HOW.EDU.VN sheds light on how much oil the US imports and why it remains a crucial aspect of the nation’s energy security and economic stability, addressing complexities surrounding energy demands. Discover insights from industry experts and explore the United States’ oil import requirements, import volumes, and global energy dependence.
1. Understanding U.S. Oil Imports: An Overview
The United States, despite being a major oil producer, still relies significantly on oil imports to meet its vast energy demands. This dependency stems from several factors, including the types of crude oil U.S. refineries are equipped to process and the economic considerations of transporting domestically produced oil. To accurately assess How Much Oil Does The Us Import, it’s vital to examine the specifics of these imports, including sources, types of crude oil, and the role they play in the U.S. energy mix.
1.1 The Significance of Crude Oil Imports
Crude oil is the lifeblood of the U.S. economy, powering transportation, industries, and homes. While domestic production has increased substantially, it has not eliminated the need for imports. Refineries in the U.S. are designed to process a variety of crude oils, including heavy and light grades, which are not all available in sufficient quantities domestically. The import of crude oil ensures that these refineries operate efficiently, maintaining a steady supply of gasoline, diesel, jet fuel, and other essential products.
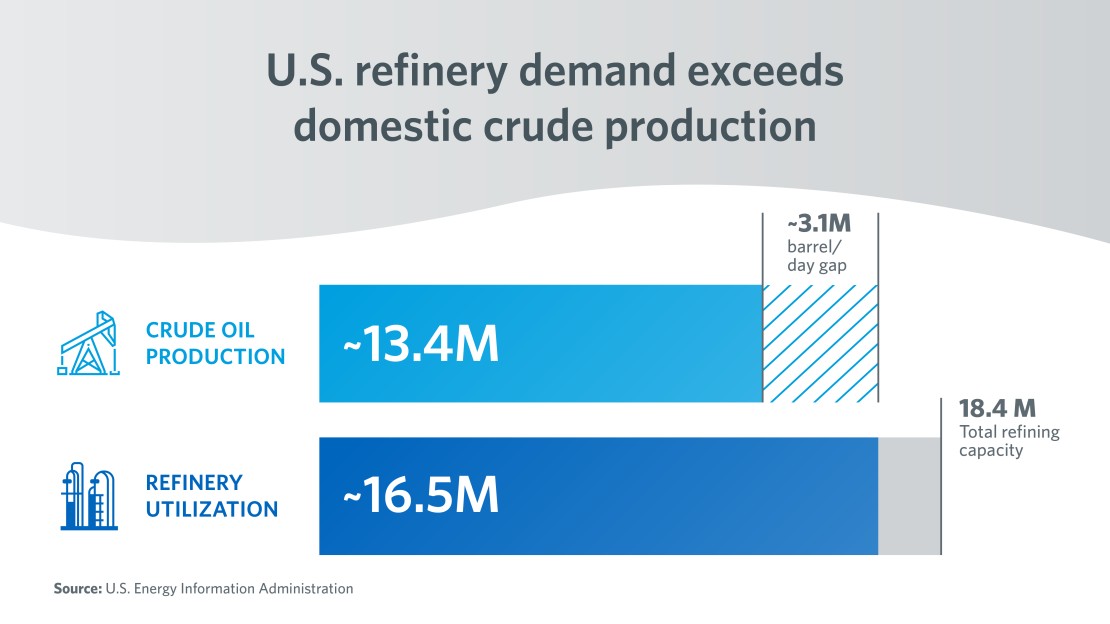 U.S. refinery demand exceeds domestic crude production
U.S. refinery demand exceeds domestic crude production
1.2 Key Sources of U.S. Oil Imports
Canada has consistently been the largest supplier of crude oil to the United States, accounting for a significant portion of total imports. Mexico is also a key source, along with other countries in the Middle East, South America, and Africa. Understanding the geopolitical dynamics and supply agreements with these countries is crucial in assessing the stability and security of U.S. energy supplies. These relationships are continually evolving due to market conditions, political factors, and changes in domestic production.
1.3 Types of Crude Oil Imported
U.S. refineries require different types of crude oil to maximize their output of various petroleum products. Light crude oil, which is abundantly produced in the United States, is not always suitable for producing certain fuels like diesel and jet fuel efficiently. Therefore, heavier crude oils are imported to fill this gap, ensuring a balanced and optimized refining process. The flexibility to process different types of crude oil enhances the operational efficiency of U.S. refineries and helps stabilize fuel prices.
2. Quantifying U.S. Oil Imports: How Much Is Imported?
Determining exactly how much oil does the US import involves analyzing data from various sources, including the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) and other industry reports. These statistics provide a clear picture of import volumes, trends, and their impact on the U.S. energy landscape. By examining these figures, we can understand the scale of U.S. reliance on foreign oil and the factors influencing these import levels.
2.1 Recent Trends in Oil Imports
In recent years, U.S. oil imports have fluctuated due to increased domestic production and shifts in global demand. Despite the rise in domestic shale oil production, imports remain a critical component of the U.S. energy strategy. Factors such as refinery capacity, the availability of suitable crude types, and economic considerations all play a role in shaping these trends. Monitoring these trends is essential for policymakers and industry stakeholders to make informed decisions.
2.2 Data from the Energy Information Administration (EIA)
The EIA is a primary source of information on U.S. energy statistics, including oil imports. According to EIA data, the U.S. imports millions of barrels of crude oil daily. These figures vary monthly and annually, reflecting changes in domestic production, refinery operations, and international market conditions. Detailed EIA reports provide insights into the specific quantities and sources of these imports, offering a comprehensive view of the U.S. oil supply.
2.3 Factors Affecting Import Volumes
Several factors influence the volume of oil imported into the United States. These include:
- Domestic Production Levels: Increased domestic production can reduce the need for imports.
- Refinery Capacity and Needs: The types of crude oil that U.S. refineries can process efficiently determine import requirements.
- Global Market Conditions: Price fluctuations and geopolitical events can impact the attractiveness of importing oil from various sources.
- Infrastructure Limitations: The availability of pipelines and other transportation infrastructure affects the ability to move domestic crude oil to refineries.
Understanding these factors is essential for predicting future import trends and ensuring a stable energy supply.
3. The Economics of Oil Imports: Costs and Benefits
The decision of how much oil does the US import is heavily influenced by economic considerations. Importing oil involves both costs and benefits, which must be carefully weighed to ensure the most efficient and reliable energy supply. These economic factors include the price of imported oil, transportation costs, and the impact on domestic industries.
3.1 Cost Analysis of Importing Oil
The cost of importing oil includes not only the purchase price but also transportation, insurance, and other logistical expenses. These costs can fluctuate significantly based on global market conditions and geopolitical events. Analyzing these costs is crucial for determining the economic viability of importing oil compared to relying solely on domestic production. Lower import costs can translate to lower fuel prices for consumers, while higher costs can put pressure on the economy.
3.2 Benefits of Oil Imports
Despite the costs, importing oil offers several benefits:
- Diversification of Supply: Relying on multiple sources of oil reduces vulnerability to disruptions from any single supplier.
- Access to Different Crude Types: Imports provide access to crude oils that are not readily available domestically, optimizing refinery operations.
- Price Competition: Imports can help keep domestic oil prices competitive, benefiting consumers and businesses.
- Energy Security: A mix of domestic and imported oil enhances overall energy security by ensuring a stable supply.
These benefits highlight the strategic importance of maintaining a diversified energy portfolio.
3.3 Impact on Domestic Oil Production
Oil imports can impact domestic oil production by influencing prices and investment decisions. Lower import prices can make domestic production less competitive, potentially reducing investment in exploration and extraction. On the other hand, higher import prices can incentivize domestic production and stimulate economic growth in the energy sector. Balancing these factors is essential for maintaining a healthy and sustainable domestic oil industry.
4. Geopolitical Implications of U.S. Oil Imports
The question of how much oil does the US import is closely tied to geopolitics. Oil is a strategic commodity, and the sources from which the U.S. imports oil have significant implications for its foreign policy and international relations. Understanding these geopolitical dynamics is crucial for assessing the long-term stability and security of U.S. energy supplies.
4.1 Relationships with Major Oil Suppliers
The United States maintains complex relationships with its major oil suppliers, including Canada, Mexico, and countries in the Middle East. These relationships involve economic, political, and security considerations. Stable and reliable partnerships with these suppliers are essential for ensuring a consistent flow of oil and mitigating potential disruptions. Diplomatic efforts and trade agreements play a key role in maintaining these relationships.
4.2 Impact of Global Events on Oil Supply
Global events, such as political instability, conflicts, and natural disasters, can significantly impact oil supply and prices. These events can disrupt production and transportation, leading to shortages and price spikes. The U.S. must be prepared to respond to these disruptions by diversifying its supply sources and maintaining strategic petroleum reserves. Monitoring global events and assessing their potential impact on oil supply is a critical aspect of energy security.
4.3 Energy Security and Foreign Policy
Energy security is a key component of U.S. foreign policy. The ability to access reliable and affordable energy sources is essential for economic stability and national security. The U.S. uses its diplomatic and economic influence to promote energy security, both domestically and internationally. This includes fostering stable relationships with oil-producing countries, supporting the development of diverse energy sources, and advocating for policies that promote energy efficiency and conservation.
5. Future of U.S. Oil Imports: Trends and Projections
Looking ahead, the future of how much oil does the US import will depend on several factors, including technological advancements in domestic production, shifts in global energy demand, and policy decisions related to climate change and energy security. Understanding these trends and projections is crucial for planning and adapting to the evolving energy landscape.
5.1 The Role of Renewable Energy
The increasing adoption of renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydropower, is expected to reduce the U.S.’s reliance on fossil fuels, including oil. As renewable energy technologies become more cost-competitive and widely deployed, the demand for oil imports may decline. Government policies that support renewable energy development and incentivize energy efficiency will play a key role in this transition.
5.2 Advancements in Domestic Oil Production
Technological advancements in domestic oil production, such as enhanced oil recovery techniques and improved drilling methods, could increase domestic supply and reduce the need for imports. Continued innovation in the energy sector is essential for maximizing domestic resources and ensuring energy independence. Investing in research and development and promoting policies that encourage responsible resource development will be critical.
5.3 Policy and Regulatory Impacts
Government policies and regulations related to energy production, consumption, and trade will significantly impact the future of U.S. oil imports. Policies that promote energy efficiency, incentivize renewable energy adoption, and regulate oil production and transportation can all influence import levels. Balancing these policies to ensure a stable and affordable energy supply while addressing environmental concerns is a key challenge for policymakers.
6. Expert Insights on U.S. Oil Import Strategy
To gain a deeper understanding of how much oil does the US import and the strategies behind it, it’s invaluable to consult with experts in the field. HOW.EDU.VN connects you with leading experts who can provide insights into the complexities of U.S. oil imports and offer informed perspectives on the future of energy in the United States.
6.1 Interview with Energy Economists
Energy economists analyze market trends, supply and demand dynamics, and policy impacts to provide insights into the economics of oil imports. They can offer perspectives on the optimal level of imports, the economic benefits of diversification, and the potential risks associated with relying on foreign oil. Their expertise is essential for making informed decisions about energy policy and investment.
6.2 Perspectives from Geopolitical Analysts
Geopolitical analysts study the political and security implications of oil imports. They can assess the risks associated with different suppliers, the impact of global events on oil supply, and the role of energy in U.S. foreign policy. Their insights are critical for ensuring energy security and maintaining stable relationships with key oil-producing countries.
6.3 Analysis by Environmental Scientists
Environmental scientists assess the environmental impacts of oil production, transportation, and consumption. They can provide insights into the environmental costs of oil imports, the potential benefits of transitioning to renewable energy, and the policies needed to mitigate environmental risks. Their expertise is essential for promoting sustainable energy practices and protecting the environment.
7. Case Studies: Real-World Impact of Oil Imports
Examining specific case studies can provide a tangible understanding of how much oil does the US import affects various sectors and regions. These examples illustrate the real-world consequences of oil import decisions and highlight the importance of a well-informed energy strategy.
7.1 Impact on the Transportation Sector
The transportation sector is heavily reliant on oil, and changes in oil imports can directly impact fuel prices and transportation costs. Case studies can illustrate how fluctuations in oil imports have affected the trucking industry, airline industry, and consumer gasoline prices. Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing policies that promote efficient and affordable transportation.
7.2 Effects on Manufacturing Industries
Manufacturing industries use oil for energy and as a raw material for producing various products. Changes in oil imports can affect the cost of production and the competitiveness of these industries. Case studies can demonstrate how oil import decisions have influenced manufacturing output, employment, and innovation.
7.3 Regional Economic Impacts
Different regions of the United States are affected differently by oil imports. Regions with significant oil production may benefit from higher domestic prices, while regions that rely heavily on transportation may be more vulnerable to price spikes. Case studies can illustrate these regional economic impacts and highlight the need for policies that address regional disparities.
8. Navigating Challenges in U.S. Oil Import Policies
Addressing how much oil does the US import requires navigating a complex web of challenges, including geopolitical risks, economic volatility, and environmental concerns. Effective policy-making requires a comprehensive understanding of these challenges and a commitment to finding sustainable solutions.
8.1 Mitigating Geopolitical Risks
Geopolitical risks can disrupt oil supply and lead to price spikes. Mitigating these risks requires diversifying supply sources, maintaining strategic petroleum reserves, and engaging in proactive diplomacy. Policies that promote energy security and foster stable relationships with oil-producing countries are essential for reducing vulnerability to geopolitical disruptions.
8.2 Addressing Economic Volatility
Oil prices can be highly volatile, leading to uncertainty and economic instability. Addressing this volatility requires implementing policies that promote price stability, such as hedging strategies and market regulation. Additionally, investing in energy efficiency and renewable energy can reduce reliance on oil and mitigate the impact of price fluctuations.
8.3 Balancing Environmental Concerns
Oil production, transportation, and consumption have significant environmental impacts, including greenhouse gas emissions and pollution. Balancing environmental concerns with energy needs requires implementing policies that promote sustainable energy practices, such as carbon pricing, emission standards, and investments in clean energy technologies.
9. Expert Consultations: Getting Your Questions Answered
At HOW.EDU.VN, we understand that navigating the complexities of how much oil does the US import can be challenging. That’s why we offer expert consultations with leading professionals who can answer your specific questions and provide tailored advice.
9.1 How to Schedule a Consultation
Scheduling a consultation with one of our experts is easy. Simply visit our website at HOW.EDU.VN, browse our directory of experts, and select the professional whose expertise aligns with your needs. You can then schedule a consultation at a time that is convenient for you.
9.2 What to Expect During a Consultation
During a consultation, you can expect to have a one-on-one discussion with an expert who will listen to your questions, provide informed answers, and offer practical advice. Our experts are committed to providing you with the knowledge and insights you need to make informed decisions.
9.3 Benefits of Consulting with Experts
Consulting with experts offers several benefits:
- Access to Specialized Knowledge: Our experts have years of experience and specialized knowledge in their respective fields.
- Personalized Advice: Our experts can provide tailored advice that is specific to your needs and circumstances.
- Informed Decision-Making: Our experts can help you make informed decisions by providing you with the information you need to weigh your options.
- Time Savings: Consulting with experts can save you time by providing you with the answers you need quickly and efficiently.
10. Why Choose HOW.EDU.VN for Expert Advice?
When it comes to understanding how much oil does the US import and its implications, you need reliable and expert advice. HOW.EDU.VN offers a unique platform for connecting with top-tier professionals across various fields.
10.1 Access to a Network of 100+ PhDs
HOW.EDU.VN provides access to a network of over 100 PhDs and leading experts from around the world. Our experts have a wide range of expertise and can provide insights into various aspects of U.S. oil imports, from economic analysis to geopolitical considerations.
10.2 Personalized and Tailored Advice
We understand that every individual’s needs are unique. That’s why we offer personalized and tailored advice that is specific to your situation. Our experts take the time to understand your questions and provide you with the information you need to make informed decisions.
10.3 Confidential and Reliable Consultations
We are committed to providing confidential and reliable consultations. Your privacy is important to us, and we take steps to protect your information. You can trust that your consultations with our experts will be conducted with the utmost professionalism and integrity.
Understanding how much oil does the US import is crucial for comprehending the nation’s energy security, economic stability, and geopolitical strategy. By leveraging the insights of experts at HOW.EDU.VN, you can gain a deeper understanding of these complexities and make informed decisions about energy policy and investment. Contact us today at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States or reach out via WhatsApp at +1 (310) 555-1212. Visit our website at HOW.EDU.VN to schedule a consultation and unlock the expertise you need to navigate the world of energy.
Don’t navigate these complex issues alone. Reach out to HOW.EDU.VN for expert guidance and clarity. Our team of over 100 PhDs is ready to provide the insights you need. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and take control of your future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Why does the U.S. import oil if it is also a major producer?
The U.S. imports oil due to refinery configurations designed for various crude types not abundantly available domestically and for strategic supply diversification.
-
Which countries are the primary sources of U.S. oil imports?
Canada and Mexico are the largest suppliers, with other contributions from the Middle East, South America, and Africa.
-
How do oil imports affect the price of gasoline in the U.S.?
Oil imports can influence gasoline prices by affecting the overall supply and competition in the market.
-
What role does the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) play in tracking oil imports?
The EIA provides data on import volumes and trends, offering a clear picture of U.S. reliance on foreign oil.
-
What are the geopolitical implications of U.S. oil imports?
They include complex relationships with major oil suppliers and impacts on foreign policy and international relations.
-
How might renewable energy sources affect future oil imports?
Increased adoption of renewables is expected to reduce reliance on fossil fuels, potentially lowering oil imports.
-
What is the Strategic Petroleum Reserve, and how does it relate to oil imports?
It is a reserve of crude oil used to mitigate supply disruptions, reducing the need for immediate import increases during crises.
-
What types of expertise can I access through HOW.EDU.VN regarding oil imports?
You can access insights from energy economists, geopolitical analysts, and environmental scientists.
-
How can expert consultations help in understanding U.S. oil import strategies?
Experts can provide tailored advice and perspectives on the complexities, aiding in informed decision-making.
-
How do I schedule a consultation with an expert on HOW.EDU.VN?
Visit how.edu.vn, browse the directory of experts, and select a professional to schedule a consultation at your convenience.