How Much Is 1 Gb of data? Understanding gigabyte (GB) and its real-world applications is crucial in today’s digital landscape. This comprehensive guide by HOW.EDU.VN breaks down the concept of a gigabyte, its historical context, and its relevance in modern technology, providing clarity on data storage and usage.
1. Defining a Gigabyte: The Basics
A gigabyte (GB) is a fundamental unit of data storage capacity, often cited when discussing computer memory, smartphone storage, and internet data plans. A gigabyte is roughly equivalent to one billion bytes. In decimal notation (base 10), one GB equals precisely 1,000,000,000 bytes. In binary notation (base 2), it’s 2^30 bytes, or 1,073,741,824 bytes. “Giga” comes from the Greek word meaning “giant,” reflecting its significant size relative to smaller units like kilobytes or megabytes.
1.1. Decimal vs. Binary: Understanding the Discrepancy
The discrepancy between decimal and binary representation often leads to confusion. Storage manufacturers typically use the decimal definition (1 GB = 1 billion bytes) because it presents larger, more appealing numbers to consumers. However, computer operating systems often use the binary definition, which results in a slightly lower reported capacity. This difference is why a 1 TB drive might show up as slightly less than 1 TB on your computer.
1.2. Gibibytes (GiB): A More Accurate Term
To address the ambiguity, the term “gibibyte” (GiB) was introduced to specifically denote the binary gigabyte (1,073,741,824 bytes). While not universally adopted, using GiB can help clarify whether you’re referring to the decimal or binary value.
2. The Historical Context of the Gigabyte
The gigabyte became a common unit of measurement for data storage in the mid-1980s. It marked a significant leap in storage capacity compared to earlier units like kilobytes and megabytes.
2.1. The IBM 3380: The First Gigabyte Hard Drive
In 1980, IBM introduced the 3380, the first hard drive to offer gigabyte capacity. This massive device, housed in a refrigerator-sized cabinet, had a capacity of 1.26 GB and cost between $81,000 and $142,000. This underscores how far storage technology has advanced.
2.2. The Evolution of Storage Capacity
Early personal computers had very limited storage. The IBM Personal Computer XT, released in 1983, was the first PC with a built-in hard drive as a standard feature, offering a meager 10 MB or 20 MB of storage. It wasn’t until 1991 that 1 GB drives became available, priced at around $3,000.
The growth of storage capacity has been exponential. Hitachi released the first 1 TB drive in 2007, highlighting the rapid pace of innovation. Today, hard drives offer up to 20 TB of storage, and solid-state drives (SSDs) can reach 100 TB.
3. Putting 1 GB into Perspective: Real-World Examples
To better understand the value of 1 GB, let’s consider some everyday examples of how much data different activities consume:
3.1. Data Consumption Examples
| Activity | Data Usage | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Downloading Songs | ~4 MB per song | Approximately 250 songs can be downloaded within 1 GB. |
| Sending/Receiving Emails | ~0.16 MB per email | Around 6,180 emails (without attachments) can be sent/received. |
| High-Resolution Photos | ~4 MB per photo | Approximately 250 10-megapixel photos can be stored. |
| Emails with Attachments | ~0.3 MB per email | About 3,333 emails with standard-sized attachments can be handled. |
| Standard Definition Movies | ~200 MB per hour | Around 5 hours of standard-definition movies can be streamed or stored. |
| YouTube Videos | ~2.8 MB per minute | Approximately 353 one-minute YouTube videos can be watched. |
| Web Browsing | Varies widely | Depends on the complexity and media content of websites visited. |
| Social Media | Highly variable | Heavily dependent on video and image consumption; can quickly deplete data allowances if not managed carefully. |
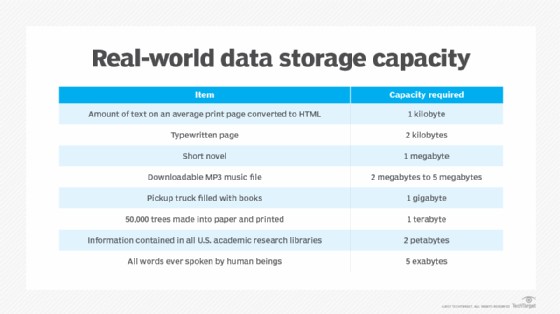 Real-world storage capacity examples
Real-world storage capacity examples
3.2. The Importance of Data Management
These examples highlight the importance of data management in the digital age. Streaming high-definition videos, downloading large files, and frequent use of social media can quickly deplete data allowances on mobile plans or fill up storage drives.
4. GB on Your Phone: Storage and Data Plans
When purchasing smartphones, storage capacity (measured in gigabytes) is a crucial consideration. The more gigabytes a phone has, the more apps, photos, videos, and files it can store.
4.1. Smartphone Storage Options
Most modern smartphones offer a range of storage options, typically starting at 128 GB and going up to 1 TB or more. For instance, the Apple iPhone 13 Pro offers 128 GB, 256 GB, 512 GB, and 1 TB options, while the Samsung Galaxy Z Flip3 5G offers 128 GB or 256 GB.
4.2. Operating System Overhead
It’s important to note that the actual usable storage is always less than the advertised capacity. The operating system (such as iOS or Android) and pre-installed apps consume a significant portion of the storage space. For example, an iPhone might use between 11 GB and 14 GB for iOS and pre-installed apps. Software updates can also affect available capacity.
4.3. Mobile Data Plans
Gigabyte measurements also play a crucial role in selecting cellular service plans. Many plans offer unlimited calling and texting but limit the amount of data that can be transferred. Data allowances are often the primary differentiator between plans.
T-Mobile, for example, offers Essentials, Magenta, and Magenta MAX plans. The Essentials plan provides 50 GB of data, Magenta provides 100 GB, and Magenta MAX offers unlimited data. The Magenta plan includes 5 GB of mobile hotspot data, while the MAX plan offers 40 GB of high-speed data and unlimited data at 3G speeds.
4.4. Choosing the Right Plan
Selecting the right data plan depends on your usage habits. If you primarily use your phone for browsing, email, and light social media, a smaller data plan might suffice. However, if you frequently stream videos, download large files, or use your phone as a mobile hotspot, a larger data plan or an unlimited option is essential.
5. Gigabytes vs. Gigabits: Understanding the Difference
It’s essential to distinguish between gigabytes (GB) and gigabits (Gb), as they are often confused. A bit (binary digit) is the smallest unit of computer data, while a byte is a group of 8 bits.
5.1. Bytes vs. Bits
- Byte (B): Typically used to describe data at rest, such as storage capacity (e.g., hard drive size or RAM).
- Bit (b): Typically used to describe data transfer rates, such as network speeds or internet connection speeds.
5.2. Conversion
There are 8 bits in a byte, so 1 GB (gigabyte) equals 8 Gb (gigabits). For example, a 10 Gigabit Ethernet connection (10 Gbps) can theoretically transfer 1.25 GB of data per second.
5.3. Application
Computer memory and storage are often measured in bytes, such as a desktop with 16 GB of RAM and 750 GB of storage. Data transfer rates are usually measured in bits, such as a 10 gigabits per second internet connection.
6. Gigabyte-Sized Storage Options and Pricing
Various storage media offer gigabyte-range capacity, with prices varying significantly.
6.1. Common Storage Types
- Hard Disk Drives (HDDs): Traditional mechanical storage devices offering large capacities at relatively low prices.
- Solid State Drives (SSDs): Faster and more durable than HDDs but typically more expensive per gigabyte.
- Flash Drives: Portable storage devices, such as USB drives and memory cards, offering convenient data transfer.
- Blu-ray Discs and DVDs: Optical storage media for storing movies, music, and data.
6.2. Price Trends
The price per gigabyte has been steadily declining over the years. In 2000, the average price per gigabyte of an HDD was nearly $8, according to IDC. By 2017, it had dropped to 3.5 cents per gigabyte. Today, some HDDs offer storage for under 2 cents per gigabyte.
SSDs have historically been more expensive per gigabyte than HDDs. However, as SSD capacities increase and prices decrease, the gap is narrowing. The average price per gigabyte for SSDs is now around 9 cents or more.
6.3. Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
When evaluating storage options, it’s important to consider factors beyond price per gigabyte. Durability, footprint, power consumption, and maintenance costs also contribute to the total cost of ownership (TCO). SSDs, for example, may have a higher upfront cost but offer lower power consumption and greater durability, potentially reducing long-term costs.
7. The Future of Data Storage: Beyond the Gigabyte
While gigabytes are still relevant in today’s digital landscape, terabytes (TB) are becoming increasingly common for describing storage capacity. As technology advances and data demands grow, even larger units like petabytes (PB) and exabytes (EB) will become more prevalent.
7.1. The Rise of Terabytes
Terabytes are now the standard unit for measuring storage capacity in many devices, including laptops, desktop computers, and external hard drives. Cloud storage providers also frequently use terabytes to describe storage plans.
7.2. Petabytes and Exabytes
Petabytes and exabytes are primarily used in enterprise environments for managing massive amounts of data. Data centers, research institutions, and large corporations often require petabytes or exabytes of storage to handle their data needs.
7.3. The Ever-Growing Demand for Storage
The demand for data storage continues to grow exponentially, driven by factors such as increasing use of digital media, the proliferation of IoT devices, and the rise of big data analytics. As a result, storage technology will continue to evolve, with new innovations and ever-larger capacities on the horizon.
8. Expert Insights and Consulting at HOW.EDU.VN
Navigating the complexities of data storage and usage can be challenging. At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with leading experts and PhDs who can provide personalized guidance and solutions.
8.1. Connecting with Experts
Our platform offers direct access to over 100 renowned PhDs and specialists across various fields. Whether you need advice on selecting the right storage solutions, optimizing data management strategies, or understanding the latest technological advancements, our experts are here to help.
8.2. Personalized Consultations
We understand that every individual and business has unique needs. Our experts provide in-depth, personalized consultations to address your specific challenges and goals. We offer tailored advice and practical solutions to help you make informed decisions and achieve optimal outcomes.
8.3. Expertise Across Disciplines
Our team of experts covers a wide range of disciplines, including:
- Computer Science and Engineering: Advice on hardware, software, and data infrastructure.
- Data Management and Analytics: Strategies for storing, processing, and analyzing large datasets.
- Cybersecurity: Guidance on protecting your data from threats and ensuring privacy.
- Business and Technology Strategy: Insights into leveraging technology for business growth and innovation.
8.4. Benefits of Expert Consultation
- Save Time and Money: Avoid costly mistakes by getting expert advice from the start.
- Make Informed Decisions: Gain a deeper understanding of the options available and choose the best solutions for your needs.
- Optimize Performance: Improve efficiency and productivity by implementing best practices and innovative strategies.
- Stay Ahead of the Curve: Keep up with the latest technological advancements and trends.
9. Addressing Common Challenges: How HOW.EDU.VN Can Help
Many individuals and businesses face common challenges when dealing with data storage and management. HOW.EDU.VN is here to provide solutions.
9.1. Difficulty Finding Qualified Experts
Many people struggle to find experts with the right qualifications and experience. Our platform offers a curated network of vetted PhDs and specialists, ensuring you have access to top-tier talent.
9.2. High Costs of Traditional Consulting
Traditional consulting services can be expensive and time-consuming. HOW.EDU.VN offers a cost-effective and efficient alternative, connecting you with experts quickly and easily.
9.3. Concerns About Data Security and Confidentiality
Protecting your data is our top priority. We maintain strict security protocols and confidentiality agreements to ensure your information is safe and secure.
9.4. Difficulty Articulating Needs
Sometimes, it can be difficult to clearly articulate your needs and challenges. Our experts are skilled at asking the right questions and understanding your specific requirements, ensuring you receive the most relevant and effective advice.
10. Call to Action: Connect with Experts at HOW.EDU.VN Today
Are you ready to unlock the power of expert guidance? Whether you have questions about data storage, technology strategy, or any other area of expertise, HOW.EDU.VN is here to help.
10.1. Contact Us
- Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
- Website: HOW.EDU.VN
10.2. Why Choose HOW.EDU.VN?
- Access to Top-Tier Experts: Connect with over 100 renowned PhDs and specialists.
- Personalized Consultations: Receive tailored advice and practical solutions.
- Cost-Effective Solutions: Get expert guidance without breaking the bank.
- Secure and Confidential: Your data is protected with the highest security standards.
10.3. Take the Next Step
Don’t let data storage challenges hold you back. Contact HOW.EDU.VN today and discover how our experts can help you achieve your goals. Visit our website or reach out via WhatsApp to schedule a consultation.
By leveraging the expertise available at HOW.EDU.VN, you can navigate the complexities of the digital world with confidence and achieve optimal results.
FAQ: Understanding Gigabytes and Data Usage
Here are some frequently asked questions about gigabytes and data usage, along with detailed answers to help you better understand this essential concept.
1. What exactly is a gigabyte (GB)?
A gigabyte (GB) is a unit of data storage capacity equal to approximately one billion bytes. In decimal notation (base 10), it’s exactly 1,000,000,000 bytes. In binary notation (base 2), it’s 1,073,741,824 bytes. It’s commonly used to measure the storage capacity of devices like hard drives, SSDs, and smartphones, as well as data allowances in mobile plans.
2. How many megabytes (MB) are in a gigabyte (GB)?
There are 1,000 megabytes (MB) in a gigabyte (GB) when using decimal notation. In binary notation, there are 1,024 MB in a GB. This difference can sometimes cause confusion, but it’s important to understand which measurement system is being used.
3. How much data does streaming a movie use?
The amount of data used when streaming a movie depends on the video quality. Standard definition (SD) movies typically use around 700 MB to 1 GB per hour. High definition (HD) movies can use between 1.5 GB and 3 GB per hour, while ultra-high definition (4K) movies can consume 5 GB or more per hour.
4. How many songs can I store in 1 GB of storage?
The number of songs you can store in 1 GB of storage depends on the audio quality and file format. A typical MP3 song with a bitrate of 128kbps (kilobits per second) is about 4 MB in size. Therefore, you can store approximately 250 songs in 1 GB of storage.
5. How much data does it take to browse the internet?
The amount of data used for browsing the internet varies widely depending on the websites you visit and the content they contain. Simple text-based websites use very little data, while websites with lots of images and videos consume more data. On average, browsing the internet might use between 50 MB and 200 MB per hour.
6. What does 1 GB of data get you on a mobile plan?
1 GB of data on a mobile plan can allow you to:
- Browse the internet for approximately 5-20 hours.
- Stream about 1 hour of standard definition video.
- Send or receive thousands of emails.
- Use social media for several hours, depending on media consumption.
- Download or stream about 250 songs.
It’s important to monitor your data usage to avoid exceeding your plan’s limits.
7. How can I check my data usage on my smartphone?
Most smartphones have built-in tools for monitoring data usage. On iPhones, you can go to Settings > Cellular to see how much data you’ve used in the current period. On Android devices, you can go to Settings > Network & Internet > Data Usage to view your data usage.
8. What’s the difference between GB and GiB?
GB (gigabyte) and GiB (gibibyte) are both units of data storage, but they use different measurement systems. GB typically refers to the decimal definition (1 GB = 1,000,000,000 bytes), while GiB refers to the binary definition (1 GiB = 1,073,741,824 bytes). GiB is often used in technical contexts to avoid ambiguity.
9. How do I choose the right data plan for my needs?
Choosing the right data plan depends on your usage habits. Consider how often you stream videos, download files, use social media, and browse the internet. If you’re a heavy data user, an unlimited plan might be the best option. If you only use data occasionally, a smaller data plan might suffice.
10. What are some tips for reducing data usage on my phone?
Here are some tips for reducing data usage on your phone:
- Connect to Wi-Fi whenever possible.
- Disable automatic app updates over cellular data.
- Download music and videos for offline listening and viewing.
- Use data-saving features in apps like YouTube and Netflix.
- Monitor your data usage regularly.
- Disable background data usage for apps you don’t use frequently.
- Use a data compression browser like Opera Mini.
By understanding these common questions and implementing data-saving strategies, you can effectively manage your data usage and choose the right data plan for your needs. If you have more complex questions or need personalized advice, consider reaching out to the experts at how.edu.vn for a consultation.