A terabyte (TB) is a significant unit of digital information storage, crucial for understanding modern data capacity. At HOW.EDU.VN, we aim to clarify what a terabyte represents in tangible terms, comparing it to other storage units and illustrating its practical applications. Understanding the size of a terabyte will empower you to make informed decisions about your storage needs, whether for personal use or professional requirements. Learn about storage solutions with expert insights.
1. Understanding the Basics of a Terabyte
A terabyte is a unit of measurement used to quantify the amount of data that a storage device can hold. To truly grasp its magnitude, let’s break it down and compare it to smaller, more familiar units.
1.1. Defining a Terabyte
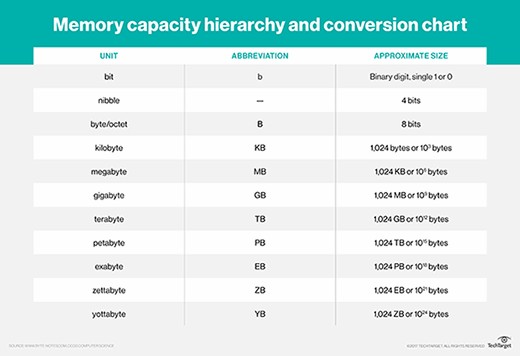
A terabyte (TB) is equal to 1,024 gigabytes (GB). In turn, a gigabyte is 1,024 megabytes (MB), and a megabyte is 1,024 kilobytes (KB). This exponential scaling highlights how quickly data capacity grows as we move up the scale.
1.2. Historical Context of the Terabyte
The concept of the terabyte became relevant as storage technology advanced. In 2007, Hitachi introduced the first terabyte-level hard drive. This milestone marked a significant leap in storage capacity, enabling users to store vast amounts of data on a single device. Today, hard drives can hold up to 18 TB of data, and SSDs can reach capacities of up to 100 TB.
1.3. The Byte and Its Origins
The foundation of all these measurements is the byte, which typically consists of eight bits. A bit, short for binary digit, is the smallest unit of data in a computer system, representing either a 0 or a 1. The term “byte” is credited to Werner Buchholz, who coined it while working on IBM’s first transistorized supercomputer, the 7030 STRETCH, in 1956.
 storage capacity chart
storage capacity chart
2. Terabyte vs. Other Units of Measurement
Understanding where a terabyte fits within the broader spectrum of storage units helps to contextualize its size and importance.
2.1. Smaller Units: Kilobytes, Megabytes, and Gigabytes
Before terabytes, kilobytes, megabytes, and gigabytes were the standard units of measurement.
- A kilobyte (KB) is approximately 1,000 bytes.
- A megabyte (MB) is approximately 1,000 kilobytes.
- A gigabyte (GB) is approximately 1,000 megabytes.
While these units were once considered large, they are now relatively small in comparison to terabytes and larger units.
2.2. Larger Units: Petabytes, Exabytes, and Beyond
As data generation continues to explode, even terabytes are becoming insufficient for some applications. This has led to the development of even larger units of measurement:
- A petabyte (PB) is 1,024 terabytes.
- An exabyte (EB) is 1,024 petabytes.
- A zettabyte (ZB) is 1,024 exabytes.
- A yottabyte (YB) is 1,024 zettabytes.
- A brontobyte (BB) is 1,024 yottabytes.
- A geopbyte (GeB) is 1,000 brontobytes.
The need for these increasingly large units underscores the relentless growth of data in the digital age.
3. What Can You Store on a Terabyte?
To provide a more concrete understanding of a terabyte’s capacity, let’s look at some real-world examples of what it can hold.
3.1. Document Storage
A terabyte can store a vast number of text-based documents. Specifically, it can hold approximately 85,899,345 pages of Word documents or around 132,150 books with 650 pages each. This makes it ideal for archiving large collections of written material.
3.2. Photo Storage
For photography enthusiasts, a terabyte offers ample space for storing high-resolution images. You can store approximately 310,000 photos on a single terabyte drive, allowing you to preserve countless memories without worrying about running out of space.
3.3. Video Storage
Video files tend to be larger than other types of data, but a terabyte can still accommodate a significant amount of video content. It can hold about 500 hours of movies or 1,000 hours of video, making it suitable for storing a large collection of films, TV shows, or personal video recordings.
3.4. Music Storage
Music lovers can rejoice in the vast storage capacity of a terabyte. It can hold approximately 17,000 hours of music, allowing you to carry your entire music library with you wherever you go.
3.5. Comparison Chart
| Type of Data | Approximate Amount Storable on 1 TB |
|---|---|
| Word Documents | 85,899,345 pages |
| 650-Page Books | 132,150 |
| Photos | 310,000 |
| Movies | 500 hours |
| Video | 1,000 hours |
| Music | 17,000 hours |
4. Practical Applications of a Terabyte
Terabytes are essential in various fields, from personal computing to enterprise data management. Understanding these applications can help you appreciate the importance of this unit of measurement.
4.1. Personal Computing
For personal computer users, a terabyte hard drive or SSD provides ample storage for operating systems, applications, and personal files. Whether you are a student, a professional, or a casual user, having a terabyte of storage ensures that you won’t run out of space anytime soon.
4.2. Gaming
Modern video games can be quite large, often exceeding 50 GB in size. A terabyte drive can comfortably accommodate a large collection of games, ensuring that you can enjoy your favorite titles without constantly deleting and reinstalling them.
4.3. Content Creation
Content creators, such as photographers, videographers, and graphic designers, often work with large files that require significant storage space. A terabyte drive provides the necessary capacity to store and edit these files, enabling them to produce high-quality content without being constrained by storage limitations.
4.4. Data Backup
Backing up your data is crucial for protecting against data loss due to hardware failure, software corruption, or accidental deletion. A terabyte drive can serve as a reliable backup solution, allowing you to create a complete copy of your important files and restore them in case of an emergency.
4.5. Cloud Storage
Cloud storage providers often offer terabyte-level storage plans, allowing users to store their data remotely and access it from anywhere in the world. This is particularly useful for individuals and businesses that need to collaborate on projects or share files with others.
4.6. Enterprise Data Management
In the enterprise world, terabytes are the standard unit of measurement for databases, virtual machines, and other critical data assets. Businesses rely on terabyte-scale storage systems to manage their operations, analyze data, and make informed decisions.
5. The Future of Storage: Beyond the Terabyte
While terabytes are currently the norm, the future of storage is rapidly moving towards even larger units of measurement. As technology advances and data generation continues to accelerate, petabytes, exabytes, and even zettabytes will become increasingly common.
5.1. The Rise of SSDs
Solid-state drives (SSDs) are rapidly replacing traditional hard disk drives (HDDs) due to their superior performance, durability, and energy efficiency. SSDs are capable of storing vast amounts of data in a small form factor, making them ideal for laptops, desktops, and other portable devices.
5.2. NVMe Technology
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) is a high-performance interface protocol designed specifically for SSDs. NVMe drives offer significantly faster data transfer rates than traditional SATA drives, enabling users to access their data more quickly and efficiently.
5.3. QLC Technology
Quad-level cell (QLC) technology is a type of flash memory that can store four bits of data per cell. QLC SSDs offer higher storage densities and lower costs than other types of flash memory, making them an attractive option for high-capacity storage solutions.
5.4. The Cloud Era
Cloud storage is becoming increasingly popular, as it offers a convenient and scalable way to store and access data. Cloud providers are constantly expanding their storage capacity to meet the growing demands of their customers, and they are investing in new technologies to improve the performance and reliability of their services.
6. Choosing the Right Storage Solution
Selecting the right storage solution depends on your specific needs and budget. Consider the following factors when making your decision:
6.1. Storage Capacity
Determine how much storage space you need based on the types of files you will be storing and how frequently you will be accessing them. If you work with large files or have a vast collection of media, you will need a larger storage capacity than someone who primarily uses their computer for basic tasks.
6.2. Performance
If you need fast access to your data, consider an SSD or NVMe drive. These drives offer significantly faster data transfer rates than traditional HDDs, which can improve your overall computing experience.
6.3. Cost
Storage prices vary depending on the type of drive, capacity, and performance. Compare prices from different vendors to find the best deal for your budget.
6.4. Reliability
Choose a storage solution from a reputable brand with a proven track record of reliability. Read reviews and compare warranties to ensure that you are getting a high-quality product that will last.
6.5. Portability
If you need to transport your data frequently, consider a portable external drive or cloud storage solution. These options allow you to access your data from anywhere with an internet connection.
7. Expert Insights from HOW.EDU.VN
At HOW.EDU.VN, we understand that navigating the world of data storage can be complex. That’s why we’ve assembled a team of experts to provide you with the guidance and support you need.
7.1. Dr. [Expert Name], Ph.D. in Computer Science
Dr. [Expert Name] is a leading expert in data storage technologies with over 20 years of experience in the field. He has published numerous research papers on topics such as SSD performance, cloud storage optimization, and data compression algorithms.
7.2. [Expert Name], Certified Data Management Professional
[Expert Name] is a certified data management professional with extensive experience in helping businesses manage their data assets. She has worked with companies of all sizes to develop and implement effective data storage strategies.
7.3. [Expert Name], IT Consultant
[Expert Name] is an IT consultant who specializes in helping individuals and small businesses choose the right storage solutions for their needs. He has a deep understanding of the latest storage technologies and can provide unbiased advice on the best options for your budget.
7.4. Benefits of Consulting with Our Experts
Consulting with our experts at HOW.EDU.VN offers numerous benefits:
- Personalized advice: Our experts will take the time to understand your specific needs and provide tailored recommendations.
- Up-to-date information: We stay on top of the latest trends in data storage to ensure that you have access to the most current information.
- Unbiased recommendations: We are not affiliated with any particular vendor, so we can provide unbiased advice on the best storage solutions for your needs.
- Cost-effective solutions: We can help you find cost-effective storage solutions that meet your needs without breaking the bank.
| Expert Name | Title | Expertise |
|---|---|---|
| Dr. Expert Name | Ph.D. in Computer Science | SSD Performance, Cloud Storage Optimization |
| Expert Name | Certified Data Management Professional | Data Management Strategies, Enterprise Solutions |
| Expert Name | IT Consultant | Personal and Small Business Storage Solutions |
8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Here are some frequently asked questions about terabytes and data storage:
8.1. How many gigabytes are in a terabyte?
There are 1,024 gigabytes (GB) in a terabyte (TB).
8.2. Is a terabyte enough storage for my needs?
Whether a terabyte is enough storage depends on your specific needs. If you primarily use your computer for basic tasks, such as web browsing and email, a terabyte may be more than enough. However, if you work with large files, such as videos or high-resolution photos, you may need more storage.
8.3. What is the difference between a hard drive and an SSD?
A hard drive (HDD) is a traditional storage device that uses spinning platters to store data. An SSD (solid-state drive) is a newer type of storage device that uses flash memory to store data. SSDs are generally faster, more durable, and more energy-efficient than HDDs.
8.4. What is cloud storage?
Cloud storage is a way to store your data remotely on servers owned by a third-party provider. This allows you to access your data from anywhere with an internet connection.
8.5. How do I back up my data?
There are several ways to back up your data, including using an external hard drive, cloud storage, or a dedicated backup service. It is important to back up your data regularly to protect against data loss.
8.6. What is NVMe?
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) is a high-performance interface protocol designed specifically for SSDs. NVMe drives offer significantly faster data transfer rates than traditional SATA drives.
8.7. What is QLC technology?
Quad-level cell (QLC) technology is a type of flash memory that can store four bits of data per cell. QLC SSDs offer higher storage densities and lower costs than other types of flash memory.
8.8. How do I choose the right storage solution for my needs?
Consider factors such as storage capacity, performance, cost, reliability, and portability when choosing a storage solution.
8.9. How can HOW.EDU.VN help me with my storage needs?
HOW.EDU.VN offers expert advice and guidance on all aspects of data storage. Our team of experts can help you choose the right storage solutions for your needs and budget.
8.10. Where can I learn more about data storage?
HOW.EDU.VN provides a wealth of information on data storage technologies, including articles, tutorials, and product reviews.
9. Take the Next Step with HOW.EDU.VN
Understanding how much storage a terabyte offers is crucial in today’s data-driven world. Whether you’re managing personal files or handling enterprise-level data, knowing the capacity and applications of a terabyte can empower you to make informed decisions.
Ready to optimize your storage solutions? Contact the experts at HOW.EDU.VN for personalized advice and guidance. Our team of Ph.D.s and certified professionals is here to help you navigate the complexities of data storage and find the perfect solutions for your unique needs.
Don’t let data challenges hold you back. Reach out to HOW.EDU.VN today and unlock the full potential of your data storage capabilities.
Contact Information:
- Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
- Website: how.edu.vn