The question of how much sugar is in a mango is a common one for those mindful of their diet and blood sugar levels. At HOW.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of making informed food choices. This article delves into the sugar content of mangoes, their nutritional benefits, and how to enjoy them while maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. Discover expert insights and practical tips to incorporate this delicious fruit into your diet. We aim to offer comprehensive information while also highlighting the expertise available at HOW.EDU.VN for personalized dietary advice. Learn about mango nutrition facts, glycemic index, and balanced diet strategies.
1. The Nutritional Powerhouse: Why Include Fruits Like Mangoes in Your Diet
Fruits, including the luscious mango, are essential components of a balanced diet, offering a wealth of vitamins, minerals, and fiber. According to the latest Dietary Guidelines for Americans, adults should consume 1.5 to 2.5 cups of fruits daily, prioritizing whole fruits over juices to maximize nutritional benefits. These guidelines emphasize that consuming a sufficient amount of fruit is a cornerstone of healthy eating. For personalized dietary advice and strategies to optimize your fruit intake, consider consulting the expert nutritionists and dietitians at HOW.EDU.VN. Understanding the role of fruits in your diet is the first step toward a healthier lifestyle. Benefits of eating fruit include reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke, aiding in weight management and contributing to modest weight loss, and reduced mortality risk.
1.1 The Multifaceted Benefits of Fruit Consumption
Research consistently demonstrates the profound health advantages of incorporating fruits into one’s daily diet. A diet rich in fruits and vegetables is linked to a reduced risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and stroke, as highlighted in a study published in the Journal of the American Heart Association. Additionally, fruits play a crucial role in weight management, offering a satisfying and nutritious alternative to processed snacks. This is supported by findings in Frontiers in Nutrition, which emphasize the impact of fruit consumption on weight loss. Moreover, a comprehensive study in Circulation revealed a correlation between fruit intake and reduced mortality risk. The key lies in the rich array of vitamins, minerals, and fiber found in whole fruits, contributing to overall well-being. These health benefits and nutritional considerations can be complex, which is why HOW.EDU.VN offers access to expert guidance from seasoned professionals.
1.2 The Concerning Gap: Insufficient Fruit Intake in the U.S. Population
Despite the well-documented health benefits of fruit consumption, a significant portion of the U.S. population falls short of meeting the recommended daily intake. According to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, approximately 80% of adults do not consume the recommended daily servings of fruits. This alarming statistic underscores the need for increased awareness and practical strategies to encourage greater fruit consumption. Factors contributing to this shortfall may include limited access to fresh produce, lack of knowledge about portion sizes and nutritional value, and dietary habits influenced by processed foods. To bridge this gap and promote healthier eating habits, HOW.EDU.VN provides resources and expert consultations to help individuals incorporate more fruits into their daily meals and snacks. A registered dietician can offer personalized advice tailored to your specific needs and preferences.
1.3 Mango Nutrition Facts: A Closer Look at the King of Fruits
Mangoes, often hailed as the “king of fruits,” boast an impressive nutritional profile, making them a valuable addition to any diet. A single serving of mango, roughly equivalent to half of a large fruit, contains a wealth of essential nutrients. Mangoes are particularly rich in vitamin C, which supports immune function and skin health, and vitamin A, vital for vision and cell growth. In addition to these key vitamins, mangoes provide a good source of dietary fiber, promoting digestive health and satiety. They also contain various antioxidants that combat oxidative stress and inflammation. By understanding the nutritional composition of mangoes, individuals can make informed choices and incorporate this delicious fruit into their meals and snacks to boost their overall nutrient intake. Individuals seeking more detailed advice on integrating mangoes into their diet can find resources at HOW.EDU.VN or can connect with one of our professionals.
2. Decoding Mangoes: Exploring the Diverse Types and Their Sugar Content
Mangoes are cultivated across the globe, with India being the world’s largest producer, yielding over 20.9 million metric tons in 2021. Other significant producers include Bangladesh, Mexico, Pakistan, and the Philippines. Even parts of the United States, like Florida, boast unique mango cultivars. The wide variety of mango types raises questions about their individual sugar and nutrient contents. Understanding these differences can help you make informed choices about which mangoes to include in your diet. For personalized dietary advice, consider consulting the experts at HOW.EDU.VN. Our dieticians can help you understand the nutritional profiles of different mango varieties. Mango varieties include Alphonso mango, Carabao mango, Sindhri mango, Ataulfo mango, Haden mango, Julie mango, Ivory mango, Tommy Atkins mango, and Hilacha mango.
2.1 A Global Palette: Popular Mango Varieties from Around the World
The world of mangoes is incredibly diverse, with various types cultivated in different regions, each possessing unique flavors, textures, and nutritional profiles. In India, the Alphonso mango stands out as a prized variety, known for its rich, creamy texture and intense sweetness. The Philippines boasts the Carabao mango, celebrated for its exceptional sweetness and smooth flesh. Pakistan offers the Sindhri mango, characterized by its vibrant yellow color and aromatic flavor. Mexico contributes the Ataulfo mango, distinguished by its small size, golden hue, and buttery texture. In Florida, the Haden mango is a popular choice, featuring a blend of sweet and tangy notes. Other notable varieties include the Julie mango from Jamaica, the Ivory mango from Thailand, the Tommy Atkins mango from Florida, and the Hilacha mango from Colombia. Each of these mango types brings its own unique characteristics to the table, offering a delightful range of flavors and textures to explore.
2.2 Sugar Composition: Understanding the Sweetness in Different Mangoes
The sweetness of mangoes primarily comes from natural sugars, including sucrose, fructose, and glucose. Sucrose, composed of glucose and fructose, is often the predominant sugar in mangoes. While all mangoes contain these sugars, the proportions can vary depending on the variety and ripeness of the fruit. Factors such as climate, soil conditions, and cultivation practices can also influence the sugar content of mangoes. To make informed choices about mango consumption, it’s essential to understand the sugar composition of different varieties. Those managing their blood sugar levels or following specific dietary guidelines may benefit from choosing mangoes with lower sugar content or opting for smaller portion sizes. It’s important to remember that even though mangoes contain natural sugars, they also offer valuable vitamins, minerals, and fiber, making them a nutritious addition to a balanced diet.
2.3 Sugar Content Comparison: A Detailed Look at Common Mango Varieties
To provide a clearer understanding of the sugar content in different mango varieties, here’s a table comparing some popular types:
| Mango Variety | Approximate Sugar Content (grams per 100g) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Alphonso | 15-17g | Known for its rich, creamy texture and intense sweetness. |
| Carabao | 13-15g | Celebrated for its exceptional sweetness and smooth flesh. |
| Sindhri | 14-16g | Characterized by its vibrant yellow color and aromatic flavor. |
| Ataulfo | 12-14g | Distinguished by its small size, golden hue, and buttery texture. |
| Haden | 13-15g | Features a blend of sweet and tangy notes. |
| Tommy Atkins | 11-13g | A widely available variety with a relatively mild sweetness. |
| Kent | 12-14g | Known for its large size and fiber-free flesh. |
| Keitt | 10-12g | Often available later in the season and has a slightly tart flavor. |
| Honey (Ataulfo) | 14-16g | This variety is extra sweet, hence the name “Honey” mango. |




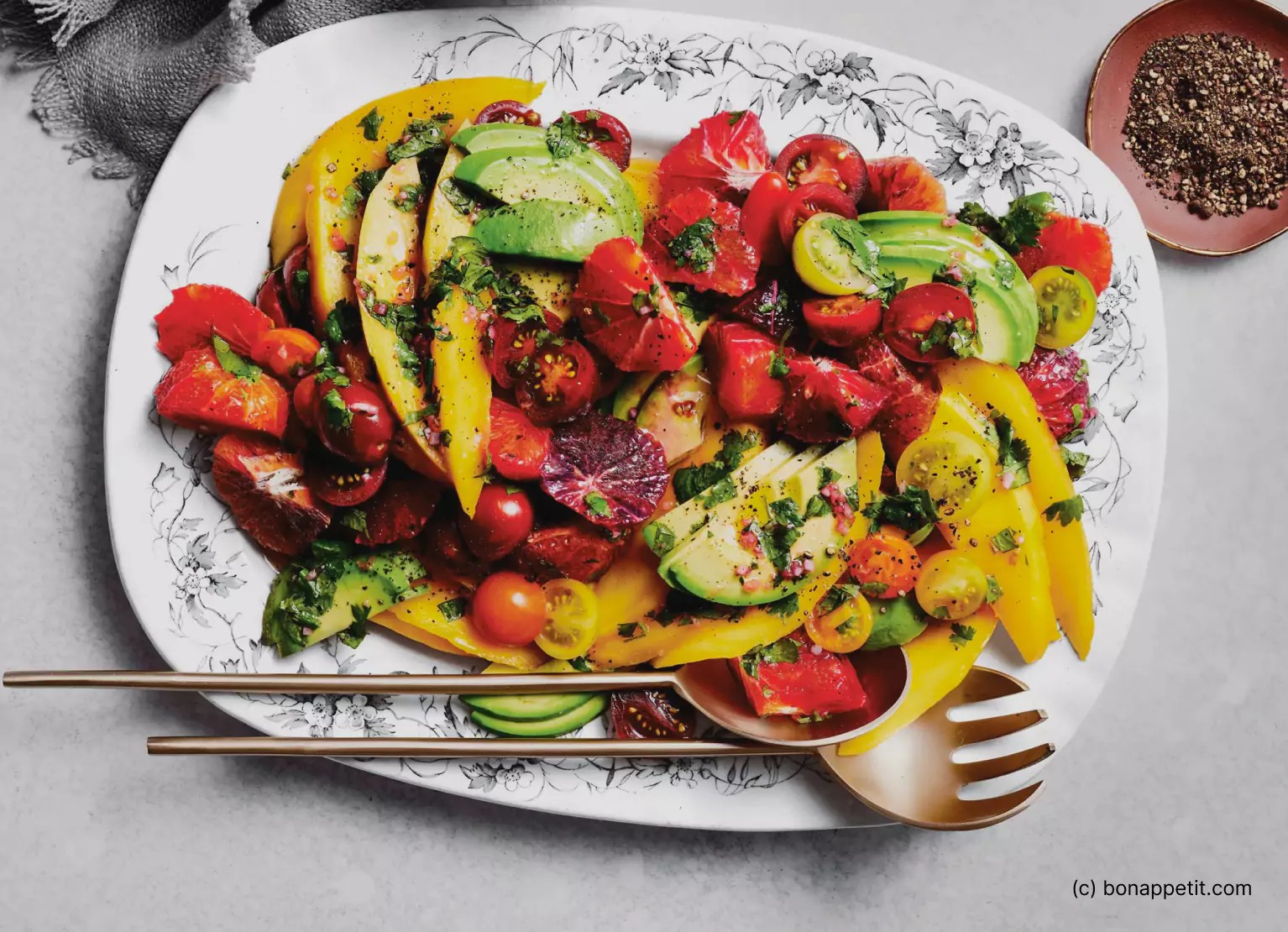


Please note that these values are approximate and can vary based on ripeness and growing conditions.
This table offers a general comparison of sugar levels. Consulting with a nutritionist at HOW.EDU.VN can provide more personalized insights tailored to your dietary needs.
3. Mangoes and Blood Glucose: Navigating the Sweetness Responsibly
Mangoes, similar to grapes, contain a moderate amount of sugar but have a low glycemic index (GI) of 51. This means that mangoes are less likely to cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels compared to high-GI foods. However, due to their sugar content, mangoes can still affect blood sugar levels, especially if eaten in large quantities or without other sources of fiber or protein. Individuals with insulin resistance, prediabetes, or diabetes should be particularly mindful of their mango consumption. Whether you have insulin resistance, are predisposed to type 2 diabetes, or even if you’re someone who is otherwise healthy, eating mangos without another source of fiber or protein can lead to a poor blood glucose response. For expert advice on managing blood sugar levels, consider the resources at HOW.EDU.VN. Our team of dieticians can offer practical strategies for incorporating mangoes into a balanced diet.
3.1 Understanding the Glycemic Index: How Mangoes Measure Up
The glycemic index (GI) is a valuable tool for understanding how different foods affect blood sugar levels. Foods with a low GI (55 or less) are digested and absorbed more slowly, resulting in a gradual rise in blood sugar. Mangoes, with a GI of 51, fall into this category, suggesting they have a relatively moderate impact on blood sugar. However, it’s essential to consider the glycemic load (GL) as well, which takes into account both the GI and the amount of carbohydrates in a serving. While mangoes have a moderate GI, their GL can be higher depending on the portion size. To manage blood sugar levels effectively, it’s recommended to consume mangoes in moderation and pair them with other foods that can help stabilize blood sugar, such as those rich in fiber, protein, or healthy fats.
3.2 Factors Influencing Blood Glucose Response to Mangoes
Several factors can influence how your blood glucose responds to mango consumption. Portion size is a key determinant, as eating a large serving of mango can lead to a more significant rise in blood sugar compared to a smaller serving. The ripeness of the mango can also play a role, as riper mangoes tend to have a higher sugar content. Consuming mangoes on an empty stomach or without any other foods can result in a more rapid absorption of sugar, leading to a sharper spike in blood sugar levels. Individual factors such as insulin sensitivity, metabolic rate, and overall health status can also affect the glucose response. Additionally, physical activity levels can impact how the body processes sugar, with exercise helping to improve insulin sensitivity and glucose control.
3.3 Practical Tips for Balancing Blood Sugar While Enjoying Mangoes
To enjoy the deliciousness of mangoes while maintaining healthy blood sugar levels, consider the following tips:
- Pair with Fiber and Healthy Fats: Combining mangoes with foods rich in fiber, such as nuts, seeds, or whole grains, can help slow down the absorption of sugar and prevent rapid spikes in blood sugar. Healthy fats, such as those found in avocados or nut butter, can also contribute to a more stable glucose response.
- Prioritize Protein Intake: Eating a protein source before or along with mangoes can help regulate blood sugar levels by slowing down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates. Opt for lean protein sources such as Greek yogurt, eggs, or poultry.
- Practice Portion Control: Be mindful of portion sizes and stick to a moderate serving of mangoes. A general guideline is to consume about half a mango at a time.
- Engage in Physical Activity: Regular exercise can improve insulin sensitivity and help the body utilize glucose more efficiently. Consider going for a walk or engaging in other forms of physical activity after enjoying mangoes.
- Consult a Nutritionist: Work with a registered dietitian or certified diabetes educator to create a personalized meal plan that includes mangoes in a way that aligns with your individual needs and health goals.
- Monitor Blood Glucose Levels: If you have diabetes or insulin resistance, consider monitoring your blood glucose levels before and after eating mangoes to understand how your body responds.
By following these tips, you can enjoy the delightful flavor and nutritional benefits of mangoes while keeping your blood sugar levels in check.
4. Delicious Mango Recipes: Combining Taste and Health
To help you incorporate mangoes into your diet in a healthy and delicious way, here are three recipes:
4.1 Mango and Avocado Salad: A Refreshing Summer Delight
This Mango and Avocado Salad recipe, featured on Bon Appetit, offers a refreshing twist on traditional salads. Combining the sweetness of mangoes with the creaminess of avocados, this salad is perfect for a light lunch under the sun.
Ingredients:
- ⅓ cup extra-virgin olive oil
- ⅓ cup fresh blood orange juice
- ¼ cup fresh lime juice
- 1 tablespoon honey
- 1 tablespoon kosher salt
- ½ teaspoon freshly ground black pepper
- 1 shallot, finely chopped
- 2 tablespoons finely chopped cilantro
- 4 blood oranges, peeled and sliced into irregular pieces
- 2 mangoes, peeled and sliced
- 2 avocados, peeled and sliced
- 1 cup halved cherry tomatoes
Why We Love It: This recipe is packed with healthy fats from olive oil and avocado, which can help balance blood sugar. Adding nuts or feta cheese can further boost protein and fat content, creating a well-rounded meal.
4.2 Paleo Mango Pudding with Coconut Milk: A Guilt-Free Dessert
This Paleo Mango Pudding with Coconut Milk, inspired by What Great Grandma Ate, offers a delicious dessert option even for those with dietary restrictions. The combination of mangoes and coconut milk creates a creamy, satisfying treat.
Ingredients:
- Mango chunks (fresh or frozen)
- Gelatin
- Full-fat coconut milk
- Coconut sugar (optional)
- Handful of pecans (optional)
Why We Love It: Using whole fruit for dessert is a great way to add vitamins and minerals to your diet. The addition of nuts provides healthy fats that help prevent glucose spikes.
4.3 Sweet and Salty Mango Lassi: An Indian-Inspired Delight
This Sweet and Salty Mango Lassi, adapted from a Bon Appetit recipe, is a traditional Indian drink made with yogurt, water, fruit, and spices. It’s easy to prepare and perfect for a warm day.
Ingredients:
- 2 tablespoons cumin seeds
- ½ cup fresh lime juice
- 2 teaspoons black salt or kosher salt
- 4 cups plain whole-milk yogurt
- 1 can of unsweetened mango pulp
- Mint sprigs (for serving)
Why We Love It: This drink is a great source of vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats. Pairing it with a protein-rich meal can help support balanced glucose levels.
5. Frequently Asked Questions About Mangoes and Sugar
To further address your questions and concerns about mangoes and their sugar content, here are some frequently asked questions:
- Are mangoes a healthy choice despite their sugar content?
- Yes, mangoes are a healthy choice when consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet. They provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
- Can people with diabetes eat mangoes?
- People with diabetes can enjoy mangoes in moderation. Monitoring blood glucose levels and pairing mangoes with protein and fiber is recommended.
- What is the best time of day to eat mangoes?
- Eating mangoes as part of a meal or snack is preferable to consuming them on an empty stomach to help regulate blood sugar.
- How does the sugar content of mangoes compare to other fruits?
- Mangoes have a moderate sugar content compared to fruits like grapes and bananas but less than dried fruits.
- Are frozen mangoes as nutritious as fresh mangoes?
- Yes, frozen mangoes are generally as nutritious as fresh mangoes, as they are typically frozen at peak ripeness.
- Can I reduce the sugar content of mangoes by cooking them?
- Cooking mangoes does not significantly reduce their sugar content, but it can alter their texture and flavor.
- What are some healthy snacks to pair with mangoes?
- Healthy snacks to pair with mangoes include nuts, seeds, Greek yogurt, and cottage cheese.
- How do I choose a ripe mango at the grocery store?
- A ripe mango will yield slightly to gentle pressure and have a fragrant aroma near the stem.
- Are green mangoes lower in sugar than ripe mangoes?
- Green mangoes are generally lower in sugar than ripe mangoes and have a more tart flavor.
- Where can I find more information on healthy eating and managing blood sugar?
For personalized dietary advice and strategies to manage blood sugar levels, consult the expert nutritionists and dieticians at HOW.EDU.VN.
Take Control of Your Health with Expert Advice from HOW.EDU.VN
Understanding the sugar content of mangoes and how they impact your health is essential for making informed dietary choices. While mangoes offer numerous nutritional benefits, it’s crucial to consume them in moderation and pair them with other foods that support balanced blood sugar levels.
Navigating these complexities can be challenging, but you don’t have to do it alone. At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with over 100 world-renowned Ph.D.s and experts who can provide personalized guidance tailored to your specific needs and health goals. Whether you’re seeking advice on managing diabetes, optimizing your diet, or simply improving your overall well-being, our team of experts is here to help.
Don’t let uncertainty hold you back. Contact us today to connect with a leading expert and take the first step toward a healthier, more informed you.
Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
Website: HOW.EDU.VN
Unlock the power of personalized expertise and achieve your health goals with how.edu.vn.
