How Much Gabapentin Should I Take is a common question for individuals seeking relief from nerve pain or managing epilepsy; finding the right gabapentin dosage is crucial for achieving optimal therapeutic benefits and minimizing potential side effects. At HOW.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of personalized guidance, connecting you with experienced doctors ready to tailor your treatment plan and address your specific concerns. Consulting our experts ensures you receive the most appropriate dosage, maximizing the drug’s effectiveness and promoting your overall well-being through proper medication management, personalized treatment strategies, and comprehensive health support.
1. Understanding Gabapentin: Uses and Forms
Gabapentin is a medication primarily used to treat:
- Epilepsy: Helps control seizures.
- Nerve Pain (Neuralgia): Often prescribed for pain caused by shingles (postherpetic neuralgia) or diabetic neuropathy.
Gabapentin is available in several forms, including:
- Capsules: Typically available in 100mg, 300mg, and 400mg strengths.
- Tablets: Available in 600mg and 800mg strengths.
- Oral Solution (Liquid): The concentration can vary, so always check the label. Generally, 2ml of the liquid form is equivalent to a 100mg capsule or tablet.
Alt text: Assorted Gabapentin capsules and tablets displaying various dosages for nerve pain and epilepsy treatment.
2. Gabapentin Dosage for Epilepsy
The appropriate gabapentin dosage for epilepsy depends on several factors, including age, weight, and the severity of the condition.
2.1. Adults and Older Children (12 Years and Older)
- Initial Dose: Typically starts at 900mg per day, divided into three doses (e.g., 300mg three times a day).
- Maintenance Dose: May be increased gradually by your doctor, depending on your response and tolerance. The usual maintenance dose ranges from 900mg to 3,600mg per day, divided into three doses.
- Maximum Dose: The maximum daily dose should not exceed 3,600mg.
2.2. Children (6 to 12 Years)
- Dosage Determination: The dosage for children is based on their weight.
- Starting Dose: Your doctor will determine the appropriate starting dose based on the child’s weight and condition.
- Adjustment: The dose may be adjusted gradually based on the child’s response and tolerance, as determined by their healthcare provider.
2.3. Important Considerations
- Divided Doses: Gabapentin is usually taken in divided doses throughout the day to maintain consistent blood levels and reduce the risk of side effects.
- Consistent Timing: Try to take your doses at the same times each day to help you remember and maintain a steady level of medication in your body.
- Individual Needs: Dosage adjustments are highly individualized and should only be made under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
3. Gabapentin Dosage for Nerve Pain
For nerve pain, gabapentin dosage also varies depending on the individual and the nature of the pain.
3.1. Adults
- Starting Dose: The typical starting dose for nerve pain is 900mg per day, divided into three doses.
- Titration: Your doctor may gradually increase the dose based on your response and tolerance.
- Effective Range: The effective dose range is generally between 1,800mg and 3,600mg per day, divided into three doses.
3.2. Important Considerations
- Individual Response: Some individuals may find relief with lower doses, while others may require higher doses to manage their pain effectively.
- Regular Assessment: Regular assessment by your doctor is crucial to ensure the dosage is optimized for pain relief while minimizing side effects.
4. How to Take Gabapentin
Proper administration of gabapentin is essential to ensure its effectiveness and minimize potential side effects.
4.1. Capsules and Tablets
- Swallowing: Swallow gabapentin capsules and tablets whole with a full glass of water or juice.
- Chewing: Do not chew, crush, or break the capsules or tablets, as this can affect how the medication is absorbed.
4.2. Oral Solution (Liquid)
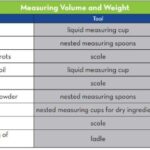
- Measuring: If you are taking gabapentin in liquid form, use a calibrated measuring spoon or oral syringe to ensure accurate dosing.
- Consistency: Do not use household spoons, as they may not provide accurate measurements.
4.3. General Tips
- With or Without Food: Gabapentin can be taken with or without food. However, it’s best to be consistent and take it the same way each day.
- Evenly Spaced Doses: Space your doses evenly throughout the day. For example, if you take gabapentin three times a day, you might take it in the morning, early afternoon, and at bedtime.
5. Duration of Gabapentin Treatment
The length of time you need to take gabapentin depends on the condition being treated.
5.1. Epilepsy
- Long-Term Treatment: If you have epilepsy, you may need to take gabapentin for many years to maintain seizure control.
- Consistent Use: It is crucial to take gabapentin regularly as prescribed and not to stop taking it suddenly, as this can trigger seizures.
5.2. Nerve Pain
- Variable Duration: The duration of treatment for nerve pain varies. Some individuals may only need to take gabapentin for a few months, while others may require longer-term management.
- Gradual Discontinuation: Once your pain is well-controlled, your doctor may gradually reduce the dose to see if you can discontinue the medication without the pain returning.
6. What to Do If You Forget a Dose
Missing a dose of gabapentin can affect its effectiveness. Here’s what to do if you forget a dose:
- If You Remember Shortly After: Take the missed dose as soon as you remember.
- If It’s Almost Time for the Next Dose: If it is within two hours of your next scheduled dose, skip the missed dose and take your next dose as usual.
- Do Not Double Dose: Never take two doses at the same time to make up for a missed dose.
- Set Reminders: If you frequently forget doses, consider setting an alarm or using a medication reminder app to help you remember.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-to-do-if-you-miss-a-dose-of-medication-5266838-v1-4489841401a7490785f7f65bc3c9893c.png)
Alt text: Pills and a reminder clock to emphasize the importance of remembering to take medication.
7. What to Do If You Take Too Much Gabapentin
Taking too much gabapentin can lead to serious side effects.
7.1. Symptoms of Overdose
Symptoms of a gabapentin overdose may include:
- Dizziness
- Sleepiness
- Double vision
- Slurred speech
- Diarrhea
- Loss of consciousness (fainting)
7.2. Emergency Actions
If you suspect you have taken too much gabapentin:
- Seek Immediate Medical Attention: Contact emergency services immediately or go to the nearest emergency room.
- Call for Advice: You can also call a poison control center for advice.
- Do Not Drive: Do not attempt to drive yourself to the hospital. Ask someone to drive you or call for an ambulance.
- Bring Information: Bring the gabapentin packet or leaflet, any remaining medication, and a list of any other medications you are taking.
8. Stopping Gabapentin: What You Need to Know
It is crucial not to stop taking gabapentin suddenly, as this can lead to serious withdrawal symptoms.
8.1. Potential Withdrawal Symptoms
Suddenly stopping gabapentin can cause:
- Anxiety
- Difficulty sleeping (insomnia)
- Nausea
- Pain
- Sweating
- Seizures (especially in individuals with epilepsy)
8.2. Gradual Dose Reduction
To prevent withdrawal symptoms, your doctor will gradually reduce your dose of gabapentin over time. This process allows your body to adjust to the lower dose and minimizes the risk of withdrawal effects.
8.3. Consult Your Doctor
Always consult your doctor before making any changes to your gabapentin dosage or stopping the medication altogether.
9. Potential Side Effects of Gabapentin
Gabapentin, like all medications, can cause side effects. Being aware of these potential side effects can help you manage them effectively.
9.1. Common Side Effects
Common side effects of gabapentin include:
- Dizziness
- Drowsiness
- Fatigue
- Uncoordinated movements
- Swelling, especially in the hands and feet
- Blurred vision
- Dry mouth
9.2. Less Common Side Effects
Less common side effects may include:
- Memory problems
- Difficulty concentrating
- Mood changes
- Anxiety or depression
- Nystagmus (rapid, involuntary eye movements)
9.3. Rare Side Effects
Rare but serious side effects include:
- Severe allergic reactions (rash, itching, swelling, difficulty breathing)
- Suicidal thoughts or behaviors
- Liver problems (jaundice, abdominal pain, dark urine)
9.4. Managing Side Effects
If you experience side effects while taking gabapentin:
- Talk to Your Doctor: Discuss your symptoms with your doctor. They may adjust your dosage or recommend strategies to manage the side effects.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to help with dry mouth and other side effects.
- Avoid Alcohol: Alcohol can worsen some side effects, such as dizziness and drowsiness.
- Be Careful with Activities: Be cautious when driving or operating heavy machinery until you know how gabapentin affects you.
10. Precautions and Warnings
Before taking gabapentin, it’s important to be aware of certain precautions and warnings.
10.1. Medical History
Inform your doctor if you have any of the following conditions:
- Kidney disease
- Liver disease
- Heart problems
- Breathing problems
- Mental health issues (depression, anxiety, suicidal thoughts)
- Allergies to any medications
10.2. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
- Pregnancy: Gabapentin may not be safe to take during pregnancy. Discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor.
- Breastfeeding: Gabapentin can pass into breast milk. Consult your doctor before breastfeeding while taking gabapentin.
10.3. Drug Interactions
Gabapentin can interact with other medications, including:
- Opioid pain relievers (e.g., morphine, codeine)
- Antacids
- Alcohol
- Other anticonvulsants
10.4. General Precautions
- Follow Instructions: Take gabapentin exactly as prescribed by your doctor.
- Regular Check-Ups: Attend regular check-ups with your doctor to monitor your condition and adjust your dosage as needed.
- Do Not Share: Do not share your medication with others, even if they have similar symptoms.
11. Gabapentin and Elderly Patients
Elderly patients may be more susceptible to certain side effects of gabapentin, such as dizziness, drowsiness, and uncoordinated movements.
11.1. Dosage Adjustments
Doctors often prescribe lower doses of gabapentin for elderly patients to minimize the risk of side effects.
11.2. Monitoring
Close monitoring is essential to ensure the medication is effective and well-tolerated.
11.3. Fall Risk
Elderly patients should be particularly careful to avoid falls, as gabapentin can increase the risk of dizziness and unsteadiness.
12. Gabapentin and Children
Gabapentin can be used to treat epilepsy in children, but the dosage must be carefully determined based on their weight and age.
12.1. Dosage Considerations
The dosage for children is typically lower than for adults and is adjusted based on their weight.
12.2. Side Effects
Children may experience different side effects than adults. Common side effects in children include drowsiness, hyperactivity, and behavioral changes.
12.3. Monitoring
Regular monitoring by a healthcare provider is crucial to ensure the medication is effective and safe for the child.
13. Alternative Treatments
In some cases, alternative treatments may be considered in addition to or instead of gabapentin.
13.1. For Epilepsy
- Other anticonvulsant medications
- Ketogenic diet
- Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS)
- Surgery (in select cases)
13.2. For Nerve Pain
- Other pain medications (e.g., NSAIDs, opioids, antidepressants)
- Physical therapy
- Nerve blocks
- Acupuncture
- Topical treatments (e.g., capsaicin cream)
13.3. Consultation
Discuss alternative treatment options with your doctor to determine the best approach for your specific condition.
14. Lifestyle Adjustments
In addition to medication, certain lifestyle adjustments can help manage epilepsy and nerve pain.
14.1. For Epilepsy
- Adequate Sleep: Getting enough sleep can help reduce the frequency of seizures.
- Stress Management: Managing stress through relaxation techniques can also be beneficial.
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet can support overall health.
- Avoid Triggers: Identify and avoid potential seizure triggers, such as flashing lights or alcohol.
14.2. For Nerve Pain
- Exercise: Regular exercise can help improve circulation and reduce pain.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help improve mobility and reduce pain.
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet can support nerve health.
- Stress Management: Managing stress through relaxation techniques can also be beneficial.
Alt text: Lifestyle adjustments for nerve pain, including exercise, physical therapy, healthy diet, and stress management.
15. Understanding Breakthrough Pain
Breakthrough pain refers to episodes of pain that occur despite taking regular pain medication.
15.1. Causes
Breakthrough pain can be caused by:
- Changes in medication effectiveness
- Increased activity levels
- Stress
- Underlying medical conditions
15.2. Management
To manage breakthrough pain:
- Talk to Your Doctor: Discuss your breakthrough pain with your doctor. They may adjust your gabapentin dosage or prescribe additional medications.
- Keep a Pain Diary: Keep a record of your pain levels, activities, and medications to help identify patterns and triggers.
- Use Non-Medication Strategies: Use non-medication strategies such as heat, ice, and relaxation techniques to help manage breakthrough pain.
16. Importance of Regular Monitoring
Regular monitoring by a healthcare professional is essential for ensuring the safe and effective use of gabapentin.
16.1. Monitoring Parameters
During regular check-ups, your doctor may monitor:
- Your response to the medication
- Any side effects you are experiencing
- Your kidney and liver function
- Your overall health
16.2. Dosage Adjustments
Based on the results of these assessments, your doctor may adjust your gabapentin dosage to optimize its effectiveness and minimize side effects.
17. Gabapentin and Mental Health
Gabapentin can affect mental health in some individuals.
17.1. Potential Effects
Some people may experience:
- Mood changes
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Suicidal thoughts or behaviors
17.2. Monitoring
If you experience any changes in your mental health while taking gabapentin, it is important to inform your doctor immediately.
17.3. Treatment
Your doctor may adjust your medication or recommend additional treatment, such as therapy or counseling.
18. Storage and Disposal
Proper storage and disposal of gabapentin are important to ensure its safety and effectiveness.
18.1. Storage
- Keep in Original Container: Store gabapentin in its original container, tightly closed.
- Protect from Moisture and Heat: Store the medication in a cool, dry place, away from moisture and heat.
- Keep Out of Reach of Children: Keep gabapentin out of the reach of children and pets.
18.2. Disposal
- Follow Instructions: Follow the instructions on the medication label for proper disposal.
- Medication Take-Back Programs: Take advantage of medication take-back programs when available.
- Do Not Flush: Do not flush gabapentin down the toilet unless specifically instructed to do so.
19. Travel Considerations
If you are traveling while taking gabapentin, there are several things to keep in mind.
19.1. Medication Supply
- Bring Enough Medication: Make sure to bring enough medication to last for the duration of your trip, plus a few extra days in case of delays.
- Original Packaging: Keep your medication in its original packaging.
19.2. Documentation
- Doctor’s Letter: Carry a letter from your doctor stating that you are taking gabapentin and explaining why you need it.
- Prescription Copy: Bring a copy of your prescription.
19.3. Regulations
- Check Regulations: Check the regulations regarding medication in the countries you will be visiting.
- Airport Security: Be prepared to show your medication and documentation to airport security.
20. Finding Support and Resources
Living with epilepsy or nerve pain can be challenging, but there are many support and resources available to help you.
20.1. Support Groups
- Local Support Groups: Join a local support group to connect with others who are living with the same condition.
- Online Forums: Participate in online forums to share experiences and get advice.
20.2. Educational Resources
- Medical Websites: Visit reputable medical websites for information about epilepsy and nerve pain.
- Patient Organizations: Contact patient organizations for educational materials and support.
20.3. Healthcare Professionals
- Doctors: Consult with your doctor for medical advice and treatment.
- Therapists: Work with a therapist or counselor to manage the emotional challenges of living with a chronic condition.
By understanding these various aspects of gabapentin, you can work with your healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan that meets your individual needs and helps you manage your condition effectively.
Navigating the complexities of gabapentin dosage and treatment requires expert guidance; don’t face it alone. At HOW.EDU.VN, we provide access to leading doctors and specialists who can offer personalized advice and support.
Are you struggling to find the right gabapentin dosage or manage its side effects? Our team of experienced doctors is ready to provide expert guidance and support; contact us today at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States, Whatsapp: +1 (310) 555-1212, or visit our website at how.edu.vn to schedule a consultation and take control of your health.
FAQ: Gabapentin Dosage and Usage
1. What is gabapentin used for?
Gabapentin is primarily used to treat epilepsy (seizures) and nerve pain (neuralgia), often associated with conditions like shingles or diabetic neuropathy.
2. How much gabapentin should I take for nerve pain?
The typical starting dose for adults is 900mg per day, divided into three doses. Your doctor may gradually increase the dose based on your response, typically up to 1,800mg to 3,600mg per day.
3. What is the maximum dosage of gabapentin?
The maximum daily dose of gabapentin is generally 3,600mg, divided into three doses.
4. Can I take gabapentin with or without food?
Gabapentin can be taken with or without food, but it’s best to be consistent and take it the same way each day.
5. What should I do if I miss a dose of gabapentin?
If you remember shortly after, take the missed dose as soon as you remember. If it’s almost time for your next dose (within two hours), skip the missed dose and take your next dose as usual. Do not double the dose to make up for a missed one.
6. What are the common side effects of gabapentin?
Common side effects include dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue, uncoordinated movements, swelling, blurred vision, and dry mouth.
7. Can I stop taking gabapentin suddenly?
No, you should not stop taking gabapentin suddenly. Stopping abruptly can lead to withdrawal symptoms like anxiety, difficulty sleeping, nausea, pain, sweating, and seizures (especially in those with epilepsy).
8. Is gabapentin safe during pregnancy?
Gabapentin may not be safe during pregnancy. Discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor.
9. Can gabapentin affect my mental health?
Yes, some people may experience mood changes, anxiety, depression, or suicidal thoughts while taking gabapentin. Report any significant changes in mental health to your doctor immediately.
10. How should I store gabapentin?
Store gabapentin in its original container, tightly closed, in a cool, dry place away from moisture, heat, and out of reach of children and pets.