How Much Electricity Does A Solar Panel Produce? That’s a crucial question for anyone considering harnessing the power of the sun, and understanding the factors influencing solar panel output is key to making informed decisions about solar energy. At HOW.EDU.VN, we provide expert guidance to help you navigate the complexities of solar technology, understand energy production, solar power generation and maximize your investment in sustainable energy solutions.
1. Understanding Solar Panel Energy Production Basics
Solar panels, the cornerstone of residential and commercial solar energy systems, convert sunlight into usable electricity. How much electricity a solar panel generates depends on various factors, including panel wattage, sunlight availability, and environmental conditions. Let’s delve into the fundamental concepts:
1.1. The Science Behind Solar Panels
Solar panels function through the photovoltaic effect, where photons (light particles) strike the silicon in solar cells, releasing electrons and creating an electric current. This direct current (DC) electricity is then converted to alternating current (AC) by an inverter for use in homes and businesses. NASA provides a detailed explanation of photovoltaic cells.
1.2. Key Terminology: Watts, Kilowatts, and Kilowatt-Hours
-
Watt (W): A unit of power, representing the rate of energy production or consumption.
-
Kilowatt (kW): Equal to 1,000 watts, commonly used to measure the power capacity of solar panels or systems.
-
Kilowatt-hour (kWh): A unit of energy, representing the amount of energy consumed by a 1,000-watt device operating for one hour. This is how electricity is billed.
-
Direct Current (DC): The type of electricity produced by solar panels.
-
Alternating Current (AC): The type of electricity used by most household appliances.
1.3. Factors Influencing Solar Panel Output
Many elements affect a solar panel’s ability to produce electricity. These encompass the panel’s quality and design, as well as external variables like geographic location, weather conditions, and shading. Recognizing these components is crucial for maximizing solar energy production and making educated judgments about system design and installation. For tailored guidance, contact our HOW.EDU.VN specialists.
2. Average Electricity Production of a Solar Panel
So, just how much electricity can you expect from a standard solar panel? Let’s break it down.
2.1. Typical Wattage Output of Solar Panels
In 2024, the typical wattage range for residential solar panels falls between 300 to 450 watts under standard testing conditions. Some high-efficiency panels can even exceed 450 watts. The higher the wattage, the more electricity the panel can generate in optimal conditions.
2.2. Calculating Daily Electricity Production
To estimate daily electricity production, you need to consider the panel’s wattage and the number of peak sun hours in your area.
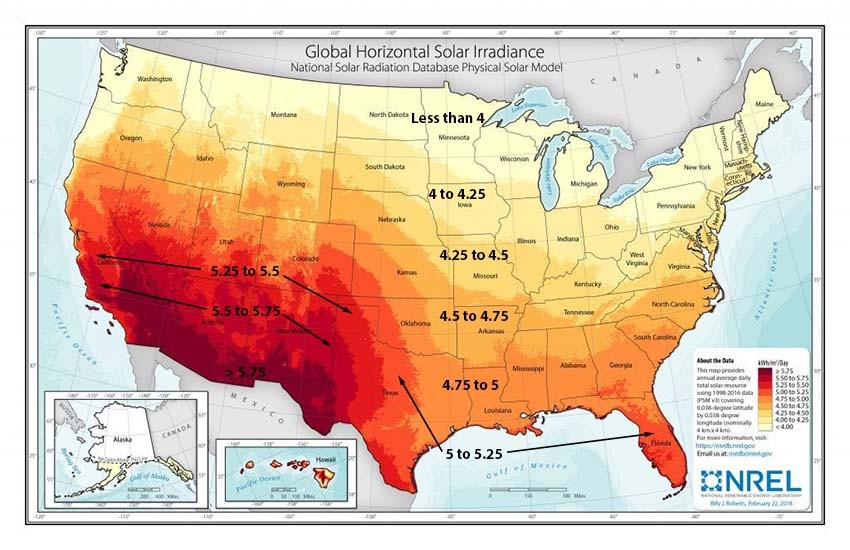
Peak sun hours represent the equivalent number of hours per day when sunlight intensity reaches 1,000 watts per square meter (kW/m²). This value varies depending on location, time of year, and weather patterns.
Formula: Solar Panel Output (Watts) x Peak Sun Hours = Daily Watt-hours
Example: A 400-watt solar panel in an area with 5 peak sun hours would produce:
400W x 5 hours = 2,000 Watt-hours (Wh) or 2 kWh per day
2.3. Monthly and Annual Electricity Production Estimates
To estimate monthly production, multiply the daily production by the number of days in the month. For annual production, multiply the daily production by 365.
Example:
-
Monthly: 2 kWh/day x 30 days = 60 kWh per month
-
Annual: 2 kWh/day x 365 days = 730 kWh per year
2.4. Understanding Energy Conversion Losses
It’s important to note that the DC electricity generated by solar panels must be converted to AC electricity for use in homes. This conversion process involves some energy loss, typically around 3-5%. Therefore, the actual AC electricity output will be slightly lower than the calculated DC output.
3. Factors That Significantly Impact Solar Panel Output
Several factors play a crucial role in determining how much electricity a solar panel can produce, including the type of panel, its placement, and environmental conditions.
3.1. Type of Solar Panel: Monocrystalline vs. Polycrystalline
Solar panels come in various types, each with its own characteristics and performance levels. The two most common types are monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels.
| Feature | Monocrystalline | Polycrystalline |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | Higher (typically 17-22%) | Lower (typically 15-17%) |
| Appearance | Uniform black color | Bluish, speckled appearance |
| Performance | Slightly better performance in low-light conditions and high temperatures | Performance can degrade more quickly in high temperatures |
| Manufacturing | Made from a single crystal of silicon, resulting in higher purity and efficiency. More expensive to produce. | Made from multiple silicon fragments melted together. Less expensive to produce but also less efficient. |
| Cost | More expensive | Less expensive |
| Lifespan | Generally longer lifespan due to higher purity of silicon; better long-term reliability | May have slightly shorter lifespan compared to monocrystalline panels due to potential for greater degradation over time |
| Space Efficiency | Higher power output per square foot due to higher efficiency, ideal for installations with limited roof space | Lower power output per square foot, requiring more panels to generate the same amount of electricity as monocrystalline panels |
| Aesthetics | Sleek, modern appearance due to uniform color, preferred by homeowners concerned with aesthetics | Less visually appealing due to speckled appearance, may be less desirable for homeowners prioritizing aesthetics |
| Temperature Coefficient | Lower temperature coefficient, meaning performance degrades less in high temperatures, better for hot climates | Higher temperature coefficient, meaning performance degrades more in high temperatures, may be less suitable for hot climates |
| Durability | Generally more durable due to robust construction and high-quality materials, able to withstand harsh weather conditions effectively | Can be slightly less durable than monocrystalline panels, may be more susceptible to damage from extreme weather conditions |
3.2. Solar Panel Orientation and Tilt Angle
The orientation and tilt angle of solar panels significantly impact their electricity production.
-
Orientation: In the Northern Hemisphere, solar panels should ideally face south to maximize sunlight exposure. In the Southern Hemisphere, they should face north.
-
Tilt Angle: The optimal tilt angle depends on your latitude. Generally, setting the tilt angle equal to your latitude is a good starting point. However, you can adjust the angle seasonally to optimize for summer or winter sun.
3.3. Shading and Environmental Factors
Shading from trees, buildings, or other obstructions can significantly reduce solar panel output. Even partial shading can disproportionately affect performance. Regular cleaning of solar panels is also essential, as dust, dirt, and debris can accumulate and block sunlight.
3.4. Temperature Effects on Solar Panel Efficiency
Solar panels perform best in moderate temperatures. High temperatures can decrease their efficiency. The temperature coefficient of a solar panel indicates how much its performance degrades with each degree Celsius increase in temperature above 25°C (77°F). Panels with a lower temperature coefficient are less affected by heat.
4. Optimizing Solar Panel Energy Production
To maximize the electricity production of your solar panels, consider the following strategies.
4.1. Proper Solar Panel Placement and Angle Adjustments
Ensure your solar panels are placed in an unshaded area with optimal orientation and tilt angle. Adjust the tilt angle seasonally to capture the most sunlight throughout the year.
4.2. Regular Solar Panel Maintenance and Cleaning
Keep your solar panels clean by periodically washing them with water and a soft brush. Remove any debris, such as leaves or bird droppings, that may block sunlight.
4.3. Monitoring Solar Panel Performance
Install a monitoring system to track the electricity production of your solar panels. This will allow you to identify any performance issues early on and take corrective action.
4.4. Upgrading to High-Efficiency Solar Panels
Consider upgrading to high-efficiency solar panels with advanced technology, such as passivated emitter rear contact (PERC) cells or bifacial panels, to increase electricity production.
5. Solar Panel Systems and Energy Needs
Understanding your energy needs is essential for designing a solar panel system that meets your requirements.
5.1. Assessing Your Home’s Energy Consumption
Review your past electricity bills to determine your average monthly and annual energy consumption. This will help you estimate the size of the solar panel system you need.
5.2. Determining the Right Size of Solar Panel System
To determine the right size of the solar panel system, consider the following factors:
-
Your energy consumption
-
The amount of sunlight in your area
-
The efficiency of your solar panels
-
Your budget
A professional solar installer can help you assess these factors and design a system that meets your needs.
5.3. Net Metering and Energy Storage Options
Net metering allows you to send excess electricity generated by your solar panels back to the grid and receive credit on your electricity bill. Energy storage systems, such as batteries, allow you to store excess electricity for use when the sun is not shining.
6. Real-World Examples: Solar Panel Production in Different Locations
Solar panel production can vary significantly depending on location.
6.1. Case Study: Solar Panel Output in California
California, with its abundant sunshine, is an ideal location for solar energy. A 5-kW solar panel system in California can produce an average of 750-850 kWh of electricity per month.
6.2. Case Study: Solar Panel Output in New York
New York, with its less sunny climate, has lower solar panel production. A 5-kW solar panel system in New York can produce an average of 550-650 kWh of electricity per month.
6.3. Comparing Solar Panel Production Across Different States
| State | Average Peak Sun Hours per Day | Estimated Monthly Production (5-kW System) |
|---|---|---|
| California | 6.5 | 825 kWh |
| Arizona | 7.0 | 875 kWh |
| Florida | 5.5 | 700 kWh |
| Texas | 5.0 | 625 kWh |
| New York | 4.0 | 550 kWh |
| Massachusetts | 4.5 | 600 kWh |
7. Innovative Solar Technologies and Energy Production
As technology advances, innovative solar solutions are emerging to enhance energy production and efficiency.
7.1. Bifacial Solar Panels and Their Advantages
Bifacial solar panels can generate electricity from both sides, increasing energy production by up to 30% compared to traditional monofacial panels.
7.2. Solar Panel Efficiency Improvements and Future Trends
Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on improving solar panel efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing durability. Future trends include the development of perovskite solar cells, quantum dot solar cells, and transparent solar panels.
7.3. Integrating Solar Technology with Smart Grids
Integrating solar technology with smart grids enables more efficient energy management, grid stability, and renewable energy integration. Smart grids use advanced sensors, controls, and communication technologies to optimize energy distribution and consumption.
8. Cost Savings and Return on Investment for Solar Panels
Investing in solar panels can provide significant cost savings and a positive return on investment.
8.1. Calculating Long-Term Energy Cost Savings
By generating your own electricity with solar panels, you can reduce or eliminate your electricity bills and protect yourself from rising energy costs. Over the lifespan of the system, these savings can add up to tens of thousands of dollars.
8.2. Government Incentives and Rebates for Solar Energy
Many governments offer incentives and rebates to encourage the adoption of solar energy. These incentives can significantly reduce the upfront cost of a solar panel system and improve its return on investment.
8.3. Increasing Property Value with Solar Panel Installation
Installing solar panels can increase the value of your property. Studies have shown that homes with solar panels sell for more than comparable homes without solar panels.
9. Addressing Common Misconceptions About Solar Panel Energy Production
There are several misconceptions about solar panel energy production that need to be addressed.
9.1. Debunking Myths About Solar Panel Efficiency
One common myth is that solar panels are not efficient enough to be worthwhile. In reality, modern solar panels have efficiencies ranging from 17% to over 22%, making them a viable source of energy.
9.2. Addressing Concerns About Solar Panel Performance in Cloudy Weather
While solar panel production is reduced in cloudy weather, it is not eliminated. Solar panels can still generate electricity from diffuse sunlight.
9.3. Dispelling Fears About Solar Panel Maintenance and Longevity
Solar panels require minimal maintenance and have a long lifespan. Most solar panels come with a 25-year warranty, guaranteeing their performance for decades.
10. Expert Insights on Maximizing Solar Panel Output
To get the most out of your solar panel system, seek expert advice from qualified professionals.
10.1. Consulting with Solar Energy Professionals at HOW.EDU.VN
At HOW.EDU.VN, we have a team of experienced solar energy professionals who can provide expert guidance on system design, installation, and maintenance.
10.2. Tips for Optimizing Solar Panel Placement and Performance
-
Conduct a shade analysis to identify potential shading issues.
-
Choose high-efficiency solar panels with a low-temperature coefficient.
-
Install a monitoring system to track performance and identify issues.
-
Keep your solar panels clean and free of debris.
10.3. Staying Informed About Solar Energy Trends and Technologies
Stay informed about the latest trends and technologies in the solar energy industry. This will help you make informed decisions about your solar panel system and maximize its performance.
 Solar Panels on a Rooftop
Solar Panels on a Rooftop
Solar panels optimally placed on a residential rooftop for maximum sun exposure.
FAQ Section: Addressing Your Solar Energy Questions
Q1: How much electricity does a typical solar panel produce in a day?
A typical 400-watt solar panel can produce around 2 kWh of electricity per day in an area with 5 peak sun hours.
Q2: What factors affect the electricity production of solar panels?
Factors include panel wattage, sunlight availability, panel orientation and tilt angle, shading, temperature, and panel type.
Q3: How can I maximize the electricity production of my solar panels?
Ensure optimal placement and orientation, keep the panels clean, monitor performance, and consider upgrading to high-efficiency panels.
Q4: How do I determine the right size of solar panel system for my home?
Review your energy consumption, assess sunlight availability, and consult with a solar professional.
Q5: What are the benefits of net metering and energy storage?
Net metering allows you to receive credit for excess electricity sent to the grid, while energy storage allows you to store excess electricity for later use.
Q6: Are solar panels efficient in cloudy weather?
Solar panels can still generate electricity in cloudy weather, although production is reduced.
Q7: How long do solar panels last?
Most solar panels come with a 25-year warranty and can last for 30 years or more.
Q8: How much does it cost to install a solar panel system?
The cost depends on the size of the system, the type of panels, and installation costs. Contact a solar professional for a custom quote.
Q9: What government incentives are available for solar energy?
Many governments offer incentives and rebates to encourage the adoption of solar energy. Check with your local and federal governments for available programs.
Q10: How do I find a reputable solar installer?
Research local solar installers, check their credentials and reviews, and get multiple quotes before making a decision.
Investing in solar panels is a smart way to reduce your carbon footprint, save money on electricity bills, and increase the value of your property. By understanding how much electricity a solar panel can produce and optimizing system performance, you can harness the power of the sun and enjoy the benefits of clean, renewable energy.
Don’t navigate the complexities of solar energy alone. At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with leading PhDs and experts who can provide personalized guidance and solutions tailored to your specific needs. Whether you’re a homeowner, business owner, or researcher, our team is here to help you make informed decisions and achieve your energy goals.
Ready to take the next step? Contact us today for a consultation and discover how HOW.EDU.VN can help you harness the power of solar energy. Reach out to our experts at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States. Whatsapp: +1 (310) 555-1212 or visit our website at how.edu.vn.
