Building a garage is a significant investment that enhances your property value and provides much-needed storage and protection. Understanding How Much Would It Cost To Build A Garage is crucial for budgeting and planning. This guide, brought to you by HOW.EDU.VN, explores the various factors influencing the cost of garage construction, offering insights to help you make informed decisions and potentially save money on your project. We delve into everything from garage size and materials to labor costs and additional features, ensuring you’re well-equipped to estimate the total expense and connect with the right professionals.
At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with experienced Ph.Ds and experts who can provide personalized advice on construction projects. By understanding the total garage construction cost, you can ensure that your project is both feasible and valuable.
1. Understanding the Average Cost to Build a Garage
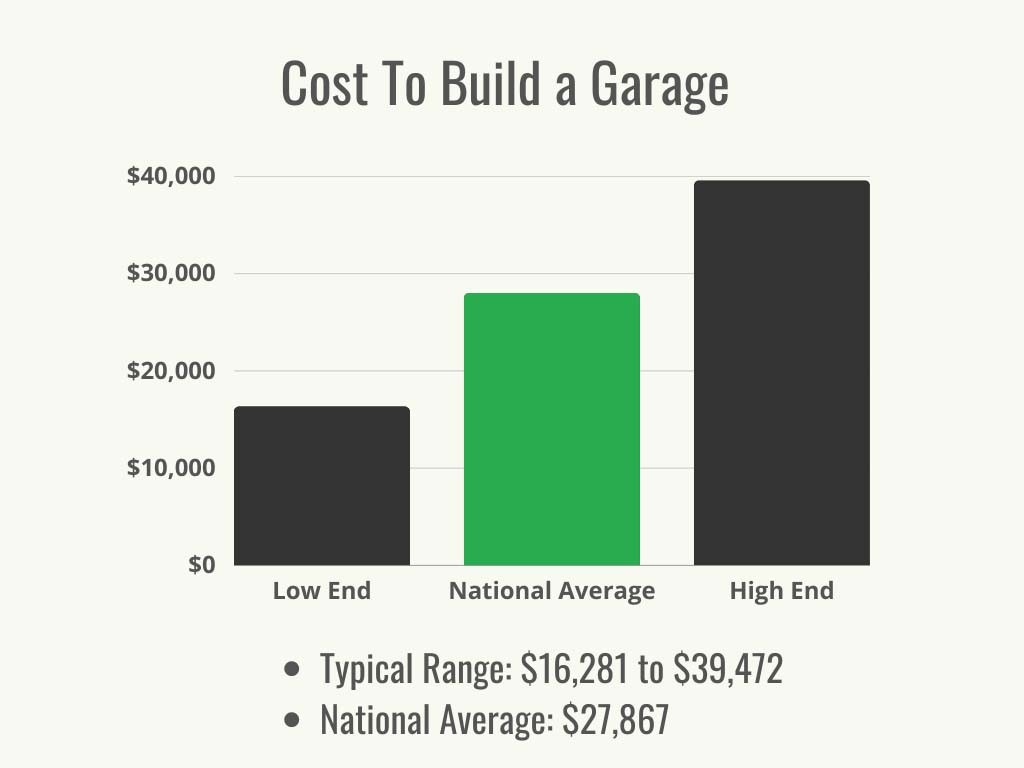
The national average cost to build a garage typically ranges from $16,281 to $39,472, averaging around $27,867, according to Angi and HomeAdvisor. However, this is a broad estimate. The actual cost can fluctuate significantly based on several factors. It’s common to estimate around $40 to $70 per square foot for a standard garage without extensive upgrades. Here’s a breakdown of key factors that influence the overall cost:
- Size: Larger garages naturally cost more due to increased material and labor needs.
- Materials: The choice of materials for the foundation, framing, roof, and siding significantly impacts the price.
- Location: Geographic location affects labor costs, material availability, and permit fees.
- Features: Additional features like insulation, electrical work, and custom doors add to the expense.
Consulting with experts at HOW.EDU.VN can provide tailored cost estimations, ensuring you’re prepared for the financial aspects of your garage project. Understanding these key cost factors from the beginning will assist you in planning your construction more effectively.
2. Key Cost Factors in Garage Construction
Several elements influence the total cost of building a garage. Let’s explore these factors in detail to provide a comprehensive understanding of the financial considerations involved.
2.1. Garage Size and Dimensions
The size of your garage is the most significant factor influencing the overall cost. Here’s a breakdown of typical garage sizes and their associated costs:
- Single-Car Garage: Ranges from 240 to 384 square feet, costing between $10,500 and $27,000.
- Two-Car Garage: Averages around 576 square feet, with costs ranging from $14,500 to $40,300.
- Three-Car Garage: Typically 624 to 720 square feet, costing between $28,200 and $57,100.
- Four-Car Garage: Could be 800 to 1,000 square feet or more, with costs ranging from $32,000 to $73,900.
- Garage with Living Space: Considerably larger and more complex, ranging from $60,000 to $270,000.
- RV Garage: Designed to accommodate recreational vehicles, costing $36,000 to $140,000.
Understanding the precise dimensions needed for your vehicles and storage requirements is crucial in determining the appropriate size and, consequently, the cost.
2.2. Foundation Installation and Framing Costs
The foundation is a critical component of any garage, ensuring stability and longevity. Foundation costs range from $2,000 to $7,000 or $4 to $25 per square foot, depending on the size and type of foundation.
Framing, which involves constructing the walls, also contributes significantly to the overall cost. Here’s a breakdown of framing material costs:
- Brick: $27 to $45 per square foot.
- Brick-Veneered: $5 to $30 per square foot.
- Cinderblock: $29 to $62 per square foot.
- Metal: $3,000 to $22,000 total.
- Prefab Pole Barn: $40 to $85 per square foot.
- Stick-Built: $40 to $70 per square foot.
Choosing the right framing material depends on your budget, aesthetic preferences, and local building codes.
2.3. Roofing and Gutter Installation Expenses
The roof is essential for protecting the garage from the elements. Asphalt shingles are the most common and affordable roofing option, with a lifespan of 20 to 40 years. Roofing costs can range from $1,600 to $16,000, depending on the size, style, and materials used.
Gutters are also crucial for directing water away from the foundation, preventing water damage. Gutter installation typically costs between $4 and $30 per linear foot, depending on the material (aluminum, vinyl, or steel).
2.4. Siding Material and Installation Pricing
Siding protects the garage walls and contributes to the overall aesthetic appeal. Here’s a breakdown of siding material costs per square foot:
- Aluminum: $4 to $7
- Brick: $11 to $15
- Engineered Wood: $3 to $8
- Fiber Cement: $6 to $10
- Stone: $11 to $18
- Vinyl: $0.70 to $3
- Wood: $3 to $10
Vinyl siding is popular for its durability and affordability, but other options provide different aesthetic and functional benefits.
2.5. Labor Costs and Permit Fees
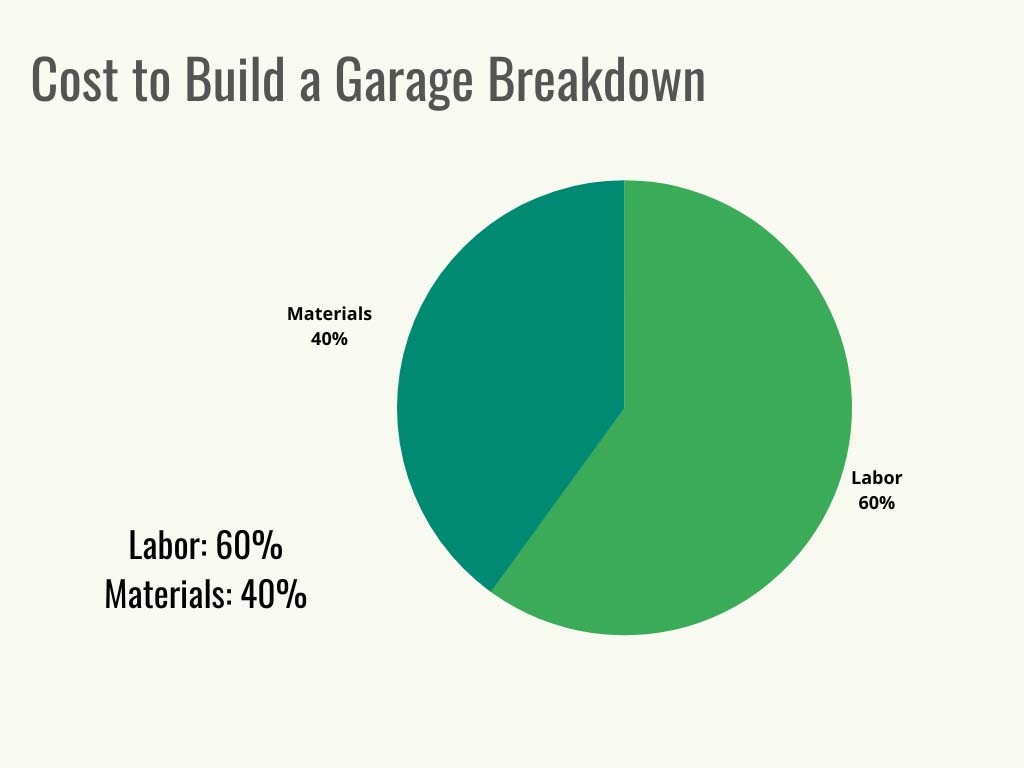
Labor accounts for a significant portion of the total cost, typically ranging from 50% to 70% of the final price. Labor costs can vary between $20 and $49 per square foot, depending on location and accessibility.
Permit fees are also necessary to ensure the construction complies with local building codes. Permits can cost between $1,200 and $1,500, depending on the region.
2.6. Impact of Geographic Location
Geographic location significantly impacts the cost of building a garage due to variations in labor rates, material availability, and local building codes. Below are some average costs to build a garage in 10 different states:
| U.S. State | Average Cost to Build a Garage |
|---|---|
| California | $44,200 |
| Colorado | $25,600 |
| Illinois | $17,250 |
| Maine | $33,600 |
| Michigan | $22,100 |
| Minnesota | $19,300 |
| New York | $26,800 |
| Oregon | $24,000 |
| Texas | $28,500 |
| Washington | $22,250 |


These figures are averages and can vary based on specific locations and project scopes.
3. Additional Costs and Considerations for Your Garage Project
Beyond the basic structure, several additional factors can influence the total cost of building a garage. Considering these elements during the planning phase ensures a comprehensive budget and minimizes unexpected expenses.
3.1. Attached vs. Detached Garages: Cost Differences
The choice between an attached and detached garage significantly affects the cost. Attached garages typically cost less, around $29 per square foot, because they share a wall with the house, reducing material and labor costs. They also simplify electrical and plumbing connections.
Detached garages, on the other hand, cost between $40 and $70 per square foot. These require independent structures and more extensive utility connections.
3.2. Site-Built vs. Prefabricated Garages: Weighing the Options
Another critical decision is whether to build the garage on-site or purchase a prefabricated (prefab) garage kit. Prefab garages are easier to install and can cost around $5,000 on average, excluding permits and labor. However, some communities may not allow prefab garages, so it’s essential to check local regulations.
Site-built garages offer more customization but involve higher costs and longer construction times.
3.3. Window Installation: Natural Light Considerations
Windows can add natural light and aesthetic appeal to a garage. The cost to install windows ranges from $200 to $2,100, depending on the size, style, and placement. Some homeowners opt for windows in the garage door, while others prefer additional windows to match the home’s exterior.
3.4. Insulation Installation: Climate Control and Energy Efficiency
Insulation is crucial for climate control and energy efficiency, particularly in attached garages. The cost to insulate a garage ranges from $2,000 to $6,000, depending on the type of insulation. Fiberglass and cellulose are cheaper options, costing $0.40 to $2.80 per square foot, while cork and polystyrene cost $1 to $15 per square foot.
3.5. Electrical Work: Powering Your Garage
Running electricity to a garage is essential for power tools, lighting, and automated garage doors. Electrical work can cost between $1,000 and $2,500, depending on the complexity of the wiring and the number of outlets and fixtures.
3.6. Garage Door Opener Installation: Convenience and Security
Garage door openers add convenience and security. Installation costs range from $220 to $520, depending on the type of opener and complexity of the installation. Hiring one of the best garage door installation companies may be necessary for this project.
3.7. Add-Ons and Accessories: Customizing Your Space
Adding a workspace, workbench (around $375 to $600), or built-in cabinets (up to $3,400) can increase functionality. All-in-one cabinet systems are available for easy installation. Other popular add-ons include refrigerators, freezers, HVAC systems (around $15 per linear foot), and plumbing fixtures ($900 to $1,300 per fixture).
3.8. Garage Finishing: Aesthetics and Functionality
Finishing a garage involves drywalling and painting the interior (around $30 per square yard and $1.50 per square foot, respectively). Epoxy flooring costs an average of $2,346. Installing a heater to make the garage more comfortable in colder months can cost around $2,075.
4. Types of Garages: Choosing the Right Structure
Selecting the right type of garage depends on your needs, budget, and aesthetic preferences. Each type offers unique benefits and considerations.
4.1. Attached Garages: Convenience and Cost Savings
Attached garages share structure space with the house, making them cheaper to build and easier to connect to utilities. A single-car attached garage typically starts at $29 per square foot.
4.2. Detached Garages: Flexibility and Design Freedom
Detached garages offer more flexibility in design and can include upper living spaces or accommodate RVs. However, they cost more due to the need for independent structures and utility connections, averaging between $40 and $70 per square foot.
4.3. 1-Car Garages: Minimalist and Efficient
1-car garages are suitable for smaller homes or single-vehicle households. The average cost ranges from $10,500 to $27,000, with typical dimensions of 12 to 16 feet wide and 20 to 24 feet long.
4.4. 2-Car Garages: Versatile and Popular
2-car garages are a common choice for most homes, offering ample space for two vehicles and some storage. Costs range from $14,500 to $40,300, with typical dimensions of 22 feet wide and 20 to 24 feet deep.
4.5. 3-Car Garages: Spacious and Functional
3-car garages are ideal for larger homes needing extra space for vehicles or recreational equipment. The average cost ranges from $28,200 to $57,100, with dimensions typically 31 to 34 feet wide and 20 to 24 feet deep.
4.6. 4-Car Garages: Ultimate Storage and Workspace
4-car garages are perfect for car enthusiasts needing workspace or storage. Costs average between $32,000 and $73,900, and additional features like plumbing or HVAC can push the cost over $100,000.
4.7. RV Garages: Accommodation for Recreational Vehicles
RV garages are custom-built to accommodate recreational vehicles, with door heights of 12 to 14 feet and lengths of 40 to 50 feet. The average cost ranges from $36,000 to $140,000, depending on materials and features.
4.8. Prefabricated Garage Kits: Affordable and Quick
Prefab garage kits offer an affordable and quick solution, costing around $5,000 on average. However, HOA approval is often required, and aesthetic appeal may be limited.
5. Benefits of Building a New or Replacement Garage
Building a new or replacement garage offers numerous benefits, from protecting vehicles and increasing storage to enhancing property value. These advantages make the investment worthwhile.
5.1. Vehicle Protection: Preserving Your Investment
Garages protect vehicles from dirt, harsh weather, vandalism, and theft, extending their lifespan and preserving resale value.
5.2. Accessibility and Convenience: Ease of Use
Having a garage ensures accessible parking and protection from the elements, saving time and effort in regions with harsh weather.
5.3. Increased Storage Space: Organized Living
Garages provide ample storage space for holiday decorations, off-season clothes, and sports equipment, keeping homes organized and clutter-free.
5.4. Increased Home Value: A Worthwhile Investment
A well-maintained garage enhances curb appeal and increases property value, making it an attractive feature for potential buyers. A new garage offers an immediate investment return of almost 80 percent on the project.
6. DIY vs. Hiring a Professional: Making the Right Choice
Deciding whether to build a garage yourself or hire a professional depends on your skills, time, and budget. While DIY can save money, professional contractors offer expertise, insurance, and warranties.
6.1. DIY Garage Construction: Potential Savings and Challenges
Skilled DIYers can handle tasks like framing, drywalling, or painting. However, specialized tasks like electrical wiring and roofing are best left to professionals.
6.2. Hiring a Professional Contractor: Expertise and Assurance
General contractors have skilled teams and subcontractors familiar with all aspects of garage construction, ensuring compliance with building codes and best practices. They also provide insurance and warranties for added peace of mind.
7. How to Save Money on Your Garage Project
Despite the significant costs, several strategies can help you save money on your garage project without compromising quality.
7.1. Strategic Planning and Design Choices
- Forgo Windows or Skylights: Opt for windows in the garage door for natural light instead of additional installations.
- Build to Size: Avoid building extra space that may not be needed.
- Eliminate Upgrades and Accessories: Assess the necessity of HVAC systems, custom cabinets, and plumbing.
7.2. Cost-Effective Material and Labor Options
- Install Your Own Shelving or Cabinets: Reduce labor fees by installing storage accessories yourself.
- Do the Finishing Work Yourself: Save money by handling painting and other finishing tasks.
- Choose an Asphalt Shingle Roof: Opt for a cheaper, more common roofing style.
- Use Reclaimed Wood: If available, reclaimed wood can offer a unique and cost-effective exterior.
7.3. Smart Procurement and Timing
- Speak with a Contractor: Contractors can offer advice on reducing costs by changing materials or making adjustments.
- Build in the Off-Season: Depending on your region, building during the cooler season may yield discounts.
- Shop Around: Get quotes from multiple contractors and factor in warranties.
- Consider a Prebuilt Garage Kit: If HOAs permit, prefab kits can significantly reduce costs.
- Review the Project: Scrutinize each line item in the contractor’s bid and ask questions.
8. Financing Options for Your New Garage
Building a garage can be a significant expense. Here are several financing options to consider:
- Personal Loan: Explore personal loans from financial institutions, paying attention to loan terms and interest rates.
- Credit Card: Consider using a credit card, especially if you have a rewards card that earns cash back or other rewards.
- Home Equity Loan: If you have sufficient equity in your home, consider a home equity loan from U.S. Bank or Flagstar Bank.
9. Essential Questions to Ask a Garage Building Professional
Hiring a trusted professional ensures a smooth and successful project. Ask these questions to evaluate potential contractors:
- Are you licensed and insured?
- What kind of warranties do you offer?
- How long have you been building garages?
- Do you have photos of other garages you’ve built?
- How long will it take to complete my project?
- What could affect the timeline?
- Will you need to hire subcontractors? Who hires them?
- Who pays the subcontractors?
- Am I responsible for permits, or do you obtain them and bill me separately?
- Do you require a down payment?
- Can we review the itemized project or quote together?
- Can I do the finishing work myself?
- What if I want to add a feature after we’ve started the project?
- What’s the best insulation choice for our region if I want to avoid increasing my home’s energy bill?
- How will you handle any problems that arise during this project?
- Do you have a recommendation for a garage door company to maintain and service my garage door after it’s installed?
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Garage Construction Costs
Here are some common questions homeowners have about the cost of building a garage:
Q. How much does it cost to build an unfinished garage?
The cost varies, but typically it’s only a small percentage less than a finished garage. Savings come from omitting painting (averaging $1.50 per square foot) or installing cabinets as a DIY project.
Q. How much does it cost to build a 24-foot-by-24-foot garage?
A 24-foot-by-24-foot garage, which can hold two or three cars, typically costs between $28,200 and $57,100 to build.
Q. How much does it cost to remodel a garage?
Remodeling a garage costs between $6,010 and $25,280, with garage conversions averaging around $15,157.
Q. How much value does a garage add to a home?
A new garage can add $12,750 to $33,150 to a home’s value.
Q. How long does it take to build a garage?
Garage construction typically takes between 6 and 8 weeks, depending on factors like material availability and contractor schedules.
Conclusion: Planning Your Garage Project with Confidence
Understanding how much would it cost to build a garage involves considering various factors, from size and materials to labor and additional features. By thoroughly researching these elements and planning accordingly, you can ensure your project stays within budget and meets your needs. For personalized guidance and expert advice, contact HOW.EDU.VN to connect with experienced Ph.Ds who can assist you in every step of the process.
Ready to build your dream garage? Connect with our experts at HOW.EDU.VN for personalized advice and guidance. Our team of over 100 Ph.Ds are ready to answer your questions and help you make informed decisions. Contact us today to start your garage building journey with confidence.
Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
Website: HOW.EDU.VN
Unlock the expertise of top Ph.Ds at how.edu.vn and transform your garage construction project into a success.