Are you concerned about the potential impact of alcohol consumption during pregnancy on your child’s health? At HOW.EDU.VN, we understand your worries and offer expert guidance to navigate these complex issues. Understanding How Much Drinking Causes Fetal Alcohol Syndrome is crucial for making informed decisions and ensuring a healthy pregnancy. Discover the facts and find expert advice on preventing fetal alcohol syndrome.
1. Defining Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS) and Its Causes
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS) is a severe condition that results from prenatal alcohol exposure (PAE). It leads to permanent birth defects and developmental disabilities. FAS is characterized by a combination of growth deficiencies, distinctive facial abnormalities, and central nervous system (CNS) dysfunction. Understanding the causes and diagnostic criteria is essential for prevention.
Key Characteristics of FAS
- Growth Deficiency: Prenatal and/or postnatal height and weight at or below the 10th percentile.
- Facial Dysmorphia: Specific facial features including short palpebral fissure lengths (PFLs), a smooth philtrum, and a thin upper lip.
- CNS Abnormalities: Structural, neurological, or functional abnormalities in the central nervous system.
 Child with Fetal Alcohol Syndrome facial features
Child with Fetal Alcohol Syndrome facial features
Diagnostic Schemes for FASD
Several diagnostic schemes are used worldwide to identify Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD). These schemes emphasize an interdisciplinary approach, focusing on growth, facial features, and CNS abnormalities. One notable scheme is the 4-Digit Code, which provides specific criteria for diagnosis.
The 4-Digit Code Diagnostic Criteria
- Growth Deficiency: Height and/or weight at or below the 10th percentile.
- Facial Dysmorphia: All three facial features: short PFLs, smooth philtrum, and thin upper lip.
- CNS Evidence: Significant structural, neurological, and/or functional abnormalities.
- Prenatal Alcohol Exposure: Confirmed or unknown history of alcohol exposure. The presence of specific facial features can confirm exposure even without a known history.
2. Exploring the Link Between Prenatal Alcohol Exposure and FAS
The magnitude of expression of FAS facial features correlates significantly with increasing severity of growth deficiency, microcephaly, and CNS dysfunction. This correlation validates the causal association between prenatal alcohol exposure and FAS characteristics. Understanding this link helps to emphasize the importance of abstaining from alcohol during pregnancy.
Impact of Alcohol Exposure on Facial Features
The FAS facial phenotype exists along a continuum from mild to severe. The severity of the phenotype increases with higher levels of prenatal alcohol exposure. The facial features are not merely present or absent but vary in expression.
Correlation with Other Diagnostic Features
The magnitude of the FAS facial phenotype is significantly correlated with other diagnostic features, including growth deficiency, microcephaly, and CNS dysfunction. These correlations validate the causal link between prenatal alcohol exposure and FAS.
The Lifestyle During Pregnancy Study (LDPS)
The LDPS collected prenatal alcohol exposure history during early pregnancy and used standardized measures of growth, facial features, and CNS function. This study provides valuable insights into the effects of low-to-moderate alcohol intake and binge drinking on children.
3. Analyzing the Effects of Low-to-Moderate Alcohol Consumption
Even low-to-moderate levels of prenatal alcohol exposure can pose risks to the developing fetus. Studies have shown that children exposed to an average of 1 to 4 drinks per week are more likely to present with FAS/PFAS facial phenotypes. This underscores the importance of avoiding alcohol consumption during pregnancy.
Findings from the LDPS Analysis
The LDPS analysis assessed the potential effects of low-to-moderate average weekly alcohol consumption and binge drinking in early pregnancy on facial features associated with FAS among children 5 years of age. The study documented the occurrence of individual FAS facial features and assessed the association between prenatal alcohol exposure and the magnitude of expression of the FAS facial features.
Key Results
- Children exposed to 1 to 4 drinks/week were 8.5-fold more likely to present with FAS/PFAS facial phenotypes.
- Children with a single binge exposure in gestational weeks 3 to 4 were 2.5-fold more likely to present with FAS/PFAS facial phenotypes.
- The magnitude of expression of the FAS facial phenotype correlated significantly with other diagnostic features, including growth deficiency, microcephaly, and CNS dysfunction.
Implications of Low-to-Moderate Exposure
These findings suggest that even low-to-moderate levels of prenatal alcohol exposure can place some fetuses at risk for FAS/PFAS. Therefore, it is crucial to adhere to the conservative advice of abstaining from alcohol consumption during pregnancy.
4. Investigating the Impact of Binge Drinking During Pregnancy
Binge drinking during pregnancy, defined as consuming five or more drinks on a single occasion, is particularly harmful to the developing fetus. A single binge episode, especially during critical periods of embryogenesis, can significantly increase the risk of FAS/PFAS facial phenotypes. Understanding this risk is crucial for preventing alcohol-related birth defects.
Timing of Binge Drinking
The gestational timing of binge drinking episodes significantly impacts the odds of presenting with FAS/PFAS facial phenotypes. Binge episodes during gestational weeks 3 to 4 are particularly detrimental, increasing the likelihood of FAS/PFAS facial phenotypes by 2.5-fold.
Study Findings on Binge Drinking
The LDPS analysis revealed that even a single binge episode is associated with a significantly increased risk of FAS/PFAS facial phenotypes. This highlights the importance of avoiding binge drinking throughout pregnancy.
Critical Periods of Embryogenesis
Gestational weeks 3 and 4 are critical periods of embryogenesis, reflecting the primitive streak and gastrulation stage. Exposure to alcohol during these stages can induce significant craniofacial alterations.
5. Examining Facial Features and Their Diagnostic Significance
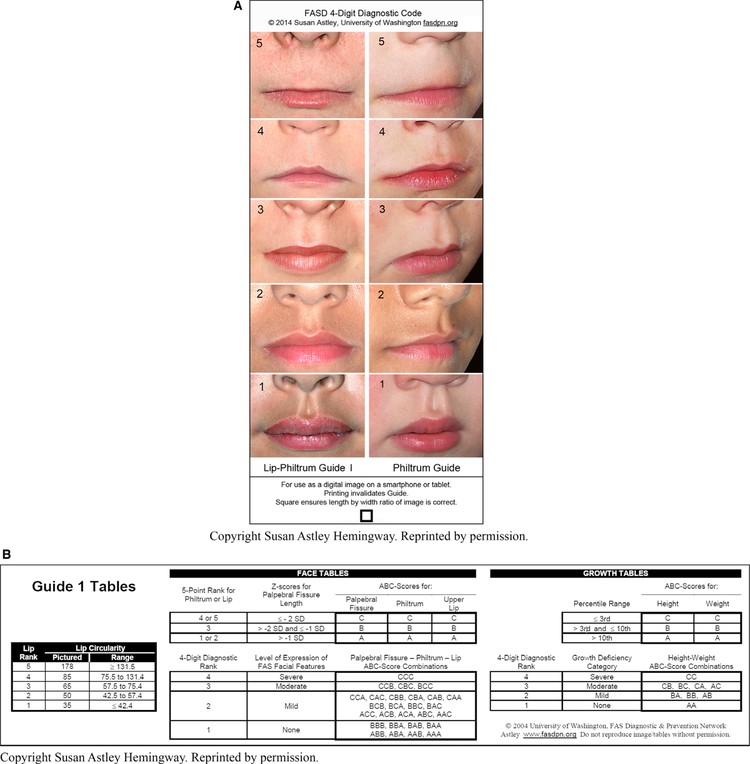
Facial features play a crucial role in the diagnosis of FAS. Short palpebral fissure lengths (PFLs), smooth philtrum, and thin upper lip are key indicators of prenatal alcohol exposure. Understanding how these features are measured and interpreted is essential for accurate diagnosis and early intervention.
Measuring Facial Features
The University of Washington FAS Facial Photographic Analysis Software is used to measure the magnitude of expression of the three diagnostic facial features of FAS. These measurements are crucial for determining the presence and severity of FAS-related facial abnormalities.
Specific Facial Features
- Short Palpebral Fissure Lengths (PFLs): Measured in relation to standard deviations below the mean.
- Smooth Philtrum: Ranked using the University of Washington Lip-Philtrum Guide.
- Thin Upper Lip: Also ranked using the University of Washington Lip-Philtrum Guide.
Magnitude of Expression
The magnitude of expression of the FAS facial phenotype is ranked on a 4-point Likert scale, ranging from normal (Rank 1) to severe (Rank 4). This ranking helps in assessing the overall impact of prenatal alcohol exposure.
6. Evaluating the Correlation Between Facial Phenotypes and Other FASD Features
The magnitude of expression of the FAS facial phenotype is significantly correlated with other diagnostic features of FAS, including growth deficiency, microcephaly, and CNS dysfunction. These correlations underscore the systemic impact of prenatal alcohol exposure and the importance of comprehensive diagnostic evaluations.
Link to Growth Deficiency
Mean birthweight, birth length, and birth head circumference decrease significantly with increasing magnitude of expression of the FAS facial phenotype. This indicates a direct link between facial features and growth-related outcomes.
Association with Microcephaly
Microcephaly, a condition characterized by an abnormally small head circumference, is also correlated with the FAS facial phenotype. This highlights the impact of alcohol exposure on brain development.
Impact on CNS Dysfunction
The FAS facial phenotype is significantly associated with measures of CNS dysfunction. Individuals with short PFLs and smooth philtrums tend to have lower IQ scores, indicating cognitive impairment.
7. Understanding Study Limitations and Implications
While studies like the LDPS provide valuable insights, it is important to acknowledge their limitations. These limitations can include sample selection bias and the challenges of accurately reporting prenatal alcohol exposure. Understanding these limitations is crucial for interpreting findings and guiding future research.
Sample Representativeness
The DNBC represents approximately 30% of all Danish pregnant women, and the LDPS sample is a stratified sample within the DNBC. This selection may make the sample less representative of the background population.
Reporting Bias
Information bias is a potential problem in observational studies. The accuracy of reported prenatal alcohol exposure may vary, affecting the reliability of study findings.
Statistical Power
The small number of children presenting with the Rank 3 to 4 facial phenotypes may limit the representativeness of this group. However, the statistical power was sufficient to identify significant associations with the level and timing of prenatal alcohol exposure.
8. Expert Insights and Guidance from HOW.EDU.VN
At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with leading experts who can provide personalized guidance on preventing and managing FASD. Our team of over 100 Ph.Ds offers insights into understanding risk factors, diagnostic processes, and intervention strategies. Benefit from the expertise of top professionals who can help you make informed decisions and secure the best possible outcomes for your child.
Access to Leading Experts
We provide direct access to Ph.Ds and experts who specialize in FASD. These professionals can offer tailored advice based on the latest research and best practices.
Comprehensive Support
Our services extend beyond initial consultations, offering ongoing support and resources to families affected by FASD. We are committed to helping you navigate the complexities of diagnosis and treatment.
Personalized Advice
Receive personalized advice that addresses your specific concerns and circumstances. Our experts take the time to understand your situation and provide guidance that is tailored to your needs.
9. Steps for Prevention and Early Intervention
Prevention is the most effective strategy for addressing FASD. Abstaining from alcohol during pregnancy is the safest course of action. Early intervention can mitigate the effects of FASD, improving outcomes for affected children. Implementing preventive measures and seeking early support are crucial steps.
Abstinence During Pregnancy
The most effective way to prevent FASD is to abstain from alcohol consumption during pregnancy. This ensures that the developing fetus is not exposed to alcohol-related risks.
Early Intervention Strategies
Early intervention programs can help children with FASD develop essential skills and improve their quality of life. These programs may include therapies, educational support, and behavioral interventions.
Support for Families
Families affected by FASD need access to support networks and resources. These resources can provide emotional support, practical advice, and guidance on navigating the challenges of raising a child with FASD.
10. Seeking Professional Advice and Support
Navigating the complexities of prenatal alcohol exposure and FASD can be challenging. Seeking professional advice and support is essential for making informed decisions and accessing appropriate resources. HOW.EDU.VN connects you with over 100 Ph.Ds ready to provide expert consultations and support.
Connecting with Experts at HOW.EDU.VN
At HOW.EDU.VN, we offer a platform for connecting with leading experts in various fields, including FASD. Our team of over 100 Ph.Ds is ready to provide expert consultations and support.
Benefits of Expert Consultation
- Personalized Guidance: Receive tailored advice that addresses your specific concerns and circumstances.
- Access to Resources: Gain access to valuable resources and support networks.
- Informed Decision-Making: Make informed decisions based on the latest research and best practices.
Take the Next Step
Contact us today to connect with an expert and receive the support you need. Visit HOW.EDU.VN to learn more and schedule a consultation.
Are you looking for expert advice on prenatal health and preventing FASD? At HOW.EDU.VN, we offer access to over 100 Ph.Ds ready to provide personalized guidance. Contact us today to learn more and schedule a consultation. Our experts can help you navigate these complex issues and secure the best possible outcomes for your child.
Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
Website: HOW.EDU.VN
Understanding how much drinking causes fetal alcohol syndrome is crucial for making informed decisions and ensuring a healthy pregnancy. Trust HOW.EDU.VN for expert advice and personalized support.
FAQ: Fetal Alcohol Syndrome and Prenatal Alcohol Exposure
-
What is Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS)?
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS) is a condition resulting from prenatal alcohol exposure, characterized by growth deficiencies, facial abnormalities, and central nervous system dysfunction.
-
How much alcohol consumption is safe during pregnancy?
The safest course of action is to abstain from alcohol consumption during pregnancy, as there is no known safe level of alcohol exposure for the developing fetus.
-
What are the key facial features associated with FAS?
The key facial features include short palpebral fissure lengths (PFLs), a smooth philtrum, and a thin upper lip.
-
Can low-to-moderate alcohol consumption cause FAS?
Studies suggest that even low-to-moderate alcohol consumption can increase the risk of FAS/PFAS facial phenotypes.
-
How does binge drinking affect the risk of FAS?
Binge drinking, especially during critical periods of embryogenesis, can significantly increase the risk of FAS/PFAS facial phenotypes.
-
What is the 4-Digit Code diagnostic scheme?
The 4-Digit Code is a diagnostic scheme that assesses growth, facial features, CNS abnormalities, and prenatal alcohol exposure to diagnose FASD.
-
What is the role of early intervention in managing FASD?
Early intervention programs can help children with FASD develop essential skills and improve their quality of life through therapies, educational support, and behavioral interventions.
-
How can HOW.EDU.VN help with FASD-related concerns?
HOW.EDU.VN connects you with leading experts who can provide personalized guidance on preventing and managing FASD, offering insights into risk factors, diagnostic processes, and intervention strategies.
-
What should I do if I suspect my child has FASD?
Consult with a healthcare professional or an expert at HOW.EDU.VN for a comprehensive evaluation and guidance on appropriate interventions and support.
-
Where can I find reliable resources and support for families affected by FASD?
how.edu.vn offers access to valuable resources and support networks, providing emotional support, practical advice, and guidance on navigating the challenges of raising a child with FASD.
