Water is essential for life, but How Much Water Makes Up The Human Body? At HOW.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of this vital question and offer expert insights into maintaining optimal hydration. Our team of leading PhDs provides comprehensive guidance on understanding your body’s water composition and its impact on your health, as well as how much water is enough. Discover how to balance your water intake and ensure you’re adequately hydrated with personalized advice from our experts.
1. Understanding the Composition of the Human Body: The Role of Water
The human body is a marvel of biological engineering, and water plays a pivotal role in its functionality. Understanding just how much of our bodies are composed of water, and its importance can help you better manage your health. Let’s dive in.
1.1 Water: An Essential Component for Life
Water is not just a simple liquid; it’s a fundamental building block for life as we know it. Every cell, tissue, and organ in our body depends on water to function correctly. Water acts as a solvent, transporting nutrients, regulating temperature, and facilitating numerous chemical reactions essential for life.
1.2 Percentage of Water in the Human Body
The amount of water in the human body varies depending on several factors, including age, sex, and body composition. Here’s a general overview:
- Infants: Newborn babies have the highest percentage of water, making up about 78% of their body weight. This high water content is crucial for their rapid growth and development.
- Children: As children grow, the percentage of water in their bodies gradually decreases to around 65%.
- Adult Men: Adult men typically have about 60% of their body weight as water.
- Adult Women: Adult women generally have a lower percentage of water, around 55%, due to having more fatty tissue than men.
1.3 Factors Affecting Water Percentage
Several factors influence the proportion of water in the human body.
1.3.1 Age
As we age, our body water percentage tends to decrease. This is primarily due to a reduction in muscle mass, which is high in water content, and an increase in fatty tissue, which contains less water.
1.3.2 Sex
Men typically have a higher percentage of water than women due to having more muscle mass. Muscle tissue holds more water than fatty tissue, leading to this difference.
1.3.3 Body Composition
Body composition plays a significant role in determining water percentage. Individuals with a higher proportion of lean muscle mass will have a greater percentage of water compared to those with more fatty tissue.
1.4 Water Distribution in Different Organs
Water is not evenly distributed throughout the body. Different organs have varying water content, reflecting their specific functions and metabolic activity.
| Organ | Water Percentage |
|---|---|
| Brain | 73% |
| Heart | 73% |
| Lungs | 83% |
| Skin | 64% |
| Muscles | 79% |
| Kidneys | 79% |
| Bones | 31% |
1.5 The Importance of Maintaining Hydration
Maintaining adequate hydration is essential for overall health and well-being. Water is involved in numerous bodily functions, and even mild dehydration can lead to a range of symptoms, including fatigue, headaches, and impaired cognitive function.
1.6 Seeking Expert Advice
Understanding the importance of water in the human body is the first step toward maintaining optimal health. However, determining your specific hydration needs can be complex. At HOW.EDU.VN, our team of experienced PhDs offers personalized advice and guidance to help you understand your body’s unique requirements. Connect with our experts today to learn how to optimize your hydration and improve your overall well-being.
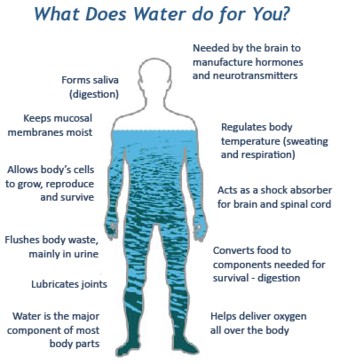 Graphic showing what water is for in a human body.
Graphic showing what water is for in a human body.
2. Vital Functions of Water in the Human Body
Water is involved in virtually every bodily function, from regulating temperature to transporting nutrients. Without sufficient water, our bodies cannot perform these functions efficiently, leading to various health problems.
2.1 Regulation of Body Temperature
One of water’s most critical roles is regulating body temperature. Through sweating, our bodies can release excess heat, preventing overheating and maintaining a stable internal environment.
2.2 Transportation of Nutrients and Oxygen
Water serves as a medium for transporting essential nutrients and oxygen to cells throughout the body. It helps dissolve these substances and ensures they reach the tissues and organs where they are needed.
2.3 Waste Removal
Water is crucial for flushing out waste products through urine and sweat. The kidneys rely on water to filter toxins from the blood, and adequate hydration ensures efficient waste removal.
2.4 Joint Lubrication
Water lubricates our joints, allowing for smooth movement and preventing friction between bones. Dehydration can lead to joint pain and stiffness.
2.5 Shock Absorption
Water acts as a shock absorber for the brain, spinal cord, and fetus, protecting these sensitive structures from injury.
2.6 Formation of Saliva
Saliva, which is primarily composed of water, is essential for digestion. It helps break down food and moistens it for easy swallowing.
2.7 Maintaining Cell Function
Water is a vital component of every cell in the body. It maintains cell structure, facilitates chemical reactions, and supports overall cell function.
2.8 Impacts of Dehydration
Dehydration can have numerous negative effects on the body, including:
- Fatigue
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Constipation
- Muscle cramps
- Impaired cognitive function
- Kidney problems
2.9 Personalized Hydration Plans
Every individual has unique hydration needs based on their activity level, climate, and overall health. At HOW.EDU.VN, our team of PhDs can help you develop a personalized hydration plan to ensure you’re getting enough water to support your body’s functions. Contact us today for expert guidance on maintaining optimal hydration.
3. Daily Water Intake: How Much Do You Need?
Determining the right amount of water to drink each day is essential for maintaining optimal health. However, the ideal intake varies based on individual factors. Understanding these factors and how they influence your hydration needs can help you stay properly hydrated.
3.1 General Recommendations
General guidelines suggest that adult men should consume about 3 liters (13 cups) of water per day, while adult women should aim for around 2.2 liters (9 cups). These recommendations include water from all sources, including beverages and food.
3.2 Factors Influencing Water Needs
Several factors can affect your daily water requirements:
3.2.1 Activity Level
People who engage in regular physical activity need more water to replace fluids lost through sweat. Athletes and those who work in physically demanding jobs should increase their water intake accordingly.
3.2.2 Climate
Hot and humid climates increase sweat production, leading to greater fluid loss. Individuals living in these environments need to drink more water to stay hydrated.
3.2.3 Health Conditions
Certain health conditions, such as diabetes and kidney problems, can affect fluid balance. Individuals with these conditions may need to adjust their water intake based on their doctor’s recommendations.
3.2.4 Diet
A diet high in sodium can increase water loss, while a diet rich in fruits and vegetables can contribute to hydration. Adjust your water intake based on your dietary habits.
3.2.5 Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Pregnant and breastfeeding women have increased fluid needs to support fetal development and milk production. They should drink more water than usual to stay adequately hydrated.
3.3 Sources of Water
While drinking water is the most obvious way to stay hydrated, it’s important to remember that you can also get water from other sources:
- Beverages: Water, juice, tea, and coffee all contribute to your daily fluid intake.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Many fruits and vegetables have high water content, such as watermelon, cucumbers, and spinach.
- Soups and Broths: Soups and broths can be a significant source of hydration, especially during colder months.
3.4 How to Monitor Hydration
Monitoring your hydration levels is crucial for ensuring you’re drinking enough water. Here are some tips:
- Check Your Urine: Pale yellow urine indicates good hydration, while dark yellow urine may be a sign of dehydration.
- Pay Attention to Thirst: Thirst is a sign that your body needs water, so drink up when you feel thirsty.
- Monitor Physical Symptoms: Headaches, fatigue, and dizziness can be signs of dehydration.
3.5 Personalized Hydration Strategies
Determining your ideal water intake can be challenging, especially if you have specific health conditions or lifestyle factors to consider. At HOW.EDU.VN, our team of PhDs offers personalized hydration strategies tailored to your unique needs. Connect with our experts today to learn how to optimize your hydration and improve your overall health.
4. Understanding Water Loss: How Your Body Loses Water
Knowing how your body loses water is essential for understanding your hydration needs. Water is constantly being lost through various processes, and understanding these pathways can help you adjust your fluid intake accordingly.
4.1 Primary Routes of Water Loss
The body loses water through several primary routes:
4.1.1 Urination
Urination is the primary way the body eliminates excess water and waste products. The kidneys filter blood and produce urine, which is then excreted.
4.1.2 Sweat
Sweating is a crucial mechanism for regulating body temperature. As sweat evaporates from the skin, it cools the body, but it also leads to water loss.
4.1.3 Respiration
We lose water through breathing, especially in dry environments. As we exhale, water vapor is released from the lungs.
4.1.4 Bowel Movements
Feces contain water, and bowel movements contribute to daily water loss.
4.2 Factors Increasing Water Loss
Certain factors can increase water loss, requiring you to adjust your fluid intake:
4.2.1 Physical Activity
Exercise and other physical activities increase sweat production, leading to greater water loss.
4.2.2 Hot Weather
Hot weather promotes sweating, increasing the risk of dehydration.
4.2.3 High Altitude
At higher altitudes, the body loses water more quickly due to increased respiration and lower humidity.
4.2.4 Certain Medications
Some medications, such as diuretics, can increase urination and lead to greater water loss.
4.2.5 Medical Conditions
Conditions like diarrhea and vomiting can cause significant fluid loss, leading to dehydration.
4.3 Recognizing Signs of Dehydration
Recognizing the signs of dehydration is crucial for preventing more severe health problems. Common symptoms include:
- Thirst
- Dry mouth
- Dark urine
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Muscle cramps
4.4 Replenishing Lost Fluids
To replenish lost fluids, focus on drinking water and other hydrating beverages throughout the day. Consider these tips:
- Carry a water bottle with you and refill it regularly.
- Drink water before, during, and after physical activity.
- Choose hydrating foods like fruits and vegetables.
- Avoid excessive consumption of caffeine and alcohol, which can dehydrate you.
4.5 Staying Ahead of Dehydration
Staying ahead of dehydration requires proactive hydration habits. Don’t wait until you feel thirsty to drink water. Instead, make it a habit to sip water throughout the day.
4.6 Expert Guidance on Fluid Replacement
Understanding your individual fluid needs and how to effectively replace lost fluids can be complex. At HOW.EDU.VN, our team of PhDs offers expert guidance on fluid replacement strategies tailored to your lifestyle and health conditions. Connect with us today to learn how to stay properly hydrated and maintain optimal health.
5. Hydration and Health: The Benefits of Staying Hydrated
Staying adequately hydrated offers numerous health benefits, impacting everything from cognitive function to physical performance. Understanding these benefits can motivate you to prioritize hydration in your daily routine.
5.1 Cognitive Function
Proper hydration is essential for optimal cognitive function. Dehydration can impair concentration, memory, and overall mental performance. Studies have shown that even mild dehydration can lead to decreased cognitive abilities.
5.2 Physical Performance
Hydration plays a crucial role in physical performance. Water helps regulate body temperature, lubricates joints, and transports nutrients to muscles. Dehydration can lead to fatigue, muscle cramps, and reduced endurance.
5.3 Kidney Health
Adequate hydration is vital for kidney health. Water helps the kidneys filter waste products from the blood and prevents the formation of kidney stones.
5.4 Digestive Health
Water is essential for healthy digestion. It helps break down food, prevents constipation, and promotes regular bowel movements.
5.5 Skin Health
Hydration contributes to skin health by keeping the skin moisturized and supple. Dehydration can lead to dry, itchy skin and may exacerbate skin conditions like eczema.
5.6 Cardiovascular Health
Staying hydrated supports cardiovascular health by maintaining blood volume and circulation. Dehydration can lead to increased heart rate and blood pressure.
5.7 Mood and Energy Levels
Dehydration can affect mood and energy levels. Studies have shown that even mild dehydration can lead to irritability, fatigue, and decreased energy.
5.8 Long-Term Health
Maintaining good hydration habits over the long term can contribute to overall health and well-being. It can help prevent chronic diseases and promote healthy aging.
5.9 Personalizing Your Hydration
The benefits of staying hydrated are clear, but tailoring your hydration strategy to your individual needs is essential. Factors like activity level, climate, and health conditions can influence your hydration requirements.
5.10 Expert Advice for Optimal Hydration
At HOW.EDU.VN, our team of PhDs provides expert advice on achieving optimal hydration for your unique circumstances. We can help you understand your body’s needs and develop a personalized hydration plan to maximize the health benefits of staying hydrated. Contact us today to learn more.
6. Common Misconceptions About Hydration
Many misconceptions surround hydration, leading to confusion about how much water we need and the best ways to stay hydrated. Clarifying these myths can help you make informed choices about your fluid intake.
6.1 Myth: You Need to Drink Eight Glasses of Water a Day
Fact: The “eight glasses a day” rule is a general guideline, but individual water needs vary. Factors like activity level, climate, and health conditions can influence how much water you need.
6.2 Myth: Thirst Is a Reliable Indicator of Hydration
Fact: Thirst is a sign that your body needs water, but it’s not always a reliable indicator of hydration. By the time you feel thirsty, you may already be mildly dehydrated.
6.3 Myth: All Beverages Are Equally Hydrating
Fact: While all beverages contribute to your fluid intake, some are more hydrating than others. Water, herbal teas, and fruit-infused water are excellent choices, while sugary drinks and alcohol can be dehydrating.
6.4 Myth: You Can Overhydrate by Drinking Too Much Water
Fact: While it’s possible to overhydrate, it’s rare and typically only occurs in individuals with certain medical conditions or those who engage in extreme endurance activities.
6.5 Myth: Coffee and Tea Are Dehydrating
Fact: Coffee and tea have a mild diuretic effect, but they can still contribute to your daily fluid intake. The hydrating effects generally outweigh the diuretic effects for most people.
6.6 Myth: You Only Need to Hydrate When Exercising
Fact: Hydration is essential throughout the day, not just during exercise. Staying properly hydrated supports numerous bodily functions, regardless of your activity level.
6.7 Myth: Clear Urine Always Means You’re Well-Hydrated
Fact: While pale yellow urine is a good indicator of hydration, clear urine can sometimes indicate overhydration. It’s essential to balance your fluid intake and pay attention to other signs of hydration.
6.8 Addressing Hydration Myths with Expert Guidance
Sorting through the many myths about hydration can be challenging. At HOW.EDU.VN, our team of PhDs offers expert guidance on understanding your hydration needs and debunking common misconceptions. Contact us today to get personalized advice and ensure you’re making informed choices about your fluid intake.
7. Hydration for Specific Populations
Hydration needs vary across different populations, including athletes, pregnant women, children, and older adults. Understanding these specific needs can help you tailor your fluid intake to support optimal health.
7.1 Athletes
Athletes require more water than the average person to replace fluids lost through sweat during exercise. They should drink water before, during, and after workouts to stay properly hydrated.
7.2 Pregnant Women
Pregnant women have increased fluid needs to support fetal development and amniotic fluid production. They should drink at least 8-10 glasses of water per day and consume hydrating foods.
7.3 Children
Children are more susceptible to dehydration than adults due to their smaller body size and higher metabolic rate. Encourage children to drink water throughout the day and offer hydrating snacks like fruits and vegetables.
7.4 Older Adults
Older adults may experience decreased thirst sensation and reduced kidney function, making them more vulnerable to dehydration. They should make a conscious effort to drink water regularly, even if they don’t feel thirsty.
7.5 Tailoring Hydration to Unique Needs
Different populations have different hydration needs, and understanding these differences is crucial for supporting optimal health. Whether you’re an athlete, a pregnant woman, a child, or an older adult, tailoring your fluid intake to your unique needs can help you stay properly hydrated and maintain overall well-being.
7.6 Expert Hydration Advice for Specific Groups
At HOW.EDU.VN, our team of PhDs offers expert hydration advice tailored to specific populations. We can help you understand your unique needs and develop a personalized hydration plan to support your health and well-being. Contact us today to learn more.
8. Practical Tips for Staying Hydrated
Staying hydrated doesn’t have to be a chore. By incorporating simple habits into your daily routine, you can ensure you’re getting enough water to support your health and well-being.
8.1 Carry a Water Bottle
Carry a reusable water bottle with you throughout the day and refill it regularly. This serves as a visual reminder to drink water and makes it easy to stay hydrated on the go.
8.2 Set Reminders
Set reminders on your phone or computer to drink water at regular intervals. This can help you develop a consistent hydration routine.
8.3 Drink Before Meals
Drink a glass of water before each meal. This can help you stay hydrated and may also aid in digestion.
8.4 Choose Hydrating Snacks
Opt for hydrating snacks like fruits and vegetables, which have high water content. These snacks can contribute to your overall fluid intake.
8.5 Infuse Your Water
Add flavor to your water by infusing it with fruits, vegetables, or herbs. This can make drinking water more enjoyable and encourage you to drink more.
8.6 Keep Water Visible
Keep a pitcher of water on your desk or kitchen counter. Having water readily visible can prompt you to drink more throughout the day.
8.7 Drink After Exercise
Replenish fluids lost during exercise by drinking water or a sports drink after your workout.
8.8 Monitor Urine Color
Check your urine color regularly. Pale yellow urine indicates good hydration, while dark yellow urine may be a sign of dehydration.
8.9 Make Hydration a Habit
Incorporate these tips into your daily routine and make hydration a habit. The more consistent you are with your fluid intake, the easier it will be to stay properly hydrated.
8.10 Expert-Backed Hydration Strategies
Implementing practical hydration tips can help you stay properly hydrated and support your overall health. At HOW.EDU.VN, our team of PhDs offers expert-backed hydration strategies to help you make hydration a seamless part of your daily routine. Contact us today to learn more.
9. When to Seek Professional Advice on Hydration
While many people can manage their hydration needs on their own, certain situations may warrant seeking professional advice. Consulting with a healthcare provider or a hydration expert can help you address specific concerns and develop a personalized hydration plan.
9.1 Chronic Dehydration
If you experience persistent symptoms of dehydration, such as headaches, fatigue, and dizziness, despite increasing your fluid intake, it’s essential to seek medical advice. Chronic dehydration can be a sign of an underlying health condition.
9.2 Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions, such as kidney problems, diabetes, and heart failure, can affect fluid balance. Individuals with these conditions should consult with their healthcare provider to determine their optimal fluid intake.
9.3 Medications
Some medications, such as diuretics, can increase fluid loss and may require adjustments to your hydration plan. Discuss your medication regimen with your doctor to ensure you’re staying properly hydrated.
9.4 Extreme Physical Activity
Athletes who engage in intense or prolonged physical activity may benefit from consulting with a sports medicine specialist or a hydration expert. These professionals can help you develop a personalized hydration strategy to support your performance and prevent dehydration.
9.5 Unexplained Fluid Retention
If you experience unexplained fluid retention or swelling, it’s essential to seek medical advice. Fluid retention can be a sign of an underlying health condition, such as kidney or heart problems.
9.6 Tailored Hydration Plans from Experts
Knowing when to seek professional advice on hydration is crucial for addressing specific concerns and ensuring you’re meeting your individual needs. At HOW.EDU.VN, our team of PhDs offers tailored hydration plans and expert guidance to help you optimize your fluid intake and support your health. Contact us today to learn more.
10. The Future of Hydration Research
Hydration research is an evolving field, with ongoing studies exploring the complex interactions between water, health, and performance. Staying informed about the latest findings can help you make evidence-based decisions about your fluid intake.
10.1 Personalized Hydration Strategies
Future research is likely to focus on developing more personalized hydration strategies based on individual factors like genetics, lifestyle, and health conditions.
10.2 The Role of Electrolytes
Electrolytes play a crucial role in fluid balance, and future studies may explore the optimal balance of electrolytes for different populations and activities.
10.3 Hydration and Cognitive Function
Ongoing research continues to investigate the link between hydration and cognitive function, with studies exploring the impact of hydration on memory, attention, and mood.
10.4 Hydration and Chronic Disease
Future research may examine the role of hydration in the prevention and management of chronic diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and kidney disease.
10.5 Technological Advancements
Technological advancements, such as wearable sensors, may provide real-time monitoring of hydration status, allowing individuals to adjust their fluid intake as needed.
10.6 Staying Informed with HOW.EDU.VN
Staying informed about the latest hydration research can empower you to make informed decisions about your fluid intake and support your health and well-being. At HOW.EDU.VN, our team of PhDs stays up-to-date on the latest research and provides expert insights to help you optimize your hydration. Connect with us today to learn more and stay informed about the future of hydration.
Understanding how much water makes up the human body is essential for maintaining optimal health. From regulating body temperature to transporting nutrients, water plays a vital role in numerous bodily functions. At HOW.EDU.VN, we provide expert guidance and personalized advice to help you understand your body’s unique hydration needs, promoting healthy hydration habits. Contact us now and consult with our team of over 100 world-renowned PhDs to optimize your health and well-being.
Don’t let dehydration hold you back. Connect with the experts at HOW.EDU.VN today for personalized advice and guidance on optimizing your hydration. Our team of leading PhDs is here to answer your questions and help you develop a hydration plan that supports your health and well-being. Contact us at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States, Whatsapp: +1 (310) 555-1212, or visit our website at how.edu.vn.