How much is an eye exam and what does it entail? Regular eye checkups are paramount for preserving optimal vision and overall ocular well-being. HOW.EDU.VN provides expert insights on eye exams, ensuring you understand the costs, types, and benefits. Discover the importance of routine vision checks, comprehensive evaluations, and vision screenings, and find the best approach for maintaining your eye health through professional guidance and the latest ophthalmic advancements.
1. Understanding the Different Types of Eye Exams
Maintaining healthy vision requires regular check-ups, but what kind of eye exam do you need? Knowing the differences between routine, comprehensive, and vision screenings is essential.
1.1 Routine Eye Exams
During a routine eye exam, an eye doctor assesses your vision for common refractive errors. These include:
- Myopia: Nearsightedness, where distant objects appear blurry.
- Hyperopia: Farsightedness, where close-up objects are unclear.
- Astigmatism: Blurred vision due to an irregularly shaped cornea.
- Presbyopia: Age-related farsightedness, making it difficult to see objects up close.
This exam also evaluates your current prescription for eyeglasses or contact lenses to determine if adjustments are necessary. Routine eye exams are crucial for detecting and correcting vision problems early.
1.2 Comprehensive Eye Exams
Unlike routine exams that focus on basic vision issues, comprehensive eye exams delve deeper to identify potential eye diseases and underlying health conditions. These exams can detect early signs of:
- Cataracts: Clouding of the eye’s natural lens.
- Diabetic Eye Problems: Retinopathy and other complications from diabetes.
- Glaucoma: Damage to the optic nerve, often due to high eye pressure.
- Macular Degeneration: Deterioration of the central part of the retina.
- Retinal Disorders: Conditions affecting the retina, such as detachment or tears.
Early detection and treatment are vital to preventing irreversible vision loss. Your eye doctor may recommend additional tests, such as specialized imaging, to gain a more detailed understanding of your eye health. Consulting with the esteemed experts at HOW.EDU.VN can provide additional insights and clarity.
1.3 Vision Screenings
Vision screenings are basic tests that quickly assess your ability to see objects at various distances. They are often conducted in schools or during routine check-ups. Vision screenings primarily check for:
- Visual Acuity: How well you can see at different distances using an eye chart.
- Eye Muscle Function: Ensuring the eye muscles work correctly, particularly in children.
- Early Childhood Conditions: Identifying conditions like amblyopia (lazy eye) or strabismus (crossed eyes).
If a vision screening reveals potential issues, a referral to an eye-care specialist such as an ophthalmologist or optometrist is recommended for a more thorough evaluation.
2. How Much Does an Eye Exam Cost?
The cost of an eye exam varies based on several factors, including the type of exam, geographic location, and whether you have vision insurance.
2.1 Average Costs in the United States
The national average cost for a routine eye exam in the United States is approximately $136 without insurance, but it can range from $105 to $257. With vision insurance, the average cost is around $25, but it may vary from $20 to $49. Comprehensive eye exams tend to be more expensive due to the additional tests and evaluations performed.
2.2 Factors Influencing the Cost
Several factors can influence the price of an eye exam:
- Type of Exam: Comprehensive exams are more expensive than routine screenings due to the more extensive evaluation.
- Geographic Location: Costs vary significantly by state and even within different cities.
- Insurance Coverage: Having vision insurance can significantly reduce out-of-pocket expenses.
- Additional Testing: If your doctor recommends additional tests or imaging, this will increase the overall cost.
- Doctor’s Experience and Training: Highly experienced specialists may charge more for their services.
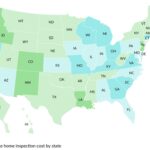
2.3 Cost Comparison by State
The following table shows the average costs of an annual eye exam with and without insurance across all 50 states and the District of Columbia.
| State/District | Average Cost (With Insurance) | Average Cost (Without Insurance) |
|---|---|---|
| Alabama | $22 | $113 |
| Alaska | $31 | $165 |
| Arizona | $26 | $136 |
| Arkansas | $22 | $116 |
| California | $31 | $166 |
| Colorado | $25 | $137 |
| Connecticut | $25 | $143 |
| Delaware | $25 | $135 |
| District of Columbia | $36 | $174 |
| Florida | $25 | $136 |
| Georgia | $23 | $124 |
| Hawaii | $38 | $196 |
| Idaho | $26 | $139 |
| Illinois | $24 | $126 |
| Indiana | $22 | $121 |
| Iowa | $22 | $119 |
| Kansas | $22 | $118 |
| Kentucky | $24 | $123 |
| Louisiana | $23 | $127 |
| Maine | $26 | $140 |
| Maryland | $29 | $159 |
| Massachusetts | $28 | $164 |
| Michigan | $23 | $124 |
| Minnesota | $23 | $129 |
| Mississippi | $23 | $120 |
| Missouri | $22 | $119 |
| Montana | $25 | $135 |
| Nebraska | $23 | $122 |
| Nevada | $25 | $137 |
| New Hampshire | $26 | $143 |
| New Jersey | $28 | $153 |
| New Mexico | $23 | $123 |
| New York | $26 | $142 |
| North Carolina | $23 | $126 |
| North Dakota | $23 | $124 |
| Ohio | $23 | $122 |
| Oklahoma | $22 | $117 |
| Oregon | $27 | $147 |
| Pennsylvania | $24 | $131 |
| Rhode Island | $27 | $139 |
| South Carolina | $23 | $126 |
| South Dakota | $23 | $125 |
| Tennessee | $23 | $123 |
| Texas | $23 | $126 |
| Utah | $24 | $136 |
| Vermont | $26 | $146 |
| Virginia | $25 | $132 |
| Washington | $27 | $155 |
| West Virginia | $22 | $125 |
| Wisconsin | $24 | $127 |
| Wyoming | $23 | $130 |
2.4 Understanding Insurance Coverage
Vision insurance plans typically cover routine eye exams, eyeglass frames, eyeglass lenses, and contact lenses. However, the specifics can vary significantly. It’s essential to check with your insurance provider to understand the extent of your coverage, including:
- Frequency of Coverage: Some plans cover exams annually, while others cover them every other year.
- Discounts: Many plans offer discounts on frames, lenses, and contact lenses.
- Medical vs. Vision Insurance: Medical insurance often covers eye exams needed to treat specific eye problems or diseases, such as glaucoma, cataracts, or diabetic retinopathy.
Consulting the expert team at HOW.EDU.VN can help you navigate the complexities of insurance coverage.
3. The Importance of Regular Eye Exams
Regular eye exams are a critical component of preventive healthcare, helping to detect potential vision issues and eye diseases before they become serious problems.
3.1 Detecting Vision Problems Early
Regular eye exams can identify common vision problems such as nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism. Early detection allows for timely correction with eyeglasses, contact lenses, or other treatments, improving vision and quality of life.
3.2 Preventing Eye Diseases
Many serious eye diseases, such as glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy, and macular degeneration, often have no obvious symptoms in their early stages. Regular comprehensive eye exams can detect these conditions early, allowing for prompt treatment to prevent vision loss.
3.3 Overall Health Benefits
Eye exams can also provide insights into your overall health. Eye doctors can detect signs of systemic diseases such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and autoimmune disorders during a comprehensive eye exam.
3.4 Recommendations for Different Age Groups
The frequency of eye exams varies depending on age and risk factors:
- Children: Children should have regular vision screenings as part of their routine wellness checks. The American Academy of Ophthalmology recommends screenings at newborn, 6 to 12 months, 12 to 36 months, 3 to 5 years, and 5 years old.
- Adults: Adults with good vision and overall health should have a routine eye exam at least once in their 20s and twice in their 30s. A comprehensive eye exam is recommended at age 40 to establish a baseline.
- Seniors: Adults aged 65 or older should have eye exams every one to two years to check for age-related eye diseases.
- Specific Conditions: More frequent exams are needed for those with diabetes, high blood pressure, a family history of eye disease, or those who wear contact lenses or glasses.
4. Choosing the Right Eye Care Professional
Selecting the right eye care professional is crucial for receiving quality care and ensuring your vision needs are met.
4.1 Optometrist vs. Ophthalmologist
Understanding the difference between an optometrist and an ophthalmologist is essential:
- Optometrists: Provide primary vision care, including routine eye exams, vision testing and correction, and diagnosis and management of common eye conditions.
- Ophthalmologists: Are medical doctors specializing in eye care. They can perform medical and surgical procedures to treat eye diseases and conditions, as well as provide routine eye exams and vision correction.
4.2 Considerations When Choosing a Provider
When choosing an eye care provider, consider the following:
- Qualifications and Experience: Ensure the provider is board-certified and has extensive experience in the area of eye care you need.
- Services Offered: Determine if the provider offers the specific services you require, such as comprehensive eye exams, contact lens fittings, or treatment for eye diseases.
- Insurance Coverage: Verify that the provider accepts your vision insurance plan.
- Patient Reviews and Referrals: Read online reviews and ask for referrals from friends or family to gauge the provider’s reputation.
- Location and Accessibility: Choose a provider whose office is conveniently located and accessible.
5. Preparing for Your Eye Exam
Proper preparation can help ensure your eye exam is thorough and efficient.
5.1 What to Bring
- Insurance Card: Bring your vision and medical insurance cards.
- Eyeglasses and Contact Lenses: Wear your eyeglasses or bring your contact lenses, along with their prescription.
- List of Medications: Provide a list of all medications you are currently taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements.
- Medical History: Be prepared to discuss your medical history, including any eye conditions or systemic diseases.
- Questions: Write down any questions or concerns you have about your vision or eye health.
5.2 What to Expect
During your eye exam, you can expect the following:
- Visual Acuity Testing: You will be asked to read an eye chart to assess your vision at various distances.
- Refraction: The doctor will use a phoropter to determine your eyeglass prescription.
- Eye Muscle Testing: Your eye muscles will be evaluated to ensure they are working properly.
- Slit-Lamp Examination: The doctor will use a slit lamp to examine the structures of your eyes, including the cornea, iris, and lens.
- Tonometry: This test measures the pressure inside your eyes to screen for glaucoma.
- Retinal Examination: The doctor will use special instruments to examine your retina and optic nerve.
5.3 Questions to Ask Your Eye Doctor
- What is my current vision prescription?
- Do I have any signs of eye disease?
- What can I do to protect my vision?
- How often should I have eye exams?
- Are there any specific concerns about my eye health?
6. Advanced Technologies in Eye Exams
Modern eye care utilizes advanced technologies to provide more precise diagnoses and treatments.
6.1 Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive imaging technique that provides detailed cross-sectional images of the retina. This technology helps in the early detection and management of conditions like macular degeneration, glaucoma, and diabetic retinopathy.
6.2 Digital Retinal Imaging
Digital retinal imaging captures high-resolution images of the retina, allowing eye doctors to document and monitor changes over time. This is particularly useful for tracking the progression of retinal diseases.
6.3 Corneal Topography
Corneal topography maps the surface of the cornea, providing valuable information for fitting contact lenses, diagnosing corneal diseases like keratoconus, and planning refractive surgery.
6.4 Visual Field Testing
Visual field testing assesses the extent of your peripheral vision. This test is crucial for detecting glaucoma and other conditions that affect the visual field.
7. Addressing Common Eye Concerns
Many people experience common eye concerns that can be addressed with proper care and attention.
7.1 Dry Eye Syndrome
Dry eye syndrome occurs when your eyes do not produce enough tears or the tears are of poor quality. Symptoms include dryness, burning, itching, and blurred vision. Treatment options include artificial tears, prescription eye drops, and lifestyle changes.
7.2 Eye Strain
Eye strain can result from prolonged use of digital devices, reading, or other visually intensive activities. Symptoms include headache, blurred vision, and dry eyes. Taking frequent breaks, adjusting your workstation, and using proper lighting can help reduce eye strain.
7.3 Allergies
Eye allergies can cause itching, redness, and watering. Treatment options include antihistamine eye drops, mast cell stabilizer eye drops, and avoiding allergens.
7.4 Cataracts
Cataracts are a clouding of the eye’s natural lens, causing blurred vision. Cataracts typically develop with age and can be treated with surgery to replace the cloudy lens with a clear artificial lens.
8. Vision Correction Options
Various vision correction options are available to help improve your vision and reduce your dependence on glasses or contact lenses.
8.1 Eyeglasses
Eyeglasses are a simple and effective way to correct vision problems such as nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism. A wide variety of frames and lens options are available to suit your individual needs and preferences.
8.2 Contact Lenses
Contact lenses offer a convenient alternative to eyeglasses. They are available in various types, including daily disposable, extended wear, and multifocal lenses.
8.3 LASIK Surgery
LASIK (laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis) is a refractive surgery that reshapes the cornea to correct vision problems. LASIK can provide long-term vision correction and reduce or eliminate the need for glasses or contact lenses.
8.4 Other Surgical Options
Other surgical options for vision correction include PRK (photorefractive keratectomy), SMILE (small incision lenticule extraction), and refractive lens exchange.
9. Maintaining Eye Health at Home
In addition to regular eye exams, there are several steps you can take to maintain your eye health at home.
9.1 Proper Nutrition
A healthy diet rich in vitamins and antioxidants can help protect your eyes from damage and disease. Key nutrients for eye health include:
- Vitamin A: Found in carrots, sweet potatoes, and leafy green vegetables.
- Vitamin C: Found in citrus fruits, berries, and broccoli.
- Vitamin E: Found in nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils.
- Lutein and Zeaxanthin: Found in leafy green vegetables and eggs.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts.
9.2 Protecting Your Eyes from the Sun
Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation can increase your risk of cataracts and macular degeneration. Wear sunglasses that block 100% of UV rays when you are outdoors.
9.3 Proper Lighting
Good lighting is essential for reducing eye strain and preventing headaches. Use adequate lighting when reading, working, or using digital devices.
9.4 Regular Breaks
Taking frequent breaks from visually intensive activities can help reduce eye strain. Follow the 20-20-20 rule: every 20 minutes, look at an object 20 feet away for 20 seconds.
10. Innovative Telehealth Solutions for Eye Care
Telehealth is transforming the way eye care is delivered, making it more accessible and convenient.
10.1 Remote Consultations
Remote consultations allow you to connect with eye care professionals from the comfort of your home. This is particularly useful for follow-up appointments, managing chronic conditions, and seeking advice on minor eye problems.
10.2 Virtual Vision Tests
Virtual vision tests use online tools and mobile apps to assess your visual acuity and screen for common vision problems. While these tests are not a substitute for a comprehensive eye exam, they can provide a convenient way to monitor your vision.
10.3 Remote Monitoring
Remote monitoring devices can track various aspects of your eye health, such as intraocular pressure for glaucoma management. This allows eye doctors to monitor your condition remotely and adjust treatment as needed.
10.4 Benefits of Telehealth
Telehealth offers several benefits for eye care:
- Increased Accessibility: Telehealth makes eye care more accessible to people in rural areas or with limited mobility.
- Convenience: Telehealth eliminates the need to travel to the eye doctor’s office, saving time and money.
- Improved Monitoring: Remote monitoring allows for more frequent and detailed tracking of eye health.
- Cost Savings: Telehealth can reduce the cost of eye care by eliminating the need for in-person visits.
11. FAQs About Eye Exams
11.1 How Often Should I Get an Eye Exam?
The frequency of eye exams depends on your age, health, and risk factors. Children should have regular vision screenings, adults should have an exam at least once in their 20s and twice in their 30s, and seniors should have an exam every one to two years.
11.2 What Happens During a Comprehensive Eye Exam?
A comprehensive eye exam includes visual acuity testing, refraction, eye muscle testing, slit-lamp examination, tonometry, and retinal examination.
11.3 How Much Does an Eye Exam Cost Without Insurance?
The average cost of an eye exam without insurance is around $136, but it can range from $105 to $257.
11.4 What is the Difference Between an Optometrist and an Ophthalmologist?
An optometrist provides primary vision care, while an ophthalmologist is a medical doctor specializing in eye care and surgery.
11.5 Can Eye Exams Detect Other Health Problems?
Yes, eye exams can detect signs of systemic diseases such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and autoimmune disorders.
11.6 How Can I Prepare for My Eye Exam?
Bring your insurance card, eyeglasses and contact lenses, a list of medications, and any questions you have.
11.7 What are the Benefits of Telehealth for Eye Care?
Telehealth offers increased accessibility, convenience, improved monitoring, and cost savings.
11.8 What are Common Vision Correction Options?
Common vision correction options include eyeglasses, contact lenses, LASIK surgery, and other surgical procedures.
11.9 How Can I Maintain My Eye Health at Home?
Eat a healthy diet, protect your eyes from the sun, use proper lighting, and take regular breaks.
11.10 What are Some Common Eye Concerns?
Common eye concerns include dry eye syndrome, eye strain, allergies, and cataracts.
12. Connect With Experts at HOW.EDU.VN
Navigating the world of eye care can be complex, but with the expertise available at HOW.EDU.VN, you can make informed decisions and take proactive steps to protect your vision.
12.1 Access to Top-Tier Experts
HOW.EDU.VN offers direct access to over 100 renowned doctors and specialists worldwide. Our experts provide personalized advice and solutions tailored to your specific needs.
12.2 Personalized Consultations
Receive in-depth, personalized consultations from leading professionals. Our experts can address your specific concerns and provide actionable advice to improve your eye health.
12.3 Convenient and Secure Platform
Our platform ensures secure and confidential communication with our experts. Get the advice you need from the comfort of your own home.
12.4 Comprehensive Support
Whether you need guidance on choosing the right type of eye exam, understanding your insurance coverage, or finding the best treatment options, HOW.EDU.VN is here to support you every step of the way.
Don’t let concerns about the cost or complexity of eye care prevent you from taking care of your vision. Connect with the experts at HOW.EDU.VN today and take the first step towards a lifetime of healthy vision.
Ready to take control of your eye health? Contact HOW.EDU.VN today for personalized advice and expert guidance.
Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
Website: HOW.EDU.VN
Ensure your vision is in the best hands with how.edu.vn.