How Much Electric Does A Solar Panel Generate is a common question for homeowners considering renewable energy. At HOW.EDU.VN, we provide expert answers, offering solutions to understand solar panel output and maximize its benefits for your home. Explore solar energy production, solar power efficiency, and solar panel systems to make informed decisions.
1. Understanding Solar Panel Electricity Generation
The amount of electricity a solar panel generates is a critical factor for anyone considering solar energy. On average, a single solar panel can produce around 400 watts of power under direct sunlight, translating to approximately 2 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of energy per day. However, this figure can fluctuate based on various factors. For homeowners, understanding these factors is key to optimizing solar panel performance and maximizing energy savings. Consulting with experts at HOW.EDU.VN can provide personalized insights and guidance.
1.1. Typical Home Solar Panel Output
Most residential solar installations involve around 18 solar panels. This setup can generate an average of 36 kWh of solar energy daily. This amount is often sufficient to cover a typical household’s energy consumption. The exact figure, however, depends on several variables, making it important to assess your specific energy needs and local solar conditions.
1.2. Factors Influencing Solar Panel Output
Several key factors affect how much electricity a solar panel generates:
- Available sunlight: The intensity and duration of sunlight exposure significantly impact energy production.
- Panel characteristics: The type and efficiency of the solar panel determine how effectively it converts sunlight into electricity.
- Geographical location: The amount of sunlight varies by region, affecting the overall energy yield.
- Panel age: Solar panels degrade over time, leading to a gradual reduction in electricity generation.
Understanding these factors allows homeowners to make informed decisions about solar panel selection and installation.
2. Detailed Look at Solar Panel Power Output
Power output refers to the amount of electricity a solar panel generates at any given time, measured in watts. Modern residential solar panels typically have an output of around 400 watts per hour under ideal conditions. This rating, however, is determined under specific laboratory conditions that may not reflect real-world scenarios.
2.1. Power Ratings of Popular Solar Panels
Here’s a comparison of power ratings from some of the top solar panel brands:
| Brand | Model Series | Output |
|---|---|---|
| Qcells | Q.PEAK DUO | 400 – 405 W |
| JA Solar | Deep Blue 3.0 | 390 – 400 W |
| Canadian Solar | HiKu6 All-Black | 395 – 400 W |
| Silfab Solar | Silfab Prime | 400 – 410 W |
| REC Solar | Alpha Pure | 400 – 410 W |
These power ratings are based on Standard Test Conditions (STC), which simulate perfect illumination at 25 degrees Celsius.
2.2. Real-World vs. Lab Conditions
In reality, solar panels will likely produce less power than their STC ratings due to variations in temperature, sunlight, and other environmental factors. Rooftop solar installations are designed to account for these variations to ensure they meet your home’s energy needs. Consulting with solar experts can help you understand these nuances and optimize your system for actual conditions.
3. Energy Production Over Time
Energy is the total amount of power a solar panel produces over a period, typically measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). A single solar panel will generate about 2 kWh of energy each day, enough to power small appliances or run a TV for 24 hours.
3.1. Energy Production Table
The following table illustrates the energy produced by a single solar panel over different time frames:
| Time | Energy Produced by One Solar Panel |
|---|---|
| 1 Day | 2 kWh |
| 1 Week | 14 kWh |
| 1 Month | 60 kWh |
| 1 Year | 730 kWh |
Most homeowners install multiple solar panels to meet their energy needs. A typical 6 kW solar installation can generate around 915 kWh of electricity per month.
3.2. Estimating Your Home’s Solar Energy Potential
To estimate how much energy solar panels can generate on your roof, consider factors such as panel wattage, peak sun hours, and the number of panels. Tools and resources are available to help you calculate potential energy production, or consult with solar professionals for a detailed assessment.
4. Factors That Affect Electricity Production
Four primary factors influence the amount of electricity solar panels produce: sunlight, panel characteristics, roof conditions, and panel age. Understanding each factor is essential for optimizing your solar investment.
4.1. Sunlight Availability
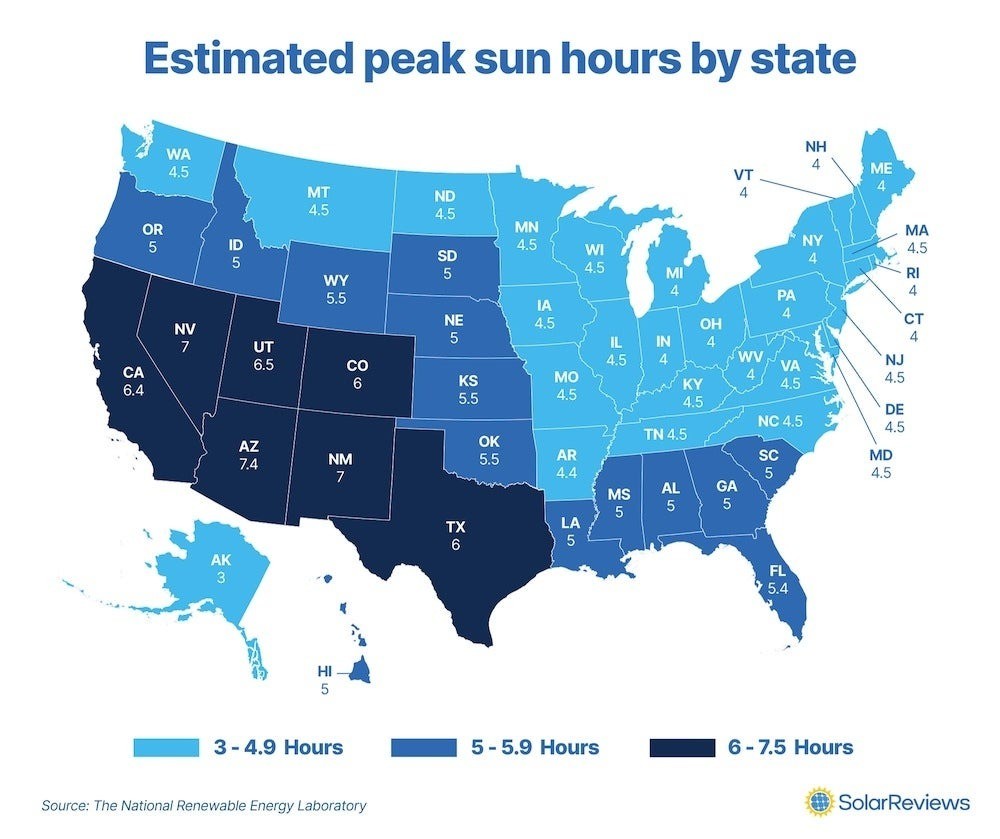
The amount of sunlight that reaches a solar panel is a critical determinant of electricity generation. More sunlight equates to more electricity. Regions with higher peak sun hours, such as Arizona, will see greater energy production compared to areas with less sunlight, like Alaska.
4.2. Solar Panel Characteristics
The type and construction of solar panels also impact energy production. Monocrystalline panels are popular for their efficiency, while polycrystalline and thin-film panels offer alternative options. The size of the solar panel and the technology used in its cells (e.g., PERC, heterojunction, TOPCon) also play a significant role.
4.3. Roof Conditions
Your roof’s characteristics are crucial for solar panel performance. Unshaded roofs with a south-facing orientation are ideal for maximizing solar production in the United States. The angle and direction of the roof influence how much sunlight the panels receive.
4.4. Panel Age and Degradation
Solar panels degrade over time, typically losing about 0.5% of their ability to generate power each year. This degradation is normal, and most panels are designed to operate at around 85% of their initial capacity by the end of their 25-year warranty period. Regular maintenance and monitoring can help mitigate the impact of degradation.
5. Calculating Electricity Production: A Practical Guide
Calculating how much electricity a solar panel can produce involves considering the panel’s wattage and the peak sun hours in your area. By multiplying these two values, you can estimate the daily electricity production.
5.1. Step-by-Step Calculation
Here’s a simple formula to calculate electricity production:
Panel Wattage x Peak Sun Hours = Watt-Hours per Day
To convert watt-hours to kilowatt-hours, divide by 1,000.
5.2. Example Calculation
For example, a 400-watt solar panel with four peak sun hours produces:
400 watts x 4 peak sun hours = 1,600 watt-hours per day
1,600 watt-hours / 1,000 = 1.6 kWh per day
To estimate monthly and yearly production, multiply the daily value by the number of days in the respective period.
- 6 kWh per day x 30 days = 48 kWh per month
- 6 kWh per day x 365 days = 584 kWh per year
Multiplying the yearly production by the number of panels in your system provides an estimate of total solar energy production.
584 kWh per panel per year x 18 panels = 10,512 kWh per year
5.3. Professional Consultation
While these calculations provide a rough estimate, consulting with a local solar installer is the best way to determine how much energy solar panels will generate on your roof. Professionals can consider all relevant factors and provide a more accurate assessment.
6. Maximizing Your Solar Investment: Powering Your Home and Saving Money
Installing solar panels not only allows you to power your home with renewable energy but also helps you save money on electricity bills. By using the electricity generated by your solar panels, you reduce your reliance on the utility grid and lower your monthly costs.
6.1. Potential Savings
A 6 kW solar system can save the average American homeowner around $140 a month. However, savings vary based on factors such as location, energy consumption, and solar incentives.
6.2. Solar Savings Calculator
Using a solar savings calculator can provide a more accurate estimate of potential savings. Additionally, connecting with vetted local solar installers can help you obtain real solar quotes tailored to your specific home and energy needs.
7. Solar Panel Efficiency: What You Need to Know
Solar panel efficiency is a measure of how well a solar panel converts sunlight into electricity. Higher efficiency panels generate more electricity from the same amount of sunlight, making them a valuable investment for homeowners.
7.1. Understanding Efficiency Ratings
Efficiency ratings are typically expressed as a percentage. For example, a solar panel with an efficiency rating of 20% converts 20% of the sunlight that hits it into electricity. The remaining 80% is lost as heat or reflected.
7.2. Factors Affecting Efficiency
Several factors can affect a solar panel’s efficiency, including:
- Material Quality: High-quality materials contribute to better energy conversion.
- Manufacturing Process: Advanced manufacturing techniques improve efficiency.
- Temperature: High temperatures can reduce efficiency.
- Shading: Shading from trees or buildings can significantly decrease efficiency.
7.3. Types of Solar Cells and Efficiency
Different types of solar cells offer varying levels of efficiency:
- Monocrystalline: Known for high efficiency, typically ranging from 17% to 22%.
- Polycrystalline: Slightly less efficient than monocrystalline, with ratings around 15% to 17%.
- Thin-Film: Generally less efficient, but can be more cost-effective for large-scale installations.
7.4. Choosing High-Efficiency Panels
Choosing high-efficiency solar panels can maximize energy production, especially in limited roof space. While they may have a higher upfront cost, the long-term benefits often outweigh the initial investment.
8. Solar Panel Systems: Components and Functionality
A solar panel system consists of several components working together to convert sunlight into usable electricity. Understanding these components is essential for making informed decisions about your solar installation.
8.1. Key Components
The main components of a solar panel system include:
- Solar Panels: Convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity.
- Inverter: Converts DC electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is used to power homes and businesses.
- Mounting System: Secures the solar panels to the roof or ground.
- Wiring: Connects the solar panels to the inverter and the electrical grid.
- Monitoring System: Tracks the system’s performance and energy production.
8.2. How Solar Panel Systems Work
Solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into DC electricity. The inverter then transforms this DC electricity into AC electricity, which can be used to power your home’s appliances and electronics. Excess electricity can be sent back to the grid, earning you credits on your electricity bill through net metering programs.
8.3. Types of Solar Panel Systems
There are several types of solar panel systems, including:
- Grid-Tied Systems: Connected to the utility grid, allowing you to send excess electricity back to the grid.
- Off-Grid Systems: Not connected to the utility grid, requiring battery storage to provide power when the sun isn’t shining.
- Hybrid Systems: Combine grid-tied and off-grid features, offering both grid connectivity and battery storage.
8.4. System Size and Configuration
The size and configuration of your solar panel system depend on your energy needs, roof size, and local solar conditions. Consulting with a solar installer can help you determine the best system for your home.
9. Optimizing Solar Panel Performance
To maximize the electricity generated by your solar panels, it’s essential to optimize their performance through proper installation, maintenance, and monitoring.
9.1. Proper Installation Techniques
Proper installation is crucial for ensuring optimal solar panel performance. Key considerations include:
- Roof Orientation: South-facing roofs are ideal for maximizing sunlight exposure.
- Tilt Angle: Adjusting the tilt angle of the panels can optimize sunlight capture throughout the year.
- Shading Avoidance: Minimizing shading from trees, buildings, and other obstructions is essential for maximizing energy production.
9.2. Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance can help keep your solar panels operating at peak performance. Key maintenance tasks include:
- Cleaning: Removing dirt, dust, and debris from the panels can improve sunlight absorption.
- Inspection: Regularly inspecting the panels for damage or wear can help identify and address potential issues.
- Vegetation Management: Trimming trees and other vegetation can prevent shading and maintain optimal sunlight exposure.
9.3. Performance Monitoring
Monitoring your solar panel system’s performance can help you identify and address any issues that may be affecting energy production. Monitoring systems track energy production, system health, and other key metrics, providing valuable insights into your system’s performance.
10. Solar Panel Innovations and Future Trends
The solar industry is constantly evolving, with new innovations and trends emerging to improve solar panel efficiency, reduce costs, and expand applications.
10.1. Technological Advancements
Recent technological advancements in solar panel technology include:
- Bifacial Solar Panels: Capture sunlight from both the front and back of the panel, increasing energy production.
- Perovskite Solar Cells: Offer the potential for higher efficiency and lower costs compared to traditional silicon solar cells.
- Smart Solar Panels: Incorporate advanced electronics and monitoring systems to optimize performance and detect issues.
10.2. Emerging Trends
Emerging trends in the solar industry include:
- Energy Storage: Combining solar panels with battery storage systems to provide backup power and increase energy independence.
- Community Solar: Allowing multiple households to share the benefits of a single solar panel system.
- Floating Solar Farms: Deploying solar panels on bodies of water to maximize land use and reduce evaporation.
10.3. The Future of Solar Energy
The future of solar energy is bright, with continued innovation and decreasing costs making solar an increasingly attractive option for homeowners and businesses alike.
11. Common Misconceptions About Solar Panel Electricity Generation
There are several common misconceptions about solar panel electricity generation that can deter homeowners from investing in solar. Addressing these misconceptions can help dispel doubts and encourage wider adoption of solar energy.
11.1. Myth: Solar Panels Don’t Work on Cloudy Days
Fact: Solar panels can generate electricity even on cloudy days, although at a reduced rate. Diffuse sunlight can still be captured and converted into electricity, albeit less efficiently than direct sunlight.
11.2. Myth: Solar Panels Require Constant Sunlight
Fact: Solar panels do not require constant sunlight to generate electricity. They can generate power as long as there is daylight, and excess electricity can be stored in batteries or sent back to the grid for later use.
11.3. Myth: Solar Panels are Too Expensive
Fact: The cost of solar panels has decreased significantly in recent years, making them more affordable than ever. Additionally, government incentives, tax credits, and net metering programs can help offset the initial cost and provide long-term savings.
11.4. Myth: Solar Panels Require a Lot of Maintenance
Fact: Solar panels require very little maintenance. Regular cleaning and occasional inspections are typically all that is needed to keep them operating at peak performance.
11.5. Myth: Solar Panels Will Damage My Roof
Fact: When installed properly, solar panels will not damage your roof. Professional installers use mounting systems designed to protect your roof and prevent leaks.
12. Ensuring Reliability and Longevity of Solar Panel Systems
Ensuring the reliability and longevity of your solar panel system requires careful planning, quality components, and proper maintenance. By taking these steps, you can maximize your solar investment and enjoy years of clean, renewable energy.
12.1. Choosing Quality Components
Selecting high-quality solar panels, inverters, and mounting systems is essential for ensuring the reliability and longevity of your system. Look for reputable brands with proven track records and long warranties.
12.2. Professional Installation
Hiring a qualified and experienced solar installer is crucial for ensuring proper installation and optimal performance. Professional installers can assess your roof’s condition, design a system tailored to your energy needs, and ensure that all components are installed correctly.
12.3. Regular Inspections
Regular inspections can help identify and address any issues that may be affecting your system’s performance. Inspections should include checking the panels for damage, verifying the integrity of the mounting system, and testing the functionality of the inverter and other components.
12.4. Warranty Coverage
Understanding your warranty coverage is essential for protecting your solar investment. Most solar panels come with a 25-year performance warranty, which guarantees that the panels will generate a certain amount of electricity over their lifespan.
12.5. Monitoring System Performance
Monitoring your system’s performance can help you identify and address any issues that may be affecting energy production. Monitoring systems track energy production, system health, and other key metrics, providing valuable insights into your system’s performance.
13. Environmental Benefits of Solar Energy
Solar energy offers numerous environmental benefits compared to traditional fossil fuels. By reducing your reliance on fossil fuels, you can help decrease air pollution, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and conserve natural resources.
13.1. Reduced Air Pollution
Solar energy does not produce air pollutants such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, which can contribute to respiratory problems and other health issues.
13.2. Decreased Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Solar energy does not emit greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, which contribute to climate change. By switching to solar, you can significantly reduce your carbon footprint and help mitigate the impacts of climate change.
13.3. Conservation of Natural Resources
Solar energy relies on sunlight, a renewable resource that is abundant and freely available. By harnessing solar energy, you can reduce your reliance on fossil fuels, which are finite resources that must be extracted from the earth.
13.4. Water Conservation
Solar energy does not require water for electricity generation, unlike many traditional power plants that use water for cooling. By switching to solar, you can help conserve water resources and reduce the strain on local water supplies.
13.5. Land Use
Solar energy can be deployed on rooftops, parking lots, and other developed areas, minimizing the need for new land development. Additionally, solar farms can be located on marginal lands that are not suitable for agriculture or other uses.
14. Government Incentives and Rebates for Solar Panel Installations
Many governments offer incentives and rebates to encourage the adoption of solar energy. These incentives can significantly reduce the cost of solar panel installations and make solar more accessible to homeowners and businesses.
14.1. Federal Tax Credit
The federal government offers a tax credit for solar panel installations, which can significantly reduce the cost of your system. The tax credit is typically a percentage of the total cost of the system, including installation.
14.2. State and Local Incentives
Many states and local governments offer additional incentives for solar panel installations, such as rebates, tax credits, and grants. These incentives can vary depending on your location and the type of system you install.
14.3. Net Metering Programs
Net metering programs allow you to send excess electricity generated by your solar panels back to the grid and receive credits on your electricity bill. This can help offset the cost of your system and provide long-term savings.
14.4. Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs)
Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) are tradable commodities that represent the environmental benefits of renewable energy generation. You can sell RECs generated by your solar panel system to utilities or other organizations to earn additional income.
14.5. Financing Options
Several financing options are available to help you pay for your solar panel installation, such as loans, leases, and power purchase agreements (PPAs). These options can make solar more accessible and affordable, even if you don’t have the cash to pay for the system upfront.
15. Solar Panel Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Proper maintenance and troubleshooting are essential for ensuring the optimal performance and longevity of your solar panel system. By following these guidelines, you can keep your system running smoothly and maximize your solar investment.
15.1. Regular Cleaning
Regular cleaning can help remove dirt, dust, and debris from your solar panels, improving their ability to absorb sunlight. Cleaning should be done at least twice a year, or more frequently in areas with high levels of pollution or dust.
15.2. Visual Inspections
Visual inspections can help identify any signs of damage or wear on your solar panels, such as cracks, scratches, or discoloration. Inspections should be done at least once a year, or more frequently if you notice any issues.
15.3. Vegetation Management
Vegetation management can help prevent shading from trees or other plants, ensuring that your solar panels receive maximum sunlight exposure. Trees and other vegetation should be trimmed regularly to prevent shading.
15.4. Monitoring System Performance
Monitoring your system’s performance can help you identify any issues that may be affecting energy production. Monitoring systems track energy production, system health, and other key metrics, providing valuable insights into your system’s performance.
15.5. Troubleshooting Common Issues
Common issues with solar panel systems include inverter failures, wiring problems, and shading issues. Troubleshooting these issues may require the assistance of a qualified solar technician.
16. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Solar Panel Electricity Generation
Here are some frequently asked questions about solar panel electricity generation:
-
How much electricity does a typical solar panel generate in a day?
A typical solar panel generates about 2 kWh of electricity per day.
-
What factors affect the amount of electricity a solar panel generates?
Factors include sunlight, panel characteristics, roof conditions, and panel age.
-
How can I calculate how much electricity my solar panels will generate?
Multiply the panel’s wattage by the peak sun hours in your area.
-
How much money can I save by installing solar panels?
Savings vary, but a 6 kW system can save around $140 a month.
-
What is solar panel efficiency?
It’s a measure of how well a panel converts sunlight into electricity.
-
What are the key components of a solar panel system?
Solar panels, inverters, mounting systems, wiring, and monitoring systems.
-
How can I optimize solar panel performance?
Proper installation, regular maintenance, and performance monitoring.
-
What are the environmental benefits of solar energy?
Reduced air pollution, decreased greenhouse gas emissions, and conservation of natural resources.
-
Are there government incentives for solar panel installations?
Yes, including federal tax credits, state rebates, and net metering programs.
-
How do I maintain my solar panel system?
Regular cleaning, visual inspections, and vegetation management.
17. Case Studies: Real-World Examples of Solar Panel Electricity Generation
Examining real-world case studies can provide valuable insights into the performance and benefits of solar panel systems. These examples illustrate the impact of various factors on electricity generation and the potential savings for homeowners.
17.1. Case Study 1: Residential Installation in Arizona
A homeowner in Arizona installed a 6 kW solar panel system on their south-facing roof. The system generated an average of 950 kWh of electricity per month, covering 100% of their energy needs and saving them $150 per month on their electricity bill.
17.2. Case Study 2: Commercial Installation in California
A business in California installed a 50 kW solar panel system on their rooftop. The system generated an average of 7,000 kWh of electricity per month, covering 80% of their energy needs and saving them $1,000 per month on their electricity bill.
17.3. Case Study 3: Rural Installation in Vermont
A homeowner in Vermont installed a 4 kW solar panel system with battery storage on their property. The system generated an average of 400 kWh of electricity per month, providing backup power during grid outages and reducing their reliance on fossil fuels.
17.4. Key Takeaways from Case Studies
- Solar panel systems can provide significant energy savings for homeowners and businesses.
- The amount of electricity generated by a solar panel system depends on various factors, including location, system size, and roof orientation.
- Government incentives and rebates can help offset the cost of solar panel installations.
- Solar panel systems can provide backup power during grid outages when combined with battery storage.
18. The Role of Solar Energy in a Sustainable Future
Solar energy plays a crucial role in creating a sustainable future by providing clean, renewable electricity and reducing our reliance on fossil fuels. As the cost of solar continues to decrease and technology improves, solar energy is poised to become an increasingly important part of the global energy mix.
18.1. Reducing Carbon Emissions
Solar energy does not emit carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases, making it a key tool for mitigating climate change. By switching to solar, we can significantly reduce our carbon footprint and help protect the planet for future generations.
18.2. Creating Jobs and Economic Opportunities
The solar industry is a rapidly growing sector that creates jobs and economic opportunities in manufacturing, installation, maintenance, and other areas. Investing in solar energy can help stimulate economic growth and create a more sustainable economy.
18.3. Enhancing Energy Security
Solar energy reduces our reliance on fossil fuels, which are subject to price volatility and geopolitical instability. By generating our own electricity from solar, we can enhance our energy security and reduce our vulnerability to external factors.
18.4. Promoting Energy Independence
Solar energy empowers individuals and communities to take control of their energy supply and reduce their dependence on centralized power grids. By generating our own electricity from solar, we can become more energy independent and resilient.
18.5. Building a Cleaner, Healthier World
Solar energy contributes to a cleaner, healthier world by reducing air pollution, conserving water resources, and protecting natural habitats. By embracing solar energy, we can create a more sustainable future for ourselves and future generations.
19. Conclusion: Embracing Solar Energy for a Brighter Tomorrow
Understanding how much electricity a solar panel can generate is the first step toward embracing the benefits of solar energy. From reducing your carbon footprint to saving money on your electricity bill, solar energy offers a multitude of advantages for homeowners and businesses alike. By considering the factors that affect solar panel output, choosing the right system for your needs, and taking advantage of available incentives, you can harness the power of the sun to create a brighter, more sustainable future.
Ready to take the next step? Contact our team of expert PhDs at HOW.EDU.VN for personalized advice and solutions tailored to your unique needs. We’re here to help you navigate the complexities of solar energy and make informed decisions that will benefit you and the planet.
Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
Whatsapp: +1 (310) 555-1212
Website: HOW.EDU.VN
Contact how.edu.vn today and start your journey toward energy independence and sustainability. Our team of over 100 renowned PhDs is ready to provide you with the expert guidance you need to succeed.