Understanding how many people are born each day is essential for grasping global population dynamics. At HOW.EDU.VN, we provide expert insights into demographic trends and offer personalized advice to help you understand and navigate the complexities of our changing world. Let’s explore the numbers behind global birth rates and demographic changes and connect with leading PhD experts for tailored guidance on demographic trends and analysis.
1. Global Birth Statistics: A Daily Overview
How many people are born each day? To understand this, it’s crucial to delve into the statistics that shape our world’s population. Globally, birth rates play a significant role in determining population growth, impacting various aspects of society, from healthcare to education and economic planning.
1.1. Daily Birth Rate Worldwide
On average, approximately 360,000 babies are born each day around the world. This remarkable number highlights the continuous growth and renewal of the global population.
1.2. Regional Variations in Birth Rates
Birth rates vary significantly across different regions. Factors such as economic development, access to healthcare, cultural norms, and government policies all influence these variations.
- Africa: Generally has the highest birth rates, with many countries exceeding 40 births per 1,000 people annually.
- Asia: Shows a wide range, with some countries like Japan and South Korea having very low birth rates, while others like Afghanistan and Pakistan have high rates.
- Europe: Typically has the lowest birth rates, with many countries struggling to maintain their population size.
- North America: Has moderate birth rates, with the United States and Canada seeing relatively stable numbers.
- Latin America: Birth rates are declining in many countries but still remain higher than those in Europe and North America.
1.3. Factors Influencing Birth Rates
Several factors contribute to the differences in birth rates across regions:
- Economic Development: Higher levels of economic development often correlate with lower birth rates due to increased access to education and family planning resources.
- Access to Healthcare: Improved healthcare, including prenatal and postnatal care, influences birth rates and infant mortality rates.
- Cultural Norms: Cultural beliefs and traditions can significantly impact family size preferences and attitudes toward contraception.
- Government Policies: Policies such as parental leave, childcare subsidies, and family planning programs can influence decisions about having children.
1.4. The Role of Fertility Rate
The fertility rate, defined as the average number of children a woman is expected to have in her lifetime, is a key indicator of population growth. A fertility rate of 2.1 is generally considered the replacement rate, meaning it is the rate needed to maintain a stable population size, without considering migration.
- Many developed countries have fertility rates below the replacement rate, leading to concerns about aging populations and declining workforces.
- In contrast, many developing countries have fertility rates above the replacement rate, leading to rapid population growth and potential challenges related to resource management and infrastructure development.
1.5. Impact of Birth Rates on Society
Understanding birth rates is crucial for policymakers and researchers as they plan for the future. High birth rates can strain resources and infrastructure, while low birth rates can lead to economic stagnation and an aging population.
1.6. Connect with Experts at HOW.EDU.VN
Do you want to delve deeper into global birth statistics and understand the trends affecting your region? At HOW.EDU.VN, our team of PhD experts can provide personalized insights and advice to help you navigate the complexities of demographic data. Contact us today for a consultation.
{width=850 height=600}2. Understanding Global Population Growth
To understand the impact of daily births, it’s important to consider the broader context of global population growth. This growth is influenced by the balance between births and deaths, as well as other factors like migration and life expectancy.
2.1. Current World Population
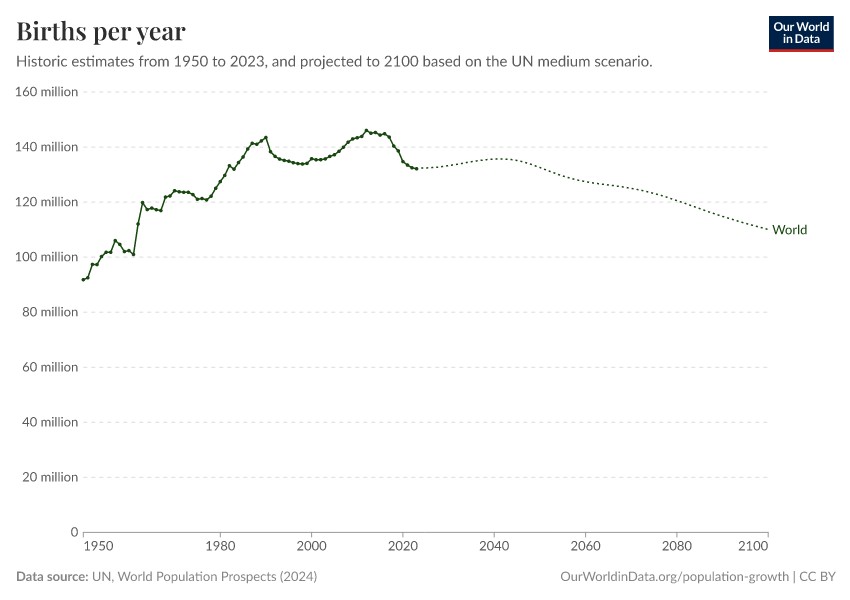
As of 2024, the world population is approximately 8.2 billion people. This number has grown rapidly over the past century, driven by advances in healthcare, agriculture, and sanitation.
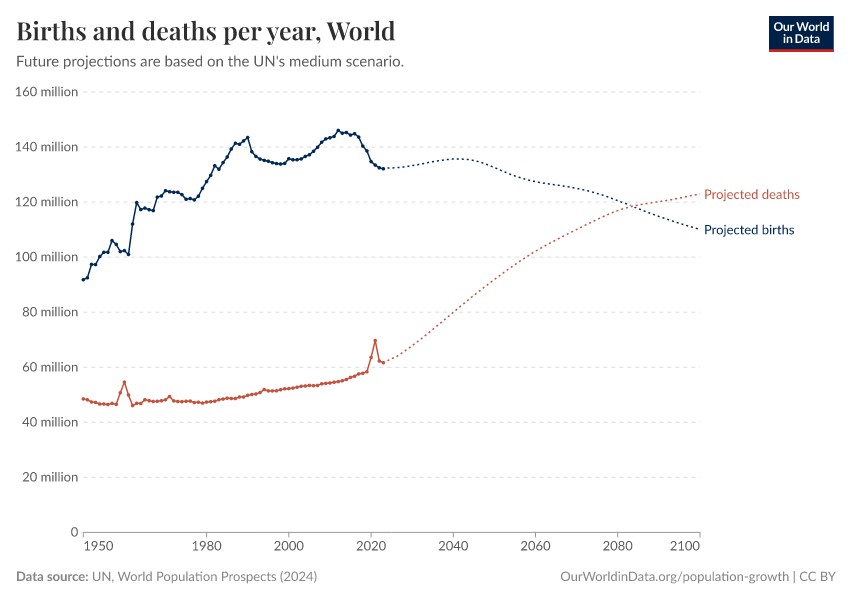
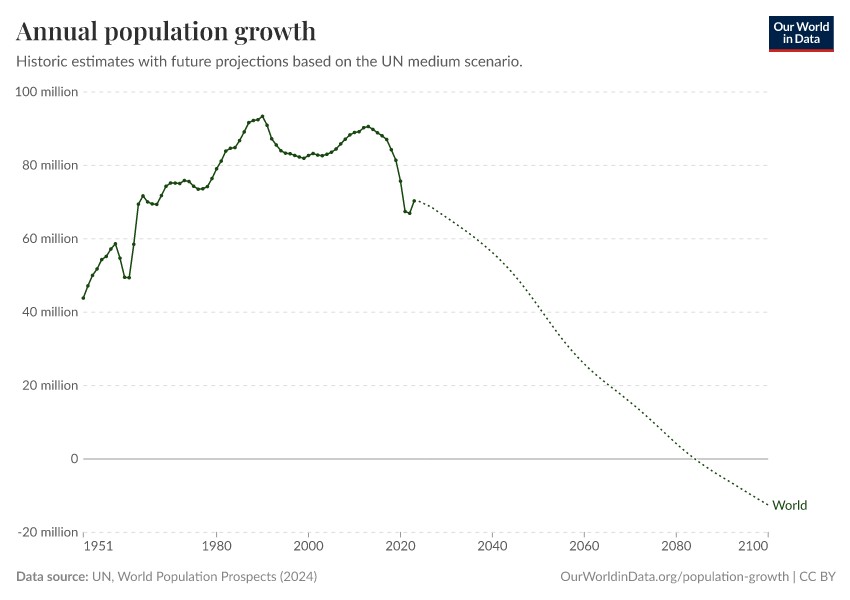
2.2. Annual Population Increase
In 2024, the world population increased by approximately 70 million people. This increase is the result of 132 million births minus 62 million deaths.
2.3. Factors Driving Population Growth
Several factors contribute to global population growth:
- Increased Life Expectancy: Advances in healthcare and nutrition have led to increased life expectancy in many parts of the world.
- Declining Mortality Rates: Improvements in sanitation, hygiene, and disease prevention have reduced mortality rates, particularly among infants and children.
- High Fertility Rates: In some regions, high fertility rates continue to drive population growth, despite declines in other parts of the world.
2.4. Demographic Transition Model
The demographic transition model provides a framework for understanding how population growth changes over time as countries develop economically and socially.
- Stage 1 (High Stationary): High birth and death rates, resulting in slow population growth.
- Stage 2 (Early Expanding): High birth rates but declining death rates, leading to rapid population growth.
- Stage 3 (Late Expanding): Declining birth rates and low death rates, resulting in slower population growth.
- Stage 4 (Low Stationary): Low birth and death rates, resulting in stable or declining population.
- Stage 5 (Declining): Death rates higher than birth rates, leading to population decline.
2.5. Future Population Projections
The United Nations projects that the world population will continue to grow in the coming decades, reaching approximately 10 billion by 2050. However, the rate of growth is expected to slow as fertility rates decline and mortality rates stabilize.
2.6. Connect with Experts at HOW.EDU.VN
Are you curious about future population trends and their potential impact on your business or community? Our PhD experts at HOW.EDU.VN can provide customized analysis and strategic advice to help you prepare for the challenges and opportunities of a changing world. Contact us today to learn more.
3. Regional Analysis of Birth Rates and Population
Analyzing birth rates and population trends at a regional level provides valuable insights into the unique challenges and opportunities facing different parts of the world.
3.1. Africa: High Birth Rates and Rapid Growth
Africa has the highest birth rates in the world, with many countries experiencing rapid population growth. This growth presents both opportunities and challenges.
- Opportunities: A young and growing population can provide a large labor force and a potential source of innovation and entrepreneurship.
- Challenges: Rapid population growth can strain resources, infrastructure, and social services, leading to challenges related to poverty, unemployment, and environmental degradation.
3.2. Asia: Diverse Trends and Declining Fertility
Asia is home to some of the world’s most populous countries, but birth rates vary widely across the region.
- China and India: These two countries account for a significant portion of the world’s population, but both have seen declines in fertility rates in recent decades.
- Japan and South Korea: These countries have some of the lowest birth rates in the world, leading to concerns about aging populations and declining workforces.
3.3. Europe: Low Birth Rates and Aging Populations
Europe has the lowest birth rates in the world, with many countries struggling to maintain their population size.
- Challenges: Aging populations can lead to labor shortages, increased healthcare costs, and strains on pension systems.
- Solutions: Some countries are implementing policies to encourage higher birth rates, such as parental leave, childcare subsidies, and immigration programs.
3.4. North America: Moderate Growth and Immigration
North America has moderate birth rates compared to other regions, with the United States and Canada experiencing relatively stable population growth.
- Immigration: Immigration plays a significant role in population growth in North America, helping to offset low birth rates and maintain a diverse and dynamic workforce.
3.5. Latin America: Declining Birth Rates and Urbanization
Latin America has seen declines in birth rates in recent decades, along with increasing urbanization and economic development.
- Challenges: Urbanization can lead to challenges related to housing, infrastructure, and social services, while declining birth rates can lead to concerns about aging populations and labor shortages.
3.6. Connect with Experts at HOW.EDU.VN
Do you need expert analysis of regional birth rates and population trends for your business or organization? Our PhD experts at HOW.EDU.VN can provide customized reports and strategic advice to help you make informed decisions. Contact us today to learn more.
{width=850 height=600}4. The Impact of Birth Rates on Healthcare Systems
Birth rates significantly impact healthcare systems worldwide. Understanding these impacts is crucial for effective planning and resource allocation to ensure adequate care for both mothers and children.
4.1. Maternal Healthcare
High birth rates in certain regions necessitate robust maternal healthcare systems to manage prenatal, delivery, and postnatal care. Key components include:
- Prenatal Care: Regular check-ups to monitor the health of the mother and fetus, provide education on nutrition and lifestyle, and screen for potential complications.
- Skilled Birth Attendants: Ensuring that deliveries are attended by trained healthcare professionals to reduce the risk of complications and maternal mortality.
- Postnatal Care: Providing care and support to mothers and newborns in the weeks and months following delivery, including breastfeeding support and vaccinations.
4.2. Pediatric Healthcare
High birth rates also require well-equipped pediatric healthcare systems to address the needs of infants and children. Essential services include:
- Immunization Programs: Vaccinating children against common diseases to reduce morbidity and mortality.
- Child Nutrition Programs: Promoting breastfeeding and providing nutritional supplements to ensure healthy growth and development.
- Pediatric Emergency Care: Ensuring access to timely and appropriate care for sick and injured children.
4.3. Resource Allocation
Effective resource allocation is critical for healthcare systems to meet the demands of varying birth rates. This includes:
- Infrastructure: Investing in hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare facilities to provide adequate capacity for maternal and pediatric care.
- Healthcare Workforce: Training and recruiting healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, and midwives, to ensure an adequate supply of skilled personnel.
- Medical Supplies and Equipment: Procuring and distributing essential medical supplies and equipment, such as medications, vaccines, and diagnostic tools.
4.4. Challenges in Low-Birth-Rate Countries
In countries with low birth rates, healthcare systems face different challenges, such as:
- Aging Workforce: A declining birth rate can lead to an aging healthcare workforce, making it difficult to maintain adequate staffing levels.
- Shifting Healthcare Needs: As the population ages, healthcare systems need to adapt to meet the needs of older adults, such as chronic disease management and geriatric care.
4.5. Connect with Experts at HOW.EDU.VN
Are you involved in healthcare planning and need expert guidance on how to address the challenges of changing birth rates? Our PhD experts at HOW.EDU.VN can provide customized analysis and strategic advice to help you optimize your healthcare system. Contact us today to learn more.
5. Economic Implications of Birth Rates
Birth rates have significant economic implications, affecting everything from labor force size to consumer demand and government spending.
5.1. Labor Force Dynamics
High birth rates can lead to a larger labor force in the future, potentially boosting economic growth. However, this requires investments in education and training to ensure that young people have the skills needed to succeed in the workforce.
Low birth rates can lead to labor shortages and an aging workforce, potentially slowing economic growth. This can be mitigated through policies such as immigration and encouraging older workers to remain in the workforce longer.
5.2. Consumer Demand
Birth rates influence consumer demand for various goods and services, such as baby products, childcare, education, and healthcare.
- High birth rates can stimulate demand for these products and services, creating economic opportunities for businesses.
- Low birth rates can lead to declining demand in these sectors, requiring businesses to adapt to changing market conditions.
5.3. Government Spending
Birth rates affect government spending on various programs and services, such as education, healthcare, and social security.
- High birth rates can increase the demand for these services, requiring governments to increase spending.
- Low birth rates can lead to decreased demand for some services, but increased demand for others, such as geriatric care.
5.4. Pension Systems
Low birth rates can strain pension systems, as there are fewer workers contributing to support a growing number of retirees.
- This can lead to the need for reforms, such as increasing the retirement age, raising contribution rates, or reducing benefits.
5.5. Connect with Experts at HOW.EDU.VN
Do you want to understand the economic implications of birth rates for your business or investment decisions? Our PhD experts at HOW.EDU.VN can provide customized analysis and strategic advice to help you navigate the complexities of demographic economics. Contact us today to learn more.
{width=850 height=600}6. Environmental Impact of Population Growth
Population growth, driven by birth rates, has significant environmental implications. Understanding these impacts is crucial for promoting sustainable development and protecting the planet.
6.1. Resource Depletion
A growing population places increasing demands on natural resources, such as water, land, and energy.
- This can lead to resource depletion, environmental degradation, and conflicts over resources.
6.2. Deforestation
Population growth can drive deforestation as more land is cleared for agriculture, housing, and infrastructure.
- Deforestation contributes to climate change, biodiversity loss, and soil erosion.
6.3. Pollution
A growing population generates more waste and pollution, which can contaminate air, water, and soil.
- Pollution can have negative impacts on human health and the environment.
6.4. Climate Change
Population growth contributes to climate change through increased greenhouse gas emissions from energy consumption, transportation, and agriculture.
- Climate change can lead to rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and disruptions to ecosystems and human societies.
6.5. Biodiversity Loss
Population growth can lead to biodiversity loss as habitats are destroyed and species are driven to extinction.
- Biodiversity loss can have negative impacts on ecosystem services, such as pollination, water purification, and climate regulation.
6.6. Sustainable Solutions
Addressing the environmental impacts of population growth requires a combination of strategies, such as:
- Promoting Sustainable Consumption: Encouraging people to consume fewer resources and reduce waste.
- Investing in Renewable Energy: Transitioning to renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydro, to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Protecting and Restoring Ecosystems: Conserving forests, wetlands, and other ecosystems to maintain biodiversity and ecosystem services.
- Promoting Family Planning: Providing access to family planning services to help people make informed decisions about family size.
6.7. Connect with Experts at HOW.EDU.VN
Are you concerned about the environmental impacts of population growth and want to explore sustainable solutions? Our PhD experts at HOW.EDU.VN can provide customized analysis and strategic advice to help you promote environmental sustainability. Contact us today to learn more.
7. Technological Advances and Birth Rates
Technological advancements in healthcare, contraception, and reproductive technologies are significantly impacting birth rates and family planning decisions worldwide.
7.1. Advancements in Contraception
The development and widespread availability of various contraceptive methods have empowered individuals to plan their families more effectively.
- Hormonal Contraceptives: Birth control pills, patches, and injections provide highly effective means of preventing pregnancy.
- Intrauterine Devices (IUDs): Long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARCs) like IUDs offer a convenient and reliable option for family planning.
- Barrier Methods: Condoms and diaphragms provide protection against both pregnancy and sexually transmitted infections.
7.2. Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)
Assisted reproductive technologies (ART) such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) and intrauterine insemination (IUI) have enabled many couples to overcome infertility and conceive.
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): Involves fertilizing an egg outside the body and then implanting the embryo in the uterus.
- Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): Involves placing sperm directly into the uterus to increase the chances of fertilization.
7.3. Healthcare Innovations
Advances in maternal and neonatal healthcare have reduced infant mortality rates and improved maternal health outcomes.
- Prenatal Screening: Allows for the early detection of potential health issues in the mother and fetus.
- Advanced Delivery Techniques: Help manage complicated pregnancies and deliveries, reducing the risk of complications.
- Neonatal Intensive Care: Provides specialized care for premature and sick newborns, improving their chances of survival.
7.4. Digital Health Solutions
Digital health solutions, such as telemedicine and mobile apps, are making healthcare more accessible and convenient, particularly for family planning and reproductive health services.
- Telemedicine: Allows individuals to consult with healthcare providers remotely, improving access to care in underserved areas.
- Mobile Apps: Provide information on contraception, fertility, and reproductive health, empowering individuals to make informed decisions.
7.5. Ethical Considerations
While technological advancements offer many benefits, they also raise ethical considerations related to reproductive rights, access to healthcare, and the potential for genetic engineering.
7.6. Connect with Experts at HOW.EDU.VN
Are you interested in exploring the ethical and societal implications of technological advancements in reproductive health? Our PhD experts at HOW.EDU.VN can provide customized analysis and strategic advice to help you navigate these complex issues. Contact us today to learn more.
8. The Role of Education and Empowerment
Education and empowerment, particularly for women, play a critical role in shaping birth rates and promoting sustainable development.
8.1. Female Education
Educated women are more likely to delay marriage and childbearing, have fewer children, and invest more in their children’s health and education.
- Economic Empowerment: Education enables women to participate more fully in the workforce, increasing their economic independence and decision-making power.
- Health Awareness: Educated women are more likely to seek prenatal care, use contraception, and adopt healthy behaviors.
8.2. Access to Information
Providing access to accurate information about family planning, reproductive health, and contraception empowers individuals to make informed decisions about family size.
- Comprehensive Sex Education: Helps young people understand their bodies, relationships, and reproductive health.
- Public Health Campaigns: Raise awareness about the benefits of family planning and the importance of maternal and child health.
8.3. Gender Equality
Promoting gender equality and empowering women to participate fully in society is essential for achieving sustainable development and reducing birth rates.
- Legal Reforms: Ensuring that women have equal rights under the law, including the right to own property, inherit assets, and access credit.
- Social Norms: Challenging traditional social norms that limit women’s opportunities and perpetuate gender inequality.
8.4. Community Engagement
Engaging communities in discussions about family planning, reproductive health, and gender equality is essential for building support for these issues and promoting behavior change.
- Community Health Workers: Play a key role in providing information and services at the grassroots level.
- Religious Leaders: Can influence attitudes and behaviors related to family planning and reproductive health.
8.5. Connect with Experts at HOW.EDU.VN
Do you want to explore how education and empowerment can promote sustainable development in your community or organization? Our PhD experts at HOW.EDU.VN can provide customized analysis and strategic advice to help you design and implement effective programs. Contact us today to learn more.
9. Policy Implications and Government Interventions
Government policies and interventions play a crucial role in influencing birth rates and addressing the challenges associated with population growth and decline.
9.1. Family Planning Policies
Governments can implement policies to promote family planning and provide access to contraception, such as:
- Subsidizing Contraceptives: Reducing the cost of contraceptives to make them more affordable and accessible.
- Expanding Access to Services: Increasing the availability of family planning services through public health clinics, hospitals, and community health centers.
- Training Healthcare Providers: Providing training to healthcare providers to ensure they can provide quality family planning services.
9.2. Parental Leave Policies
Governments can implement parental leave policies to support parents in balancing work and family responsibilities, such as:
- Paid Parental Leave: Providing paid leave to mothers and fathers following the birth or adoption of a child.
- Job Protection: Guaranteeing that parents can return to their jobs after taking parental leave.
- Childcare Subsidies: Providing subsidies to help parents afford childcare.
9.3. Immigration Policies
Governments can use immigration policies to address labor shortages and maintain population size, such as:
- Attracting Skilled Workers: Implementing policies to attract skilled workers from other countries.
- Providing Pathways to Citizenship: Offering pathways to citizenship for immigrants who contribute to the economy and society.
9.4. Incentives for Childbearing
Some governments have implemented policies to incentivize childbearing, such as:
- Cash Payments: Providing cash payments to families for each child they have.
- Tax Breaks: Offering tax breaks to families with children.
- Housing Subsidies: Providing housing subsidies to families with children.
9.5. Addressing Aging Populations
Governments can implement policies to address the challenges associated with aging populations, such as:
- Raising the Retirement Age: Increasing the age at which people can retire and receive social security benefits.
- Encouraging Older Workers to Remain in the Workforce: Implementing policies to encourage older workers to remain in the workforce longer.
- Investing in Geriatric Care: Increasing investment in geriatric care services to meet the needs of older adults.
9.6. Connect with Experts at HOW.EDU.VN
Are you a policymaker looking for expert guidance on how to address the challenges of changing birth rates and population dynamics? Our PhD experts at HOW.EDU.VN can provide customized analysis and strategic advice to help you design and implement effective policies. Contact us today to learn more.
10. Future Trends and Predictions
Looking ahead, several key trends and predictions are shaping the future of birth rates and population growth worldwide.
10.1. Declining Fertility Rates
Fertility rates are expected to continue declining in many parts of the world, particularly in developed countries.
- This trend is driven by factors such as increased access to education and contraception, changing social norms, and economic pressures.
10.2. Aging Populations
Aging populations will continue to be a major challenge for many countries, particularly in Europe and East Asia.
- This trend will lead to labor shortages, increased healthcare costs, and strains on pension systems.
10.3. Urbanization
Urbanization is expected to continue, with more people moving to cities in search of economic opportunities.
- This trend will lead to challenges related to housing, infrastructure, and social services in urban areas.
10.4. Climate Change Impacts
Climate change will have significant impacts on population distribution and migration patterns, as people are displaced by rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and resource scarcity.
10.5. Technological Disruptions
Technological disruptions, such as automation and artificial intelligence, will transform the labor market and create new economic opportunities and challenges.
10.6. Global Health Crises
Global health crises, such as pandemics, can have significant impacts on birth rates, mortality rates, and population growth.
10.7. The Rise of Longevity
Advances in healthcare and technology are leading to increased longevity, with more people living longer and healthier lives.
10.8. Connect with Experts at HOW.EDU.VN
Are you seeking expert insights into the future of birth rates and population growth? Our PhD experts at HOW.EDU.VN can provide customized analysis and strategic advice to help you prepare for the challenges and opportunities of a changing world. Contact us today to learn more.
{width=1200 height=630}FAQ: Understanding Birth Rates and Population Dynamics
Here are some frequently asked questions about birth rates and population dynamics:
Q1: How many babies are born each day worldwide?
A: Approximately 360,000 babies are born each day.
Q2: What is the global fertility rate?
A: The global fertility rate is currently around 2.4 children per woman.
Q3: Which regions have the highest birth rates?
A: Africa generally has the highest birth rates.
Q4: Which regions have the lowest birth rates?
A: Europe typically has the lowest birth rates.
Q5: What factors influence birth rates?
A: Factors include economic development, access to healthcare, cultural norms, and government policies.
Q6: What is the demographic transition model?
A: The demographic transition model explains how population growth changes over time as countries develop.
Q7: How does population growth impact the environment?
A: Population growth can lead to resource depletion, deforestation, pollution, and climate change.
Q8: How does education affect birth rates?
A: Educated women tend to have fewer children and invest more in their children’s health and education.
Q9: What policies can governments implement to influence birth rates?
A: Governments can implement family planning policies, parental leave policies, and immigration policies.
Q10: What are some future trends in birth rates and population growth?
A: Future trends include declining fertility rates, aging populations, and urbanization.
For personalized advice and in-depth analysis on these complex topics, contact our team of PhD experts at HOW.EDU.VN.
Understanding the intricacies of global birth rates and population dynamics is essential for informed decision-making in various sectors. At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with leading PhD experts who provide tailored guidance and insights to address your specific needs. Whether you’re navigating healthcare challenges, exploring economic implications, or seeking sustainable solutions, our team is here to support you.
Don’t navigate these complex issues alone. Contact HOW.EDU.VN today for expert consultation and personalized solutions. Reach us at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States. WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212. Visit our website at how.edu.vn to learn more.

