How Much Theft Is A Felony often depends on the value of the stolen property and jurisdictional laws. At HOW.EDU.VN, we provide expert insights into the legal definitions, variations across states, and potential consequences of felony theft, assisting you in navigating these complex legal matters. Understanding theft classification is crucial for both legal professionals and individuals seeking clarity on property crime severity.
1. Understanding Felony Theft: A Comprehensive Overview
Theft, in its most basic form, is the unlawful taking of someone else’s property with the intent to permanently deprive them of it. However, the legal system classifies theft into different categories based on factors like the value of the stolen goods, the nature of the property, and the circumstances surrounding the act. One of the most significant distinctions is between misdemeanor and felony theft. A misdemeanor is generally considered a less serious crime, while a felony carries much harsher penalties, including imprisonment for more than one year.
1.1. Defining Theft and Its Legal Classifications
Theft encompasses a wide range of actions, from shoplifting a small item to embezzling large sums of money. Each state has its own set of laws defining theft and classifying it based on various criteria. Generally, theft requires the following elements:
- Taking: Physically taking possession of the property.
- Carrying Away: Moving the property, even a short distance.
- Intent to Deprive: The intention to permanently keep the property from its rightful owner.
- Property of Another: The property must belong to someone other than the person taking it.
The classification of theft—whether as a misdemeanor or a felony—depends largely on the value of the stolen property. Other factors, such as the type of property (e.g., firearms, vehicles) and the offender’s prior criminal record, can also influence the classification. For reliable legal consultation tailored to your specific needs, connect with our experienced team of legal experts at HOW.EDU.VN.
1.2. Misdemeanor vs. Felony Theft: Key Distinctions
The line between misdemeanor and felony theft is primarily drawn by the value of the stolen property. However, this threshold varies significantly from state to state.
-
Misdemeanor Theft: Typically involves theft of property with a value below a certain threshold, which can range from a few hundred dollars to over $1,000 in some states. Penalties for misdemeanor theft usually include fines, community service, probation, and possibly a short jail sentence (less than one year).
-
Felony Theft: Involves theft of property with a value exceeding the state’s felony threshold. This threshold can range from a few hundred dollars to several thousand dollars. Penalties for felony theft are much more severe, including imprisonment for more than one year, substantial fines, and a criminal record that can significantly impact future employment and other opportunities.
It’s important to note that some states may also classify theft as a felony regardless of the value of the property if certain conditions are met, such as the theft of a firearm or a vehicle, or if the offender has a prior history of theft convictions. Our experts at HOW.EDU.VN are available to provide detailed insights and legal advice specific to your jurisdiction.
1.3. Factors Influencing the Severity of Theft Charges
Several factors can influence whether a theft charge is classified as a misdemeanor or a felony:
- Value of the Stolen Property: The most common factor is the monetary value of the stolen items. States set specific thresholds that determine whether the theft is a misdemeanor or a felony.
- Type of Property: Some states have specific laws that automatically classify the theft of certain types of property (e.g., firearms, vehicles, credit cards) as a felony, regardless of their value.
- Prior Criminal Record: A defendant’s prior criminal history, especially prior theft convictions, can elevate a current theft charge from a misdemeanor to a felony.
- Circumstances of the Theft: The manner in which the theft was committed can also impact the severity of the charges. For example, theft that involves violence, threats, or breaking and entering may be charged as a more serious offense.
- State Laws: Each state has its own unique set of laws and regulations regarding theft, so the specific rules and penalties can vary significantly depending on the jurisdiction.
1.4. The Role of Intent in Theft Offenses
Intent plays a crucial role in determining whether an act of taking property constitutes theft. To be convicted of theft, the prosecution must prove that the defendant intended to permanently deprive the owner of the property. This means that accidental or unintentional taking of property is generally not considered theft.
- Proving Intent: Establishing intent can be challenging. Prosecutors often rely on circumstantial evidence, such as the defendant’s actions, statements, and the surrounding circumstances, to prove that the defendant intended to steal the property.
- Lack of Intent as a Defense: A common defense in theft cases is that the defendant did not have the intent to steal the property. For example, a person might argue that they mistakenly took someone else’s property, or that they intended to return the property but were unable to do so.
1.5. Examples of Scenarios That Can Be Classified as Felony Theft
To illustrate how theft can be classified as a felony, here are a few examples:
- Grand Larceny: Stealing a large sum of money or valuable property, such as jewelry or electronics, that exceeds the state’s felony threshold.
- Auto Theft: Stealing a vehicle, regardless of its value, as many states classify auto theft as a felony.
- Theft of a Firearm: Stealing a firearm, which is often classified as a felony due to the potential danger it poses.
- Embezzlement: Misappropriating funds or property from an employer or organization, where the value of the misappropriated items exceeds the felony threshold.
- Shoplifting with Intent to Resell: Shoplifting items with the intent to resell them for profit, where the total value of the items exceeds the felony threshold.
2. State-by-State Analysis of Felony Theft Thresholds
Felony theft thresholds vary significantly across the United States, reflecting differing state laws and priorities. Understanding these variations is crucial for anyone facing theft charges or seeking to understand the legal landscape of property crimes.
2.1. Overview of How States Define Felony Theft
Each state has its own specific laws defining felony theft, including the monetary threshold that triggers felony charges. These thresholds can range from a few hundred dollars to several thousand dollars. In addition to the value of the stolen property, some states consider other factors, such as the type of property stolen or the defendant’s prior criminal record, when determining whether to charge a theft offense as a felony.
2.2. Comparison of Felony Theft Thresholds Across Different States
Here is a comparison of felony theft thresholds in a few selected states:
| State | Felony Theft Threshold | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| California | $950 | |
| Texas | $2,500 | |
| New York | $1,000 | |
| Florida | $300 | |
| Pennsylvania | $2,000 | |
| Illinois | $500 | |
| Massachusetts | $1,200 | |
| Michigan | $1,000 | |
| Ohio | $1,000 | |
| Georgia | $1,500 |
This table illustrates the wide range of felony theft thresholds across different states. It’s important to note that these thresholds are subject to change, so it’s always best to consult with a legal professional or review the most current state statutes for accurate information. Contact HOW.EDU.VN to connect with experienced legal experts who can provide up-to-date and reliable guidance.
2.3. States with the Lowest and Highest Felony Theft Thresholds
- States with the Lowest Thresholds: States like Florida ($300) and North Carolina ($1,000) have relatively low felony theft thresholds. This means that even theft of property with a modest value can result in felony charges.
- States with the Highest Thresholds: States like Texas ($2,500) and Pennsylvania ($2,000) have higher felony theft thresholds. In these states, a larger amount of stolen property is required to trigger felony charges.
2.4. Factors Influencing the Setting of Felony Theft Thresholds
Several factors can influence a state’s decision to set its felony theft threshold at a particular level:
- Cost of Living: States with a higher cost of living may set higher thresholds to account for the increased value of goods and services.
- Crime Rates: States with higher property crime rates may set lower thresholds to deter theft and punish offenders more severely.
- Political Considerations: Political factors, such as the influence of law enforcement lobbies or public opinion on crime, can also play a role in setting felony theft thresholds.
- Economic Conditions: Economic conditions, such as inflation and unemployment rates, can also influence decisions about felony theft thresholds.
2.5. Recent Changes and Trends in State Felony Theft Laws
In recent years, there has been a trend toward increasing felony theft thresholds in some states. This trend is driven by several factors, including:
- Criminal Justice Reform: Efforts to reduce incarceration rates and divert offenders from the criminal justice system.
- Inflation: The rising cost of goods and services, which makes existing thresholds outdated.
- Data Analysis: Studies showing that raising felony theft thresholds does not necessarily lead to an increase in property crime.
For example, in 2020, Louisiana raised its felony theft threshold from $750 to $1,000. Similarly, in 2018, Mississippi raised its threshold from $500 to $1,000. These changes reflect a growing recognition that felony theft laws can have unintended consequences and that it may be more effective to focus resources on addressing more serious crimes. Stay updated on the latest legal changes and insights with our experts at HOW.EDU.VN.
3. Consequences of Felony Theft Convictions
A felony theft conviction can have severe and long-lasting consequences, impacting various aspects of a person’s life. Understanding these potential consequences is crucial for anyone facing felony theft charges.
3.1. Criminal Penalties: Imprisonment, Fines, and Probation
The criminal penalties for felony theft convictions can vary depending on the state, the value of the stolen property, and the defendant’s prior criminal record. However, in general, felony theft convictions carry much harsher penalties than misdemeanor theft convictions.
- Imprisonment: Felony theft convictions can result in imprisonment for more than one year, and in some cases, for many years. The length of the prison sentence will depend on the factors mentioned above.
- Fines: In addition to imprisonment, felony theft convictions can also result in substantial fines. These fines can range from a few thousand dollars to tens of thousands of dollars, depending on the severity of the offense.
- Probation: In some cases, a defendant may be sentenced to probation instead of, or in addition to, imprisonment. Probation involves supervision by a probation officer and compliance with certain conditions, such as drug testing, counseling, and community service. Violating the terms of probation can result in imprisonment.
3.2. Impact on Employment Opportunities
A felony theft conviction can significantly impact a person’s employment opportunities. Many employers conduct background checks on potential employees, and a felony conviction can be a major red flag.
- Difficulty Finding a Job: A felony theft conviction can make it difficult to find a job, especially in certain industries, such as finance, retail, and security.
- Loss of Professional Licenses: A felony theft conviction can also result in the loss of professional licenses, such as those for lawyers, doctors, and real estate agents.
- Limited Career Advancement: Even if a person is able to find a job after a felony theft conviction, they may face limited opportunities for career advancement.
3.3. Housing Restrictions and Limitations
A felony theft conviction can also create housing restrictions and limitations:
- Difficulty Renting an Apartment: Landlords often conduct background checks on potential tenants, and a felony conviction can make it difficult to rent an apartment.
- Ineligibility for Public Housing: A felony theft conviction can also make a person ineligible for public housing assistance.
- Restrictions on Living in Certain Areas: Some states have laws that restrict where convicted felons can live, such as near schools or parks.
3.4. Loss of Rights and Privileges
In addition to the criminal penalties and practical consequences, a felony theft conviction can also result in the loss of certain rights and privileges:
- Right to Vote: In many states, convicted felons lose the right to vote while they are incarcerated and sometimes even after they are released from prison.
- Right to Own a Firearm: Federal law prohibits convicted felons from owning or possessing firearms.
- Right to Serve on a Jury: Convicted felons are typically ineligible to serve on a jury.
- Travel Restrictions: Some countries may deny entry to individuals with felony convictions.
3.5. Social Stigma and Personal Relationships
Beyond the legal and practical consequences, a felony theft conviction can also carry a significant social stigma. This can lead to:
- Damaged Relationships: A felony conviction can strain relationships with family and friends.
- Difficulty Building Trust: People may be hesitant to trust someone with a felony theft conviction.
- Social Isolation: The stigma of a felony conviction can lead to social isolation and loneliness.
The weight of these consequences underscores the importance of seeking expert legal guidance when facing theft charges. At HOW.EDU.VN, our team of experienced legal professionals can provide you with the support and representation you need to navigate the complexities of the legal system and protect your rights.
4. Defenses Against Felony Theft Charges
Facing felony theft charges can be a daunting experience, but it’s important to remember that you have the right to defend yourself. There are several potential defenses that can be raised in a felony theft case, depending on the specific facts and circumstances.
4.1. Common Legal Defenses in Theft Cases
- Lack of Intent: As mentioned earlier, intent is a crucial element of theft. If the prosecution cannot prove that you intended to permanently deprive the owner of the property, you cannot be convicted of theft. This defense might be used if you mistakenly took someone else’s property or if you intended to return the property but were unable to do so.
- Mistake of Fact: This defense applies if you honestly believed that you had a right to possess the property. For example, if you believed that the property was yours or that you had permission to take it, you may be able to argue that you did not commit theft.
- Claim of Right: This defense applies if you took the property under a good-faith claim of right. For example, if you took property that you believed was owed to you as payment for a debt, you may be able to argue that you did not commit theft.
- Entrapment: This defense applies if you were induced to commit the theft by law enforcement officers or government agents. To succeed with this defense, you must show that you were not predisposed to commit the crime and that the government agents actively encouraged you to do so.
- Insufficient Evidence: The prosecution must prove your guilt beyond a reasonable doubt. If the prosecution’s evidence is weak or insufficient, you may be able to argue that they have not met their burden of proof.
4.2. The Importance of Evidence and Witness Testimony
Evidence and witness testimony play a crucial role in any criminal case, including felony theft cases.
- Evidence: Evidence can include physical evidence, such as stolen property, documents, and surveillance footage. It can also include forensic evidence, such as fingerprints and DNA.
- Witness Testimony: Witness testimony can come from the alleged victim, law enforcement officers, and other individuals who have knowledge of the events in question.
It’s important to gather and preserve any evidence that supports your defense. This may include receipts, photographs, videos, and witness statements. Contact HOW.EDU.VN to consult with legal experts who can help you gather and present your evidence effectively.
4.3. The Role of a Criminal Defense Attorney
A criminal defense attorney can play a critical role in defending you against felony theft charges.
- Investigating the Case: An attorney can investigate the case, gather evidence, and interview witnesses.
- Negotiating with the Prosecution: An attorney can negotiate with the prosecution to try to get the charges reduced or dismissed.
- Representing You in Court: An attorney can represent you in court and present your defense to a judge or jury.
- Protecting Your Rights: An attorney can ensure that your rights are protected throughout the criminal justice process.
4.4. Negotiating Plea Bargains and Reduced Charges
In many cases, it may be possible to negotiate a plea bargain with the prosecution. A plea bargain is an agreement in which you plead guilty to a lesser charge in exchange for a reduced sentence.
- Benefits of a Plea Bargain: A plea bargain can help you avoid the risk of a lengthy prison sentence and a felony conviction.
- Factors to Consider: When considering a plea bargain, it’s important to weigh the potential benefits against the potential risks. You should also consult with your attorney to determine whether a plea bargain is in your best interest.
4.5. Seeking Expert Legal Counsel for Your Defense
If you are facing felony theft charges, it’s essential to seek expert legal counsel as soon as possible. An experienced criminal defense attorney can evaluate your case, advise you of your rights, and help you develop a strong defense strategy.
- Finding the Right Attorney: When choosing an attorney, look for someone who has experience handling felony theft cases and who is familiar with the laws in your state.
- Consulting with Multiple Attorneys: It’s a good idea to consult with multiple attorneys before making a decision. This will give you the opportunity to compare their qualifications, experience, and fees.
5. The Impact of Proposition 47 on Felony Theft in California
Proposition 47, also known as the “Safe Neighborhoods and Schools Act,” was a ballot initiative passed by California voters in 2014. It reclassified certain non-violent property and drug offenses from felonies to misdemeanors. This had a significant impact on felony theft laws in California.
5.1. Overview of Proposition 47 and Its Objectives
The main objectives of Proposition 47 were to:
- Reduce Incarceration Rates: By reclassifying certain felonies as misdemeanors, Proposition 47 aimed to reduce the number of people incarcerated in California’s prisons and jails.
- Save Taxpayer Money: By reducing incarceration rates, Proposition 47 aimed to save taxpayer money on prison and jail costs.
- Reinvest Savings in Community Programs: Proposition 47 required the state to reinvest the savings from reduced incarceration rates into programs that address crime prevention, mental health, and substance abuse treatment.
5.2. Changes to California’s Felony Theft Threshold After Proposition 47
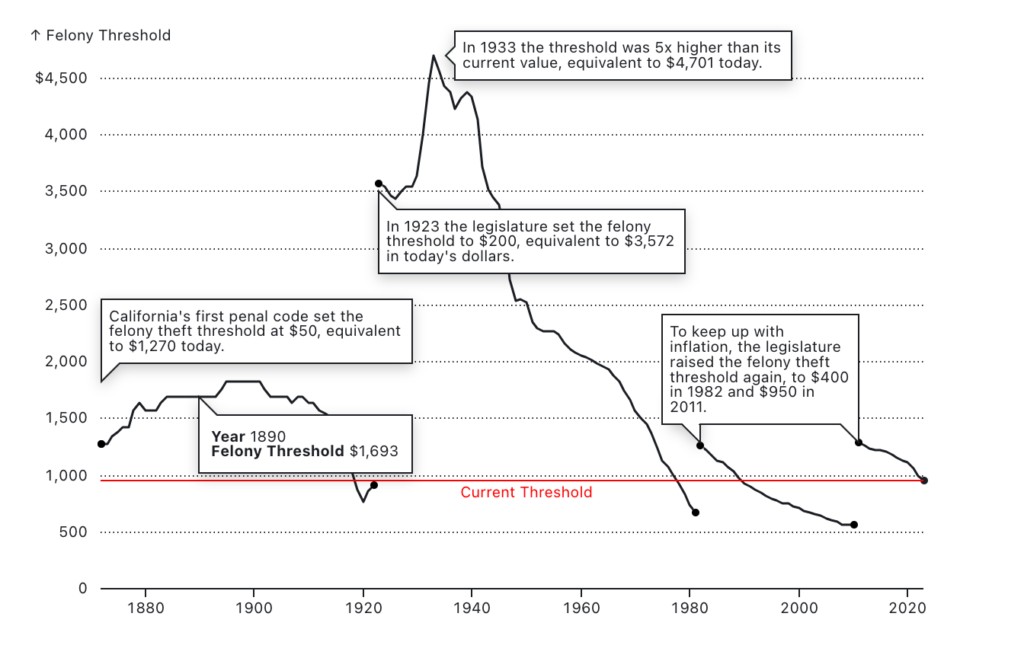
Prior to Proposition 47, California’s felony theft threshold was $400. This meant that theft of property valued at more than $400 was a felony, while theft of property valued at $400 or less was a misdemeanor. Proposition 47 raised the felony theft threshold to $950. This means that, as of 2014, theft of property valued at $950 or less is a misdemeanor, while theft of property valued at more than $950 is a felony.
5.3. Impact on Sentencing and Penalties for Theft Offenses
Proposition 47 had a significant impact on sentencing and penalties for theft offenses in California.
- Reduced Penalties for Certain Theft Offenses: Under Proposition 47, certain theft offenses that were previously felonies, such as shoplifting and grand theft, are now misdemeanors if the value of the stolen property is $950 or less. This means that individuals convicted of these offenses face reduced penalties, such as shorter jail sentences and lower fines.
- Retroactive Application: Proposition 47 was applied retroactively, meaning that individuals who were previously convicted of felonies that were reclassified as misdemeanors under Proposition 47 were able to petition the court to have their convictions reduced to misdemeanors.
5.4. Debates and Controversies Surrounding Proposition 47
Proposition 47 has been the subject of much debate and controversy.
- Supporters: Supporters of Proposition 47 argue that it has been successful in reducing incarceration rates, saving taxpayer money, and reinvesting savings in community programs. They also argue that it has helped to reduce racial disparities in the criminal justice system.
- Opponents: Opponents of Proposition 47 argue that it has led to an increase in property crime and that it has made it more difficult for law enforcement to hold offenders accountable. They also argue that it has undermined public safety.
5.5. Long-Term Effects and Future Implications for Theft Laws
The long-term effects of Proposition 47 on theft laws in California are still being studied. However, it is clear that Proposition 47 has had a significant impact on the way theft offenses are classified and punished in the state.
- Potential for Further Reforms: Some advocates are calling for further reforms to California’s theft laws, such as raising the felony theft threshold even higher or decriminalizing certain types of theft altogether.
- Influence on Other States: Proposition 47 has also influenced discussions about criminal justice reform in other states, and some states have considered adopting similar reforms.
6. How.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Navigating Legal Complexities
Navigating the complexities of theft laws can be challenging. Whether you’re facing charges, seeking legal clarity, or aiming to understand your rights, HOW.EDU.VN is here to provide expert guidance and support.
6.1. Connecting You with Expert Legal Professionals
At HOW.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of having access to knowledgeable and experienced legal professionals. That’s why we’ve built a network of over 100 distinguished PhDs and experts in various fields, including criminal law.
- Access to Top-Tier Experts: Our platform connects you directly with leading legal minds who can provide you with accurate, reliable, and personalized advice.
- Diverse Expertise: Whether you need assistance with understanding state-specific theft laws, developing a defense strategy, or negotiating a plea bargain, our experts have the skills and experience to help.
- Personalized Guidance: We recognize that every legal situation is unique. Our experts take the time to understand your specific circumstances and provide you with tailored guidance that meets your needs.
6.2. Providing Personalized Legal Advice and Support
We go beyond simply connecting you with legal experts. We also provide a range of personalized services designed to help you navigate the legal system with confidence.
- Case Evaluation: Our experts can evaluate your case and provide you with an honest assessment of your options.
- Legal Research: We can conduct in-depth legal research to help you understand the laws and regulations that apply to your situation.
- Document Review: Our experts can review legal documents, such as police reports and court filings, to identify potential issues and develop a strong defense strategy.
- Negotiation Assistance: We can assist you with negotiating with the prosecution to try to get the charges reduced or dismissed.
- Court Representation: If necessary, we can represent you in court and advocate for your rights.
6.3. Benefits of Seeking Professional Consultation Through HOW.EDU.VN
Choosing HOW.EDU.VN for your legal consultation needs offers numerous benefits:
- Expertise: Access to a network of highly qualified and experienced legal professionals.
- Convenience: Get the legal advice you need from the comfort of your own home or office.
- Affordability: Our services are competitively priced, making expert legal guidance accessible to everyone.
- Confidentiality: We understand the importance of confidentiality. All consultations are conducted in a secure and private environment.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing that you have the support of experienced legal professionals can give you peace of mind during a stressful time.
6.4. How to Get Started with HOW.EDU.VN for Your Legal Needs
Getting started with HOW.EDU.VN is easy:
- Visit Our Website: Go to HOW.EDU.VN to learn more about our services and experts.
- Create an Account: Sign up for a free account to access our platform.
- Find an Expert: Browse our directory of legal experts and select the one who best fits your needs.
- Schedule a Consultation: Schedule a consultation with your chosen expert at a time that is convenient for you.
- Get Expert Guidance: Receive personalized legal advice and support from our experienced professionals.
6.5. Success Stories and Testimonials from Satisfied Clients
Don’t just take our word for it. Here are some success stories and testimonials from satisfied clients:
- “I was facing serious felony theft charges and didn’t know where to turn. HOW.EDU.VN connected me with an amazing attorney who helped me get the charges reduced to a misdemeanor. I am so grateful for their help ” – John D.
- “I needed help understanding the theft laws in my state. HOW.EDU.VN provided me with the expert guidance I needed to navigate the legal system with confidence.” – Sarah L.
- “The experts at HOW.EDU.VN were incredibly knowledgeable and helpful. They took the time to understand my situation and provided me with personalized advice that made all the difference.” – Michael B.
Don’t navigate the complexities of theft laws alone. Let HOW.EDU.VN connect you with the expert legal guidance you need to protect your rights and achieve the best possible outcome.
If you’re grappling with legal challenges or simply seeking expert advice, don’t hesitate. Reach out to us today:
Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
Website: HOW.EDU.VN
7. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Felony Theft
Understanding the nuances of felony theft can be complex. Here are some frequently asked questions to help clarify common concerns:
7.1. What is the difference between theft, larceny, and robbery?
- Theft: A broad term encompassing various forms of unlawful taking of property.
- Larceny: The unlawful taking and carrying away of someone else’s personal property with the intent to permanently deprive the owner of it.
- Robbery: Theft that involves the use of force or the threat of force.
7.2. How is the value of stolen property determined in theft cases?
The value of stolen property is typically determined by its fair market value at the time of the theft. This can be established through appraisals, receipts, or expert testimony.
7.3. Can I be charged with felony theft if I didn’t physically steal the property?
Yes, you can be charged with felony theft even if you didn’t physically steal the property. If you aided, abetted, or conspired with someone else to commit the theft, you can be held criminally liable.
7.4. What should I do if I am accused of felony theft?
If you are accused of felony theft, it’s crucial to:
- Remain Silent: Do not speak to law enforcement without an attorney present.
- Seek Legal Counsel: Contact a criminal defense attorney as soon as possible.
- Gather Information: Collect any evidence that supports your defense.
7.5. Can a felony theft charge be expunged from my record?
In some states, it may be possible to expunge a felony theft conviction from your record, but this depends on the specific laws in your state and the circumstances of your case. Consult with an attorney to determine if you are eligible for expungement.
7.6. What is the statute of limitations for felony theft?
The statute of limitations for felony theft varies by state, but it is typically longer than the statute of limitations for misdemeanor theft. The statute of limitations sets a deadline for the prosecution to file charges.
7.7. How does a prior criminal record affect a felony theft charge?
A prior criminal record, especially prior theft convictions, can significantly impact a felony theft charge. It can increase the severity of the penalties and make it more difficult to negotiate a plea bargain.
7.8. Can I represent myself in a felony theft case?
While you have the right to represent yourself in a felony theft case, it is generally not advisable. Criminal law is complex, and an experienced attorney can provide you with the guidance and representation you need to protect your rights.
7.9. What are some alternatives to incarceration for felony theft?
Some alternatives to incarceration for felony theft include:
- Probation: Supervised release with certain conditions.
- Community Service: Performing unpaid work for the benefit of the community.
- Restitution: Paying compensation to the victim for their losses.
- Drug or Alcohol Treatment: If substance abuse is a factor in the theft.
7.10. How can HOW.EDU.VN help me with my felony theft case?
HOW.EDU.VN can connect you with experienced legal professionals who can provide you with personalized advice and representation. Our experts can evaluate your case, develop a strong defense strategy, and advocate for your rights throughout the criminal justice process.
 Criminal Justice System
Criminal Justice System
Connect with Leading Legal Minds
Don’t leave your future to chance. Trust the experts at how.edu.vn to guide you through the complexities of felony theft law and help you achieve the best possible outcome. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and take the first step toward protecting your rights and your future.
