Understanding how much to change a catalytic converter involves several factors; let HOW.EDU.VN guide you through the complexities of catalytic converter replacement costs and options. Whether it’s understanding the purpose of this crucial component or exploring cost-effective replacement solutions, let’s delve into all aspects of catalytic converter replacement. You can explore options for maintaining vehicle emissions standards and avoiding costly repairs.
1. Understanding the Catalytic Converter and Its Function
The catalytic converter is a critical component of your vehicle’s exhaust system, playing a vital role in reducing harmful emissions. Positioned similarly to a muffler on the underside of your car, its primary function is to convert pollutants into less harmful substances before they are released into the atmosphere.
1.1. The Science Behind Catalytic Conversion
Catalytic converters use a chemical process to reduce hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides – all harmful byproducts of combustion engines. These components flow through the converter, where metallic catalysts like rhodium, palladium, and platinum facilitate reactions that transform these pollutants into carbon dioxide, water, and nitrogen.
1.2. History and Mandate of Catalytic Converters
First introduced in the mid-1970s, catalytic converters became standard on all cars to meet increasingly stringent air quality regulations. The integration of oxygen sensors post-1995 near the converter enhances its efficiency by monitoring and adjusting the air-fuel mixture, ensuring optimal performance and emissions reduction. This also aids in signaling when a converter isn’t functioning correctly.
 Catalytic Converter Location
Catalytic Converter Location
2. Types of Catalytic Converters
The market offers various catalytic converters to cater to different vehicle needs and environmental standards. Understanding these options is crucial when considering a replacement.
2.1. Direct Fit vs. Universal Catalytic Converters
-
Direct Fit Catalytic Converters: These are specifically designed for particular vehicle models and years. They offer easier installation as they match the car’s existing exhaust system.
-
Universal Catalytic Converters: These are more adaptable but require welding and adjustments to fit properly, making installation more labor-intensive.
2.2. Emission Standard Types: Federal vs. California (CARB)
- Federal Catalytic Converters: Comply with the emission standards required in most states and are aligned with federal regulations.
- California (CARB) Catalytic Converters: Meet the stricter standards set by the California Air Resources Board. These are required in California, New York, Colorado, and Maine due to their rigorous environmental protections.
Choosing the right type ensures your vehicle complies with local environmental laws and optimizes its performance.
3. Factors Influencing Catalytic Converter Replacement Cost
Several factors can affect the cost to change catalytic converter, including the type of converter needed, the vehicle’s make and model, and labor costs.
3.1. Vehicle Make and Model
The make and model of your vehicle significantly impact the cost of a catalytic converter replacement. Luxury or high-performance vehicles often require more expensive, specialized converters compared to standard models. For instance, a catalytic converter for a Volkswagen Passat might cost significantly more than one for a Toyota Camry.
3.2. Type of Catalytic Converter Required
As discussed earlier, the choice between a direct fit and a universal converter, along with whether a federal or CARB-compliant model is needed, will influence the price. Direct fit converters generally cost more upfront but can save on labor costs.
3.3. Labor Costs
Labor costs vary widely by location and the complexity of the installation. Urban areas or specialized repair shops may charge higher hourly rates.
3.4. Aftermarket vs. OEM Catalytic Converters
- Aftermarket Converters: These are typically less expensive than OEM parts but may not offer the same level of performance or durability.
- Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) Converters: These are made by the vehicle manufacturer and ensure a precise fit and optimal performance, but come at a higher cost.
3.5. Location of Service
The location where you choose to have the replacement done also affects the cost. Dealerships usually charge more than independent repair shops due to higher overhead and the use of OEM parts.
4. Average Catalytic Converter Replacement Costs
Pinpointing the exact cost to change catalytic converter is challenging due to the numerous variables involved. However, providing a cost breakdown can help manage expectations.
4.1. National Average Cost Range
According to RepairPal, the average cost to replace a catalytic converter ranges from $2,224 to $2,309. This figure includes both parts and labor. However, costs can vary significantly based on the specific factors mentioned earlier.
4.2. Cost Estimates for Different Vehicle Models
To provide a more concrete idea, here are estimated costs for replacing catalytic converters on different vehicle models across various locations in the U.S.:
| Vehicle | Location | Estimated Cost Range |
|---|---|---|
| 2020 Toyota Camry SE | Raleigh, NC | $1,184 to $1,254 |
| 2019 Chevrolet Equinox | Houston, TX | $1,390 to $1,466 |
| 2021 Volkswagen Passat | San Diego, CA | $2,533 to $2,631 |
| 2018 Ford F-150 Raptor | Atlanta, GA | $2,522 to $2,654 |
These estimates should be considered as guidelines, and actual costs may vary. It is always advisable to get a detailed quote from a reputable mechanic.
4.3. Breakdown of Costs: Parts vs. Labor
Typically, the cost of the catalytic converter itself makes up a significant portion of the total expense. High-quality OEM converters can be particularly pricey due to the precious metals they contain. Labor costs can vary, depending on the complexity of the installation, with direct fit converters generally requiring less labor.
5. Why Catalytic Converters Are Valuable and Prone to Theft
The high value of catalytic converters has made them a frequent target for thieves. Understanding why they are so coveted can help in taking preventive measures.
5.1. Precious Metals Used in Catalytic Converters
Catalytic converters contain valuable precious metals such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium. These metals act as catalysts to convert harmful emissions into less toxic substances. Rhodium, in particular, can be extremely valuable, sometimes fetching prices as high as $20,000 per ounce.
5.2. Impact of Supply Chain Shortages
Supply chain disruptions, especially those experienced during the COVID-19 pandemic, have further driven up the prices of these metals. This scarcity increases the resale value of stolen converters, making them an attractive target for thieves.
5.3. Ease of Theft
Catalytic converters are relatively easy to steal. They are typically located underneath the vehicle and can be removed quickly with simple tools like a saw or wrench. This accessibility, combined with the high resale value, makes vehicles vulnerable, particularly in areas with low security.
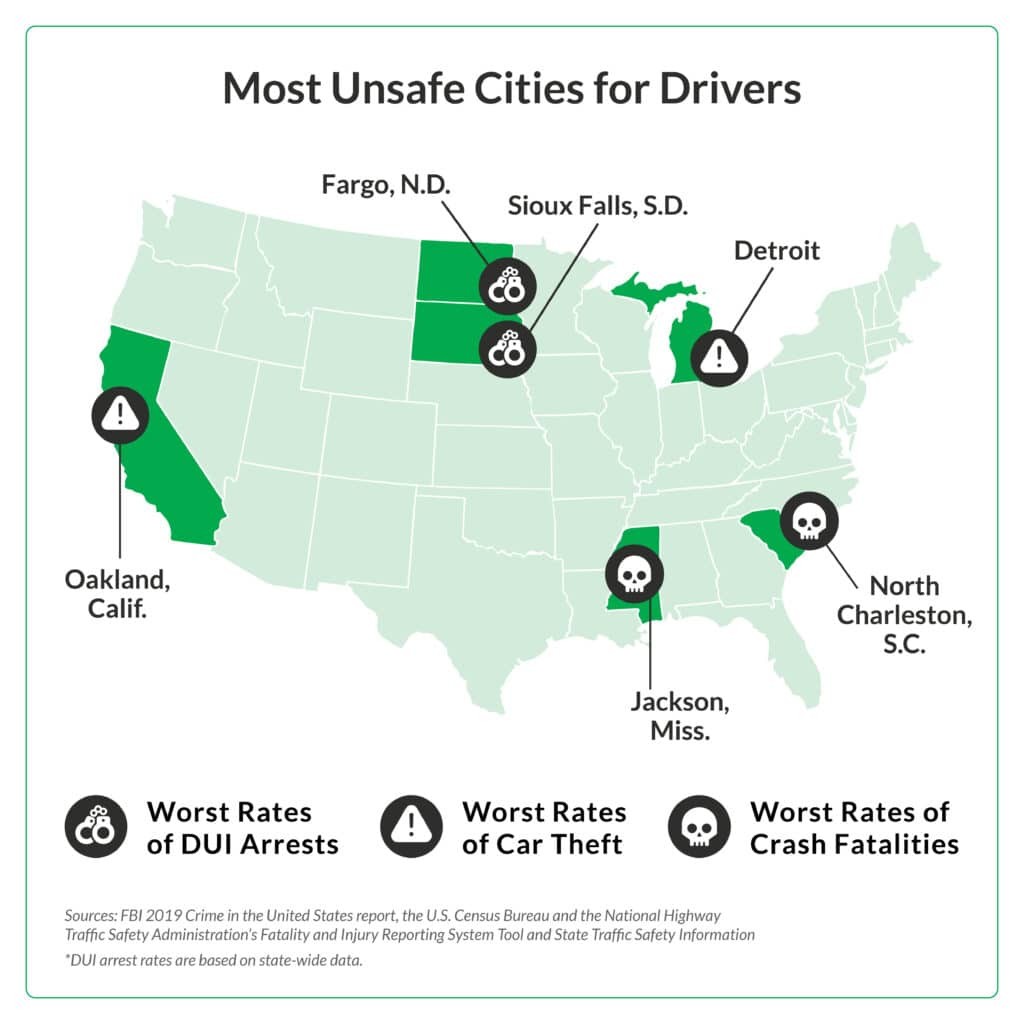
6. Preventive Measures Against Catalytic Converter Theft
Given the high cost of replacing a stolen catalytic converter, taking preventive measures is crucial. Several strategies can help protect your vehicle and deter thieves.
6.1. Installing a Catalytic Converter Lock
A catalytic converter lock is a protective device installed around the converter to make it more difficult to steal. These locks come in various forms, including cages and shields, which add a physical barrier that deters thieves.
6.2. Etching the VIN on the Catalytic Converter
Etching your vehicle identification number (VIN) onto the catalytic converter can deter theft by making the part traceable. Stolen parts with a VIN are harder to sell and can be identified by law enforcement.
6.3. Installing a Car Alarm System
Installing or upgrading your car alarm system can provide an added layer of security. Many modern alarms can detect vibrations or movement under the car and will sound an alert if someone attempts to tamper with the catalytic converter.
6.4. Parking in Well-Lit Areas
Parking your vehicle in well-lit and high-traffic areas can also deter theft. Thieves are less likely to target vehicles that are easily visible and exposed to potential witnesses.
6.5. Adjusting Vehicle Parking
If possible, park in a way that makes it harder to access the undercarriage of your car. For example, parking close to a curb or other obstacle can make it more challenging for thieves to get under the vehicle.
7. Catalytic Converter Replacement and the Law
Understanding the legal aspects of catalytic converter replacement is important to ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
7.1. State Laws Regarding Catalytic Converter Theft
All 50 states have laws designed to reduce catalytic converter theft. These laws often include measures to regulate the sale of used converters, requiring proof of ownership to deter illegal sales.
7.2. Emission Testing Requirements
Many states require vehicles to undergo regular emission testing to ensure they meet environmental standards. A vehicle without a functioning catalytic converter will fail these tests, leading to fines and the inability to legally operate the vehicle.
7.3. Penalties for Driving Without a Catalytic Converter
Driving without a catalytic converter is illegal in most states and can result in significant penalties, including fines, vehicle impoundment, and legal charges. Additionally, removing or tampering with a catalytic converter can void your vehicle’s warranty and negatively impact its resale value.
8. Potential Symptoms of a Failing Catalytic Converter
Recognizing the symptoms of a failing catalytic converter can help you address the issue promptly, potentially preventing further damage and costs.
8.1. Reduced Engine Performance
A clogged or failing catalytic converter can restrict exhaust flow, leading to reduced engine performance. You may notice a decrease in acceleration, especially when trying to merge onto a highway or climb hills.
8.2. Dark Exhaust Smoke
Dark or black smoke coming from the exhaust pipe can indicate a problem with the catalytic converter. This symptom is often associated with an engine running too rich, where there is an excess of fuel in the air-fuel mixture.
8.3. Unusual Odors
A failing catalytic converter may produce unusual odors, often described as smelling like sulfur or rotten eggs. This smell is due to the converter’s inability to properly process sulfur compounds in the exhaust.
8.4. Check Engine Light
The check engine light is a common indicator of various vehicle issues, including problems with the catalytic converter. If the oxygen sensors detect abnormal readings, the check engine light will illuminate, signaling the need for inspection.
8.5. Rattling Noises
Internal damage to the catalytic converter can cause rattling noises. The catalyst material inside the converter can break apart over time, leading to loose pieces that rattle around inside the housing.
9. DIY vs. Professional Catalytic Converter Replacement
Deciding whether to replace a catalytic converter yourself or hire a professional depends on your mechanical skills, available tools, and the complexity of the job.
9.1. Considerations for DIY Replacement
Replacing a catalytic converter yourself can save on labor costs, but it requires a good understanding of automotive mechanics and access to the right tools. You will need tools such as a wrench set, socket set, hacksaw or reciprocating saw, and potentially a welding machine if installing a universal converter.
Additionally, you must be comfortable working under your vehicle and handling potentially hazardous materials. Incorrect installation can lead to exhaust leaks, poor engine performance, and failure to meet emission standards.
9.2. Benefits of Professional Installation
Professional installation ensures the job is done correctly and efficiently. Mechanics have the expertise and equipment to diagnose the problem accurately, select the appropriate converter, and install it properly.
Professional installation also comes with the peace of mind that the work is guaranteed, and any issues that arise will be addressed by the shop. While it is more expensive than DIY replacement, professional service can save you time, hassle, and potential long-term problems.
10. Extended Car Warranties and Catalytic Converter Coverage
Extended car warranties can provide financial protection against unexpected repair costs, including catalytic converter replacement. Understanding the terms and coverage of these warranties is crucial.
10.1. Types of Extended Car Warranties
- Exclusionary Warranties: These offer the most comprehensive coverage, listing only the parts that are not covered. They typically cover most components of the vehicle, including the catalytic converter.
- Inclusionary Warranties: These specify the parts that are covered, and anything not listed is excluded. Coverage for catalytic converters may vary, so it’s important to review the terms carefully.
- Powertrain Warranties: These cover the most critical components of the vehicle, such as the engine, transmission, and drivetrain. Catalytic converters are usually not covered under powertrain warranties.
10.2. What to Look for in a Warranty Policy
When considering an extended car warranty, look for policies that offer comprehensive coverage, flexible terms, and a reputable provider. Check for deductibles, coverage limits, and any exclusions that may apply to catalytic converter replacement.
10.3. Benefits of Having Warranty Coverage
Having warranty coverage can provide peace of mind and financial security, especially if your vehicle is prone to catalytic converter issues. It can save you thousands of dollars in repair costs and protect you from unexpected expenses.
11. Maintaining Your Catalytic Converter to Prolong Its Life
Proper maintenance can extend the life of your catalytic converter and prevent premature failure. Here are some key maintenance tips:
11.1. Regular Engine Maintenance
Keeping your engine properly maintained is crucial for the health of your catalytic converter. Regular oil changes, tune-ups, and air filter replacements ensure the engine runs efficiently and reduces the risk of damage to the converter.
11.2. Avoiding Fuel Contamination
Fuel contamination can damage the catalytic converter. Avoid using low-quality or contaminated fuel, and address any engine issues that cause excessive fuel consumption or incomplete combustion.
11.3. Addressing Engine Issues Promptly
Addressing engine issues promptly can prevent them from damaging the catalytic converter. Problems such as misfires, oil leaks, and coolant leaks can cause the converter to overheat and fail prematurely.
11.4. Avoiding Short Trips
Short trips can prevent the catalytic converter from reaching its optimal operating temperature. This can lead to a buildup of deposits and reduce its efficiency over time. Try to take longer trips occasionally to allow the converter to heat up and burn off these deposits.
12. The Future of Catalytic Converters: Innovations and Alternatives
As environmental regulations become more stringent, the future of catalytic converters may involve new technologies and alternative solutions.
12.1. Advances in Catalytic Converter Technology
Ongoing research is focused on developing more efficient and durable catalytic converters. This includes the use of new materials and designs that can reduce emissions more effectively and withstand higher temperatures and stresses.
12.2. Electric Vehicles and the Shift Away From Catalytic Converters
Electric vehicles (EVs) do not require catalytic converters, as they produce zero tailpipe emissions. As the adoption of EVs continues to grow, the demand for catalytic converters may decrease over time, leading to a shift in the automotive industry.
12.3. Alternative Emission Control Technologies
Alternative emission control technologies are also being developed to reduce reliance on catalytic converters. These include advanced engine designs, improved fuel efficiency, and alternative fuels such as hydrogen and biofuels.
13. How HOW.EDU.VN Can Help
Navigating the complexities of catalytic converter replacement can be daunting. At HOW.EDU.VN, we provide expert guidance and resources to help you make informed decisions.
13.1. Access to Expert Advice
HOW.EDU.VN connects you with leading PhDs and experts who can provide personalized advice and solutions tailored to your specific needs. Whether you need help diagnosing a problem, selecting the right catalytic converter, or understanding warranty options, our experts are here to assist you.
13.2. Cost-Effective Solutions
We help you explore cost-effective solutions for catalytic converter replacement, including finding reputable mechanics, comparing prices, and understanding the pros and cons of different options.
13.3. Comprehensive Support
From initial consultation to final resolution, HOW.EDU.VN offers comprehensive support to ensure you have a smooth and successful experience. Our goal is to empower you with the knowledge and resources you need to make confident decisions about your vehicle.
14. FAQs About Catalytic Converter Replacement
Here are some frequently asked questions about catalytic converter replacement:
14.1. Is it illegal to drive without a catalytic converter?
Yes, it is illegal to drive without a catalytic converter in most states. Doing so can result in fines, vehicle impoundment, and legal charges.
14.2. How do I know if my catalytic converter is bad?
Symptoms of a bad catalytic converter include reduced engine performance, dark exhaust smoke, unusual odors, the check engine light illuminating, and rattling noises.
14.3. Can a bad catalytic converter affect gas mileage?
Yes, a bad catalytic converter can reduce fuel efficiency by restricting exhaust flow and causing the engine to work harder.
14.4. How long does a catalytic converter typically last?
A catalytic converter typically lasts between 100,000 and 150,000 miles, but its lifespan can be affected by factors such as engine maintenance, fuel quality, and driving conditions.
14.5. Can I clean a catalytic converter instead of replacing it?
While some products claim to clean catalytic converters, they are often ineffective and may cause further damage. Replacement is usually the best option for a severely clogged or damaged converter.
14.6. Will an aftermarket catalytic converter pass emissions testing?
Aftermarket catalytic converters can pass emissions testing if they meet the required standards for your vehicle and location. However, it’s important to choose a reputable brand and ensure it is properly installed.
14.7. Does insurance cover catalytic converter theft?
Comprehensive insurance coverage typically covers catalytic converter theft. Contact your insurance provider to understand your policy and file a claim if necessary.
14.8. What is the difference between a federal and a CARB catalytic converter?
A federal catalytic converter meets the emission standards required in most states, while a CARB catalytic converter meets the stricter standards set by the California Air Resources Board and is required in California, New York, Colorado, and Maine.
14.9. Can a catalytic converter be repaired instead of replaced?
In most cases, a catalytic converter cannot be repaired and must be replaced. However, minor issues such as exhaust leaks near the converter may be repairable.
14.10. How much does it cost to replace a catalytic converter on a Toyota Prius?
The cost to replace a catalytic converter on a Toyota Prius can range from $1,500 to $3,000 or more, depending on the factors mentioned earlier, such as the type of converter, labor costs, and location.
Is your catalytic converter causing you trouble? Don’t wait for the problem to escalate. Contact HOW.EDU.VN today for expert advice and cost-effective solutions. Our team of PhDs and specialists is ready to help you navigate the complexities of catalytic converter replacement and ensure your vehicle meets environmental standards. Reach out now to schedule a consultation and get back on the road with confidence. Contact us at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States, via Whatsapp at +1 (310) 555-1212, or visit our website at how.edu.vn.