How Much Is A 1 Gigabyte worth in today’s digital landscape? At HOW.EDU.VN, we provide you with expert insights into the cost, usage, and value of a gigabyte, ensuring you’re well-informed. Understanding the value of data storage and transfer is crucial in making informed decisions about your digital needs, whether it’s choosing a phone plan, upgrading your storage devices, or managing cloud services.
1. Understanding the Basics of a Gigabyte (GB)
A gigabyte (GB) is a unit of data storage capacity, crucial for understanding digital device capabilities and data plans. Essentially, a gigabyte is approximately one billion bytes, used to measure the amount of data that can be stored or transferred. This measurement is fundamental in today’s digital world, influencing decisions from smartphone purchases to data plan selections.
1.1. What Exactly is a Gigabyte?
In the realm of digital storage, a gigabyte is a substantial unit, commonly used to quantify storage space on devices like hard drives, SSDs, and smartphones, learn with our doctors at HOW.EDU.VN. It’s essential to differentiate between decimal (base 10) and binary (base 2) notations. In decimal, 1 GB equals 1 billion bytes, while in binary, it’s 1,073,741,824 bytes. This difference often leads to discrepancies in reported storage capacity, which will be handled by our expert team.
1.2. Evolution of the Gigabyte
The gigabyte became a standard measurement in the mid-1980s, marking a significant advancement in data storage technology. As technology evolved, the gigabyte paved the way for larger units like terabytes and petabytes. Despite the emergence of these larger units, the gigabyte remains a relevant and practical measure for everyday digital activities.
1.3. Gigabytes vs. Other Data Units
Understanding how gigabytes relate to other data units helps contextualize their value:
- Megabyte (MB): 1 GB = 1,000 MB (decimal) or 1,024 MB (binary)
- Kilobyte (KB): 1 GB = 1,000,000 KB (decimal) or 1,048,576 KB (binary)
- Byte: 1 GB = 1,000,000,000 bytes (decimal) or 1,073,741,824 bytes (binary)
- Terabyte (TB): 1 TB = 1,000 GB (decimal) or 1,024 GB (binary)
2. Real-World Examples: What Can You Store in a Gigabyte?
To put the size of a gigabyte into perspective, let’s look at what it can hold. A single gigabyte can accommodate a variety of digital content, making it easier to understand its capacity in practical terms.
2.1. Media Storage
- Music: Approximately 250 songs (assuming an average song size of 4MB).
- Photos: Around 250 high-resolution photos (10-megapixel).
- Videos: About 5 hours of standard-definition video.
- YouTube: Roughly 353 one-minute videos.
2.2. Documents and Emails
- Emails: Up to 50,000 emails without attachments.
- Emails with Attachments: Approximately 3,333 emails with standard-sized attachments.
- Documents: Thousands of text-based documents.
2.3. Software and Apps
- Mobile Apps: Depending on the app size, you can store multiple apps, but larger games may require more than 1 GB.
- Software: Smaller software programs can fit within 1 GB, but more complex applications need more space.
3. How Much Does a Gigabyte Cost in Different Contexts?
The cost of a gigabyte varies depending on how you’re using it. From mobile data plans to cloud storage, understanding these costs can help you make informed decisions and manage your expenses effectively.
3.1. Mobile Data Plans
Mobile data plans often price data in gigabyte increments. Here’s a general idea of what you might expect:
- Budget Plans: $5 – $10 per gigabyte.
- Mid-Range Plans: $2 – $5 per gigabyte.
- Premium Plans: Often include unlimited data, but may throttle speeds after a certain amount of usage (e.g., 50 GB).
3.2. Cloud Storage
Cloud storage services like Google Drive, Dropbox, and Amazon S3 charge based on the amount of storage you use. Here’s a typical pricing range:
- Free Tier: Often includes a few gigabytes (e.g., 15 GB with Google Drive).
- Basic Plans: $2 – $5 per month for 100 GB to 200 GB, which translates to a few cents per gigabyte.
- Business Plans: Vary widely but are generally more cost-effective per gigabyte for large storage needs.
3.3. USB Drives and Memory Cards
The cost of USB drives and memory cards has decreased significantly over the years. As of 2023:
- USB Drives: $5 – $15 for a 32 GB drive, translating to about $0.15 – $0.47 per gigabyte.
- Memory Cards: Similar pricing to USB drives, with slight variations based on brand and speed.
3.4. Hard Drives and SSDs
Internal and external storage devices offer varying costs per gigabyte.
- HDDs: $0.02 – $0.05 per gigabyte.
- SSDs: $0.09 or more per gigabyte, offering faster performance at a higher cost.
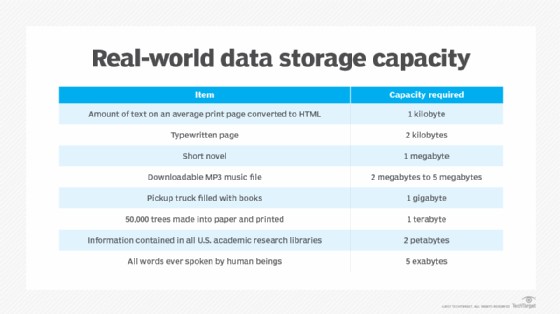 Real-world storage capacity examples showing HDD, SDD, USB Drive, and Cloud Storage
Real-world storage capacity examples showing HDD, SDD, USB Drive, and Cloud Storage
4. Factors Influencing the Price of a Gigabyte
Several factors affect the price of a gigabyte, including technology, market demand, and competition. Let’s explore these in detail.
4.1. Technology and Innovation
Advancements in storage technology have led to increased capacities and lower prices. As new technologies like high-density SSDs emerge, the cost per gigabyte tends to decrease over time.
4.2. Market Demand
High demand for storage solutions drives innovation and production, leading to economies of scale. Conversely, lower demand can result in higher prices due to reduced production volumes.
4.3. Competition Among Providers
Intense competition among cloud storage providers and hardware manufacturers drives prices down. Companies often offer competitive pricing and promotional deals to attract and retain customers.
4.4. Geographic Location
Prices can vary based on geographic location due to factors like local taxes, import duties, and regional market conditions.
4.5. Contract Length and Bundling
Long-term contracts and bundled services can affect the price per gigabyte. Providers often offer discounts for extended commitments or when combining multiple services.
5. How Much Data Do You Really Need?
Determining your data needs is crucial for making cost-effective decisions. Understanding your usage patterns can help you choose the right data plan or storage solution without overspending.
5.1. Assessing Your Data Usage
Start by monitoring your current data usage. Most smartphones and operating systems have built-in tools to track data consumption. Look at your monthly usage trends to identify patterns and estimate future needs.
5.2. Common Data Usage Scenarios
- Light User: Primarily uses data for email, browsing, and occasional social media. A few gigabytes per month may suffice.
- Moderate User: Regularly streams music and videos, engages in social media, and uses apps. 10-20 GB per month may be necessary.
- Heavy User: Streams high-definition videos, plays online games, and frequently downloads large files. 50 GB or more per month may be required.
5.3. Tips for Managing Data Usage
- Use Wi-Fi: Connect to Wi-Fi whenever possible to reduce mobile data usage.
- Download Content: Download music, videos, and podcasts for offline use.
- Optimize Streaming Settings: Adjust streaming quality to reduce data consumption.
- Monitor App Usage: Identify data-hungry apps and adjust their settings or usage.
6. Gigabytes in Smartphones: Storage vs. Data Plans
When buying a smartphone, it’s essential to consider both internal storage (measured in gigabytes) and the amount of data provided in your mobile plan.
6.1. Internal Storage
Internal storage determines how many apps, photos, videos, and files you can store on your device. Most smartphones offer options ranging from 64 GB to 1 TB.
- 64 GB: Suitable for light users who primarily use cloud storage.
- 128 GB: A good balance for most users, providing enough space for apps, media, and files.
- 256 GB or More: Ideal for heavy users who store a lot of high-resolution media and large files.
6.2. Mobile Data Plans
Mobile data plans dictate how much data you can use for activities like browsing, streaming, and downloading while not connected to Wi-Fi.
- Limited Data Plans: Offer a set amount of gigabytes per month.
- Unlimited Data Plans: Provide unlimited data but may throttle speeds after a certain usage threshold.
6.3. Choosing the Right Combination
Consider your storage needs and data usage patterns when selecting a smartphone and data plan. It’s often better to have more internal storage and a moderate data plan than vice versa.
7. Decimal vs. Binary: Understanding the Discrepancy
The difference between decimal and binary measurements can be confusing. It’s important to understand how these systems affect reported storage capacity.
7.1. Decimal (Base 10) vs. Binary (Base 2)
- Decimal: Uses powers of 10 (10^3 = 1,000). Storage manufacturers often use decimal measurements because they make the capacity appear larger.
- Binary: Uses powers of 2 (2^10 = 1,024). Computer operating systems typically use binary measurements, resulting in lower reported capacities.
7.2. The Impact on Reported Storage
A hard drive advertised as 500 GB (decimal) may only show up as 466 GB (binary) on your computer. This discrepancy is due to the different ways of calculating a gigabyte.
7.3. Gibibytes (GiB) vs. Gigabytes (GB)
To reduce confusion, the term “gibibyte” (GiB) was introduced to specifically refer to binary gigabytes. However, many systems still use “GB” for both decimal and binary measurements, leading to continued ambiguity.
8. The Future of Gigabytes: What’s Next?
As technology advances, the role of the gigabyte is evolving. While terabytes and petabytes are becoming more common for large storage needs, gigabytes remain relevant for everyday use.
8.1. The Rise of Terabytes and Petabytes
Terabytes (TB) and petabytes (PB) are increasingly used to measure storage capacity in data centers, cloud storage, and high-end devices. These larger units accommodate the growing demand for data storage.
8.2. Gigabytes in Niche Applications
Gigabytes still have niche applications, such as in embedded systems, IoT devices, and smaller storage solutions. They provide a practical measurement for devices with limited storage needs.
8.3. Innovations in Storage Technology
New storage technologies like DNA storage and holographic storage could revolutionize data storage in the future. These innovations promise even higher capacities and lower costs per gigabyte.
9. Saving Money on Gigabytes: Practical Tips
Managing your data usage and storage effectively can save you money. Here are some practical tips to reduce your expenses.
9.1. Optimize Cloud Storage
- Regularly Review Files: Delete unnecessary files and folders to free up space.
- Compress Files: Use compression tools to reduce the size of large files.
- Utilize Shared Folders: Share files instead of duplicating them.
- Take Advantage of Free Tiers: Use free storage options offered by cloud providers.
9.2. Manage Mobile Data
- Connect to Wi-Fi: Use Wi-Fi for data-intensive activities like streaming and downloading.
- Monitor App Usage: Identify and limit data-hungry apps.
- Download Content: Download content for offline use.
- Use Data-Saving Features: Enable data-saving features in your browser and apps.
9.3. Choose the Right Storage Devices
- Assess Your Needs: Determine how much storage you really need before buying a new device.
- Compare Prices: Shop around for the best deals on storage devices.
- Consider Refurbished Options: Refurbished devices can offer significant savings.
10. FAQs About Gigabytes
Here are some frequently asked questions about gigabytes to help clarify any remaining doubts.
10.1. How many photos can 1 GB hold?
Approximately 250 high-resolution photos (10-megapixel).
10.2. How many songs can 1 GB hold?
Around 250 songs (assuming an average song size of 4MB).
10.3. How much video can 1 GB hold?
About 5 hours of standard-definition video.
10.4. Is 1 GB enough for a smartphone?
No, 1 GB is not enough for a smartphone in today’s digital landscape. Modern apps, operating systems, and media files require significantly more storage.
10.5. How much data do I need per month?
This depends on your usage. Light users may need a few gigabytes, while heavy users may require 50 GB or more.
10.6. What is the difference between GB and GiB?
GB (gigabyte) is typically used in decimal notation (1 billion bytes), while GiB (gibibyte) is used in binary notation (1,073,741,824 bytes).
10.7. How can I check my data usage?
Most smartphones and operating systems have built-in tools to track data consumption.
10.8. What is data throttling?
Data throttling is when a provider reduces your data speeds after you’ve used a certain amount of data.
10.9. How can I save money on data?
Connect to Wi-Fi, monitor app usage, download content for offline use, and use data-saving features.
10.10. Are unlimited data plans really unlimited?
Unlimited data plans typically have a threshold after which speeds may be throttled.
11. Connect with Experts at HOW.EDU.VN
Navigating the complexities of data storage and usage can be challenging. At HOW.EDU.VN, we offer expert guidance and personalized solutions to help you make informed decisions.
11.1. Expert Consultations
Connect directly with our team of PhDs and specialists for personalized advice tailored to your specific needs. Whether you need help choosing a data plan or optimizing your cloud storage, our experts are here to assist.
11.2. Customized Solutions
We provide customized solutions to address your unique challenges. Our experts work with you to develop strategies that optimize your data usage and storage, saving you time and money.
11.3. Timely and Reliable Advice
Stay ahead of the curve with our timely and reliable advice. We keep you informed about the latest trends and innovations in data storage technology, ensuring you always have the information you need.
Don’t navigate the complexities of data storage alone. Contact us today and experience the benefits of expert guidance.
Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
Website: HOW.EDU.VN
12. Call to Action: Get Expert Advice Now
Are you struggling to manage your data usage or storage costs? Do you need help choosing the right data plan or storage solution? Contact HOW.EDU.VN today and connect with our team of expert. Let us help you optimize your data management and save money.
At HOW.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges of navigating the digital landscape. That’s why we offer personalized solutions and expert guidance to help you make informed decisions. Our team of experienced PhDs and specialists is dedicated to providing you with timely and reliable advice.
Don’t wait any longer to take control of your data. Contact us today and experience the benefits of expert guidance.
Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
Website: HOW.EDU.VN
Let how.edu.vn be your trusted partner in data management. Reach out today and discover how we can help you optimize your digital life.