3D printing costs can vary significantly, influenced by factors like material, labor, and machine operation. At HOW.EDU.VN, we delve into the intricacies of 3D printing expenses to provide a clear understanding of pricing. Whether you’re a hobbyist or a business owner, mastering 3D printing pricing ensures profitability and customer satisfaction. Let’s explore the economics of additive manufacturing, 3D printing service costs, and the overall 3D printing market to help you make informed decisions.
1. Understanding the Core Components of 3D Printing Costs
How much does 3D printing cost? The real cost of 3D printing goes beyond just the price of the filament or resin; it encompasses a variety of factors, including material expenses, labor costs, machine operation, and a necessary margin for potential failures and maintenance. To accurately estimate the price of a 3D print, let’s break down these components in detail.
1.1. Material Costs: Filament, Resin, and More
How much do materials impact 3D printing costs? The type of material you choose for your 3D print significantly influences the overall cost. Different materials have different prices per kilogram or liter, and the amount of material used depends on the size and density of your print.
-
Filament (FDM Printing): For Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) printers, filament cost is a primary factor. Common filaments like PLA (Polylactic Acid) are relatively inexpensive, while specialty filaments such as carbon fiber composites or flexible TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) can be significantly more expensive.
- Example: A 1kg spool of standard PLA might cost $20-$30, while a 750g spool of carbon fiber composite could cost $50-$70.
-
Resin (SLA/DLP Printing): For Stereolithography (SLA) or Digital Light Processing (DLP) printers, resin is the key material. Standard resins are generally cheaper, but specialized resins like those with enhanced toughness, flexibility, or biocompatibility can drive up costs.
- Example: A liter of standard resin might cost $40-$60, while a liter of specialized resin could cost $100 or more.
To calculate material costs, use the following formula:
*Material Cost = (Material Price / Material Weight or Volume) Model Weight or Volume**
For example, if you’re printing with a PLA filament that costs $25 per kg and your model weighs 50g, the material cost would be:
*Material Cost = ($25 / 1000g) 50g = $1.25**
1.2. Labor Costs: Time Spent on Design, Preparation, and Post-Processing
How much do labor costs affect the price of 3D printing? Labor costs are a crucial but often overlooked component of 3D printing expenses. These costs encompass the time spent on designing, preparing, and post-processing the 3D printed object.
- Design Time: Creating a 3D model from scratch can take anywhere from a few hours to several days, depending on the complexity of the design. Hiring a professional designer can add to the cost.
- Print Preparation: Preparing the model for printing involves slicing, setting print parameters, and generating supports. This can take anywhere from a few minutes for simple models to several hours for complex ones.
- Post-Processing: Once the print is complete, post-processing may be required to remove supports, smooth surfaces, or apply finishes. This can include sanding, painting, and assembling multiple parts.
To calculate labor costs, determine your hourly rate and multiply it by the total time spent on each stage of the process.
*Labor Cost = Hourly Rate Total Time Spent**
For instance, if your hourly rate is $20 and you spend 2 hours designing, 30 minutes preparing, and 1 hour post-processing, the labor cost would be:
*Labor Cost = $20 (2 + 0.5 + 1) = $70**
1.3. Machine Operation Costs: Electricity, Maintenance, and Depreciation
How much do machine operation costs contribute to 3D printing expenses? The operational costs of a 3D printer include electricity, maintenance, and depreciation. While electricity costs are typically low, maintenance and depreciation can add up over time.
-
Electricity: 3D printers consume electricity while running. The amount of electricity depends on the printer’s power consumption and the print time.
- Example: A printer that consumes 150W and runs for 10 hours would use 1.5 kWh. At an electricity rate of $0.10 per kWh, the electricity cost would be $0.15.
-
Maintenance: Regular maintenance is essential to keep your 3D printer running smoothly. This includes cleaning, lubricating, and replacing worn parts.
-
Depreciation: 3D printers have a limited lifespan, and their value decreases over time. Accounting for depreciation ensures you recoup the cost of the printer.
To calculate machine operation costs, consider the following factors:
- Electricity Cost = Printer Power Consumption (kW) Print Time (hours) Electricity Rate ($/kWh)
- *Maintenance Cost = Estimated Annual Maintenance Cost / Total Print Hours per Year Print Time (hours)**
- *Depreciation Cost = (Printer Purchase Price / Estimated Lifespan in Hours) Print Time (hours)**
1.4. Margin: Accounting for Failures, Waste, and Profit
How much margin should be added to 3D printing costs? A margin is essential to cover unexpected costs, such as failed prints, material waste, and the need for profit. This percentage is typically added to the total cost of materials, labor, and machine operation.
- Failure Rate: 3D printing isn’t always perfect, and prints can fail due to various reasons, such as incorrect settings, material defects, or mechanical issues.
- Material Waste: Support structures, rafts, and misprints contribute to material waste. Factoring in a percentage for waste ensures you don’t lose money on these inevitable losses.
- Profit Margin: To run a successful 3D printing business, you need to add a profit margin to your costs. This margin should be high enough to cover your expenses and provide a reasonable return on investment.
A typical margin ranges from 20% to 50%, depending on the complexity of the print, the materials used, and your target market.
*Total Cost = (Material Cost + Labor Cost + Machine Operation Costs) (1 + Margin)**
2. Factors Influencing 3D Printing Costs
How do various factors influence the final cost of 3D printing? Several factors can significantly affect the cost of 3D printing, including the size and complexity of the model, the choice of materials, the printing technology used, and the required print quality. Understanding these factors can help you optimize your printing process and reduce costs.
2.1. Model Size and Complexity
How do model size and complexity impact 3D printing costs? The size and complexity of a 3D model directly affect the amount of material and printing time required, both of which significantly influence the overall cost.
- Size: Larger models require more material and longer print times, increasing both material and machine operation costs.
- Complexity: Complex models often require more support structures, which increase material usage and post-processing time. Intricate designs may also require slower print speeds, further extending the printing time.
2.2. Material Selection: Impact on Cost and Performance
How does material selection influence 3D printing costs and performance? The choice of material is a critical factor in 3D printing, affecting both the cost and the performance of the final product.
- Cost: Different materials have different prices per unit. Standard materials like PLA and ABS are typically cheaper than specialized materials like carbon fiber, nylon, or metal.
- Performance: The material’s properties, such as strength, flexibility, heat resistance, and chemical resistance, determine its suitability for specific applications.
2.3. Printing Technology: FDM, SLA, SLS, and More
How does the choice of printing technology affect 3D printing costs? The printing technology used has a significant impact on the cost and quality of 3D printed objects. Each technology has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, making it suitable for different applications.
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): FDM is the most common and affordable 3D printing technology. It uses filaments, which are generally cheaper, but the print quality and precision may not be as high as other methods.
- Stereolithography (SLA) and Digital Light Processing (DLP): SLA and DLP use resins, which can be more expensive than filaments. However, they offer higher resolution and smoother surface finishes, making them ideal for detailed models.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): SLS uses powdered materials, such as nylon or metal, and a laser to fuse them together. It can produce strong, durable parts without the need for support structures but is more expensive than FDM or SLA.
2.4. Print Quality: Resolution, Layer Height, and Infill Density
How does print quality affect the costs associated with 3D printing? The desired print quality, including resolution, layer height, and infill density, affects the printing time and material usage, thereby influencing the overall cost.
- Resolution and Layer Height: Higher resolution and lower layer heights result in smoother surface finishes but require longer print times.
- Infill Density: Infill density refers to the amount of material used inside the model. Higher infill densities increase the strength and weight of the object but also increase material usage and print time.
3. Estimating 3D Printing Costs: Practical Examples
How can you accurately estimate 3D printing costs for different projects? To provide a clear understanding of how to estimate 3D printing costs, let’s look at a few practical examples using different materials, technologies, and complexities.
3.1. Example 1: Printing a Simple PLA Model on an FDM Printer
How much would it cost to print a small PLA model using an FDM printer? Consider a simple model, such as a small figurine, printed using PLA filament on an FDM printer.
- Model: Small Figurine
- Material: PLA Filament
- Printer: FDM Printer
- Material Cost: $1.00 (50g of PLA at $20/kg)
- Labor Cost: $5.00 (15 minutes of prep time + 30 minutes of post-processing at $20/hour)
- Machine Operation Cost: $0.50 (2 hours of printing at 100W and $0.10/kWh)
- Margin (30%): $1.95
- Total Estimated Cost: $8.45
3.2. Example 2: Printing a Detailed Resin Model on an SLA Printer
How much would it cost to print a detailed resin model using an SLA printer? Now, consider a more detailed model, such as a miniature, printed using resin on an SLA printer.
- Model: Detailed Miniature
- Material: Standard Resin
- Printer: SLA Printer
- Material Cost: $5.00 (100ml of resin at $50/liter)
- Labor Cost: $15.00 (30 minutes of prep time + 1 hour of post-processing at $20/hour)
- Machine Operation Cost: $2.00 (4 hours of printing at 50W and $0.10/kWh)
- Margin (40%): $8.80
- Total Estimated Cost: $30.80
3.3. Example 3: Printing a Large and Complex Part with Carbon Fiber on an FDM Printer
How much would it cost to print a large, complex part using carbon fiber on an FDM printer? For a more complex project, consider printing a large, structural part using carbon fiber composite filament on an FDM printer.
- Model: Large Structural Part
- Material: Carbon Fiber Composite Filament
- Printer: FDM Printer
- Material Cost: $60.00 (750g of carbon fiber at $80/kg)
- Labor Cost: $40.00 (1 hour of prep time + 2 hours of post-processing at $20/hour)
- Machine Operation Cost: $10.00 (20 hours of printing at 150W and $0.10/kWh)
- Margin (50%): $55.00
- Total Estimated Cost: $165.00
4. Strategies to Reduce 3D Printing Costs
How can you reduce costs associated with 3D printing without sacrificing quality? There are several strategies you can implement to reduce 3D printing costs, including optimizing designs, choosing cost-effective materials, improving print settings, and minimizing waste.
4.1. Optimizing Designs for Cost-Effectiveness
How can you optimize your designs to reduce 3D printing costs? Optimizing your designs can significantly reduce material usage and printing time, leading to lower costs.
- Hollowing Models: Hollowing out the interior of a model reduces the amount of material needed without compromising its structural integrity.
- Minimizing Support Structures: Designing models with fewer overhangs and angles reduces the need for support structures, which consume extra material and require post-processing.
- Simplifying Geometry: Simplifying complex geometries can reduce printing time and material usage.
4.2. Choosing Cost-Effective Materials
How can selecting cost-effective materials help reduce 3D printing costs? Choosing the right material for your project can balance cost and performance.
- PLA vs. ABS: PLA is generally cheaper and easier to print than ABS. If your application doesn’t require the higher temperature resistance of ABS, PLA is a cost-effective alternative.
- Generic vs. Brand-Name Filaments: Generic filaments are often cheaper than brand-name filaments. While quality may vary, testing different brands can help you find a cost-effective option that meets your needs.
4.3. Improving Print Settings for Efficiency
How can optimizing print settings improve efficiency and reduce 3D printing costs? Adjusting print settings can optimize the printing process, reducing both time and material usage.
- Layer Height: Increasing the layer height can reduce printing time, although it may result in a slightly less smooth surface finish.
- Infill Density: Lowering the infill density reduces material usage. For non-structural parts, a low infill density (e.g., 10-20%) is often sufficient.
- Print Speed: Increasing the print speed can reduce printing time, but it may also affect the print quality. Finding the right balance between speed and quality is essential.
4.4. Minimizing Waste and Failures
How can minimizing waste and failures contribute to reducing overall 3D printing costs? Reducing waste and preventing failures can save both material and time, contributing to lower costs.
- Proper Filament Storage: Storing filaments in a dry environment prevents moisture absorption, which can lead to printing problems and failures.
- Regular Printer Maintenance: Keeping your printer clean and well-maintained ensures smooth operation and reduces the risk of failures.
- Calibrated Print Bed: A properly calibrated print bed ensures good adhesion, preventing warping and print failures.
5. 3D Printing Price Calculators and Tools
How can 3D printing price calculators and tools help estimate costs accurately? Several online tools and calculators can help you estimate 3D printing costs accurately. These tools take into account factors like material usage, printing time, and labor costs, providing a more precise estimate than manual calculations.
5.1. Overview of Popular 3D Printing Price Calculators
How can you leverage popular 3D printing price calculators for accurate cost estimation? Several online calculators are designed to help estimate 3D printing costs accurately. These tools often allow you to input various parameters such as material type, print time, and labor rates. Some popular options include:
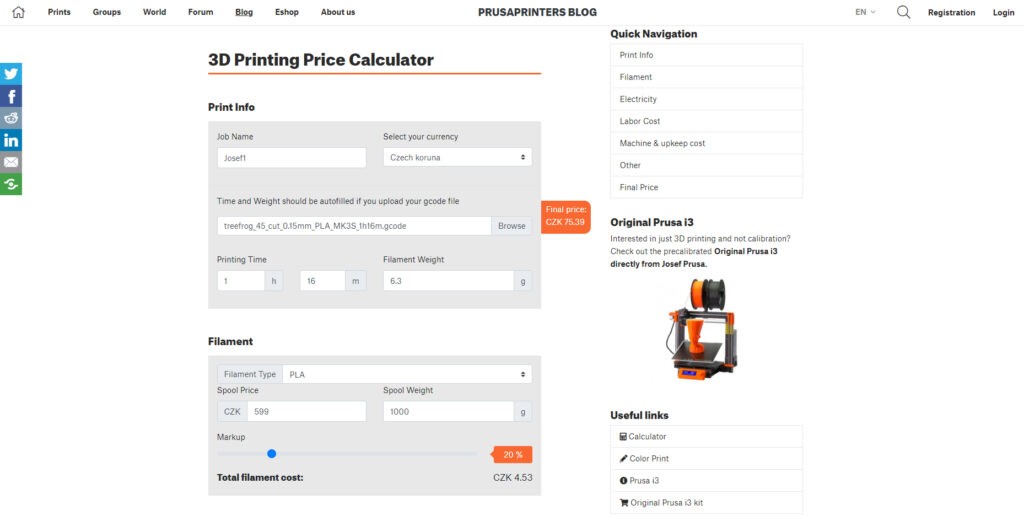
- Prusa 3D Printing Price Calculator: A comprehensive calculator that allows you to input material costs, labor rates, and machine operation costs. It also supports importing G-codes to estimate print time and material usage automatically.
- Treatstock 3D Printing Cost Calculator: A user-friendly calculator that provides a quick estimate of printing costs based on material, volume, and print time.
- 3DCompare Price Comparison Tool: This tool not only calculates the estimated cost but also compares prices from different 3D printing services.
5.2. Using Software to Estimate Material Usage and Print Time
How can software tools help in estimating material usage and print time for 3D printing projects? Many slicing software programs, such as Cura, Simplify3D, and PrusaSlicer, provide detailed information about material usage and print time. These tools can help you optimize your print settings and estimate costs more accurately.
- Material Usage: Slicing software estimates the amount of material required for a print based on the model’s volume, infill density, and support structures.
- Print Time: Slicing software calculates the estimated print time based on the model’s complexity, layer height, and print speed.
6. 3D Printing Services: Cost Considerations
How do costs vary when using 3D printing services compared to in-house printing? Outsourcing your 3D printing needs to a service provider can be a convenient option, but it’s essential to understand the cost considerations.
6.1. Factors Affecting the Cost of 3D Printing Services
How do different factors influence the cost of using 3D printing services? Several factors can affect the cost of 3D printing services, including:
- Service Provider: Different service providers have different pricing structures. Some may charge based on volume, while others charge based on print time or material usage.
- Material Selection: The cost of materials can vary significantly between service providers.
- Print Quality: Higher print quality and tighter tolerances may come at a premium.
- Turnaround Time: Faster turnaround times often result in higher costs.
- Post-Processing Services: Additional services like support removal, sanding, painting, and assembly can add to the overall cost.
6.2. Comparing In-House vs. Outsourced 3D Printing Costs
How do the costs of in-house 3D printing compare with outsourcing to a 3D printing service? Deciding whether to invest in your own 3D printer or outsource to a service provider depends on your specific needs and budget. Here’s a comparison of the costs involved:
- In-House 3D Printing:
- Initial Investment: Purchasing a 3D printer, software, and tools can be a significant upfront cost.
- Operating Costs: Ongoing costs include materials, electricity, maintenance, and labor.
- Expertise: Requires skilled personnel to operate and maintain the printer.
- Outsourced 3D Printing:
- No Initial Investment: No need to purchase a printer or software.
- Variable Costs: Costs are incurred only when you need to print something.
- Access to Expertise: Access to a team of experts who can handle complex projects.
7. The Future of 3D Printing Costs
How is the cost of 3D printing expected to evolve in the future? The 3D printing industry is constantly evolving, and costs are expected to decrease as technology advances and materials become more affordable.
7.1. Technological Advancements and Cost Reduction
How will technological advancements drive down the cost of 3D printing in the future? Advancements in 3D printing technology are expected to drive down costs in several ways:
- Faster Printing Speeds: New technologies like Continuous Liquid Interface Production (CLIP) and Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) offer significantly faster printing speeds, reducing machine operation costs.
- More Efficient Material Usage: Improved algorithms and print settings can optimize material usage, reducing waste and lowering material costs.
- Lower Printer Prices: As 3D printing technology becomes more mainstream, the prices of 3D printers are expected to decrease.
7.2. Trends in Material Costs and Availability
How are trends in material costs and availability expected to shape the future of 3D printing expenses? Material costs are also expected to decrease as production volumes increase and new materials become available.
- Increased Production Volumes: As the demand for 3D printing materials grows, manufacturers will be able to produce them at a lower cost per unit.
- New Materials: The development of new materials with improved properties and lower costs will expand the range of applications for 3D printing.
- Recycled Materials: The use of recycled materials can reduce material costs and promote sustainability.
8. Consulting with Experts at HOW.EDU.VN
Are you facing challenges in estimating 3D printing costs or optimizing your 3D printing projects? At HOW.EDU.VN, our team of expert PhDs is ready to provide personalized guidance and solutions.
8.1. Benefits of Consulting with Our PhD Experts
What are the advantages of seeking advice from the PhD experts at HOW.EDU.VN? Consulting with our PhD experts at HOW.EDU.VN offers numerous benefits:
- Expert Knowledge: Gain insights from professionals with years of experience in 3D printing technologies and cost optimization strategies.
- Personalized Advice: Receive tailored recommendations based on your specific needs and project requirements.
- Cost-Effective Solutions: Identify strategies to reduce costs without compromising the quality of your 3D printed products.
- Access to Cutting-Edge Information: Stay updated on the latest trends and advancements in 3D printing technology and materials.
8.2. How HOW.EDU.VN Can Help You Optimize Your 3D Printing Projects
How can HOW.EDU.VN assist in optimizing your 3D printing projects for maximum efficiency and cost-effectiveness? HOW.EDU.VN can assist you in optimizing your 3D printing projects by:
- Cost Analysis: Providing a detailed breakdown of your current 3D printing costs and identifying areas for improvement.
- Design Optimization: Recommending design modifications to reduce material usage and printing time.
- Material Selection: Helping you choose the most cost-effective materials for your specific application.
- Print Setting Optimization: Adjusting print settings to improve efficiency and reduce waste.
- Troubleshooting: Identifying and resolving any issues that may be causing print failures or quality problems.
Navigating the world of 3D printing costs can be complex, but with the right knowledge and strategies, you can optimize your projects for both quality and affordability. Whether you’re a hobbyist or a business owner, understanding the factors that influence 3D printing expenses will help you make informed decisions and achieve your desired outcomes.
Ready to take your 3D printing projects to the next level? Contact our team of expert PhDs at HOW.EDU.VN for personalized advice and solutions. We’re here to help you optimize your designs, choose the right materials, and implement cost-effective strategies to achieve your 3D printing goals.
Contact us today:
- Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
- Website: HOW.EDU.VN
9. FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About 3D Printing Costs
9.1. What is the average cost of a 3D printer?
The average cost of a 3D printer can vary widely depending on the type and capabilities of the printer. Entry-level FDM printers can cost as little as $200-$500, while professional-grade FDM printers can range from $2,000 to $10,000 or more. SLA printers typically start around $500-$1,000, while high-end industrial printers can cost tens of thousands of dollars.
9.2. How much does it cost to 3D print a small object?
The cost to 3D print a small object can range from a few dollars to several dollars, depending on the material used, the size and complexity of the object, and the printing technology. A small PLA object printed on an FDM printer might cost $1-$5, while a more detailed resin object printed on an SLA printer could cost $5-$15.
9.3. Is 3D printing cheaper than traditional manufacturing?
3D printing can be cheaper than traditional manufacturing for small production runs or prototypes, especially for complex geometries. However, for large-scale production, traditional manufacturing methods like injection molding are often more cost-effective.
9.4. What are the main factors that affect 3D printing costs?
The main factors that affect 3D printing costs include material costs, labor costs, machine operation costs, and margin. These factors can be influenced by the size and complexity of the model, the choice of materials, the printing technology used, and the desired print quality.
9.5. How can I reduce the cost of 3D printing?
You can reduce the cost of 3D printing by optimizing designs for cost-effectiveness, choosing cost-effective materials, improving print settings for efficiency, and minimizing waste and failures.
9.6. What is the difference between FDM and SLA printing costs?
FDM printing typically has lower material costs since filaments are generally cheaper than resins. However, SLA printing can offer higher resolution and smoother surface finishes, which may justify the higher material costs for certain applications.
9.7. How do I calculate the material cost for a 3D print?
To calculate the material cost for a 3D print, use the following formula: Material Cost = (Material Price / Material Weight or Volume) * Model Weight or Volume.
9.8. What is infill density, and how does it affect the cost?
Infill density refers to the amount of material used inside the model. Higher infill densities increase the strength and weight of the object but also increase material usage and print time, thereby increasing the cost.
9.9. How much should I charge for 3D printing services?
The amount you should charge for 3D printing services depends on your costs, desired profit margin, and the pricing of your competitors. It’s essential to calculate your costs accurately and factor in a reasonable profit margin to run a successful 3D printing business.
9.10. Where can I find expert advice on 3D printing costs?
You can find expert advice on 3D printing costs at how.edu.vn, where our team of PhD experts can provide personalized guidance and solutions to optimize your 3D printing projects.