Are you wondering, How Much Are Private Schools and whether this educational path is financially feasible for your family? At HOW.EDU.VN, we understand that navigating the costs of private education can be overwhelming. This guide offers a detailed breakdown of private school expenses, providing clarity and expert insights to help you make informed decisions about your child’s education. We’ll explore tuition costs, financial aid opportunities, and the value of investing in a private school education.
1. Understanding the Average Cost of Private School Education
The cost of private school education can vary significantly based on several factors, including the type of school (day or boarding), its location, and the grade level of your child. It’s essential to consider these variables when estimating the overall financial commitment.
1.1. National Averages for Private School Tuition
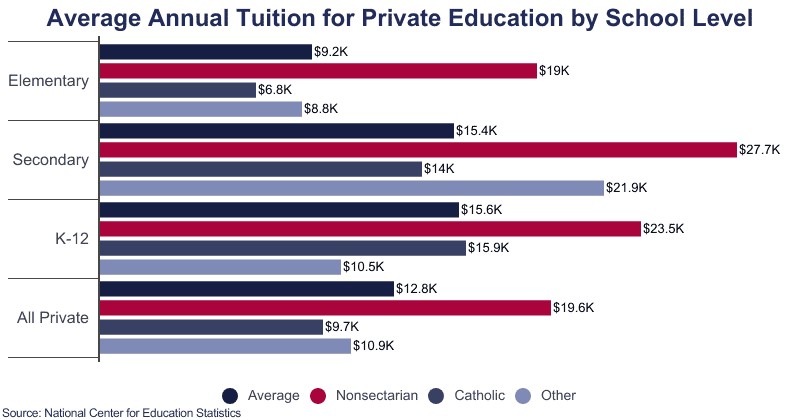
Nationwide, the average annual tuition for private schools in 2021 was $12,790, encompassing both elementary and secondary institutions. However, this figure provides only a baseline, as costs can fluctuate widely. According to Education Data Initiative’s 2021 report, the average annual tuition at a private high school is $15,344, while private university tuition averages $35,248 annually. For families considering private education from kindergarten through postsecondary studies, the total estimated cost can reach $307,262.
1.2. Day School vs. Boarding School Costs
One of the most significant factors influencing private school costs is whether the school is a day school or a boarding school. Day schools, similar to public schools, offer daytime classes without accommodation. Boarding schools, on the other hand, provide room and board in addition to classes, leading to higher tuition rates.
- Private Day Schools: According to the National Association of Independent Schools (NAIS), the average tuition at private day schools is $30,692. Median tuition for first graders is approximately $26,800, while middle school tuition averages $30,535. High school students can expect to pay around $35,105 annually.
- Private Boarding Schools: Boarding schools are generally more expensive due to the inclusion of accommodation and meals. The average annual tuition at a 5-day boarding school is $55,425, while a 7-day boarding school averages $69,150. Some of the top boarding schools can cost upwards of $60,000 per year.
1.3. Factors Influencing Tuition Costs
Several factors influence the tuition costs of private schools:
- Location: Private schools in certain states or regions tend to have higher tuition rates. For example, schools in New England and the East Coast are generally more expensive than those in the Midwest or South.
- School Type: Independent, religious, and specialized schools may have varying tuition costs depending on their resources, facilities, and programs.
- Grade Level: Tuition often increases as students advance to higher grade levels, reflecting the more complex curriculum and resources required.
- Extracurricular Activities: Additional costs may arise from extracurricular activities, sports, clubs, and other programs offered by the school.
2. State-by-State Breakdown of Private School Costs
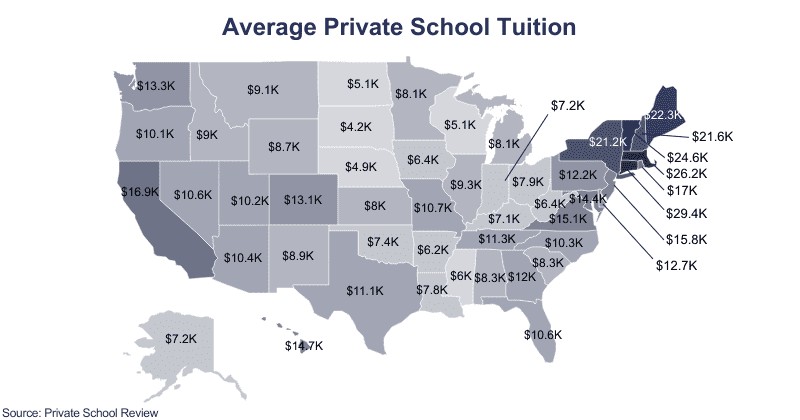
Private school costs vary considerably from state to state. Certain regions, particularly those in the Northeast, tend to have the highest private school tuition rates. This section provides a detailed overview of the average costs in each state, helping you understand the financial landscape in your area.
2.1. States with the Highest Private School Tuition
The most expensive private schools are predominantly located in the New England region. Connecticut leads the nation with the highest average tuition, followed by the District of Columbia and Massachusetts.
| State | Elementary Tuition | Secondary Tuition | Average Tuition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Connecticut | $23,900 | $42,032 | $29,433 |
| District Of Columbia | $29,281 | $34,064 | $27,474 |
| Massachusetts | $23,202 | $38,658 | $26,203 |
| Vermont | $19,348 | $33,421 | $24,628 |
| Maine | $14,573 | $29,502 | $22,341 |
| New Hampshire | $13,613 | $31,159 | $21,604 |
| New York | $21,415 | $27,322 | $21,158 |
| Rhode Island | $14,319 | $29,277 | $16,999 |
| California | $16,066 | $22,153 | $16,884 |

2.2. States with the Most Affordable Private School Tuition
Conversely, several states offer more affordable private education options. These are typically located in the Midwest and South. South Dakota consistently ranks as one of the most affordable states for private schooling.
| State | Elementary Tuition | Secondary Tuition | Average Tuition |
|---|---|---|---|
| South Dakota | $4,125 | $6,156 | $4,212 |
| Nebraska | $4,474 | $9,043 | $4,896 |
| North Dakota | $4,142 | n/a | $5,050 |
| Wisconsin | $4,483 | $9,443 | $5,058 |
| Mississippi | $5,894 | $6,458 | $5,994 |
| Arkansas | $6,187 | $7,057 | $6,228 |
| Iowa | $5,810 | $10,792 | $6,363 |
| West Virginia | $6,621 | $6,730 | $6,416 |
| Kentucky | $6,863 | $7,880 | $7,129 |
| Indiana | $6,098 | $9,216 | $7,161 |
2.3. Regional Differences in Tuition Costs
Analyzing the cost of private school by region provides a more nuanced understanding. The Northeast generally has the highest costs due to a concentration of prestigious and well-funded institutions. The South and Midwest offer more affordable options, while the West Coast, particularly California, can be relatively expensive as well.
Understanding these regional differences can help you narrow down your search and plan your budget more effectively.
3. Detailed Costs for Specific States
To give you a clearer picture, let’s delve into the costs for private schools in a few specific states.
3.1. Private School Costs in California
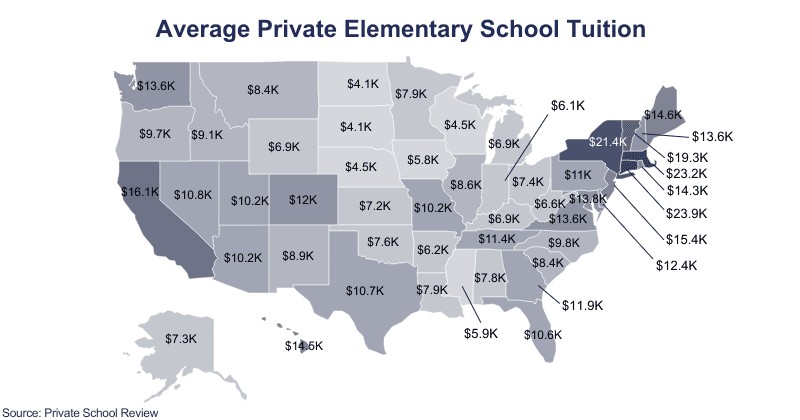
California is known for its high cost of living, and private school tuition is no exception. The average tuition among all K-12 private schools in California is $16,884. Elementary schools average around $16,066, while secondary schools cost about $22,153 annually.
3.2. Private School Costs in New York
New York also has some of the highest private school tuition rates in the country. The average tuition among all K-12 private schools is $21,158, with elementary schools costing around $21,415 and secondary schools averaging $27,322 per year.
3.3. Private School Costs in Texas
In contrast to California and New York, Texas offers more affordable private education options. The average tuition among all K-12 private schools in Texas is $11,050. Elementary schools average around $10,729, while secondary schools cost about $12,161 annually.
3.4. Private School Costs in Florida
Florida’s private schools are moderately priced compared to the national average. The average tuition across all K-12 private schools in Florida is approximately $10,617. Private elementary schools average around $10,592, while private secondary schools are slightly higher, averaging $11,829 per year.
3.5. Private School Costs in Illinois
Illinois has a diverse range of private schools with varying tuition rates. The average tuition among all K-12 private schools in Illinois is $9,287. Private elementary schools are more affordable, averaging $8,639, while private secondary schools are pricier, costing around $13,923 annually.
4. Additional Expenses Beyond Tuition
While tuition is the primary cost of private school education, it’s essential to consider other expenses that can add to the financial burden.
4.1. Application Fees and Enrollment Deposits
Most private schools charge an application fee, which can range from $50 to $150. Once accepted, a non-refundable enrollment deposit is usually required to secure your child’s spot. This deposit can range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars.
4.2. Books, Supplies, and Uniforms
Textbooks and school supplies can be a significant expense, particularly in higher grades. Depending on the school, the cost for books and supplies can range from $200 to $1,000 per year. Many private schools also require students to wear uniforms, which can cost between $100 and $500 per set.
4.3. Extracurricular Activities and Field Trips
Participation in sports, clubs, and other extracurricular activities often comes with additional fees. These can include equipment costs, travel expenses, and membership dues. Field trips can also add to the overall cost, with expenses for transportation, accommodation, and entry fees.
4.4. Technology Fees and Other Charges
Some private schools charge technology fees to cover the cost of computers, software, and internet access. These fees can range from $100 to $500 per year. Other potential charges may include insurance fees, lab fees, and graduation fees.
5. Financial Aid and Scholarship Opportunities
Despite the high costs of private education, financial aid and scholarship opportunities are available to help make it more accessible. Many private schools offer need-based financial aid, while others provide merit-based scholarships.
5.1. Need-Based Financial Aid
Need-based financial aid is awarded based on a family’s financial situation. To apply, families typically need to complete a financial aid application, such as the School and Student Services (SSS) form or the Financial Aid for School Tuition (FAST) application. These applications assess a family’s income, assets, and expenses to determine the amount of financial aid they need.
5.2. Merit-Based Scholarships
Merit-based scholarships are awarded based on a student’s academic achievements, talents, or skills. These scholarships may be offered by the school itself or by external organizations. To apply, students typically need to submit transcripts, test scores, essays, and letters of recommendation.
5.3. External Scholarship Programs
Numerous external organizations offer scholarships for private school students. These include:
- The Children’s Scholarship Fund: Provides scholarships to low-income families to help them afford private school tuition.
- The Jack Kent Cooke Foundation: Offers scholarships to high-achieving students with financial need.
- The National Merit Scholarship Program: Provides scholarships to students who score well on the PSAT/NMSQT.
5.4. Financial Aid Statistics
Financial aid is a significant factor in making private education accessible. According to the National Association of Independent Schools (NAIS), a median of 25.6% of students at NAIS member schools receive some form of financial aid. For those receiving aid in the form of grants, the median award is $20,912 per recipient. Boarding school students receive an even higher average grant award of $33,047, with 33.3% of boarding school students receiving some form of financial assistance.
6. Alternatives to Traditional Private Schools
If traditional private schools are beyond your budget, several alternatives can provide a high-quality education without the hefty price tag.
6.1. Parochial Schools
Parochial schools are affiliated with a religious institution, such as a church or synagogue. These schools often have lower tuition rates than independent private schools due to financial support from the religious organization.
6.2. Charter Schools
Charter schools are publicly funded but independently run. They offer a tuition-free alternative to traditional public schools, with the flexibility to implement innovative teaching methods and specialized programs.
6.3. Online Private Schools
Online private schools offer a flexible and affordable way to access a private education. These schools provide virtual classes, online resources, and personalized support, often at a lower cost than traditional brick-and-mortar schools.
7. The Value of a Private School Education
Despite the costs, many families believe that a private school education is a worthwhile investment. Private schools often offer smaller class sizes, more individualized attention, and a rigorous academic curriculum.
7.1. Academic Advantages
Private schools often have a strong focus on academic excellence, with high expectations for student achievement. They may offer advanced placement (AP) courses, honors programs, and specialized electives to challenge and engage students.
7.2. College Preparation
Private schools often have a strong track record of preparing students for college. They may offer college counseling services, standardized test preparation, and guidance on the college application process. According to popular opinion, which is echoed at Harvard, Princeton, and the U.S. Department of Education, private schools improve a student’s chances of college acceptance and scholarship awards.
7.3. Social and Extracurricular Opportunities
Private schools offer a wide range of social and extracurricular opportunities, including sports, clubs, arts programs, and community service projects. These activities can help students develop leadership skills, build friendships, and explore their interests.
8. Private Postsecondary Education Costs
The journey through private education doesn’t end with high school. Many families also consider private colleges and universities for their children’s postsecondary education. Understanding these costs is essential for long-term financial planning.
8.1. Average Costs of Private Universities
Private colleges and universities typically have higher tuition rates compared to public institutions. On average, a student attending a traditional private university spends approximately $55,487 per academic year. Tuition and fees account for the largest portion of this cost, averaging $39,389 or 71% of the total annual expense.
8.2. Breakdown of Expenses
The total cost of attending a private university includes several components:
- Tuition and Fees: The primary expense, covering instructional costs and institutional resources.
- Room and Board: Expenses for housing and meals, which can vary depending on the university and accommodation type.
- Books and Supplies: Costs for textbooks, course materials, and academic supplies.
- Personal Expenses: Miscellaneous costs for personal care, entertainment, and other living expenses.
- Transportation: Expenses for travel to and from campus, as well as local transportation.
8.3. Long-Term Investment
Earning a degree from a private university is a significant long-term investment. Over four years, the total cost of a private university degree can reach $221,948. Families need to consider this substantial investment when planning their educational finances.
8.4. Trends in Tuition Costs
Tuition costs at private four-year colleges have been steadily increasing. Between 2010 and 2020, the cost of attendance at private four-year colleges increased by 19%. This trend underscores the importance of planning and exploring financial aid options.
9. Student Financial Aid for Private Postsecondary School
Just as with K-12 private schools, financial aid opportunities are available for students attending private colleges and universities.
9.1. Types of Financial Aid
Several types of financial aid can help offset the cost of private postsecondary education:
- Grants: Need-based aid that does not need to be repaid.
- Scholarships: Merit-based aid awarded based on academic achievement, talent, or other criteria.
- Federal Student Loans: Loans provided by the federal government with favorable interest rates and repayment terms.
- Private Student Loans: Loans from private lenders, which may have higher interest rates and less flexible repayment options.
9.2. Application Process
To apply for financial aid, students typically need to complete the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA). This form assesses a family’s financial situation and determines their eligibility for federal aid programs. Additionally, many private colleges and universities require students to complete the College Scholarship Service (CSS) Profile to be considered for institutional aid.
9.3. Maximizing Financial Aid Opportunities
To maximize financial aid opportunities, students should:
- Apply Early: Submit financial aid applications as soon as possible, as aid is often awarded on a first-come, first-served basis.
- Research Scholarships: Explore scholarship opportunities from various sources, including the college or university, private organizations, and community groups.
- Understand Loan Options: Carefully consider federal and private loan options, and choose the loan that best fits their financial situation.
- Seek Advice: Consult with financial aid advisors at the college or university to understand the available aid programs and application process.
9.4. Considering Long-Term Financial Implications
While financial aid can help make private postsecondary education more affordable, it’s crucial to consider the long-term financial implications of taking on student loan debt. Students should carefully evaluate their potential earnings after graduation and ensure they can comfortably manage their loan repayments.
10. Case Studies: Is Private School Worth It?
Families often weigh the financial burden against the potential benefits of private education. Some studies suggest that graduates of private schools may earn more over their lifetimes. Is private school a worthwhile investment for you and your family? Let’s consider some real-world examples and factors.
10.1. Individual Attention and Resources
Private schools often boast lower student-to-teacher ratios, allowing for more individualized attention. Access to better resources, such as well-equipped libraries and advanced technology, can also enhance the learning experience.
10.2. College Admissions Success
Graduates from private schools often have higher college acceptance rates. This advantage can lead to attending prestigious universities and pursuing successful careers.
10.3. Networking Opportunities
Private schools often have strong alumni networks, which can provide valuable networking opportunities for students as they transition into higher education and the professional world.
10.4. Personal Development and Extracurriculars
The wide range of extracurricular activities in private schools promotes personal development and leadership skills. These experiences can contribute to a well-rounded education and future success.
11. Expert Advice on Budgeting for Private School
Financial planning for private school can be daunting, but with expert advice, it can become more manageable.
11.1. Create a Realistic Budget
Start by creating a detailed budget that includes all potential costs, such as tuition, fees, books, uniforms, and extracurricular activities. Be sure to factor in potential increases in tuition over time.
11.2. Explore All Financial Aid Options
Thoroughly research and apply for all available financial aid and scholarship opportunities. Don’t assume that you won’t qualify – many families receive some form of assistance.
11.3. Consider Payment Plans
Many private schools offer payment plans that allow you to spread tuition payments over several months. This can make the cost more manageable by breaking it down into smaller installments.
11.4. Seek Professional Financial Advice
Consider consulting with a financial advisor who can help you create a long-term financial plan that includes private school tuition. They can offer personalized advice based on your financial situation and goals.
11.5. Prioritize Education Savings
If you’re planning to send your child to private school, start saving early. Consider opening a 529 education savings plan, which offers tax advantages for education expenses.
11.6. Negotiate with the School
In some cases, it may be possible to negotiate tuition costs with the school, especially if you have a strong financial need or your child is a particularly talented student.
12. HOW.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Educational Planning
At HOW.EDU.VN, we understand the challenges and complexities of planning for private education. Our team of experienced PhDs and education experts is dedicated to providing you with the guidance and support you need to make informed decisions about your child’s future.
12.1. Personalized Consultation Services
We offer personalized consultation services to help you navigate the private school landscape. Our experts can provide insights into school selection, financial aid options, and long-term educational planning.
12.2. Expert Insights and Resources
Our website features a wealth of expert insights and resources on private education, including articles, guides, and tools to help you make the best decisions for your family.
12.3. Connect with Top Educators
Through HOW.EDU.VN, you can connect with top educators and professionals who can provide valuable advice and support throughout your child’s educational journey.
12.4. Addressing Your Challenges
We understand the challenges you face:
- Difficulty finding qualified experts: Our network includes over 100 renowned PhDs ready to assist.
- High costs of quality advice: We offer efficient, personalized consultations to save you time and money.
- Concerns about privacy: We ensure the highest level of confidentiality and trust.
- Difficulty articulating your needs: Our experts guide you in clearly defining your goals for the best support.
12.5. Meeting Your Needs
Our services help you:
- Connect with leading experts: Get direct access to PhDs and specialists worldwide.
- Receive personalized advice: Tailored guidance for your specific educational challenges.
- Save time and money: Efficient consultations to reduce the costs of expert advice.
- Ensure confidentiality: Your information is always secure and private.
- Obtain practical solutions: Actionable advice that you can implement immediately.
Don’t let the complexities of private education planning overwhelm you. Contact HOW.EDU.VN today for expert guidance and personalized support. Let us help you make the best decisions for your child’s future.
Contact us:
- Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
- Website: HOW.EDU.VN
13. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Private School Costs
Here are some common questions about private school costs, answered by our experts at HOW.EDU.VN:
13.1. What is the average cost of private school in the US?
The average annual tuition for private schools in the US is around $12,790, but this can vary widely depending on the type of school and location.
13.2. How can I afford private school tuition?
Explore financial aid options, scholarships, payment plans, and consider alternatives such as parochial or charter schools.
13.3. What are the additional costs beyond tuition?
Additional costs may include application fees, enrollment deposits, books, supplies, uniforms, extracurricular activities, and technology fees.
13.4. Are private schools worth the investment?
Private schools often offer academic advantages, college preparation, and social opportunities that can provide long-term benefits.
13.5. How do I apply for financial aid at a private school?
Complete financial aid applications such as the SSS form or FAST application, and research external scholarship programs.
13.6. What are the most expensive states for private school tuition?
Connecticut, the District of Columbia, and Massachusetts tend to have the highest private school tuition rates.
13.7. What are some alternatives to traditional private schools?
Consider parochial schools, charter schools, or online private schools as more affordable options.
13.8. How much does it cost to attend a private boarding school?
The average annual tuition at a 7-day boarding school is around $69,150.
13.9. Can I negotiate tuition costs with a private school?
In some cases, it may be possible to negotiate tuition costs, especially if you have a strong financial need.
13.10. Where can I get expert advice on private school planning?
Contact how.edu.vn for personalized consultation services and expert insights on private education.
