Cheapest State: North Dakota boasts the lowest average electricity rate at 8.70¢/kWh.
- Most Expensive State: Hawaii has the highest average electricity rate, standing at 40.32¢/kWh.
- U.S. Average: The average electricity rate in the U.S. is 12.89¢ per kWh.
- Rate Ranges: Residential rates range from 10.21¢ (North Dakota) to 42.34¢ (Hawaii), while commercial rates vary from 7.18¢ (North Dakota) to 38.29¢ (Hawaii).
These takeaways highlight the significant disparities in electricity costs across different regions of the country.
4. Factors Determining Energy Rates
Understanding the various factors that influence energy rates can help consumers make informed decisions about their energy consumption and budgeting. Here are the primary determinants of electricity prices:
4.1. Residential vs. Commercial Rates
Providers typically offer different rate structures for residential, commercial, and industrial customers. Commercial rates often differ from residential rates due to variations in energy usage patterns and demand.
4.2. Usage
The amount of electricity you consume each month, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), is a major determinant of your electric bill. The more energy you use, the higher your bill will be.
4.3. Time of Use (TOU) Rates
Time-of-use rates vary depending on the time of day, reflecting fluctuations in demand. Peak rates are typically charged during periods of high demand, while off-peak rates are applied during lower demand periods.
5. Regulated vs. Deregulated Energy Markets
The structure of energy markets also plays a crucial role in determining electricity rates. There are two primary types of energy markets: regulated and deregulated.
5.1. Regulated Markets
In regulated markets, consumers are typically limited to the rate provided by their local utility company. There is little to no competition among providers, and prices are set by regulatory bodies.
5.2. Deregulated Markets
In deregulated energy markets, consumers have the option to shop around and choose their electricity provider. This competition can lead to more competitive rates and greater consumer choice.
6. Detailed Analysis of Factors Influencing Electricity Prices
To provide a more in-depth understanding, let’s explore each of the factors that influence electricity prices in greater detail.
6.1. Fuel Costs: The Backbone of Electricity Pricing
Fuel costs are a primary driver of electricity prices. Power plants rely on fuels like natural gas, coal, nuclear energy, and renewable sources to generate electricity.
- Natural Gas: Natural gas is a widely used fuel for electricity generation. Its price volatility can significantly impact electricity rates.
- Coal: While its use is declining, coal remains a significant fuel source in some regions. Coal prices and transportation costs affect electricity rates.
- Nuclear Energy: Nuclear power plants have high upfront costs but relatively low operating costs. The cost of nuclear fuel and plant maintenance is a factor in electricity pricing.
- Renewable Energy: The cost of renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydropower, has decreased significantly in recent years. Government incentives and technological advancements are driving further cost reductions.
6.2. Infrastructure and Maintenance: The Unseen Costs
Maintaining a reliable electricity grid requires substantial investment in infrastructure and ongoing maintenance. These costs are essential for ensuring a stable and efficient power supply.
- Power Plants: Power plants require regular maintenance and upgrades to operate efficiently and safely. These costs are factored into electricity rates.
- Transmission Lines: High-voltage transmission lines transport electricity over long distances. Maintaining these lines and building new infrastructure is a significant expense.
- Distribution Networks: Local distribution networks deliver electricity to homes and businesses. Maintaining these networks and upgrading equipment is essential for reliability.
6.3. Regulations and Policies: Shaping the Energy Landscape
Government regulations and policies play a significant role in shaping the energy landscape and influencing electricity prices.
- Environmental Regulations: Regulations aimed at reducing emissions from power plants can increase operating costs. These costs are often passed on to consumers.
- Renewable Energy Standards: Many states have implemented renewable energy standards (RES) that require utilities to generate a certain percentage of their electricity from renewable sources. Complying with these standards can impact electricity rates.
- Energy Efficiency Programs: Government-sponsored energy efficiency programs can help reduce overall electricity demand, potentially lowering rates for all consumers.
6.4. Demand and Supply: The Balancing Act
The balance between electricity demand and supply is a critical factor in determining prices. During peak demand periods, utilities may need to use more expensive generation sources to meet the increased demand.
- Peak Demand: Peak demand periods, such as during summer heatwaves or winter cold snaps, can strain the electricity grid and drive up prices.
- Supply Constraints: Supply constraints, such as power plant outages or transmission line bottlenecks, can also lead to higher prices.
- Demand Response Programs: Demand response programs incentivize consumers to reduce their electricity usage during peak demand periods, helping to stabilize the grid and lower prices.
6.5. Regional Differences: The Geography of Energy Costs
Geographic factors, such as access to resources and population density, contribute to variations in electricity rates across different regions of the country.
- Access to Resources: States with abundant natural resources, such as natural gas or hydropower, may have lower electricity rates.
- Population Density: Densely populated areas may have higher electricity rates due to increased demand and infrastructure costs.
- Climate: Climate can also play a role, as regions with extreme temperatures may experience higher electricity demand for heating and cooling.
7. Strategies for Managing and Reducing Electricity Costs
Given the complexity of electricity pricing, consumers and businesses can adopt various strategies to manage and reduce their energy costs. Here are some effective approaches:
7.1. Energy Audits
Conducting an energy audit can help identify areas where energy is being wasted and opportunities for improvement.
- Professional Audits: Professional energy auditors can assess your home or business and provide recommendations for energy efficiency upgrades.
- DIY Audits: You can also conduct a DIY energy audit by inspecting your insulation, sealing air leaks, and evaluating your appliances.
7.2. Energy-Efficient Appliances and Equipment
Investing in energy-efficient appliances and equipment can significantly reduce your electricity consumption.
- ENERGY STAR Certified Products: Look for ENERGY STAR certified products, which meet strict energy efficiency guidelines set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
- LED Lighting: Replace incandescent light bulbs with LED bulbs, which use up to 75% less energy and last much longer.
7.3. Insulation and Weatherization
Proper insulation and weatherization can help reduce heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer, lowering your heating and cooling costs.
- Insulation: Add insulation to your attic, walls, and floors to improve energy efficiency.
- Sealing Air Leaks: Seal air leaks around windows, doors, and other openings to prevent drafts.
7.4. Smart Thermostats
Smart thermostats can help you optimize your heating and cooling schedule and reduce energy waste.
- Programmable Thermostats: Set your thermostat to automatically adjust the temperature when you are away or asleep.
- Smart Features: Some smart thermostats can learn your habits and adjust the temperature accordingly, further optimizing energy savings.
7.5. Renewable Energy Options
Consider investing in renewable energy options, such as solar panels, to generate your own electricity and reduce your reliance on the grid.
- Solar Panels: Solar panels can generate clean, renewable electricity for your home or business.
- Net Metering: Net metering allows you to sell excess electricity back to the utility company, offsetting your electricity bill.
7.6. Energy Conservation Habits
Adopting simple energy conservation habits can also make a difference in your electricity consumption.
- Turn off Lights: Turn off lights when you leave a room.
- Unplug Electronics: Unplug electronics when they are not in use to prevent standby power consumption.
- Use Appliances Wisely: Use appliances, such as washing machines and dishwashers, during off-peak hours to take advantage of lower electricity rates.
8. The Role of Experts in Navigating Electricity Costs
Navigating the complexities of electricity costs and energy management can be challenging. Consulting with experts can provide valuable insights and tailored solutions.
8.1. Benefits of Expert Consultation
- Personalized Advice: Experts can assess your specific needs and provide personalized advice on how to reduce your electricity costs.
- Technical Expertise: Experts have the technical knowledge and experience to identify energy efficiency opportunities and recommend appropriate solutions.
- Cost-Effective Solutions: Experts can help you identify cost-effective solutions that will deliver the greatest energy savings.
8.2. Finding the Right Expert
- Certifications: Look for experts with relevant certifications, such as Certified Energy Manager (CEM) or Building Performance Institute (BPI) certification.
- Experience: Choose an expert with a proven track record of helping clients reduce their electricity costs.
- References: Ask for references and check online reviews to ensure the expert is reputable and reliable.
9. Case Studies: Real-World Examples of Energy Cost Savings
To illustrate the potential for energy cost savings, let’s examine a few real-world case studies.
9.1. Residential Case Study: John’s Home
John, a homeowner in California, was concerned about his high electricity bills. He contacted a professional energy auditor who identified several areas for improvement.
- Insulation Upgrades: John added insulation to his attic and walls, reducing heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer.
- LED Lighting: He replaced all of his incandescent light bulbs with LED bulbs, significantly reducing his lighting costs.
- Smart Thermostat: He installed a smart thermostat that automatically adjusted the temperature when he was away from home.
As a result of these upgrades, John reduced his electricity consumption by 30% and saved over $500 per year on his electricity bills.
9.2. Commercial Case Study: ABC Company
ABC Company, a small business in Texas, was struggling with high energy costs. They hired an energy consultant to help them identify ways to reduce their energy consumption.
- Energy-Efficient Equipment: ABC Company replaced their old HVAC system with a new, energy-efficient model.
- Lighting Retrofit: They replaced their fluorescent lighting with LED lighting, reducing their lighting costs by 50%.
- Demand Response Program: They enrolled in a demand response program, which incentivized them to reduce their electricity usage during peak demand periods.
These measures helped ABC Company reduce their electricity consumption by 25% and save over $2,000 per year on their energy bills.
10. Future Trends in Electricity Pricing
The electricity landscape is constantly evolving, with new technologies and policies shaping the future of electricity pricing. Here are some key trends to watch:
10.1. Increasing Renewable Energy Adoption
Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, are becoming increasingly competitive with traditional fossil fuels. As renewable energy adoption continues to grow, electricity prices are likely to become more stable and predictable.
10.2. Smart Grid Technologies
Smart grid technologies, such as advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) and grid automation, are improving the efficiency and reliability of the electricity grid. These technologies can help reduce costs and improve grid resilience.
10.3. Electric Vehicle (EV) Adoption
The increasing adoption of electric vehicles is expected to put additional strain on the electricity grid. Utilities are developing new rate structures and programs to manage EV charging and ensure grid stability.
10.4. Energy Storage Solutions
Energy storage solutions, such as batteries, are becoming more affordable and widespread. Energy storage can help balance the electricity grid, reduce peak demand, and improve the integration of renewable energy sources.
11. Resources for Further Information
For those seeking more information on electricity pricing and energy management, here are some valuable resources:
- U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA): The EIA provides comprehensive data and analysis on energy production, consumption, and prices.
- ENERGY STAR: The ENERGY STAR program provides information on energy-efficient products and practices.
- State Energy Offices: State energy offices offer resources and programs to help residents and businesses reduce their energy consumption.
12. Expertise from HOW.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Energy Management
Understanding and managing electricity costs can be a complex undertaking. That’s where HOW.EDU.VN comes in. Our team of experts, including over 100 renowned PhDs, offers unparalleled expertise and personalized solutions to help you navigate the intricacies of energy pricing and consumption. We provide strategic insights, practical advice, and tailored recommendations to help you optimize your energy usage and achieve significant cost savings.
12.1. How HOW.EDU.VN Can Help You
- Expert Consultation: Connect with our PhD-level experts for personalized advice tailored to your specific needs.
- Customized Strategies: We develop customized energy management strategies that align with your goals and budget.
- Comprehensive Analysis: Our team conducts thorough analyses of your energy consumption patterns and identifies opportunities for improvement.
- Cutting-Edge Insights: Stay ahead of the curve with our access to the latest research and trends in energy management.
12.2. Connecting with Our Experts
Connecting with our team of experts is easy. Simply visit our website, HOW.EDU.VN, or contact us directly to schedule a consultation. We are committed to providing you with the knowledge and support you need to make informed decisions about your energy usage.
13. FAQs About Electricity Costs
1. What is a kilowatt-hour (kWh)?
A kilowatt-hour (kWh) is a unit of energy equal to 1,000 watts of power consumed for one hour. It’s the standard unit used to measure electricity consumption.
2. How are electricity rates determined?
Electricity rates are determined by factors such as fuel costs, infrastructure maintenance, regulations, demand, and regional differences.
3. What is the average electricity rate in the U.S.?
The average electricity rate in the U.S. is approximately 12.89¢ per kWh.
4. Which state has the cheapest electricity rates?
North Dakota has the cheapest electricity rates, with an average of 8.70¢ per kWh.
5. Which state has the most expensive electricity rates?
Hawaii has the most expensive electricity rates, with an average of 40.32¢ per kWh.
6. How can I reduce my electricity bill?
You can reduce your electricity bill by conducting an energy audit, investing in energy-efficient appliances, improving insulation, and adopting energy conservation habits.
7. What is a smart thermostat?
A smart thermostat is a device that can automatically adjust your heating and cooling schedule to optimize energy savings.
8. What are renewable energy options?
Renewable energy options include solar panels, wind turbines, and hydropower systems.
9. What is net metering?
Net metering allows you to sell excess electricity generated by your renewable energy system back to the utility company, offsetting your electricity bill.
10. How can HOW.EDU.VN help me manage my electricity costs?
HOW.EDU.VN connects you with PhD-level experts who provide personalized advice and customized strategies to help you reduce your electricity costs.
14. Call to Action: Connect with Our Experts Today
Are you struggling with high electricity bills or looking for ways to optimize your energy consumption? Don’t navigate the complexities alone. At HOW.EDU.VN, our team of over 100 renowned PhDs is ready to provide you with personalized advice and tailored solutions to help you achieve significant cost savings.
Contact us today to schedule a consultation and take the first step towards a more energy-efficient future.
Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
Website: HOW.EDU.VN
Let how.edu.vn be your trusted partner in energy management. Our experts are dedicated to helping you navigate the ever-changing electricity landscape and achieve your energy-saving goals. Reach out today and experience the difference that expert guidance can make.