Key Takeaways
- Deep sleep, also known as stage 3 NREM sleep, is vital for physical and mental recovery, contributing to muscle and bone repair and immune system strength.
- Improve deep sleep by prioritizing consistent sleep hygiene practices, effectively managing stress, and making mindful dietary choices.
- If sleep problems persist and affect your daily life or sleep cycle, seeking advice from a healthcare professional is recommended.
Deep sleep is a critical phase of the sleep cycle, essential for waking up feeling rejuvenated and energized. This stage, also known as stage 3 NREM sleep, offers significant health benefits, including the repair and regrowth of bone and muscle tissues, and the fortification of the immune system. Notably, the majority of deep sleep occurs during the first half of the night.
This article will explore actionable strategies to naturally enhance your deep sleep, emphasizing the importance of a regular sleep schedule, effective stress management techniques, the impact of caffeine and alcohol, and the creation of a conducive sleep environment. If sleep difficulties persist despite implementing these recommendations, or if they significantly disrupt your daily life, consulting a doctor is advisable.
Are You Getting Enough Deep Sleep?
Several factors can negatively impact your sleep quality. Consider these questions to assess whether your deep sleep might be a concern:
Tips for Getting More Deep Sleep
The most effective approach to increasing deep sleep is to ensure you are getting sufficient total sleep hours and adopting evidence-based healthy sleep habits. Deep sleep is most prominent in the initial one to two hours of sleep. Consequently, strategies that help you fall asleep faster can indirectly contribute to achieving more deep sleep naturally.
Furthermore, identifying and minimizing factors that impede deep sleep is crucial. While some adjustments can be made independently, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional if you suspect a medical condition or medication is affecting your sleep.
Maintain a Consistent Sleep Schedule
Adhering to a regular bedtime and wake-up time every day is paramount. While varying sleep schedules on weekends might seem appealing, research indicates that inconsistent sleep-wake patterns disrupt your body’s natural circadian rhythm. Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule promotes faster sleep onset, facilitating the deep sleep your body needs.
Practice Relaxation and Stress Management
Stress and anxiety are notorious sleep disruptors. Studies have shown a direct correlation between high stress levels and reduced deep sleep. Incorporating calming activities to mitigate stress can significantly improve deep sleep quality.
Engaging in relaxation exercises, deep breathing techniques, yoga, and meditation can naturally alleviate anxiety and enhance sleep. Establishing a calming bedtime routine, such as taking a warm bath, reading a book, or listening to soothing music, can also prepare your mind and body for deep sleep. It’s also beneficial to avoid stressful conversations or dwelling on anxieties before bedtime.
If stress and anxiety persist despite self-care efforts or significantly interfere with your well-being, seeking professional medical advice is recommended.
Limit or Avoid Caffeine and Alcohol
Both caffeine and alcohol are detrimental to sleep quality, hindering your ability to achieve deep sleep. To optimize sleep, it’s advisable to avoid caffeine and alcohol, especially in the hours leading up to bedtime. Individuals who regularly consume significant amounts of alcohol should consult their doctor before drastically reducing or ceasing alcohol intake, as alcohol withdrawal can pose health risks.
Optimize Your Bedroom Environment for Comfort
Physical discomfort or pain can significantly impede deep sleep. Similarly, disruptive environmental factors like loud noises and bright lights can negatively affect sleep quality. Creating a sleep sanctuary that is dark, quiet, and cool is essential for deep sleep. Ensure your bed and pillows are comfortable and supportive. For those living in noisy or brightly lit environments, consider using earplugs, white noise machines, or blackout curtains to enhance sleep conditions.
How Much Deep Sleep Do I Need?
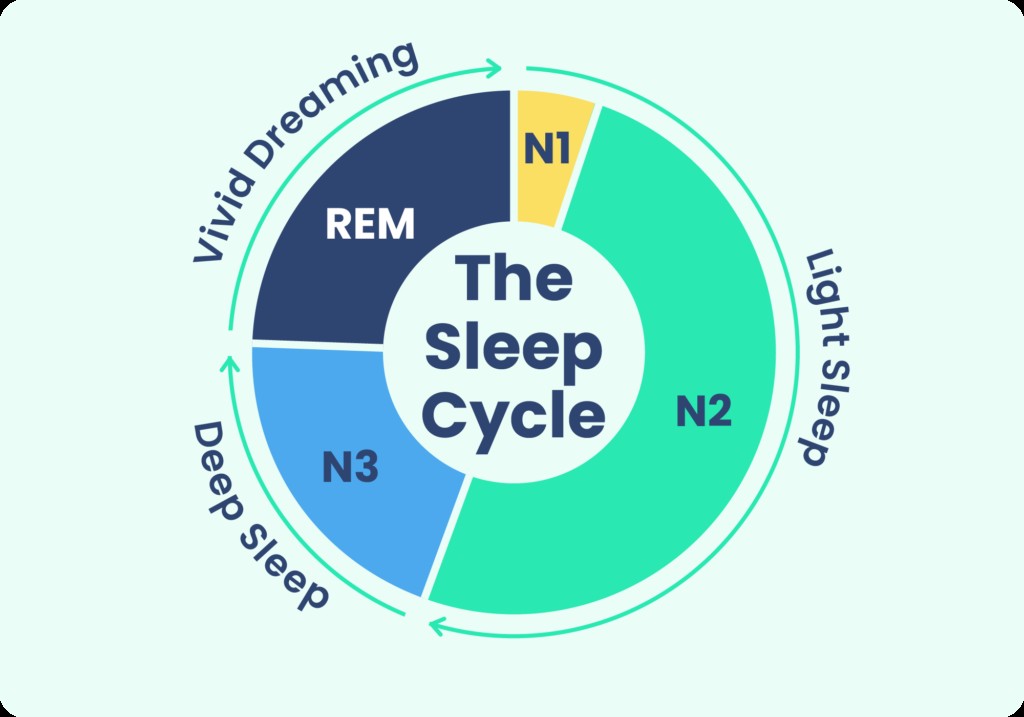
Sleep is broadly categorized into two main types: non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. As you transition into sleep, you progress through three stages of NREM sleep, culminating in a period of REM sleep. This complete cycle through all sleep stages typically repeats four to six times throughout a night.
Stage 3 NREM sleep is synonymous with deep sleep, characterized by high-quality rest that leaves you feeling refreshed upon waking. During deep sleep, your heart rate, breathing, and brain wave activity reach their slowest points, and your muscles are profoundly relaxed. The majority of deep sleep occurs in the first half of the night.
While there are no specific guidelines for the ideal amount of deep sleep, most adults typically spend about 10% to 20% of their nightly sleep in this stage. Older adults generally experience less deep sleep and REM sleep compared to middle-aged adults. Various substances and medical conditions can also influence the duration of deep sleep.
The body naturally regulates the amount of deep sleep obtained each night. For instance, individuals experiencing sleep deprivation may experience “rebound sleep,” leading to an increase in deep sleep to compensate for lost rest. Rebound sleep involves a higher proportion of REM and deep sleep following a period of insufficient sleep.
Benefits of Deep Sleep
While ongoing research continues to unveil the precise roles and benefits of each sleep stage, deep sleep is recognized for its significant health advantages. Studies suggest that deep sleep is crucial for feeling refreshed upon waking, physical restoration, and supporting learning and memory consolidation.
- Hormone Regulation: Deep sleep plays a vital role in regulating key hormones, including growth hormone and prolactin. Growth hormone is essential for growth and metabolism, while prolactin is crucial for breast growth and lactation, particularly in pregnant individuals.
- Immune System Enhancement: Deep sleep strengthens the immune system by facilitating the hormonal shifts necessary for effective responses to pathogens and diseases.
- Learning and Memory Consolidation: Researchers believe that NREM sleep stages, especially deep sleep, are instrumental in learning and memory formation. While the exact mechanisms are still being explored, deep sleep’s role in memory processes is increasingly recognized.
- Waste Product Clearance: Deep sleep facilitates the removal of waste products from the cerebrospinal fluid that accumulate throughout the day. This cleansing process is thought to be particularly important in preventing the buildup of substances associated with dementia.
What If I Don’t Get Enough Deep Sleep?
Insufficient deep sleep can disrupt hormone release, impair learning and memory, and impede the removal of metabolic waste from the brain.
General sleep deprivation is known to cause difficulty concentrating and thinking clearly. It can also lead to mood fluctuations and excessive fatigue that interferes with daily activities. Furthermore, sleep loss elevates the risk of accidents and errors at work or school due to increased sleepiness.
Over the long term, chronic sleep deficiency is linked to an increased risk of serious health conditions, including heart disease, hypertension, and stroke. Long-term sleep deprivation is also associated with a higher likelihood of obesity and type 2 diabetes.
When to Talk to a Doctor About Sleep Problems
It is advisable to consult a doctor if sleep problems persist despite adopting healthy sleep habits, or if these issues significantly disrupt your daily life. Seeking medical advice is also important if you suspect an underlying health condition or medication is contributing to your sleep difficulties.
Depending on your specific situation, a doctor may recommend tests or treatments for your sleep problems. This might include keeping a detailed sleep diary to analyze sleep patterns. If a sleep disorder is suspected, a sleep study may be recommended for diagnosis. If a medical condition is thought to be the root cause, further medical evaluations may be necessary.
Still have questions? Ask our community!
Join our Sleep Care Community — a supportive and reliable platform connecting you with sleep health professionals, product experts, and individuals facing similar experiences. Whether you need expert advice for insomnia or are looking for the ideal mattress, our community offers personalized guidance from sleep specialists.