Are you concerned about the cost of brake replacement and ensuring your vehicle’s safety? The price of replacing your vehicle’s brakes can vary widely, but HOW.EDU.VN connects you with expert mechanics and automotive engineers who can help you understand brake replacement costs, maintenance, and safety. Learn how to budget for brake service and replacement, and how to maintain your brakes for optimal performance and longevity, ensuring reliable stopping power and vehicle safety.
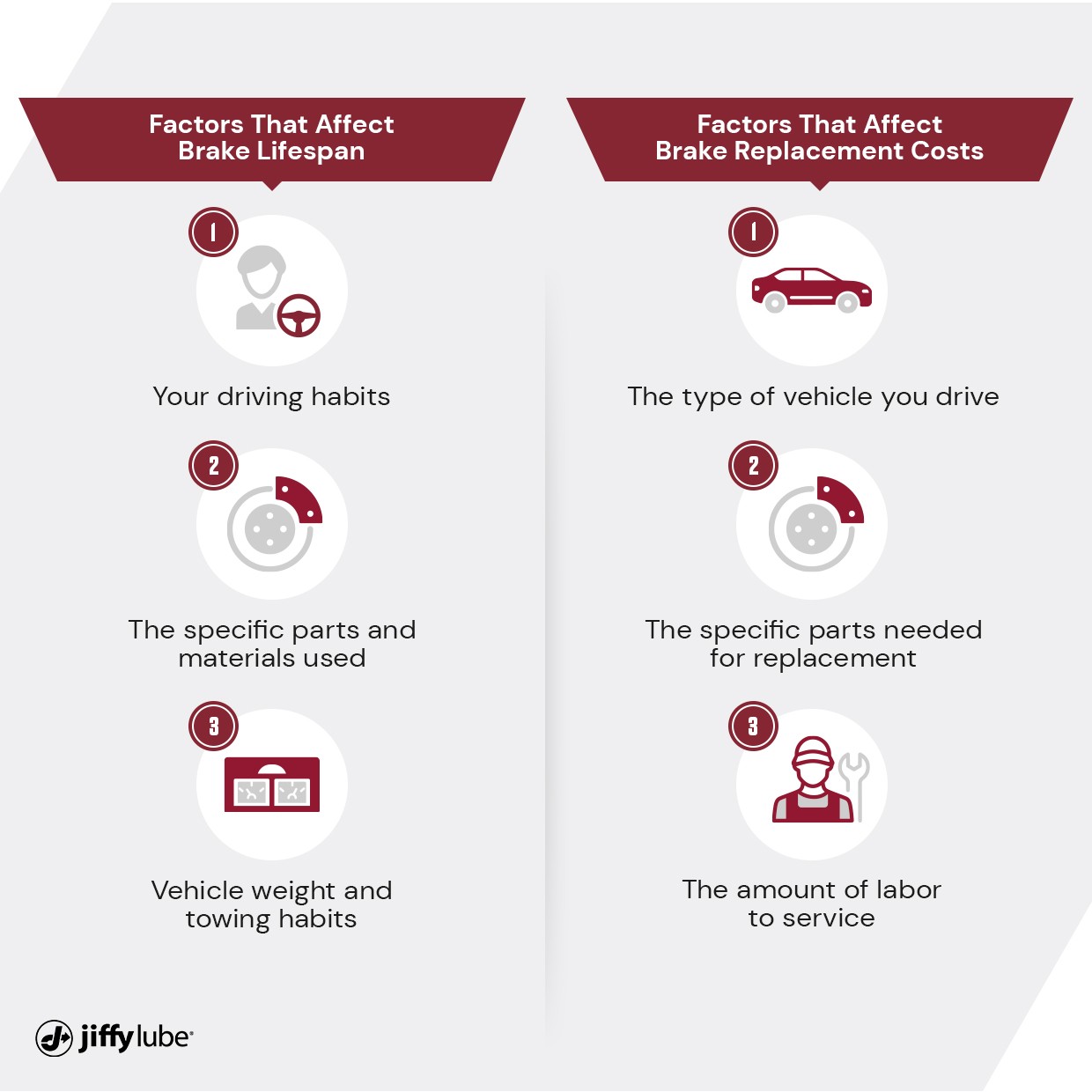
1. Factors Influencing the Cost of Brake Replacement
1.1. Driving Conditions and Brake Wear
Where and how you drive significantly impacts brake wear. Urban environments with frequent stop-and-go traffic and mountainous regions requiring constant brake use on descents can dramatically shorten the life of your brakes. According to a study by the University of California, Berkeley, aggressive driving habits can increase brake wear by up to 60%.
1.2. Quality and Type of Brake Materials
The type of materials used in your brake pads, rotors, and calipers affects their durability and cost. High-performance or severe-duty brake pads made from high-carbon compounds are more expensive but can last longer than standard semi-metallic pads.
- Semi-Metallic Brake Pads: These are a common choice, offering a good balance of performance and cost.
- Ceramic Brake Pads: Known for quieter operation and less dust, but may not offer the same level of long-term braking performance as semi-metallic options.
- Organic Brake Pads: Typically the least expensive, but may wear out faster.
Always replace brake pads with those that meet or exceed the manufacturer’s recommendations to ensure safety and performance.
2. The Benefits of Regular Brake Maintenance and Replacement
2.1. Minimizing Extensive Repairs
Regular brake maintenance is crucial. Neglecting brake service can lead to a metal-to-metal situation, where the brake pads wear through their friction material. This not only compromises safety but also causes significant damage to rotors and drums, leading to costly repairs.
2.2. Extending Caliper Life
Replacing brake fluid regularly can significantly extend the life of your calipers. Check your vehicle’s owner’s manual for specific recommendations on how often to replace brake fluid. If your manual doesn’t include this information, consult a trained technician at HOW.EDU.VN for expert advice.
2.3. Preventing Corrosion in the Hydraulic System
Contaminated brake fluid can cause corrosion in the brake hydraulic system, especially in vehicles with anti-lock brakes (ABS). Regularly exchanging the fluid in your brake hydraulic system helps prevent this issue. A study by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) found that vehicles with regular brake fluid exchanges had 30% fewer brake-related accidents.
2.4. Ensuring Road Safety
A well-maintained brake system is essential for safe vehicle control and operation under various conditions. If you suspect any brake issues, get your system checked immediately, as it’s your vehicle’s most critical safety feature.
3. Understanding Brake Replacement Costs
3.1. Factors Affecting the Price
There is no standard cost for brake replacement. Prices vary based on the repair center’s hourly rate and the manufacturer’s pricing of parts. However, understanding these factors can help you plan your budget.
3.2. Key Components and Their Costs
- Rotors: Replacing rotors when replacing brake pads is crucial for optimizing braking performance and ensuring safety. New pads on worn rotors can cause vibration and reduce braking efficiency. Aftermarket rotors typically cost between $30 and $75 each.
- Labor: Labor costs for brake service can range from $90 to $200 per hour. Complete brake service generally costs approximately $200 to $500 per axle at a professional repair center.
- Calipers: Calipers are often the most expensive part to service. A single caliper can cost up to $130, and some can exceed this price.
- Complete Brake Repair: A comprehensive brake repair, including pads, rotors, and calipers, typically averages between $200 and $800, depending on the vehicle and parts used.
4. How to Get the Best Price on Brake Service
4.1. Request Multiple Quotes
To ensure you get the best value, request quotes from multiple service providers. An accurate quote requires more than just asking, “How much are new brakes?” Technicians will ask specific questions about your vehicle and driving habits.
4.2. Questions Technicians May Ask
- Vehicle Type: Parts for European vehicles (BMW, Mercedes, Audi, Jaguar, etc.) typically cost more than those for domestic or Japanese vehicles. European systems may also require more service time, increasing labor costs.
- Vehicle Model: The make and model of your vehicle affect brake costs. For instance, a Chevy 3500 Diesel truck will have more expensive brakes than a Ford Fiesta. Many 4WD and AWD cars require more complex and time-consuming rotor replacement.
- Driving Style: If you frequently tow or engage in severe-duty work, you will need specific brake pads designed for heavy use.
- Material Preference: Brake pads come in ceramic, semi-metallic, and organic materials, each with different performance characteristics and prices.
- Brand Preference: Choosing aftermarket, off-brand, or OEM (original equipment manufacturer) brake pads will also impact the price estimate.
5. Brake Pad Materials: Choosing the Right Option
5.1. Semi-Metallic Brake Pads
Semi-metallic brake pads are a popular choice due to their balance of performance and cost. They contain a mix of metal fibers, fillers, and friction modifiers, providing good stopping power and heat dissipation. However, they can be noisier and produce more brake dust compared to other types.
5.2. Ceramic Brake Pads
Ceramic brake pads are made from ceramic fibers, fillers, and bonding agents. They offer quieter operation, less brake dust, and consistent performance over a wide range of temperatures. However, they may be more expensive and may not provide the same level of stopping power as semi-metallic pads in extreme conditions.
5.3. Organic Brake Pads
Organic brake pads, also known as non-asbestos organic (NAO) pads, are made from organic materials like rubber, carbon, and fiberglass. They are typically the least expensive option and produce less noise. However, they tend to wear out faster and may not offer the same level of braking performance as semi-metallic or ceramic pads.
5.4. Choosing the Right Brake Pad
The best type of brake pad for your vehicle depends on your driving habits, vehicle type, and budget. Consider the following factors:
- Driving Conditions: If you drive in stop-and-go traffic or frequently tow heavy loads, semi-metallic or ceramic pads may be a better choice.
- Noise and Dust: If you prioritize quiet operation and minimal brake dust, ceramic pads are a good option.
- Budget: Organic pads are the most affordable, but may require more frequent replacement.
6. The Importance of Brake Fluid
6.1. Understanding Brake Fluid
Brake fluid is a hydraulic fluid that transmits the force from your foot on the brake pedal to the brake calipers, which then apply pressure to the brake pads to stop the vehicle. Over time, brake fluid can become contaminated with moisture, dirt, and debris, which can reduce its effectiveness and damage the brake system.
6.2. Why Brake Fluid Replacement is Crucial
- Prevents Corrosion: Contaminated brake fluid can cause corrosion in the brake lines, calipers, and master cylinder, leading to costly repairs.
- Maintains Performance: Fresh brake fluid has a higher boiling point, which prevents brake fade, a dangerous condition where the brakes lose effectiveness due to overheating.
- Ensures Safety: Regular brake fluid replacement ensures that the brake system operates reliably and provides optimal stopping power.
6.3. How Often to Replace Brake Fluid
Most manufacturers recommend replacing brake fluid every two to three years, or every 30,000 miles. However, the frequency may vary depending on driving conditions and vehicle type. Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual or a qualified technician for specific recommendations.
7. The Role of Calipers in Brake Function
7.1. Understanding Calipers
Brake calipers are essential components of the braking system. They house the brake pads and use hydraulic pressure to clamp the pads against the rotors, creating friction that slows or stops the vehicle. Calipers can be either fixed or floating.
7.2. Signs of Caliper Problems
- Pulling to One Side: If the vehicle pulls to one side during braking, it could indicate a stuck or seized caliper.
- Uneven Brake Pad Wear: Uneven wear on the brake pads can be a sign of a malfunctioning caliper.
- Leaking Brake Fluid: Leaks around the caliper indicate a damaged seal or piston.
- Noisy Brakes: Unusual noises like squealing or grinding can be a sign of caliper issues.
7.3. Caliper Maintenance and Replacement
Regular inspection and maintenance of the calipers are crucial for ensuring proper brake function. If you notice any signs of caliper problems, have them inspected by a qualified technician. Caliper replacement may be necessary if they are damaged, corroded, or malfunctioning.
8. DIY Brake Service vs. Professional Service
8.1. DIY Brake Service
Performing brake service yourself can save money, but it requires mechanical knowledge, experience, and the right tools. It’s essential to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and take all necessary safety precautions.
8.2. Professional Brake Service
Professional brake service offers several advantages:
- Expertise: Trained technicians have the knowledge and experience to diagnose and repair brake problems accurately.
- Proper Tools: Professional repair shops have the necessary tools and equipment for brake service.
- Warranty: Many repair shops offer warranties on their work, providing peace of mind.
- Safety: Professional brake service ensures that the job is done correctly, maintaining the vehicle’s safety.
8.3. Deciding on DIY or Professional Service
If you have the mechanical skills and experience, DIY brake service can be a cost-effective option. However, if you are not comfortable with the task or lack the necessary tools, it’s best to seek professional service to ensure safety and reliability.
9. Safety First: Prioritizing Brake Maintenance
9.1. Brake System as a Safety Feature
Your brakes are one of your car’s most critical safety features. They need to be in good working order to ensure your safety and the safety of others on the road.
9.2. Why Regular Checks Are Essential
Regular brake checks can identify potential issues early, preventing costly repairs and ensuring optimal braking performance. Schedule regular inspections with a trusted mechanic at HOW.EDU.VN to maintain your brake system.
10. What to Expect During a Brake Service Visit
10.1. Questions About Your Driving Style
Technicians may ask about your driving style to understand the wear and tear on your brakes.
10.2. Visual Inspection
A complete visual inspection of your brake system will be performed to identify any potential issues.
10.3. Thorough Brake Inspection
A more thorough inspection may be performed during a tire rotation to check brake pad thickness and rotor condition.
10.4. Brake Fluid Testing
Brake fluid will be tested for moisture content and additive package strength to ensure it meets specifications.
10.5. Service Recommendations
Service recommendations will be presented, and no work will be performed without your approval.
10.6. Vehicle Testing
Your vehicle will be driven before and after the brake service to ensure it operates as intended.
11. Understanding Common Brake Problems
11.1. Squealing Brakes
Squealing brakes are a common issue that can be caused by worn brake pads, glazed rotors, or loose brake hardware. While some squealing is normal, excessive or persistent squealing should be inspected by a technician.
11.2. Grinding Brakes
Grinding brakes indicate that the brake pads have worn down to the metal backing plates, which are rubbing against the rotors. This can cause significant damage to the rotors and should be addressed immediately.
11.3. Pulsating Brakes
Pulsating brakes, also known as brake pedal pulsation, can be caused by warped rotors or uneven brake pad wear. This can be felt as a vibration in the brake pedal or steering wheel during braking.
11.4. Soft or Spongy Brake Pedal
A soft or spongy brake pedal indicates air in the brake lines or a leak in the hydraulic system. This can reduce braking performance and should be inspected by a technician.
12. How to Properly Use Your Brakes
12.1. Avoiding Hard Braking
Avoid hard braking whenever possible, as it can cause excessive wear on the brake pads and rotors. Instead, try to anticipate traffic conditions and brake gradually.
12.2. Using Engine Braking
Using engine braking can help reduce wear on the brakes, especially when descending hills. Downshift to a lower gear to use the engine’s resistance to slow the vehicle.
12.3. Maintaining a Safe Following Distance
Maintaining a safe following distance provides more time to react to changing traffic conditions and reduces the need for sudden braking.
13. Advanced Brake Technologies
13.1. Anti-Lock Braking System (ABS)
ABS prevents the wheels from locking up during braking, allowing the driver to maintain steering control. ABS is a standard feature on most modern vehicles.
13.2. Electronic Stability Control (ESC)
ESC helps prevent skidding and loss of control by automatically applying brakes to individual wheels. ESC is an advanced safety feature that can improve vehicle stability and handling.
13.3. Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB)
AEB automatically applies the brakes if it detects an imminent collision. AEB is a driver-assistance technology that can help prevent or mitigate accidents.
14. Choosing a Brake Service Provider
14.1. Reputation and Reviews
Check online reviews and ask for recommendations from friends and family to find a reputable brake service provider.
14.2. Certifications and Training
Ensure that the technicians are certified and trained to perform brake service on your vehicle.
14.3. Warranty
Choose a brake service provider that offers a warranty on their work to provide peace of mind.
14.4. Transparency and Communication
Look for a brake service provider that is transparent about their pricing and communicates clearly about the work that needs to be done.
15. Extending the Life of Your Brakes: Expert Tips
15.1. Regular Inspections
Schedule regular brake inspections to identify potential issues early and prevent costly repairs.
15.2. Proper Driving Habits
Avoid aggressive driving habits like hard braking and rapid acceleration, which can cause excessive wear on the brakes.
15.3. Brake Fluid Maintenance
Replace brake fluid regularly to prevent corrosion and maintain optimal braking performance.
15.4. Quality Brake Components
Use high-quality brake pads, rotors, and calipers that meet or exceed the manufacturer’s recommendations.
16. Addressing Emergency Brake Situations
16.1. Understanding the Emergency Brake
The emergency brake, also known as the parking brake, is a secondary braking system that can be used in emergency situations or when parking on a hill.
16.2. How to Use the Emergency Brake Properly
To use the emergency brake, firmly apply the brake pedal and then engage the emergency brake lever or pedal. Release the brake pedal and ensure that the vehicle is securely held in place.
16.3. When to Use the Emergency Brake
Use the emergency brake when parking on a hill, in emergency situations when the primary brakes fail, or when the vehicle needs to be immobilized.
17. The Impact of Vehicle Weight on Brake Wear
17.1. Understanding the Relationship
The weight of the vehicle directly impacts brake wear. Heavier vehicles require more force to stop, which puts more stress on the brakes and causes them to wear out faster.
17.2. Tips for Reducing Brake Wear on Heavy Vehicles
- Maintain a Safe Following Distance: Allow more time to react to changing traffic conditions and reduce the need for sudden braking.
- Use Engine Braking: Downshift to a lower gear to use the engine’s resistance to slow the vehicle, especially when descending hills.
- Regular Brake Inspections: Schedule regular brake inspections to identify potential issues early and prevent costly repairs.
18. How Brakes Affect Fuel Efficiency
18.1. Understanding the Connection
Brakes can affect fuel efficiency. If the brakes are dragging or not releasing properly, it can create additional resistance, which reduces fuel economy.
18.2. Tips for Improving Fuel Efficiency with Brakes
- Ensure Proper Brake Function: Make sure that the brakes are releasing properly and not dragging.
- Regular Brake Maintenance: Schedule regular brake maintenance to keep the brake system in good condition.
- Avoid Aggressive Driving: Avoid aggressive driving habits like hard braking and rapid acceleration, which can reduce fuel economy.
19. The Future of Brake Technology
19.1. Regenerative Braking
Regenerative braking captures the energy generated during braking and uses it to recharge the vehicle’s battery. This technology is commonly used in hybrid and electric vehicles.
19.2. Brake-by-Wire Systems
Brake-by-wire systems use electronic sensors and actuators to control the brakes, eliminating the need for a direct mechanical connection between the brake pedal and the brakes. This technology can improve braking performance and safety.
19.3. Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)
ADAS technologies like automatic emergency braking (AEB) and adaptive cruise control (ACC) rely on advanced brake systems to provide enhanced safety and convenience.
20. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Brake Service
20.1. How often should I replace my brake pads?
Brake pad replacement frequency depends on driving habits and brake pad material. Generally, replace them every 25,000 to 70,000 miles.
20.2. How much does it cost to replace brake pads and rotors?
The cost varies by vehicle and parts quality, typically ranging from $200 to $800 per axle.
20.3. What are the signs that I need new brakes?
Signs include squealing, grinding, pulsating pedal, and longer stopping distances.
20.4. Can I replace my brakes myself?
Yes, if you have the skills and tools. Otherwise, professional service is recommended.
20.5. How important is brake fluid replacement?
Very important to prevent corrosion and maintain braking performance. Replace every two to three years.
20.6. What are the different types of brake pads?
Common types are semi-metallic, ceramic, and organic, each with different performance and cost characteristics.
20.7. How do I choose the right brake pads for my vehicle?
Consider driving habits, vehicle type, and budget. Consult a technician for the best recommendation.
20.8. What is the role of brake calipers?
Calipers house the brake pads and apply pressure to the rotors to stop the vehicle.
20.9. How can I extend the life of my brakes?
Avoid aggressive driving, maintain brake fluid, and schedule regular inspections.
20.10. What is ABS and how does it work?
ABS prevents wheel lockup during braking, allowing you to maintain steering control.
Your safety depends on well-maintained brakes. Trust the experts at HOW.EDU.VN to guide you through brake maintenance, repair options, and understanding costs. Our team of experienced mechanics and automotive engineers offers tailored advice to keep your vehicle safe and reliable. Whether you’re curious about the cost of brake replacement or need help troubleshooting brake problems, our PhDs are ready to assist.
Ready to ensure your vehicle’s safety with expert brake service advice? Contact HOW.EDU.VN today!
Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
Website: HOW.EDU.VN
Let how.edu.vn connect you with the expertise you need to make informed decisions about your vehicle’s brake maintenance and repair.