Are you considering adding a shed to your property? Knowing how much it costs to build a shed is crucial for budgeting and planning your project. At HOW.EDU.VN, our team of experts provides detailed guidance on shed construction costs, helping you make informed decisions. We offer tailored advice and expert support so you can build your shed effectively. Our resources also cover storage solutions and outdoor structures.
1. Understanding the Factors That Influence Shed Building Costs
Estimating the cost to build a shed involves considering various factors that can significantly impact the final price. Let’s explore these elements in detail.
1. 1. Size and Dimensions
The size of the shed is a primary cost driver. Larger sheds require more materials, translating to higher expenses. Here’s a general idea:
- Small Sheds (8×10 ft): These are suitable for basic storage needs.
- Medium Sheds (10×12 ft to 12×16 ft): Provide more room for gardening equipment and tools.
- Large Sheds (16×20 ft and larger): Ideal for workshops, hobby spaces, or substantial storage.
1. 2. Material Choices
The type of materials you select for your shed will greatly influence the cost. Common options include:
- Wood: A popular choice due to its durability and aesthetic appeal. Wood sheds can be customized easily.
- Metal: Known for resistance to decay and rot, offering a long-lasting solution.
- Vinyl: Provides strength and resistance to rust, cracking, and denting, though often more expensive.
Cost Comparison of Shed Materials:
| Material | Average Cost Range |
|---|---|
| Wood | $800 – $3,000 |
| Metal | $500 – $2,000 |
| Vinyl | $800 – $5,000 |
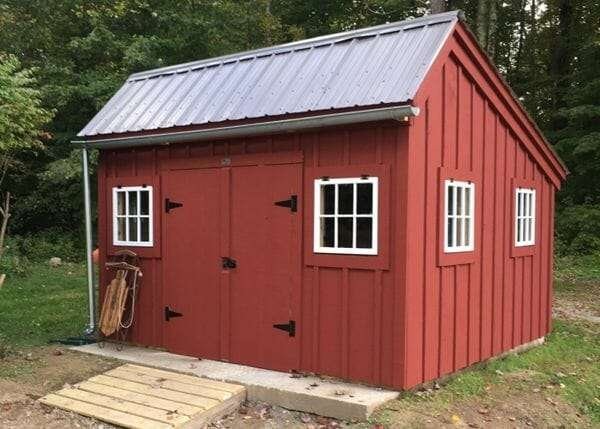


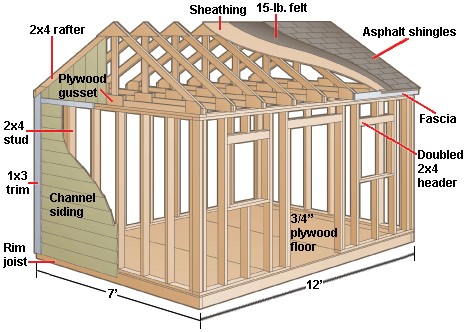

1. 3. Foundation Type
The foundation is critical for the shed’s stability and longevity. Common foundation types include:
- Wood Frame: A cost-effective option, especially on sloping ground.
- Concrete Slab: Provides a solid, level base but can be more expensive.
- Gravel Pad: Offers good drainage and is relatively easy to install.
1. 4. Design Complexity
The design of your shed also affects costs. Simple, straightforward designs are more affordable than complex ones with custom features.
- Roof Style: Gable, shed, and hip roofs all have different material and labor costs.
- Doors and Windows: The number and type of doors and windows can add to the expense.
- Custom Features: Cupolas, flower boxes, and other embellishments increase the overall cost.
1. 5. Labor Costs
If you hire a contractor, labor costs will be a significant factor. These costs vary based on location, the complexity of the project, and the contractor’s rates.
- DIY: You save on labor costs but need time and skills.
- Hiring a Contractor: Ensures professional construction but increases the overall expense.
2. Estimating the Cost: DIY vs. Kit vs. Pre-Built Sheds
When planning to add a shed to your property, you have several options: building it yourself (DIY), purchasing a shed kit, or buying a pre-built shed. Each option has different cost implications and levels of effort required. Let’s examine each one.
2. 1. DIY Shed
Building a shed yourself is often the most cost-effective option but demands time, skill, and effort.
- Cost: The primary expenses include lumber, roofing, foundation materials, doors, windows, and hardware.
- Pros: Significant cost savings, customization options, and personal satisfaction.
- Cons: Requires carpentry skills, time commitment, and potential for errors.
DIY Cost Breakdown:
- Materials: $800 – $3,000 (depending on size and materials)
- Tools: $100 – $500 (if you need to purchase new tools)
- Permits: $50 – $200 (depending on local regulations)
2. 2. Shed Kits
Shed kits offer a middle ground, providing pre-cut materials and instructions to simplify the building process.
- Cost: Generally more expensive than DIY but less than pre-built sheds.
- Pros: Reduced construction time, pre-cut materials, and easier assembly.
- Cons: Limited customization, potential for missing parts, and reliance on kit quality.
Shed Kit Cost Breakdown:
- Kit Price: $2,000 – $5,000 (depending on size and materials)
- Foundation: $100 – $500 (if not included in the kit)
- Assembly: $0 (DIY) or $500 – $1,000 (if hiring someone)
2. 3. Pre-Built Sheds
Purchasing a pre-built shed is the most convenient option, requiring no construction effort.
- Cost: The most expensive choice, reflecting the convenience and immediate usability.
- Pros: No construction needed, professional build quality, and immediate use.
- Cons: Higher cost, limited customization, and potential delivery challenges.
Pre-Built Shed Cost Breakdown:
- Shed Price: $3,000 – $10,000 (depending on size and materials)
- Delivery: $100 – $500 (depending on distance and shed size)
- Setup: Usually included, but may incur extra charges for complex setups
2. 4. Contractor-Built Sheds
Hiring a contractor to build a custom shed can offer the best of both worlds: customization and professional construction.
- Cost: Varies depending on the contractor’s rates, the complexity of the design, and the materials used.
- Pros: Custom design, professional build quality, and minimal effort on your part.
- Cons: Can be more expensive than DIY or shed kits, requires careful contractor selection.
Contractor-Built Shed Cost Breakdown:
- Materials: $1,000 – $4,000 (depending on size and materials)
- Labor: $1,000 – $5,000 (depending on complexity and location)
- Permits: $50 – $200 (depending on local regulations)
Here’s a general cost comparison for an 8×10 shed:
| Option | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|
| DIY | $1,100 |
| Shed Kit | $2,400 |
| Pre-Built Shed | $5,500 |
| Hire Contractor | $3,300 |
3. Detailed Cost Breakdown
To provide a clearer picture, let’s break down the costs associated with building a shed in more detail.
3. 1. Lumber Costs
Lumber is a significant expense in shed construction. The type of wood, dimensions, and current market prices all affect the cost.
- Framing Lumber: Used for the structural frame of the shed.
- Siding: Covers the exterior walls, providing protection and aesthetics.
- Trim: Adds decorative and protective elements.
Average Lumber Costs:
| Type of Lumber | Cost per Board Foot |
|---|---|
| Framing Lumber | $3 – $7 |
| Siding (Pine) | $2 – $5 |
| Siding (Cedar) | $5 – $10 |
| Trim | $1 – $4 |
3. 2. Roofing Costs
The roofing material protects the shed from the elements. Options include:
- Asphalt Shingles: A common and affordable choice.
- Metal Roofing: Durable and long-lasting, but more expensive.
- Wood Shakes: Provide a rustic look but require more maintenance.
Average Roofing Costs:
| Roofing Material | Cost per Square Foot |
|---|---|
| Asphalt Shingles | $1 – $3 |
| Metal Roofing | $3 – $7 |
| Wood Shakes | $4 – $8 |
3. 3. Foundation Costs
The foundation provides a stable base for the shed. Costs vary depending on the type and size.
- Gravel Pad: Requires gravel, landscape fabric, and leveling.
- Wood Frame: Involves building a frame with pressure-treated lumber.
- Concrete Slab: Requires pouring concrete and reinforcement.
Average Foundation Costs:
| Foundation Type | Cost per Square Foot |
|---|---|
| Gravel Pad | $1 – $3 |
| Wood Frame | $2 – $5 |
| Concrete Slab | $4 – $8 |
3. 4. Door and Window Costs
Doors and windows add functionality and aesthetics to the shed.
- Pre-Hung Doors: Easy to install but more expensive.
- Custom Doors: Can be built to save money but require more effort.
- Standard Windows: Affordable and readily available.
- Arch-Top Windows: A budget-friendly alternative to fancier windows.
Average Door and Window Costs:
| Item | Cost per Unit |
|---|---|
| Pre-Hung Door | $200 – $500 |
| Custom Door | $50 – $150 |
| Standard Window | $50 – $200 |
| Arch-Top Window | $50 – $70 |
3. 5. Additional Costs
Other costs to consider include:
- Hardware: Nails, screws, hinges, and latches.
- Paint/Stain: Protects and enhances the appearance of the shed.
- Permits: Required by many municipalities for shed construction.
- Delivery Fees: For materials or pre-built sheds.
4. Ways to Save Money on Your DIY Storage Shed
Building a shed can be a cost-effective way to add storage space to your property. Here are some strategies to reduce costs without compromising quality.
4. 1. Efficient Use of Materials
Plan the dimensions of your shed carefully to minimize waste and maximize the use of standard lumber sizes.
- Optimize Dimensions: Design your shed so that you can use full lengths of lumber without excessive cutting.
- Material Selection: Choose cost-effective materials like oriented strand board (OSB) for siding instead of more expensive options like cedar plywood.
4. 2. Inexpensive Door Options
Consider building a custom door instead of purchasing a pre-hung shed door.
- Custom Doors: Building a door from scratch can save you a significant amount of money compared to buying a pre-made one.
- Salvaged Doors: Look for used or salvaged doors at local building supply stores or online marketplaces.
4. 3. Trim and Window Choices
Opt for composite trim instead of solid wood and choose budget-friendly window options.
- Composite Trim: This material is cheaper, resists rot, and comes pre-primed, saving you time and money.
- Arch-Top Windows: These windows are typically less expensive than more elaborate designs.
4. 4. Salvaged or Recycled Materials
Look for opportunities to use recycled or salvaged materials in your shed construction.
- Reclaimed Wood: Using reclaimed wood can add character to your shed while reducing costs.
- Recycled Windows and Doors: Check local salvage yards for windows and doors that can be repurposed.
4. 5. DIY Labor
Do as much of the work yourself as possible to save on labor costs.
- DIY Construction: Building the shed yourself can save you thousands of dollars in labor costs.
- Enlist Help: If you need assistance, consider asking friends or family to help with the project.
4. 6. Compare Prices
Take the time to compare prices from different suppliers and contractors.
- Material Quotes: Get quotes from multiple lumberyards and home improvement stores.
- Contractor Bids: If you decide to hire a contractor, get bids from several different companies.
4. 7. Flexible Design
Keep the design simple and avoid unnecessary features.
- Simple Design: A basic, rectangular shed is easier and cheaper to build than a more complex design.
- Avoid Extras: Skip features like dormers, skylights, and elaborate trim to save money.
4. 8. Timing
Consider the time of year when purchasing materials.
- Off-Season Purchases: Prices for lumber and other building materials may be lower during the off-season.
- Sales and Discounts: Keep an eye out for sales and discounts at local home improvement stores.
5. Finding the Right Shed Size for Your Needs
Choosing the right size shed is crucial to ensure it meets your storage needs without overspending. Consider the following factors:
5. 1. Inventory Your Items
Start by making a list of everything you plan to store in the shed.
- List Contents: Categorize items by size, shape, and frequency of use.
- Estimate Space: Estimate the amount of space each category of items will require.
5. 2. Consider Future Needs
Think about potential future storage needs.
- Anticipate Growth: Plan for future acquisitions like new tools, equipment, or seasonal decorations.
- Extra Space: Add extra space to accommodate unexpected items.
5. 3. Site Limitations
Evaluate the available space in your yard.
- Measure Yard: Determine the maximum dimensions for your shed based on available space and zoning regulations.
- Accessibility: Ensure there is enough room to move around the shed and access stored items.
5. 4. Common Shed Sizes
Here are some common shed sizes and their typical uses:
| Size | Common Uses |
|---|---|
| 8×10 ft | Small garden tools, lawn equipment, seasonal decorations |
| 10×12 ft | Larger garden tools, bicycles, small workshop |
| 12×16 ft | Lawn tractors, ATVs, hobby space |
| 16×20 ft | Large workshop, storage for bulky items |
5. 5. Mock-Up
Use tape or stakes to outline the dimensions of the shed in your yard.
- Visualize Space: This helps you visualize the actual size of the shed and how it will fit in your yard.
- Adjustments: Make adjustments as needed based on your visual assessment.
5. 6. Zoning and Permits
Check local zoning regulations and permit requirements.
- Zoning Laws: Ensure the size and placement of your shed comply with local zoning laws.
- Permit Requirements: Obtain any necessary permits before starting construction.
5. 7. Height Considerations
Consider the height of the shed, especially if you plan to store tall items or use the space as a workshop.
- Wall Height: Ensure the walls are tall enough to accommodate shelves, workbenches, or tall tools.
- Roof Pitch: A steeper roof pitch can provide more headroom inside the shed.
5. 8. Door Size
Choose a door size that allows easy access for the items you plan to store.
- Wide Doors: Wider doors are necessary for storing large items like lawn tractors or ATVs.
- Double Doors: Consider double doors for maximum accessibility.
6. Navigating Permits and Regulations
Before starting your shed project, it’s essential to understand and comply with local regulations and permit requirements.
6. 1. Zoning Regulations
Check with your local zoning department to understand the regulations in your area.
- Setback Requirements: These dictate how far your shed must be from property lines, buildings, and other structures.
- Size Restrictions: Many municipalities have restrictions on the size and height of accessory buildings like sheds.
- Use Restrictions: Some areas may have restrictions on what you can use the shed for, such as prohibiting it from being used as a dwelling.
6. 2. Building Permits
Determine whether you need a building permit for your shed project.
- When Required: Permits are typically required for sheds that exceed a certain size or have electrical or plumbing connections.
- Application Process: The permit application process usually involves submitting detailed plans of your shed, including dimensions, materials, and site plan.
- Inspection: After construction, an inspector will need to inspect the shed to ensure it complies with local building codes.
6. 3. Homeowners Association (HOA) Rules
If you live in a neighborhood with a homeowners association, you’ll also need to comply with their rules and regulations.
- Approval Process: Many HOAs require you to submit plans for your shed and obtain approval before starting construction.
- Design Guidelines: HOAs may have specific guidelines regarding the size, style, and color of sheds.
- Restrictions: Some HOAs may prohibit sheds altogether or have strict rules about their placement and use.
6. 4. Electrical and Plumbing Permits
If you plan to run electricity or plumbing to your shed, you’ll need to obtain additional permits.
- Electrical Permits: Required for any electrical work, including wiring, outlets, and lighting.
- Plumbing Permits: Required for any plumbing work, including water lines, drains, and fixtures.
- Professional Installation: In many cases, electrical and plumbing work must be done by a licensed professional.
6. 5. Understanding Building Codes
Building codes set standards for the safety and structural integrity of buildings.
- Compliance: Ensure your shed complies with local building codes, including requirements for foundations, framing, roofing, and electrical and plumbing systems.
- Material Standards: Building codes may specify the types of materials that can be used in shed construction.
- Safety Requirements: Codes may include requirements for fire safety, ventilation, and accessibility.
6. 6. Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failing to comply with local regulations and permit requirements can have serious consequences.
- Fines: You may be subject to fines for building a shed without a permit or violating zoning regulations.
- Stop-Work Orders: The municipality may issue a stop-work order, halting construction until you obtain the necessary permits and approvals.
- Removal Orders: In some cases, you may be required to remove the shed altogether.
7. The Importance of a Solid Foundation
A solid foundation is essential for the stability and longevity of your shed. Let’s explore the different types of foundations and their benefits.
7. 1. Types of Shed Foundations
There are several types of foundations you can use for your shed, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
- Gravel Pad: A gravel pad provides good drainage and is relatively easy to install. It involves creating a level base of compacted gravel.
- Concrete Slab: A concrete slab provides a solid, level surface for your shed. It’s durable and long-lasting but can be more expensive and difficult to install.
- Wood Frame: A wood frame foundation involves building a frame of pressure-treated lumber. It’s a good option for sheds that are built on uneven ground.
- Pier Blocks: Pier blocks are pre-cast concrete blocks that are placed on the ground to support the shed. They’re easy to install and provide good stability.
7. 2. Preparing the Site
Proper site preparation is essential for a solid foundation.
- Clearing the Area: Remove any vegetation, rocks, and debris from the area where you’ll be building the shed.
- Leveling the Ground: Level the ground using a shovel and rake. You may need to bring in fill dirt to create a level surface.
- Compacting the Soil: Compact the soil using a hand tamper or plate compactor. This will help prevent the foundation from settling over time.
7. 3. Building a Gravel Pad Foundation
A gravel pad is a cost-effective and easy-to-install foundation option.
- Excavation: Excavate the area to a depth of several inches.
- Landscape Fabric: Line the excavated area with landscape fabric to prevent weeds from growing up through the gravel.
- Gravel: Fill the area with gravel, compacting it in layers.
7. 4. Building a Concrete Slab Foundation
A concrete slab provides a durable and level surface for your shed.
- Formwork: Build a form using lumber to create the perimeter of the slab.
- Reinforcement: Place rebar or wire mesh inside the form to reinforce the concrete.
- Pouring Concrete: Pour the concrete into the form, spreading it evenly and smoothing the surface.
- Curing: Allow the concrete to cure for several days before building on it.
7. 5. Wood Foundation
A wood foundation is easy to work with even if the ground is difficult to access.
- Pressure-Treated Lumber: Use pressure-treated lumber that is resistant to rot and decay.
- Fastening: Fasten the framing together using nails or screws.
- Leveling: Ensure the frame is level before attaching it to the shed.
7. 6. Importance of Drainage
Proper drainage is essential to prevent water from pooling around the foundation.
- Slope: Slope the ground away from the shed to encourage water runoff.
- Gutters and Downspouts: Install gutters and downspouts to direct rainwater away from the foundation.
8. Choosing the Right Materials
The choice of materials significantly impacts the cost, durability, and aesthetics of your shed.
8. 1. Framing Materials
The framing is the skeleton of your shed, so it’s essential to choose durable and sturdy materials.
- Wood: Wood is a popular choice for framing due to its strength and ease of use.
- Metal: Metal framing is more expensive but offers superior strength and durability.
8. 2. Siding Materials
The siding protects the shed from the elements and contributes to its overall appearance.
- Wood: Wood siding is attractive and can be painted or stained to match your home.
- Metal: Metal siding is durable and low-maintenance but may not be as aesthetically pleasing.
- Vinyl: Vinyl siding is affordable and easy to install but may not be as durable as other options.
- OSB: Oriented strand board (OSB) is a cost-effective alternative to plywood.
8. 3. Roofing Materials
The roofing material protects the shed from rain, snow, and sun.
- Asphalt Shingles: Asphalt shingles are affordable and easy to install.
- Metal Roofing: Metal roofing is durable and long-lasting but more expensive.
- Wood Shingles: Wood shingles are attractive but require more maintenance.
8. 4. Door Materials
The door provides access to the shed and should be sturdy and secure.
- Wood: Wood doors are attractive and can be customized to match the shed.
- Metal: Metal doors are durable and secure but may not be as aesthetically pleasing.
- Fiberglass: Fiberglass doors are lightweight and easy to install.
8. 5. Window Materials
Windows provide light and ventilation and contribute to the shed’s appearance.
- Glass: Glass windows provide good visibility but can be broken more easily.
- Acrylic: Acrylic windows are more durable than glass but may scratch more easily.
- Polycarbonate: Polycarbonate windows are lightweight and virtually unbreakable.
8. 6. Fasteners
Choose the right fasteners for the job to ensure the shed is structurally sound.
- Nails: Nails are used for general construction and are available in a variety of sizes and types.
- Screws: Screws provide a stronger hold than nails and are used for more demanding applications.
- Bolts: Bolts are used for connecting heavy timbers and provide the strongest hold.
9. Storage Shed Options: DIY vs. Kit vs. Pre-made
When it comes to acquiring a storage shed, you have several options: building it yourself (DIY), purchasing a shed kit, or buying a pre-built shed. Each option has different cost implications, levels of effort required, and degrees of customization. Let’s explore these options in detail.
9. 1. Building a Shed DIY
Building a shed yourself is often the most cost-effective option but demands time, skill, and effort.
- Cost: The primary expenses include lumber, roofing, foundation materials, doors, windows, and hardware.
- Pros: Significant cost savings, customization options, and personal satisfaction.
- Cons: Requires carpentry skills, time commitment, and potential for errors.
DIY Step-by-Step Guide:
- Planning: Design your shed and create detailed plans.
- Permits: Obtain any necessary permits from your local municipality.
- Foundation: Prepare the site and build a solid foundation.
- Framing: Construct the frame of the shed, including walls, roof, and floor.
- Siding: Install the siding to protect the shed from the elements.
- Roofing: Install the roofing material to keep the shed dry.
- Doors and Windows: Install the doors and windows.
- Finishing: Paint or stain the shed to protect it from the elements and enhance its appearance.
9. 2. Buying a Shed Kit
Shed kits offer a middle ground, providing pre-cut materials and instructions to simplify the building process.
- Cost: Generally more expensive than DIY but less than pre-built sheds.
- Pros: Reduced construction time, pre-cut materials, and easier assembly.
- Cons: Limited customization, potential for missing parts, and reliance on kit quality.
Shed Kit Selection Tips:
- Research: Research different shed kit manufacturers and read reviews to find a reputable brand.
- Compare: Compare prices and features from different kits to find the best value.
- Check Contents: Check the contents of the kit to ensure all necessary materials are included.
9. 3. Buying a Pre-Built Shed
Purchasing a pre-built shed is the most convenient option, requiring no construction effort.
- Cost: The most expensive choice, reflecting the convenience and immediate usability.
- Pros: No construction needed, professional build quality, and immediate use.
- Cons: Higher cost, limited customization, and potential delivery challenges.
Pre-Built Shed Delivery and Setup:
- Site Preparation: Prepare the site by leveling the ground and clearing any obstructions.
- Delivery Access: Ensure there is clear access for the delivery truck to reach the site.
- Setup: The delivery crew will typically set up the shed on the foundation.
9. 4. Comparing Options
Here’s a table comparing the three options based on cost, effort, and customization:
| Option | Cost | Effort | Customization |
|---|---|---|---|
| DIY | Lowest | Highest | Highest |
| Shed Kit | Medium | Medium | Medium |
| Pre-Built Shed | Highest | Lowest | Lowest |
10. Maximizing the Value of Your Shed Investment
Building or buying a shed is a significant investment. Here’s how to maximize its value and ensure it meets your needs for years to come.
10. 1. Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential to keep your shed in good condition and prevent costly repairs.
- Cleaning: Clean the shed regularly to remove dirt, debris, and mildew.
- Painting/Staining: Repaint or restain the shed every few years to protect it from the elements.
- Roof Inspection: Inspect the roof regularly for leaks or damage.
- Foundation Check: Check the foundation to ensure it’s level and stable.
10. 2. Organization
Proper organization can help you make the most of your shed’s storage space.
- Shelving: Install shelving to store items off the floor.
- Hooks: Use hooks to hang tools and equipment.
- Bins: Store small items in bins or containers.
- Labels: Label everything clearly so you can find what you need quickly.
10. 3. Security
Protect your shed and its contents from theft and vandalism.
- Locks: Install high-quality locks on the doors and windows.
- Lighting: Install exterior lighting to deter intruders.
- Security System: Consider installing a security system to protect the shed and its contents.
10. 4. Adding Value to Your Property
A well-maintained and attractive shed can add value to your property.
- Aesthetics: Choose a design and materials that complement your home and landscaping.
- Functionality: A well-organized and functional shed can be a selling point for potential buyers.
10. 5. Multi-Purpose Use
Consider using your shed for multiple purposes.
- Workshop: Use the shed as a workshop for woodworking, crafting, or other hobbies.
- Office: Convert the shed into a home office or studio.
- Storage: Use the shed to store seasonal decorations, lawn equipment, and other items.
Seeking expert advice can significantly streamline your project. At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with leading Ph.D. experts ready to provide tailored solutions and guidance.
11. Expert Consultation at HOW.EDU.VN
Navigating the complexities of shed construction can be daunting. HOW.EDU.VN offers access to a network of Ph.D. experts ready to assist you.
11. 1. Personalized Advice
Our experts provide personalized advice tailored to your specific needs and circumstances.
- Design Consultation: Get expert advice on shed design, materials, and construction techniques.
- Permit Assistance: Our experts can help you navigate the permit process and ensure compliance with local regulations.
- Troubleshooting: If you encounter problems during construction, our experts can provide troubleshooting assistance.
11. 2. Cost Optimization
Our experts can help you optimize the cost of your shed project without compromising quality.
- Material Selection: Get advice on choosing cost-effective materials that meet your needs.
- DIY vs. Contractor: Our experts can help you decide whether to build the shed yourself or hire a contractor.
- Budgeting: Our experts can help you create a realistic budget for your shed project.
11. 3. Expert Network
HOW.EDU.VN connects you with a network of Ph.D. experts in various fields.
- Construction Experts: Our construction experts have years of experience in building and renovating structures.
- Engineering Experts: Our engineering experts can provide advice on structural design and safety.
- Legal Experts: Our legal experts can help you understand local regulations and permit requirements.
11. 4. Why Choose HOW.EDU.VN?
Choosing HOW.EDU.VN for expert consultation offers several advantages.
- Expertise: Our experts have advanced degrees and years of experience in their respective fields.
- Personalized Advice: We provide personalized advice tailored to your specific needs and circumstances.
- Convenience: Our experts are available to provide advice online, saving you time and travel expenses.
- Affordability: Our consultation services are competitively priced, making expert advice accessible to everyone.
12. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. How much does it cost to build a basic 8×10 shed?
The cost to build a basic 8×10 shed ranges from $800 to $3,000 if you do it yourself, depending on the materials you choose.
2. Is it cheaper to buy a shed kit or build from scratch?
Building from scratch is generally cheaper, but requires more time and skill. Shed kits offer pre-cut materials and easier assembly.
3. What are the main factors that affect the cost of building a shed?
The main factors include size, materials, foundation type, design complexity, and labor costs.
4. Do I need a permit to build a shed on my property?
Permit requirements vary by location. Check with your local building department to determine if you need a permit.
5. What is the best foundation for a shed?
The best foundation depends on your budget and site conditions. Common options include gravel pads, concrete slabs, and wood frames.
6. How can I save money on my shed project?
You can save money by using cost-effective materials, building a simple design, doing the work yourself, and comparing prices from different suppliers.
7. What are the benefits of hiring a contractor to build a shed?
Hiring a contractor ensures professional construction, saves time, and reduces the risk of errors.
8. How long does it take to build a shed?
The time it takes to build a shed varies depending on the size and complexity of the project, but it typically takes several days to a week.
9. What are the common mistakes to avoid when building a shed?
Common mistakes include not obtaining necessary permits, building on an unlevel surface, and using low-quality materials.
10. What is the best way to organize a shed?
The best way to organize a shed is to install shelving, use hooks, store small items in bins, and label everything clearly.
Adding a shed to your property is a worthwhile investment when properly planned and executed.
For personalized guidance and expert advice, contact HOW.EDU.VN today. Our team of Ph.D. experts is ready to help you achieve your goals efficiently and effectively. Reach out to us at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States. WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212. Website: how.edu.vn. Let us help you make informed decisions and bring your vision to life with confidence and precision.