How Much Does Law School Cost? Understanding the financial commitment required for a law degree is crucial for prospective students. At HOW.EDU.VN, we provide expert insights to help you navigate the costs associated with legal education and explore potential funding options, ensuring you’re well-prepared for this significant investment in your future. Explore insights into law school expenses, tuition costs, and financial aid.
Table of Contents
1. Understanding the Components of Law School Costs
- 1.1 Tuition Fees: Public vs. Private Institutions
- 1.2 Living Expenses: A Significant Consideration
- 1.3 Books, Supplies, and Other Academic Fees
- 1.4 Application Fees: Initial Investment
2. Average Cost of Law School: A Detailed Breakdown
- 2.1 National Averages for Tuition and Fees
- 2.2 Regional Variations in Law School Costs
- 2.3 Cost of Attendance (COA): Comprehensive Estimate
3. Law School Tuition Trends: Historical Perspective and Future Projections
- 3.1 Factors Influencing Tuition Increases
- 3.2 Expert Opinions on Tuition Inflation
- 3.3 Projecting Future Law School Costs
4. Cost of Law School by Institution: Public vs. Private Schools
- 4.1 Public Law Schools: Affordability for In-State Residents
- 4.2 Private Law Schools: Higher Tuition, More Resources?
- 4.3 Ranking Law Schools by Cost: A Comprehensive List
5. Breaking Down the Costs: Detailed Look at Specific Law Schools
- 5.1 High-Cost Institutions: What Justifies the Price?
- 5.2 Low-Cost Institutions: Affordable Options for Aspiring Lawyers
- 5.3 Comparing Costs: A Practical Guide
6. Alternative Law Degrees: Exploring Cost-Effective Options
- 6.1 Juris Master (J.M.) Degree: A Specialized Alternative
- 6.2 Master of Legal Studies (M.L.S.): An Overview
- 6.3 Comparing J.D., J.M., and M.L.S. Costs and Benefits
7. Funding Your Law School Education: Financial Aid Options
- 7.1 Scholarships: Merit-Based and Need-Based Awards
- 7.2 Grants: Federal and State Programs
- 7.3 Student Loans: Federal and Private Options
- 7.4 Loan Repayment Programs: Managing Your Debt
8. Conditional Scholarships: Risks and Rewards
- 8.1 Understanding Conditional Scholarship Terms
- 8.2 Trends in Conditional Scholarships
- 8.3 Tips for Maintaining Your Scholarship
9. Additional Law School Costs: Beyond Tuition
- 9.1 Bar Exam Fees and Preparation Courses
- 9.2 Professional Development and Networking Expenses
- 9.3 Technology and Software Costs
10. Managing Law School Debt: Strategies for Financial Success
- 10.1 Creating a Budget: Tracking Your Spending
- 10.2 Exploring Income-Driven Repayment Plans
- 10.3 Refinancing Your Student Loans
- 10.4 Seeking Financial Counseling
11. Expert Advice on Affording Law School
- 11.1 Tips from Financial Aid Professionals
- 11.2 Insights from Current Law Students and Graduates
- 11.3 Leveraging Resources at HOW.EDU.VN
12. Real-World Examples: Case Studies of Law School Financing
- 12.1 Scholarship Success Stories
- 12.2 Navigating Loan Repayment Programs
- 12.3 Balancing Work and Law School
13. Future Trends in Law School Financing
- 13.1 Innovations in Financial Aid
- 13.2 The Role of Technology in Reducing Costs
- 13.3 Impact of Economic Factors on Law School Affordability
14. Resources for Prospective Law Students
15. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Law School Costs
Embarking on a legal education is a significant financial undertaking, and understanding how much does law school tuition truly cost is paramount. At HOW.EDU.VN, we recognize the importance of making informed decisions about your future, which is why we offer comprehensive resources to help you navigate the complexities of law school expenses, financial aid, and debt management. Gain insights into law degree costs, explore financing options, and discover strategies for managing your investment in legal education to achieve your professional goals.
1. Understanding the Components of Law School Costs
To effectively plan for law school, it’s essential to break down the various cost components. These include tuition fees, living expenses, books and supplies, and application fees. Understanding each element helps prospective students create a realistic budget and explore available financial aid options.
1.1 Tuition Fees: Public vs. Private Institutions
Tuition fees are a primary cost driver, with significant differences between public and private law schools. Public schools generally offer lower tuition rates for in-state residents, while private schools typically have higher, uniform tuition fees regardless of residency. For instance, the average tuition at public law schools for in-state residents can be significantly lower than that of private institutions.
1.2 Living Expenses: A Significant Consideration
Living expenses, including housing, food, transportation, and personal costs, form a substantial part of the overall cost. These expenses vary widely depending on the location of the law school. For example, living in a major metropolitan area like New York City or Los Angeles will likely result in higher living costs compared to smaller cities or rural areas.
1.3 Books, Supplies, and Other Academic Fees
Beyond tuition, students must account for the cost of textbooks, casebooks, legal research databases, and other academic materials. These expenses can add up quickly, with some sources estimating annual costs ranging from $1,000 to $3,000.
1.4 Application Fees: Initial Investment
Applying to law school involves application fees, which can range from $50 to $100 per school. Considering that many students apply to multiple schools to increase their chances of admission, these fees can accumulate significantly.
2. Average Cost of Law School: A Detailed Breakdown
Understanding the average cost of law school provides a benchmark for prospective students. This section examines national averages, regional variations, and the comprehensive cost of attendance (COA) estimate.
2.1 National Averages for Tuition and Fees
National averages for tuition and fees vary depending on whether the institution is public or private. According to EducationData.org, the average total cost of tuition alone for law school is $151,072, or $50,357 per year. These figures offer a broad overview but may not reflect the actual cost at specific schools.
2.2 Regional Variations in Law School Costs
Law school costs differ significantly by region. Schools in the Northeast and California tend to have higher tuition and living expenses than those in the Midwest or South. Factors such as the cost of living, demand for legal education, and state funding levels influence these regional disparities.
2.3 Cost of Attendance (COA): Comprehensive Estimate
The Cost of Attendance (COA) is a comprehensive estimate provided by law schools, including tuition, fees, living expenses, books, and other related costs. The COA offers a more accurate picture of the total investment required to attend a particular school and is used to determine financial aid eligibility.
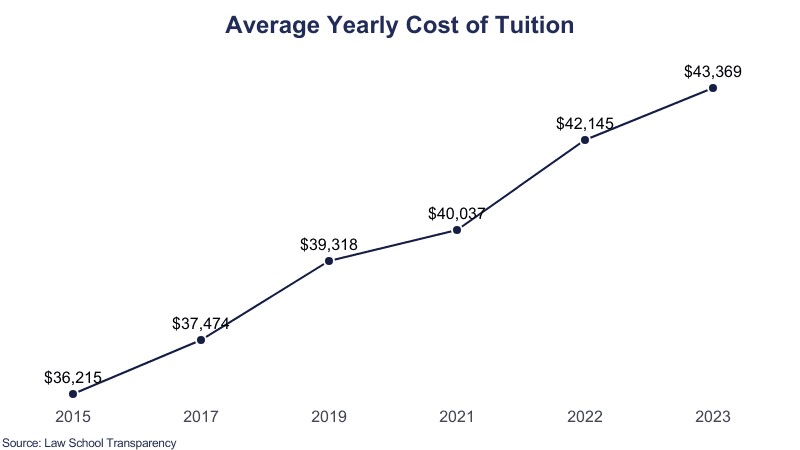
3. Law School Tuition Trends: Historical Perspective and Future Projections
Examining historical trends and future projections helps prospective students understand the dynamics of law school tuition. This section explores factors influencing tuition increases and expert opinions on tuition inflation.
3.1 Factors Influencing Tuition Increases
Several factors contribute to rising law school tuition, including declines in student-faculty ratios, increases in faculty salaries, the development of legal clinics, the growth of administrative staff, and expansive school construction projects. These factors drive up operational costs, which are often passed on to students through higher tuition fees.
3.2 Expert Opinions on Tuition Inflation
Experts attribute tuition inflation to a combination of factors, including decreased state funding for public institutions, increased demand for specialized programs, and the rising cost of maintaining high-quality educational facilities.
3.3 Projecting Future Law School Costs
Based on current trends, the average yearly cost of tuition is projected to continue rising. Understanding these projections allows prospective students to anticipate future costs and plan their finances accordingly.
4. Cost of Law School by Institution: Public vs. Private Schools
The choice between public and private law schools significantly impacts the overall cost. This section compares the affordability of public schools for in-state residents with the potential benefits of higher-priced private institutions.
4.1 Public Law Schools: Affordability for In-State Residents
Public law schools often offer lower tuition rates for in-state residents, making them an attractive option for those seeking an affordable legal education. These schools are typically funded by state governments, which subsidize tuition for residents.
4.2 Private Law Schools: Higher Tuition, More Resources?
Private law schools generally have higher tuition fees but may offer more resources, such as smaller class sizes, specialized programs, and extensive career services. The higher cost may be justified by the potential for enhanced educational and career opportunities.
4.3 Ranking Law Schools by Cost: A Comprehensive List
A comprehensive list of law schools ranked by cost can help prospective students identify affordable options and compare tuition rates.
| Law Schools | Annual Tuition Cost | Annual Living Expenses |
|---|---|---|
| University of Puerto Rico | $9,750 | $22,806 |
| Southern Illinois University | $21,555 | $16,379 |
| Northern Illinois University | $23,553 | $20,424 |
| University of The District of Columbia | $25,873 | $29,200 |
| University of Akron | $26,215 | $17,050 |
| CUNY | $26,203 | $25,588 |
| Texas Southern University | $28,633 | $24,034 |
| University of Toledo | $28,426 | $20,165 |
| University of Missouri – Kansas City | $29,774 | $20,084 |
| University of Cincinnati | $29,810 | $25,662 |
| University of Missouri – Columbia | $29,889 | $19,184 |
5. Breaking Down the Costs: Detailed Look at Specific Law Schools
Examining specific law schools provides a clearer picture of tuition rates, living expenses, and financial aid opportunities. This section highlights high-cost and low-cost institutions and offers a practical guide to comparing costs.
5.1 High-Cost Institutions: What Justifies the Price?
High-cost institutions like Columbia University and New York University offer premium legal education with extensive resources, renowned faculty, and exceptional career placement rates. The high price may be justified by the prestige and potential return on investment.
5.2 Low-Cost Institutions: Affordable Options for Aspiring Lawyers
Low-cost institutions like the University of Puerto Rico and Southern Illinois University provide affordable options for aspiring lawyers. These schools may offer lower tuition rates and living expenses, making legal education accessible to a broader range of students.
5.3 Comparing Costs: A Practical Guide
A practical guide to comparing costs involves assessing tuition fees, living expenses, financial aid opportunities, and potential career outcomes. Consider the long-term investment and weigh the costs against the potential benefits.
6. Alternative Law Degrees: Exploring Cost-Effective Options
For those seeking alternatives to the traditional Juris Doctor (J.D.) degree, exploring cost-effective options like the Juris Master (J.M.) and Master of Legal Studies (M.L.S.) can be beneficial.
6.1 Juris Master (J.M.) Degree: A Specialized Alternative
The Juris Master (J.M.) degree is a specialized alternative for professionals who want legal knowledge without becoming practicing attorneys. These programs typically last one to two years and cover specific areas of law relevant to various industries.
6.2 Master of Legal Studies (M.L.S.): An Overview
The Master of Legal Studies (M.L.S.) is another alternative designed for professionals seeking a legal foundation. M.L.S. programs often offer online options and can be completed in one to two years.
6.3 Comparing J.D., J.M., and M.L.S. Costs and Benefits
Comparing the costs and benefits of J.D., J.M., and M.L.S. degrees involves assessing tuition fees, program duration, career opportunities, and potential salary outcomes. Each degree offers unique advantages depending on individual career goals.
7. Funding Your Law School Education: Financial Aid Options
Securing financial aid is crucial for most law students. This section explores scholarships, grants, and student loans, providing insights into federal and private options.
7.1 Scholarships: Merit-Based and Need-Based Awards
Scholarships are merit-based and need-based awards that do not require repayment. Merit-based scholarships are awarded based on academic achievement, while need-based scholarships consider financial need.
7.2 Grants: Federal and State Programs
Grants are typically need-based awards from federal and state programs. These grants can significantly reduce the overall cost of law school and do not require repayment.
7.3 Student Loans: Federal and Private Options
Student loans are a common financing option, with federal and private loans available. Federal loans often offer lower interest rates and flexible repayment options, while private loans may provide additional funding but with varying terms.
7.4 Loan Repayment Programs: Managing Your Debt
Loan repayment programs, such as Income-Driven Repayment (IDR) plans and Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF), help graduates manage their debt. IDR plans adjust monthly payments based on income and family size, while PSLF forgives the remaining balance after a certain period of public service employment.
8. Conditional Scholarships: Risks and Rewards
Conditional scholarships are awarded based on maintaining a certain GPA or class rank. Understanding the terms and risks associated with these scholarships is essential for students.
8.1 Understanding Conditional Scholarship Terms
Conditional scholarships require students to maintain specific academic standards. Failing to meet these standards can result in the loss of the scholarship, increasing the overall cost of law school.
8.2 Trends in Conditional Scholarships
The prevalence of conditional scholarships has decreased in recent years. However, students who receive these scholarships are becoming less likely to lose them, indicating a shift in how schools administer these awards.
8.3 Tips for Maintaining Your Scholarship
To maintain a conditional scholarship, students should focus on academic performance, seek tutoring and academic support, and manage their time effectively.
9. Additional Law School Costs: Beyond Tuition
Beyond tuition, students must budget for additional costs, including bar exam fees, professional development expenses, and technology costs.
9.1 Bar Exam Fees and Preparation Courses
Bar exam fees and preparation courses can be significant expenses. The average cost of a multi-state bar exam is increasing, and preparation courses can cost thousands of dollars.
9.2 Professional Development and Networking Expenses
Professional development and networking expenses, such as attending conferences, joining professional organizations, and purchasing professional attire, can enhance career prospects but also add to the overall cost.
9.3 Technology and Software Costs
Technology and software costs, including laptops, legal research databases, and software subscriptions, are essential for law school. These expenses should be factored into the overall budget.
10. Managing Law School Debt: Strategies for Financial Success
Managing law school debt requires careful planning and strategic decision-making. This section provides strategies for financial success, including creating a budget, exploring income-driven repayment plans, and refinancing student loans.
10.1 Creating a Budget: Tracking Your Spending
Creating a budget helps students track their spending and identify areas to reduce costs. A well-structured budget promotes financial discipline and helps manage debt effectively.
10.2 Exploring Income-Driven Repayment Plans
Income-Driven Repayment (IDR) plans adjust monthly payments based on income and family size. These plans provide relief for graduates with high debt-to-income ratios, making loan repayment more manageable.
10.3 Refinancing Your Student Loans
Refinancing student loans involves obtaining a new loan with a lower interest rate or better terms. Refinancing can save money over the life of the loan and simplify repayment.
10.4 Seeking Financial Counseling
Seeking financial counseling from professionals can provide personalized advice and strategies for managing law school debt. Counselors offer guidance on budgeting, loan repayment options, and financial planning.
11. Expert Advice on Affording Law School
Seeking expert advice from financial aid professionals, current law students, and graduates can provide valuable insights into affording law school.
11.1 Tips from Financial Aid Professionals
Financial aid professionals offer tips on maximizing financial aid opportunities, applying for scholarships, and managing student loans. Their expertise can help students navigate the complex world of law school financing.
11.2 Insights from Current Law Students and Graduates
Current law students and graduates share their experiences and strategies for managing law school costs. Their insights provide practical advice on budgeting, finding affordable housing, and securing financial aid.
11.3 Leveraging Resources at HOW.EDU.VN
Leveraging resources at HOW.EDU.VN provides access to expert advice, financial planning tools, and scholarship databases. Our platform offers comprehensive support to help prospective and current law students make informed decisions about their education and finances.
12. Real-World Examples: Case Studies of Law School Financing
Examining real-world examples and case studies provides practical insights into how students finance their law school education. This section highlights scholarship success stories, navigating loan repayment programs, and balancing work and law school.
12.1 Scholarship Success Stories
Scholarship success stories illustrate how students have secured funding to reduce the cost of law school. These stories provide inspiration and practical tips for applying for scholarships.
12.2 Navigating Loan Repayment Programs
Case studies on navigating loan repayment programs demonstrate how graduates have effectively managed their debt through IDR plans and PSLF. These examples offer strategies for minimizing loan burdens and achieving financial stability.
12.3 Balancing Work and Law School
Examples of balancing work and law school highlight the challenges and strategies for managing both responsibilities. Working part-time can help offset costs but requires careful time management and prioritization.
13. Future Trends in Law School Financing
Understanding future trends in law school financing helps prospective students anticipate changes and plan accordingly. This section explores innovations in financial aid, the role of technology in reducing costs, and the impact of economic factors on affordability.
13.1 Innovations in Financial Aid
Innovations in financial aid, such as income-based scholarships and crowdfunding platforms, offer new ways to finance legal education. These emerging trends may provide additional opportunities for students to reduce their debt burdens.
13.2 The Role of Technology in Reducing Costs
Technology can play a significant role in reducing law school costs. Online resources, digital textbooks, and virtual learning platforms can lower expenses and enhance accessibility.
13.3 Impact of Economic Factors on Law School Affordability
Economic factors, such as inflation, interest rates, and unemployment rates, impact law school affordability. Understanding these factors helps students make informed decisions about their education and finances.
14. Resources for Prospective Law Students
Providing resources for prospective law students, including online tools, law school admissions websites, and financial aid offices, can help them navigate the complexities of law school financing.
14.1 Online Tools and Calculators
Online tools and calculators, such as loan repayment calculators and budget planners, help students estimate costs and manage their finances. These resources provide valuable insights into the financial aspects of law school.
14.2 Law School Admissions Websites
Law school admissions websites offer detailed information on tuition fees, financial aid opportunities, and application requirements. These websites are essential resources for prospective students.
14.3 Financial Aid Offices
Financial aid offices at law schools provide personalized support and guidance on financing legal education. These offices offer assistance with applying for financial aid, managing student loans, and exploring repayment options.
15. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Law School Costs
Q1: How much does law school cost on average?
A1: The average total cost of law school is approximately $230,163, including tuition and living expenses.
Q2: What is the average tuition cost for law school?
A2: The average total cost of tuition alone for law school is $151,072, or about $50,357 per year.
Q3: How can I reduce the cost of law school?
A3: You can reduce costs by attending a public law school as an in-state resident, applying for scholarships and grants, and minimizing living expenses.
Q4: What are the alternative law degrees that are more cost-effective?
A4: Alternative law degrees include the Juris Master (J.M.) and Master of Legal Studies (M.L.S.), which are typically shorter and less expensive than a J.D.
Q5: What financial aid options are available for law school?
A5: Financial aid options include scholarships, grants, federal student loans, and private student loans.
Q6: What is a conditional scholarship?
A6: A conditional scholarship requires students to maintain a certain GPA or class rank to retain the scholarship.
Q7: How can I manage my law school debt?
A7: You can manage your debt by creating a budget, exploring income-driven repayment plans, and refinancing your student loans.
Q8: What additional costs should I consider beyond tuition?
A8: Additional costs include bar exam fees, professional development expenses, and technology costs.
Q9: Are private law schools worth the higher cost?
A9: Private law schools may offer more resources and better career placement rates, but the value depends on individual career goals and financial circumstances.
Q10: Where can I find more resources on law school financing?
A10: You can find more resources at HOW.EDU.VN, law school admissions websites, and financial aid offices.
 Law school costs considerations Education Data Initiative
Law school costs considerations Education Data Initiative
Navigating the complexities of law school costs can be challenging, but with the right resources and guidance, you can make informed decisions and achieve your educational goals. At HOW.EDU.VN, our team of over 100 distinguished PhDs is dedicated to providing expert insights and personalized advice to help you succeed.
Are you ready to take the next step toward your legal career? Contact HOW.EDU.VN today for a consultation with our expert advisors. Let us help you navigate the financial aspects of law school and create a path to success.
Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
Website: how.edu.vn
