The area of a rectangle represents the space enclosed within its four sides. Understanding how to calculate this area is a fundamental concept in geometry and has practical applications in everyday life, from home improvement projects to understanding spatial dimensions. This guide will provide a detailed explanation of how to find the area of a rectangle using various methods, formulas, and examples.
Understanding the Area of a Rectangle
In geometry, area is defined as the amount of two-dimensional space a shape occupies. For a rectangle, this space is the region within its boundaries. Imagine tiling your rectangular floor – the area is the total number of tiles you would need to cover the entire surface. We measure area in square units, such as square inches, square centimeters, or square feet, reflecting that we are measuring in two dimensions. Rectangular shapes are prevalent in our daily lives, from screens and books to rooms and fields, making understanding their area essential.
Defining Area of a Rectangle
The area of a rectangle is formally defined as the measure of the surface enclosed by its length and width. It quantifies the two-dimensional space within the rectangle’s perimeter.
The Fundamental Formula: Length Times Width
The most basic and widely used formula to calculate the area of a rectangle is remarkably simple:
Area = Length × Width
Where:
- Length (l): The longer side of the rectangle.
- Width (w): The shorter side of the rectangle, also sometimes referred to as breadth.
This formula tells us that to find the area, you simply multiply the measurement of the rectangle’s length by the measurement of its width. The result will always be in square units.
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Area
Calculating the area of a rectangle using the length and width is a straightforward process. Follow these simple steps:
-
Step 1: Identify the Length and Width. Determine the measurements of the rectangle’s length and width. These values will usually be provided in the problem or can be measured directly. Ensure both dimensions are in the same units (e.g., inches, centimeters, feet).
-
Step 2: Apply the Formula. Use the area of a rectangle formula: Area = Length × Width.
-
Step 3: Calculate the Product. Multiply the length and width values together.
-
Step 4: State the Answer in Square Units. The area should always be expressed in square units. If the length and width were in inches, the area would be in square inches (in²). If they were in meters, the area would be in square meters (m²), and so on.
Example: Let’s calculate the area of a rectangle with a length of 12 inches and a width of 5 inches.
Solution:
- Length (l) = 12 inches, Width (w) = 5 inches
- Area = Length × Width
- Area = 12 inches × 5 inches = 60
- Area = 60 square inches (in²)
Therefore, the area of the rectangle is 60 square inches.
Understanding Units of Area
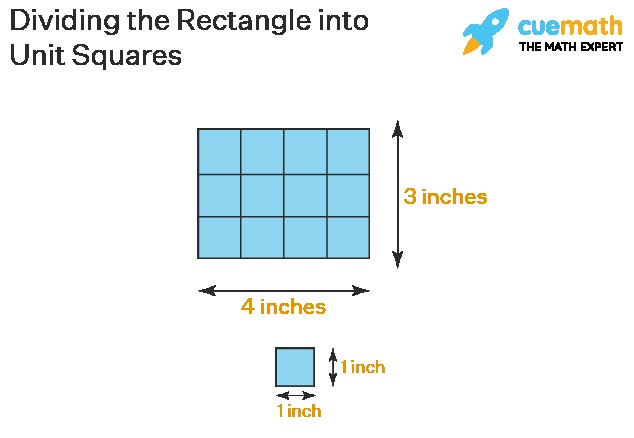
Why are units of area always squared? Consider a rectangle with a length of 4 inches and a width of 3 inches. Imagine dividing this rectangle into a grid of squares, where each square is 1 inch by 1 inch (1 square inch).
As you can see, you can fit 12 of these 1-inch square units within the rectangle. This visually demonstrates that the area is 12 square inches. When you multiply length (inches) by width (inches), you are essentially multiplying inches by inches, resulting in square inches. This principle applies to all units of length when calculating area.
Finding Area Using the Diagonal of a Rectangle
Sometimes, instead of the width, you might be given the diagonal of the rectangle and one side (either length or width). The diagonal is a line segment that connects opposite corners of the rectangle, dividing it into two right-angled triangles. We can use the Pythagorean theorem to find the missing side and then calculate the area.
Method 1: Using the Pythagorean Theorem
- Identify Given Values: You’ll know the length (or width) and the diagonal.
- Apply the Pythagorean Theorem: In a rectangle, the diagonal (d), length (l), and width (w) are related by the Pythagorean theorem: d² = l² + w².
- Solve for the Missing Side: Rearrange the formula to solve for the unknown side (width if length is given, or length if width is given):
- If finding width: w = √(d² – l²)
- If finding length: l = √(d² – w²)
- Calculate the Area: Once you have both length and width, use the standard area formula: Area = Length × Width.
Example: A rectangle has a length of 8 cm and a diagonal of 10 cm. Find its area.
Solution:
- Length (l) = 8 cm, Diagonal (d) = 10 cm
- Pythagorean Theorem: d² = l² + w²
- Solve for Width: w = √(d² – l²) = √(10² – 8²) = √(100 – 64) = √36 = 6 cm
- Calculate Area: Area = Length × Width = 8 cm × 6 cm = 48 square cm (cm²)
Therefore, the area of the rectangle is 48 square centimeters.
Method 2: Direct Formula Approach
We can derive a formula that directly calculates the area using the diagonal and one side. If we know the width (w) and diagonal (d), we can substitute the expression for length (l = √(d² – w²)) into the area formula:
Area = l × w = √(d² – w²) × w = w√(d² – w²)
Similarly, if we know the length (l) and diagonal (d):
Area = l × w = l√(d² – l²)
Example: Using the same example as above (width = 6 units, diagonal = 10 units), apply the direct formula.
Solution:
Area = w√(d² – w²) = 6√(10² – 6²) = 6√(100 – 36) = 6√64 = 6 × 8 = 48 square units.
Calculating Area with Perimeter Information
If you know the perimeter of a rectangle and one side (length or width), you can also determine its area. The perimeter (P) of a rectangle is given by the formula: P = 2(l + w).
Steps to find the area using perimeter:
- Identify Given Values: You’ll know the perimeter and either the length or width.
- Use the Perimeter Formula: P = 2(l + w)
- Solve for the Missing Side: Rearrange the perimeter formula to solve for the unknown side:
- If finding width: w = (P/2) – l
- If finding length: l = (P/2) – w
- Calculate the Area: Once you have both length and width, use the area formula: Area = Length × Width.
Example: A rectangle has a perimeter of 30 units and a width of 5 units. Find its area.
Solution:
- Perimeter (P) = 30 units, Width (w) = 5 units
- Perimeter Formula: P = 2(l + w)
- Solve for Length: 30 = 2(l + 5) => 15 = l + 5 => l = 10 units
- Calculate Area: Area = Length × Width = 10 units × 5 units = 50 square units.
Therefore, the area of the rectangle is 50 square units.
Derivation of the Area Formula
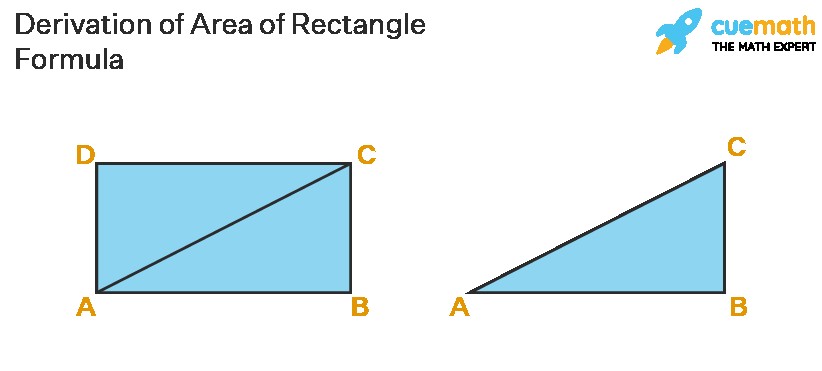
The area formula for a rectangle can be understood by dividing the rectangle along its diagonal. A diagonal divides a rectangle into two congruent right-angled triangles.
The area of the rectangle is the sum of the areas of these two triangles. The area of a triangle is given by (1/2) × Base × Height. In a right-angled triangle formed by the rectangle’s diagonal, the base and height are the length and width of the rectangle.
Area of Rectangle = Area of Triangle 1 + Area of Triangle 2
Since the triangles are congruent, their areas are equal.
Area of Rectangle = 2 × (Area of one triangle)
Area of Rectangle = 2 × (1/2 × Base × Height)
Area of Rectangle = Base × Height
In the context of the rectangle, Base = Length (l) and Height = Width (w).
Therefore, Area of Rectangle = Length × Width
Practical Examples of Area Calculation
Let’s look at some real-world examples to solidify your understanding of calculating the area of a rectangle.
-
Example 1: Farm Area
A rectangular farm is 150 yards long and 80 yards wide. What is the area of the farm?Solution:
Length = 150 yards, Width = 80 yards
Area = Length × Width = 150 yards × 80 yards = 12,000 square yards. -
Example 2: Tabletop Area
A rectangular tabletop measures 40 inches in length and 24 inches in width. Calculate the area of the tabletop.Solution:
Length = 40 inches, Width = 24 inches
Area = Length × Width = 40 inches × 24 inches = 960 square inches. -
Example 3: Area with Decimals
A rectangular garden plot is 6.5 meters long and 3 meters wide. Find the area of the garden plot.Solution:
Length = 6.5 meters, Width = 3 meters
Area = Length × Width = 6.5 meters × 3 meters = 19.5 square meters.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the Area of a Rectangle in Geometry?
The area of a rectangle in geometry is the measure of the two-dimensional space enclosed within its four sides. It is calculated by multiplying its length and width and is expressed in square units.
What is the Perimeter and Area of a Rectangle?
The perimeter of a rectangle is the total distance around its boundary, calculated as P = 2(Length + Width). The area is the space enclosed within this boundary, calculated as Area = Length × Width.
What is the Formula of Area of Rectangle?
The formula for the area of a rectangle is: Area = Length × Width.
What is the Unit of Area of a Rectangle?
The unit of area is always a square unit, derived from the units used for length and width. For example, if length and width are in meters, the area is in square meters (m²).
How to Find the Area of a Rectangle Using Diagonal?
You can find the area using the diagonal and one side by using the Pythagorean theorem to find the missing side and then applying the Area = Length × Width formula, or by using the direct formulas: Area = w√(d² – w²) or Area = l√(d² – l²).
What is a Rectangle?
A rectangle is a quadrilateral with four right angles. Its opposite sides are equal in length and parallel.
How to Find the Area of a Rectangle with Fractions?
To find the area of a rectangle with fractional dimensions, simply multiply the fractional length and width. Remember to multiply the numerators together and the denominators together. If you have mixed fractions, convert them to improper fractions first.
How to Find the Area of a Rectangle when Perimeter is Given?
If the perimeter and one side are given, use the perimeter formula P = 2(l + w) to solve for the missing side, and then use the Area = Length × Width formula to calculate the area.
By understanding these methods and formulas, you can confidently calculate the area of any rectangle, whether you are given its length and width directly, or information about its diagonal or perimeter. Practice with various examples to master this essential geometrical concept.