Understanding How Much Water Is The Human Body Made Of is crucial for maintaining optimal health and well-being, and this article dives deep into this fascinating topic. At HOW.EDU.VN, we provide insights into the vital role of water in human physiology, offering solutions for those seeking to optimize their hydration levels. Discover the importance of body water composition, fluid balance, and hydration strategies to achieve a healthier life.
1. The Significance of Water in the Human Body
Water is fundamental to life, comprising a significant portion of the human body. It plays a vital role in various physiological processes, impacting everything from cellular function to overall health. Understanding the extent to which our bodies rely on water is the first step in appreciating its importance.
1.1. Water’s Role in Physiological Functions
Water is not merely a passive component of our bodies; it is actively involved in numerous essential functions. These include:
- Nutrient Transport: Water carries nutrients to cells, ensuring they receive the necessary building blocks for energy production and repair.
- Waste Removal: Water aids in flushing out waste products through urine, sweat, and bowel movements, preventing toxic buildup.
- Temperature Regulation: Water helps regulate body temperature through sweating, which cools the body as it evaporates.
- Joint Lubrication: Water lubricates joints, reducing friction and allowing for smooth movement.
- Organ Function: Water is crucial for the proper function of organs like the brain, heart, and kidneys.
1.2. The Composition of Water in Different Body Parts
The amount of water varies across different parts of the body, reflecting their specific functions and metabolic needs. Here’s a breakdown:
| Body Part | Water Composition | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Brain | 73% | Essential for neuronal function, neurotransmitter production, and cognitive processes. |
| Heart | 73% | Vital for maintaining blood volume, circulation, and cardiovascular health. |
| Lungs | 83% | Necessary for gas exchange, maintaining moisture in the respiratory tract, and preventing dehydration. |
| Skin | 64% | Crucial for maintaining elasticity, hydration, and acting as a barrier against external elements. |
| Muscles | 79% | Important for muscle contraction, flexibility, and preventing cramps. |
| Kidneys | 79% | Necessary for filtering waste, regulating electrolyte balance, and maintaining blood pressure. |
| Bones | 31% | Important for bone strength, mineral transport, and overall skeletal health. |
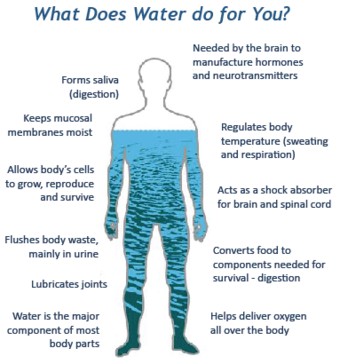 Graphic showing the essential functions of water in the human body, emphasizing its role in temperature regulation, nutrient transport, and waste removal.
Graphic showing the essential functions of water in the human body, emphasizing its role in temperature regulation, nutrient transport, and waste removal.
2. Factors Influencing Body Water Percentage
Several factors influence the percentage of water in the human body. These include age, gender, body composition, and lifestyle. Understanding these factors can help individuals tailor their hydration strategies to meet their specific needs.
2.1. Age and Water Content
Age plays a significant role in determining the amount of water in the body. Infants have the highest percentage of water, which gradually declines with age.
- Infants: Approximately 78% of an infant’s body is water. This high water content is essential for growth and development.
- Children: By one year of age, the water content drops to around 65%.
- Adults: Adult men typically have about 60% water, while adult women have around 55%.
- Seniors: As people age, their body water percentage tends to decrease further due to factors like reduced muscle mass and kidney function.
2.2. Gender Differences in Water Content
Men and women have different body water percentages primarily due to differences in body composition. Women generally have a higher percentage of body fat than men, and fat tissue contains less water than lean tissue.
- Men: Typically have around 60% water.
- Women: Typically have around 55% water.
2.3. Body Composition and Hydration
Body composition, particularly the ratio of lean muscle mass to body fat, significantly affects water content. Muscle tissue is about 79% water, while fat tissue contains much less. Therefore, individuals with more muscle mass tend to have a higher percentage of body water.
2.4. Lifestyle Factors Affecting Hydration
Lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, and climate can also influence hydration levels.
- Diet: Consuming water-rich foods like fruits and vegetables can contribute to overall hydration. Conversely, diets high in sodium can lead to dehydration.
- Exercise: Physical activity increases water loss through sweat. Athletes and active individuals need to consume more water to replenish these losses.
- Climate: Hot and humid climates increase sweat production, necessitating higher fluid intake. High altitudes can also lead to increased water loss through respiration.
3. The Importance of Maintaining Proper Hydration
Maintaining proper hydration is crucial for overall health and well-being. Dehydration can lead to various health issues, while optimal hydration supports numerous bodily functions.
3.1. Consequences of Dehydration
Dehydration occurs when the body loses more fluid than it takes in, leading to a deficit in essential functions. The consequences of dehydration can range from mild discomfort to severe health complications.
- Mild Dehydration: Symptoms include thirst, dry mouth, headache, fatigue, and dizziness.
- Moderate Dehydration: Symptoms include decreased urine output, dark urine, muscle cramps, and impaired cognitive function.
- Severe Dehydration: Symptoms include rapid heart rate, rapid breathing, confusion, and loss of consciousness. Severe dehydration can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention.
3.2. Benefits of Optimal Hydration
Optimal hydration offers numerous health benefits, including:
- Improved Physical Performance: Proper hydration enhances muscle function, endurance, and recovery.
- Enhanced Cognitive Function: Staying hydrated improves concentration, memory, and overall cognitive performance.
- Better Digestion: Water aids in digestion, preventing constipation and promoting a healthy gut.
- Healthy Skin: Adequate hydration keeps the skin moisturized, improving its elasticity and appearance.
- Kidney Health: Proper hydration helps prevent kidney stones and supports kidney function.
- Cardiovascular Health: Staying hydrated helps maintain blood volume, reducing the risk of cardiovascular issues.
3.3. How to Monitor Your Hydration Levels
Monitoring hydration levels is essential to ensure you are drinking enough water. Several methods can help you assess your hydration status:
- Urine Color: Pale yellow urine indicates good hydration, while dark yellow or amber urine suggests dehydration.
- Thirst: Feeling thirsty is an early sign of dehydration. Don’t wait until you’re thirsty to drink water.
- Skin Elasticity: Pinch the skin on the back of your hand. If it returns to normal quickly, you’re likely well-hydrated. If it stays tented for a few seconds, you may be dehydrated.
- Weight Changes: Sudden weight loss can indicate dehydration. Weigh yourself before and after exercise to estimate fluid loss.
4. Hydration Strategies for Different Lifestyles
Hydration needs vary based on individual lifestyles and activities. Tailoring your hydration strategy to your specific needs can help you maintain optimal health.
4.1. Hydration for Athletes and Active Individuals
Athletes and active individuals require more water due to increased fluid loss through sweat. Here are some tips for staying hydrated during physical activity:
- Pre-Hydration: Drink 16-20 ounces of water 2-3 hours before exercise.
- During Exercise: Drink 4-8 ounces of water every 15-20 minutes.
- Post-Hydration: Drink 16-24 ounces of water for every pound of weight lost during exercise.
- Electrolyte Replacement: Consider electrolyte drinks to replace sodium and potassium lost through sweat, especially during prolonged or intense exercise.
4.2. Hydration for Sedentary Individuals
Even sedentary individuals need to maintain adequate hydration. Aim for the general recommendation of 8 glasses of water per day, and adjust based on your individual needs.
- Keep Water Accessible: Keep a water bottle nearby and sip throughout the day.
- Set Reminders: Use apps or alarms to remind you to drink water regularly.
- Infuse Water with Flavor: Add fruits like lemon, cucumber, or berries to make water more appealing.
- Monitor Urine Color: Check your urine color regularly to ensure you’re adequately hydrated.
4.3. Hydration for Seniors
Seniors are at higher risk of dehydration due to decreased thirst sensation and kidney function. Here are some tips for seniors to stay hydrated:
- Drink Regularly: Drink water throughout the day, even if you don’t feel thirsty.
- Eat Water-Rich Foods: Consume fruits and vegetables with high water content, such as watermelon, cucumbers, and oranges.
- Limit Caffeine and Alcohol: These substances can have a diuretic effect, increasing fluid loss.
- Monitor Medications: Some medications can increase the risk of dehydration. Consult with a healthcare provider about potential side effects and hydration strategies.
4.4. Hydration in Different Climates
Climate plays a significant role in hydration needs. Hot and humid climates increase sweat production, while high altitudes can lead to increased water loss through respiration.
- Hot Climates: Drink plenty of water throughout the day, and consider electrolyte drinks to replace sodium lost through sweat.
- Cold Climates: Even in cold weather, it’s important to stay hydrated. Wear appropriate clothing to prevent excessive sweating, and drink water regularly.
- High Altitudes: Drink more water than usual, as altitude can increase water loss through respiration. Avoid alcohol and caffeine, which can worsen dehydration.
5. Types of Fluids for Hydration
While water is the best choice for hydration, other fluids can also contribute to your daily intake. Understanding the benefits and drawbacks of different beverages can help you make informed choices.
5.1. Water: The Best Choice for Hydration
Water is the most natural and effective way to stay hydrated. It’s calorie-free, readily available, and essential for numerous bodily functions.
- Plain Water: The simplest and most effective way to hydrate.
- Sparkling Water: A good alternative for those who prefer carbonation.
- Infused Water: Adding fruits or herbs can make water more appealing and increase your intake.
5.2. Electrolyte Drinks: When Are They Necessary?
Electrolyte drinks contain minerals like sodium, potassium, and magnesium, which are lost through sweat. They can be beneficial during prolonged or intense exercise, but are not necessary for everyday hydration.
- Benefits: Replenish electrolytes lost through sweat, improve hydration during prolonged exercise.
- Drawbacks: Can be high in sugar and calories, not necessary for casual hydration.
5.3. Juices and Other Beverages: Pros and Cons
Juices and other beverages can contribute to your daily fluid intake, but they also have potential drawbacks.
- Juices: Can be a source of vitamins and minerals, but often high in sugar. Opt for 100% juice and limit your intake.
- Teas: Unsweetened tea can be a healthy way to hydrate, providing antioxidants and other health benefits.
- Coffee: Coffee can have a diuretic effect, but moderate consumption is generally fine. Be sure to drink additional water to compensate for any fluid loss.
- Sodas: High in sugar and calories, sodas should be limited or avoided altogether.
6. Debunking Common Hydration Myths
Several myths surround hydration, leading to confusion and misinformation. Let’s debunk some common myths to provide clarity and accurate information.
6.1. Myth: You Need 8 Glasses of Water a Day
While the “8 glasses of water a day” rule is a common guideline, individual hydration needs vary. Factors like activity level, climate, and overall health can influence how much water you need. Focus on drinking enough to satisfy your thirst and maintain pale yellow urine.
6.2. Myth: You Can Only Hydrate with Water
While water is the best choice for hydration, other fluids can also contribute to your daily intake. Juices, teas, and even some fruits and vegetables can help you stay hydrated.
6.3. Myth: Thirst Is a Reliable Indicator of Hydration
Thirst is an early sign of dehydration, but it’s not always a reliable indicator. By the time you feel thirsty, you may already be mildly dehydrated. Drink water regularly throughout the day, even if you don’t feel thirsty.
6.4. Myth: Drinking Too Much Water Is Always Safe
While rare, it is possible to drink too much water, leading to a condition called hyponatremia. This occurs when the sodium levels in your blood become diluted, causing symptoms like nausea, headache, and confusion. Balance your fluid intake with your activity level and avoid excessive water consumption.
7. How to Consult with Top Doctors for Personalized Hydration Advice
Understanding your body’s specific needs regarding water intake can be complex, given the many factors that influence hydration levels. At HOW.EDU.VN, we offer a unique opportunity to connect with over 100 renowned PhD doctors and specialists from around the world, providing personalized advice tailored to your individual circumstances.
7.1 Benefits of Consulting with Our Experts
- Personalized Hydration Plans: Receive hydration strategies designed specifically for your age, gender, activity level, and health status.
- Expert Guidance: Get answers to your specific questions and concerns about hydration from leading experts in various fields.
- Comprehensive Assessment: Our specialists can assess your current hydration status and provide recommendations for improvement.
- Preventative Measures: Learn how to prevent dehydration and other health issues related to improper hydration.
- Access to Cutting-Edge Research: Stay informed about the latest research and advancements in hydration science.
8. Addressing the Challenges of Finding Expert Advice
Many individuals face challenges in finding reliable and personalized advice on hydration. These challenges include:
- Difficulty Finding Qualified Experts: Identifying and accessing professionals with the right expertise can be time-consuming and overwhelming.
- High Costs: Consulting with specialists can be expensive, making it inaccessible for many individuals.
- Time Constraints: Scheduling appointments and traveling to see experts can be difficult for those with busy schedules.
- Information Overload: The vast amount of information available online can be confusing and contradictory, making it hard to determine what advice is trustworthy.
9. HOW.EDU.VN: Your Solution for Expert Hydration Advice
HOW.EDU.VN provides a platform that addresses these challenges by connecting you directly with top doctors and specialists who can offer personalized hydration advice.
- Convenient Access: Consult with experts from the comfort of your own home, at a time that works for you.
- Cost-Effective: Our services are designed to be affordable, making expert advice accessible to a wider audience.
- Trusted Professionals: We carefully vet all of our specialists to ensure they have the necessary qualifications and experience.
- Personalized Approach: Our experts take the time to understand your individual needs and goals, providing tailored recommendations.
10. Real-World Examples and Case Studies
To illustrate the benefits of seeking expert hydration advice, consider the following examples:
-
Case Study 1: Athlete Optimizing Performance
- Challenge: A marathon runner struggled with dehydration during races, leading to decreased performance and muscle cramps.
- Solution: Consulted with a sports medicine specialist through HOW.EDU.VN, who developed a personalized hydration plan that included electrolyte drinks and timed fluid intake.
- Outcome: The runner improved their race times and experienced fewer cramps, leading to a more successful season.
-
Case Study 2: Senior Managing Chronic Conditions
- Challenge: An elderly woman with kidney disease had difficulty maintaining proper hydration, leading to frequent hospitalizations.
- Solution: Consulted with a nephrologist through HOW.EDU.VN, who provided guidance on fluid intake and medication management.
- Outcome: The woman was able to better manage her hydration levels, reducing the need for hospitalizations and improving her overall quality of life.
-
Case Study 3: Office Worker Enhancing Cognitive Function
- Challenge: An office worker experienced frequent headaches and fatigue due to dehydration.
- Solution: Consulted with a nutritionist through HOW.EDU.VN, who recommended incorporating water-rich foods and setting reminders to drink water throughout the day.
- Outcome: The worker’s headaches and fatigue decreased, leading to improved focus and productivity at work.
11. How to Get Started with HOW.EDU.VN
Getting started with HOW.EDU.VN is simple. Follow these steps to connect with our experts and receive personalized hydration advice:
- Visit Our Website: Go to HOW.EDU.VN to learn more about our services and browse our directory of experts.
- Create an Account: Sign up for a free account to access our platform.
- Search for Specialists: Use our search filters to find doctors and specialists who specialize in hydration and related fields.
- Schedule a Consultation: Book a consultation with the expert of your choice at a time that works for you.
- Receive Personalized Advice: During your consultation, discuss your hydration needs and goals, and receive tailored recommendations.
12. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: How much water should I drink each day?
The amount of water you need each day depends on various factors, including your activity level, climate, and overall health. A general guideline is to drink 8 glasses of water per day, but you may need more or less depending on your individual needs.
Q2: What are the signs of dehydration?
Signs of dehydration include thirst, dry mouth, headache, fatigue, dizziness, decreased urine output, and dark urine.
Q3: Can I count other beverages towards my daily fluid intake?
Yes, other beverages such as juices, teas, and even some fruits and vegetables can contribute to your daily fluid intake. However, water is still the best choice for hydration.
Q4: Are electrolyte drinks necessary for hydration?
Electrolyte drinks can be beneficial during prolonged or intense exercise to replace minerals lost through sweat, but they are not necessary for everyday hydration.
Q5: Is it possible to drink too much water?
Yes, it is possible to drink too much water, leading to a condition called hyponatremia. Balance your fluid intake with your activity level and avoid excessive water consumption.
Q6: How can I improve my hydration habits?
To improve your hydration habits, keep water accessible, set reminders to drink water, infuse water with flavor, and monitor your urine color.
Q7: What should seniors do to stay hydrated?
Seniors should drink water regularly throughout the day, even if they don’t feel thirsty, eat water-rich foods, and limit caffeine and alcohol.
Q8: How does climate affect hydration needs?
Hot climates increase sweat production, while high altitudes can lead to increased water loss through respiration. Adjust your fluid intake accordingly.
Q9: What are the benefits of consulting with a hydration expert?
Consulting with a hydration expert can provide personalized advice tailored to your individual needs, helping you optimize your hydration levels and improve your overall health.
Q10: How can HOW.EDU.VN help me with my hydration needs?
HOW.EDU.VN connects you with top doctors and specialists who can provide personalized hydration advice, comprehensive assessments, and preventative measures to help you achieve your health goals.
13. Additional Resources
For further reading and information on hydration, consider the following resources:
- World Health Organization (WHO): Provides guidelines and information on water and health.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): Offers tips and resources on staying hydrated.
- National Institutes of Health (NIH): Conducts research on hydration and its impact on health.
- American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM): Provides recommendations for hydration during exercise.
14. Conclusion: Prioritizing Hydration for a Healthier Life
Understanding how much water the human body is made of and the importance of staying properly hydrated is crucial for maintaining optimal health and well-being. By following the tips and strategies outlined in this article, you can tailor your hydration plan to your individual needs and lifestyle.
Remember, proper hydration supports numerous bodily functions, enhances physical and cognitive performance, and promotes overall health. If you have specific concerns or questions about your hydration needs, don’t hesitate to consult with the experts at HOW.EDU.VN for personalized advice and guidance. Prioritize hydration and invest in your health today!
Are you struggling to maintain optimal hydration levels or seeking personalized advice tailored to your unique needs? Do you want to connect with leading experts who can provide comprehensive assessments and effective strategies to improve your hydration habits?
Don’t wait any longer to prioritize your health and well-being. Contact us today to schedule a consultation with one of our renowned PhD doctors or specialists. Our team of experts is dedicated to helping you achieve your hydration goals and live a healthier, more vibrant life.
Visit HOW.EDU.VN now to learn more about our services and browse our directory of experts. Let us help you unlock the power of proper hydration and transform your health!
Contact Information:
- Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
- Website: how.edu.vn