Bang Energy drinks are known for their high caffeine content, but how much caffeine is in a Bang, and what are the implications? Bang Energy drinks contain a significant dose of caffeine, with 300 mg in each can, more than double many other leading energy drinks, according to HOW.EDU.VN. This high caffeine level can provide an energy boost, improve physical performance, and increase mental alertness. However, it’s essential to understand the caffeine levels in Bang Energy drinks and the potential health effects of high caffeine consumption, including energy crashes, and prioritize informed choices.
1. Understanding Caffeine Levels in Bang Energy Drinks
Energy drinks like Bang are designed to deliver a substantial dose of caffeine and other ingredients, aiming to enhance energy levels, physical performance, and mental alertness, as noted by the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health [1]. Bang Energy drinks stand out due to their high caffeine content (300 mg per can), which is significantly higher than other caffeinated beverages, exceeding the caffeine levels in an average cup of coffee by more than three times.
Comparison of Caffeine Levels in Popular Caffeinated Beverages:
| Beverage | Caffeine Content (mg) |
|---|---|
| Bang Energy Drink | 300 |
| Coffee (8 oz) | 95 |
| Black Tea (8 oz) | 47 |
| Green Tea (8 oz) | 28 |
| Coca-Cola (12 oz) | 34 |


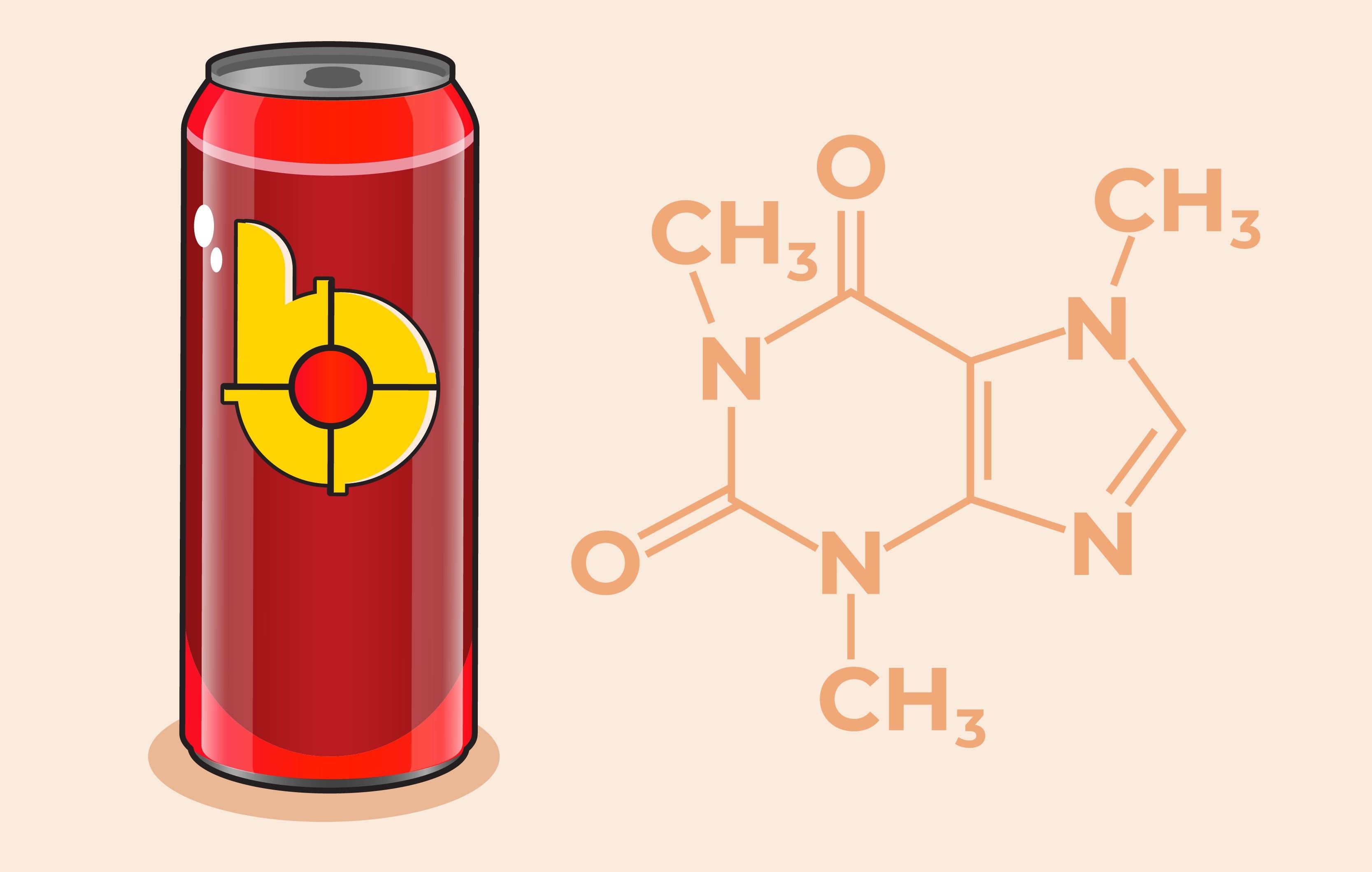
1.1 The Role of Anhydrous Caffeine
Energy drinks, including Bang, use anhydrous caffeine, a synthetic form of caffeine. This type of caffeine, similar to that found in regular coffee, is extracted from coffee plant seeds and leaves but is further refined in a lab to create a pure, highly concentrated form. According to the FDA, a single teaspoon of this potent chemical is equivalent to drinking 28 cups of coffee [3]. Caffeine works by inhibiting adenosine, a neurotransmitter in the brain that promotes sleep, making you feel more alert [2].
2. Examining the Health Implications of High Caffeine Consumption
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) suggests that most healthy adults can safely consume up to 400 mg of caffeine per day [4].
400 mg of caffeine is equal to approximately:
- 4 to 5 cups of coffee
- 8 cups of tea
- 2 standard energy drinks
Because of its high caffeine concentration, drinking more than one can of Bang per day may pose a risk of adverse health effects, including:
-
Anxiety or Nervousness: Adrenaline release triggers the “fight-or-flight” response.
-
Jitteriness: Excessive caffeine, as a stimulant, can lead to physical agitation or tremors.
-
Insomnia: Difficulty falling asleep or waking up too early.
-
Diarrhea or Vomiting: Primarily due to caffeine’s laxative properties.
-
Addiction: Can lead to psychological or physical dependency due to its habit-forming nature.
-
High Blood Pressure: Caused by stimulation of the nervous system.
-
Heart Palpitations and Chest Pains: These are especially common in young people who consume energy drinks, including increased heart rate [5].
-
Withdrawal Fatigue: As the caffeine wears off, you may experience a crash due to the loss of the energy boost.
-
Frequent Urination: Caffeine is a known diuretic, leading to increased urination.
-
Headache, Dizziness, or Delirium: These can occur when caffeine interferes with circulation and blood vessel movement in the brain.
If you experience any of these symptoms after consuming a caffeinated beverage or believe you have consumed unhealthy levels of caffeine, seek medical attention immediately. For expert advice on managing caffeine intake and addressing related health concerns, consult the experienced doctors at HOW.EDU.VN.
3. Identifying Who Should Avoid Bang Energy Drinks
Bang Energy advises that its products are not suitable for children, pregnant or nursing women, or people sensitive to caffeine. While most healthy adults can consume Bang Energy drinks in moderation without adverse effects, certain demographics should avoid them.
It is also suggested to avoid these products if you have the following conditions:
- Anxiety
- Bipolar disorder
- Bleeding disorders
- Heart conditions
- Diabetes
- Epilepsy
- Glaucoma
- High blood pressure
- Parkinson’s disease
- Schizophrenia
Everyone is different, and the FDA’s recommended daily intake is only a guideline, as personal tolerance levels vary. You should never consume more caffeine than you can safely handle. For personalized guidance on whether Bang Energy drinks are suitable for you, consult the medical professionals at HOW.EDU.VN for expert advice.
4. Tracing The Evolution of Bang Energy
Bang Energy drinks were introduced in 2012 and quickly became the fourth-highest-selling energy drink in 2023. However, the company faced challenges when its CEO and founder made unsubstantiated claims that the beverages could cure Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s disease, and other neurological disorders.
Following a multimillion-dollar lawsuit from Monster, Bang Energy declared bankruptcy in 2023 and was subsequently acquired by its competitor. While the company previously offered a wide range of products, such as Bang Keto Coffee and Bang Natural, these have been discontinued.
5. Understanding Consumer Perspectives on Bang Energy Drinks
Bang Energy drinks are very popular, with over 47 million cases sold in 2021. They have gained traction in the fitness industry and have found a place in the keto diet.
Consumer reviews of Bang Energy products are mixed. Social conversations about Bang Energy dropped by over 560% from 2023 to 2024, partly due to marketing trends and consumers’ preference for healthier beverage options, making many people wary of Bang’s high caffeine content. Rankings of the “most popular flavor” also vary widely, although Black Cherry Vanilla often ranks near the top.
6. Exploring Alternatives to High-Caffeine Energy Drinks
If you’re concerned about the high caffeine content of Bang or other energy drinks, there are several lower-caffeine alternatives for a healthier energy boost:
-
Traditional coffee – such as Cafely OG SaiGon, which is a strong dark-roast coffee made of a mix of arabica, robusta, and peaberry that offers a rich flavor with a natural boost of energy.
-
Black tea – still offers the benefits of caffeinated drinks without worrying about ingesting too much when consumed in moderation.
-
Kombucha – is a fermented drink that gives a gentle energy lift with its B vitamins and other ingredients and contains only 10-15 mg of caffeine per 8oz serving.
-
Coconut water – is loaded with electrolytes that quickly replenish and boost your energy (plus it is caffeine-free).
-
Protein shakes – are excellent post-workout beverages that can replenish nutrients and give a natural energy boost.
For personalized advice on choosing the best energy-boosting beverage for your needs, consult the nutrition experts at HOW.EDU.VN.
7. FAQs: Decoding Bang Energy Caffeine Content
If you’re still curious about the caffeine content of Bang Energy Drinks, here are answers to some frequently asked questions:
7.1 How Much Caffeine Is In A Bang Energy Drink Compared To A Cup Of Coffee?
A can of Bang contains roughly three times as much caffeine as an average cup of coffee.
7.2 Is It Safe To Drink Bang Energy Drinks Every Day?
While a single can of Bang falls under the daily caffeine intake recommended by the FDA, daily consumption is not recommended for everyone, especially for prolonged periods.
7.3 Can Bang Energy Drinks Cause Caffeine Overdose?
Yes, consuming multiple cans within a short period or even within a single day can lead to caffeine overdose.
7.4 Are There Any Caffeine-Free Versions Of Bang?
No, all available Bang Energy drinks contain the same high amount of caffeine.
7.5 How Does Bang’s High Caffeine Content Affect Workout Performance?
Bang can increase alertness and energy, potentially improving workout intensity.
7.6 Is Bang Suitable For Children?
No, Bang energy drinks are not recommended for children due to their high caffeine content.
7.7 Is Bang Suitable For Adults?
Bang Energy drinks are not recommended for pregnant or nursing women or those with caffeine sensitivity.
7.8 How Does Bang’s Caffeine Content Compare To Other Energy Drinks?
Bang Energy drinks have a higher caffeine content than most other energy drinks.
7.9 Can Bang Energy Drinks Help You Lose Weight?
While often marketed as a weight loss aid, energy drinks are often associated with poor weight loss behaviors and unhealthy body image [7].
7.10 What Are Some Natural Alternatives To Bang?
Natural coffee blends, like Cafely Sai Gon OG, have lower caffeine levels and are a healthier and more natural alternative to energy drinks.
Navigating the world of energy drinks and caffeine intake can be complex, but you don’t have to do it alone. At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with leading PhDs and experts worldwide who can provide personalized guidance and solutions tailored to your unique needs.
Are you struggling to find reliable health information?
Do you need expert advice on managing your caffeine intake or choosing healthier energy alternatives?
Are you concerned about the potential health risks of energy drinks and want a personalized assessment?
Don’t waste time and money searching for answers on your own. Our team of over 100 renowned PhDs are ready to provide you with the expertise and support you deserve.
Benefits of consulting with our experts:
- Personalized Advice: Receive tailored recommendations based on your specific health profile and lifestyle.
- Reliable Information: Get access to evidence-based insights and the latest research from leading experts.
- Peace of Mind: Make informed decisions about your health with confidence, knowing you have the support of trusted professionals.
Ready to take control of your health and well-being?
Contact HOW.EDU.VN today and let our experts guide you toward a healthier, more energized life.
Contact Information:
Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
Website: how.edu.vn
References:
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. (n.d.). Energy drinks. National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/energy-drinks
- Ribeiro, J. A., & Sebastião, A. M. (2010). Caffeine and adenosine. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease: JAD, 20 Suppl 1(20), S3-15. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-2010-1379
- Commissioner, O. of the. (n.d.). Spilling the beans: How much caffeine is too much? U.S. Food and Drug Administration. https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/spilling-beans-how-much-caffeine-too-much
- USDA. (2020). Dietary Guidelines For Americans. Ninth Edition. https://www.dietaryguidelines.gov/sites/default/files/2020-12/Dietary_Guidelines_for_Americans_2020-2025.pdf
- A;, M. A. S. A. (n.d.). Energy drinks and atrial fibrillation in young adults. Clinical nutrition (Edinburgh, Scotland). https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28527645/
- Higgins, J. P., Tuttle, T. D., & Higgins, C. L. (2010, November). Energy beverages: Content and safety. Mayo Clinic proceedings. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2966367/
- EG;, J. A. H. K. (n.d.). Energy Drinks, weight loss, and disordered eating behaviors. Journal of American College Health : J of ACH. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24635529/