How much caffeine is in chocolate, and how does it affect you? Discover the varying caffeine levels in different types of chocolate and how it interacts with other compounds for a unique experience, with expert advice from HOW.EDU.VN. Understand the stimulating effects of chocolate and consult with our Ph.D. experts for personalized insights on managing caffeine intake, maximizing cognitive benefits, and enjoying chocolate responsibly.
1. Understanding Caffeine in Chocolate
The caffeine content in chocolate is a fascinating and often misunderstood topic. While many people enjoy chocolate for its rich flavor and satisfying sweetness, its caffeine content is an important factor, especially for those sensitive to stimulants. The actual caffeine level varies greatly depending on several factors, making it difficult to provide a one-size-fits-all answer.
1.1. Factors Influencing Caffeine Levels
Several elements influence the caffeine content in chocolate:
- Type of Chocolate: Dark chocolate generally has more caffeine than milk chocolate. This is because dark chocolate contains a higher percentage of cacao, the source of caffeine. White chocolate, which doesn’t contain cacao solids, has negligible amounts of caffeine.
- Cacao Percentage: Within dark chocolate, the higher the cacao percentage, the more caffeine it is likely to contain. For example, an 85% dark chocolate bar will have significantly more caffeine than a 50% dark chocolate bar.
- Origin of Cacao Beans: The geographic origin of cacao beans plays a crucial role. Cacao beans from certain regions have naturally higher caffeine levels.
- Processing Methods: The way cacao beans are processed, including fermentation, roasting, and conching, can affect the final caffeine content in the chocolate product.
- Manufacturing Practices: Different chocolate manufacturers use varying recipes and processes, leading to variations in caffeine levels even within the same type of chocolate.
1.2. Theobromine: Chocolate’s Other Stimulant
Chocolate contains another stimulant called theobromine. While theobromine is chemically related to caffeine, it has a milder and longer-lasting effect. Theobromine also contributes to the overall stimulating experience of eating chocolate, often working in synergy with caffeine. Understanding the interaction between these two compounds is key to appreciating chocolate’s unique effects.
1.3. The Entourage Effect
The “entourage effect” describes how various compounds in chocolate, including caffeine, theobromine, terpenes, polyphenols, and endogenous cannabinoids, work together to produce a combined effect that is greater than the sum of their individual effects. This synergy can enhance mood and cognitive functions while mitigating the negative psychophysiological effects of caffeine, such as jitters or crashes. A study in “More than just caffeine: psychopharmacology of methylxanthine interactions with plant-derived phytochemicals” suggests that specific combinations of compounds, like polyphenols and theobromine, can amplify the positive effects of caffeine.
2. Caffeine Content by Chocolate Type
To provide a clearer picture, let’s break down the typical caffeine content in different types of chocolate:
2.1. Dark Chocolate
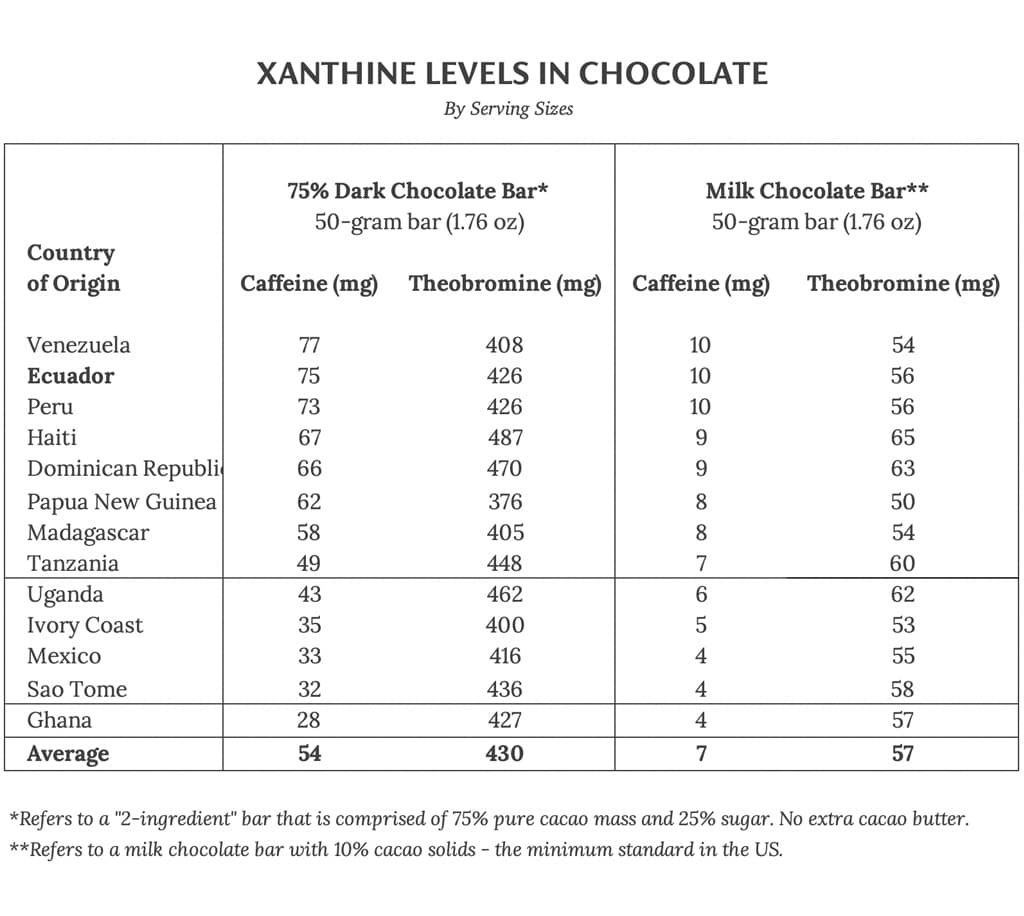
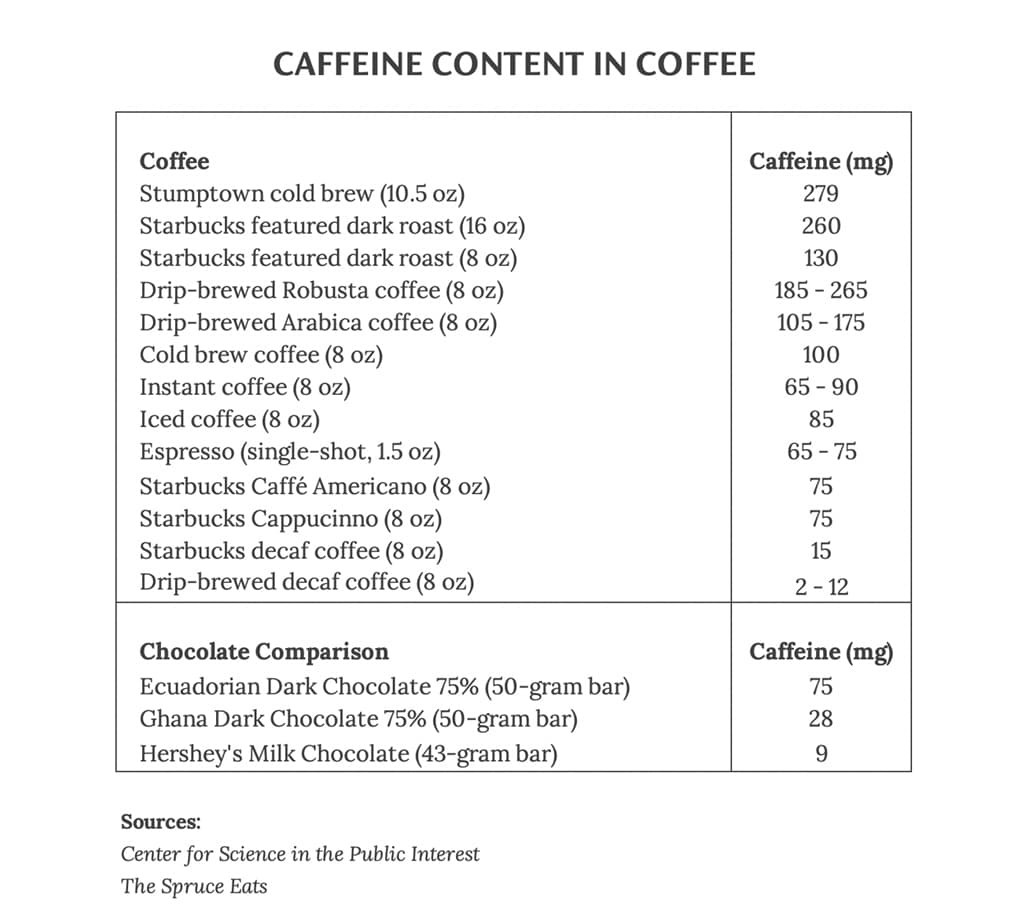
Dark chocolate is known for its intense flavor and relatively high caffeine content. A 1-ounce (28-gram) serving of dark chocolate (70-85% cacao) typically contains 50-80 mg of caffeine. However, this can vary significantly based on the factors mentioned earlier. Some high-cacao dark chocolates may contain even more caffeine, approaching levels found in a cup of coffee.
2.2. Milk Chocolate
Milk chocolate contains less caffeine than dark chocolate due to its lower cacao content. A 1-ounce (28-gram) serving of milk chocolate usually contains 10-25 mg of caffeine. The addition of milk solids and sugar dilutes the cacao, reducing the overall caffeine level.
2.3. White Chocolate
White chocolate contains virtually no caffeine. Because it is made from cocoa butter, sugar, and milk solids, it lacks the cacao solids that provide caffeine. Therefore, white chocolate is not considered a source of caffeine.
2.4. Chocolate Beverages
The caffeine content in chocolate beverages can vary based on the type and preparation method. For instance, hot chocolate made with cocoa powder typically contains less caffeine than mocha, which combines chocolate with coffee. The addition of coffee significantly increases the caffeine level in mocha beverages.
2.5. Baker’s Chocolate
Baker’s chocolate, also known as unsweetened chocolate, is pure chocolate liquor with no added sugar. It has the highest concentration of cacao and, consequently, the highest caffeine content. Baker’s chocolate is primarily used for baking and cooking, not for direct consumption.
3. Comparing Caffeine in Chocolate to Other Sources
To put the caffeine content in chocolate into perspective, it’s helpful to compare it to other common sources of caffeine:
3.1. Coffee
Coffee is one of the most popular sources of caffeine worldwide. An 8-ounce cup of coffee contains approximately 95-200 mg of caffeine, depending on the type of coffee and brewing method. Compared to chocolate, coffee generally has a higher caffeine content per serving.
3.2. Tea
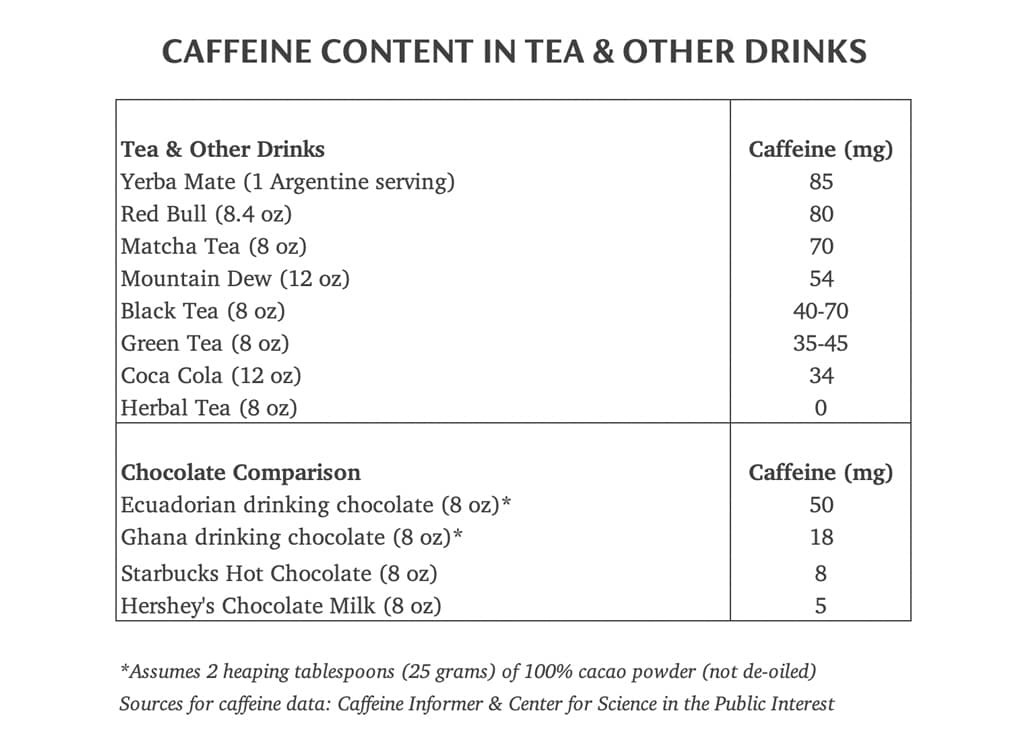
Tea is another widely consumed caffeinated beverage. The caffeine content in tea varies depending on the type of tea:
- Black Tea: 40-70 mg of caffeine per 8-ounce cup
- Green Tea: 30-50 mg of caffeine per 8-ounce cup
- White Tea: 15-30 mg of caffeine per 8-ounce cup
While some types of tea may have similar caffeine levels to milk chocolate, dark chocolate can contain comparable amounts of caffeine to certain teas.
3.3. Energy Drinks
Energy drinks are known for their high caffeine content. A typical 8-ounce serving of an energy drink can contain 70-200 mg of caffeine. Energy drinks often contain other stimulants and additives, which can amplify their effects.
3.4. Soft Drinks
Many soft drinks, particularly cola beverages, contain caffeine. A 12-ounce can of cola typically contains 30-40 mg of caffeine. While the caffeine content is lower than coffee or energy drinks, it can still contribute to overall caffeine intake.
3.5. Other Foods and Beverages
Caffeine can also be found in other foods and beverages, such as:
- Yerba Mate: A traditional South American caffeinated beverage.
- Guarana: An ingredient often added to energy drinks and supplements.
- Some Flavored Waters: Certain flavored waters contain added caffeine.
- Protein Bars: Some protein bars include caffeine for an energy boost.
3.6. Comparison Table of Caffeine Content
| Source | Caffeine Content (mg) | Serving Size |
|---|---|---|
| Dark Chocolate (70-85% Cacao) | 50-80 | 1 ounce (28 grams) |
| Milk Chocolate | 10-25 | 1 ounce (28 grams) |
| Coffee (Brewed) | 95-200 | 8 ounces |
| Black Tea | 40-70 | 8 ounces |
| Green Tea | 30-50 | 8 ounces |
| Energy Drink | 70-200 | 8 ounces |
| Cola | 30-40 | 12 ounces |

4. Health Effects of Caffeine in Chocolate
The caffeine in chocolate can have both positive and negative effects on health, depending on individual sensitivity, consumption levels, and overall health status.
4.1. Positive Effects
- Increased Alertness: Caffeine is a well-known stimulant that can increase alertness and reduce feelings of fatigue.
- Improved Cognitive Function: Moderate caffeine consumption has been linked to improved cognitive function, including enhanced memory, focus, and reaction time.
- Mood Enhancement: Caffeine can stimulate the release of dopamine and other neurotransmitters associated with mood elevation and feelings of well-being.
- Antioxidant Properties: Chocolate, especially dark chocolate, contains antioxidants that can help protect against cellular damage and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
- Potential Cardiovascular Benefits: Some studies suggest that moderate chocolate consumption may have cardiovascular benefits, such as improved blood flow and reduced blood pressure.
4.2. Negative Effects
- Anxiety and Jitters: High doses of caffeine can cause anxiety, nervousness, and jitters, particularly in sensitive individuals.
- Insomnia: Caffeine can interfere with sleep patterns, making it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep.
- Digestive Issues: Caffeine can stimulate bowel movements and may cause digestive upset in some people.
- Increased Heart Rate and Blood Pressure: High caffeine intake can temporarily increase heart rate and blood pressure.
- Addiction and Withdrawal: Regular caffeine consumption can lead to dependence, and withdrawal symptoms such as headaches, fatigue, and irritability may occur if caffeine intake is suddenly stopped.
4.3. The Importance of Moderation
To reap the potential benefits of caffeine in chocolate while minimizing negative effects, moderation is key. Most adults can safely consume up to 400 mg of caffeine per day. However, individual sensitivity varies, and some people may need to consume less to avoid adverse effects. Factors such as age, body weight, overall health, and medication use can influence caffeine sensitivity.
4.4. Recommendations for Safe Consumption
- Monitor Intake: Keep track of caffeine consumption from all sources, including chocolate, coffee, tea, and energy drinks.
- Time Consumption: Avoid consuming chocolate or other caffeinated products close to bedtime to prevent sleep disturbances.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to help mitigate the dehydrating effects of caffeine.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to how caffeine affects you and adjust your intake accordingly.
- Consult a Professional: If you have concerns about caffeine sensitivity or potential health effects, consult a healthcare professional.
5. Caffeine in Chocolate and Specific Populations
Certain populations should exercise extra caution when consuming caffeine in chocolate:
5.1. Children and Adolescents
Children and adolescents are more sensitive to the effects of caffeine than adults. Excessive caffeine intake can lead to anxiety, sleep disturbances, and behavioral problems. It is generally recommended that children and adolescents limit or avoid caffeine consumption.
5.2. Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women
Pregnant and breastfeeding women should limit their caffeine intake to no more than 200 mg per day. High caffeine consumption has been linked to an increased risk of miscarriage, preterm birth, and low birth weight. Caffeine can also pass into breast milk and affect the infant.
5.3. Individuals with Anxiety Disorders
Caffeine can exacerbate anxiety symptoms. Individuals with anxiety disorders should be particularly cautious about caffeine consumption and may need to avoid it altogether.
5.4. People with Heart Conditions
Caffeine can increase heart rate and blood pressure. People with heart conditions should consult their healthcare provider about safe caffeine intake levels.
5.5. Those with Sleep Disorders
Caffeine can disrupt sleep patterns and worsen sleep disorders such as insomnia. Individuals with sleep disorders should avoid caffeine consumption, especially in the afternoon and evening.
6. Choosing the Right Chocolate
When it comes to enjoying chocolate responsibly, selecting the right type is crucial:
6.1. Read Labels Carefully
Always read the nutrition labels on chocolate products to determine the caffeine content per serving. Pay attention to the serving size and adjust your consumption accordingly.
6.2. Opt for Lower Cacao Percentages
If you are sensitive to caffeine, choose milk chocolate or dark chocolate with lower cacao percentages. These options typically contain less caffeine.
6.3. Consider White Chocolate
If you want to avoid caffeine altogether, white chocolate is a caffeine-free option.
6.4. Look for Quality Chocolate
Choose high-quality chocolate made with ethically sourced cacao beans. Quality chocolate often has a richer flavor and may contain fewer additives.
6.5. Be Mindful of Portion Sizes
Even if you choose a chocolate with lower caffeine content, be mindful of portion sizes. Consuming large amounts of chocolate can still lead to excessive caffeine intake.
7. Regional Variations in Cacao Caffeine Levels
The caffeine levels in cacao beans can vary significantly by country and region due to differences in climate, soil composition, and agricultural practices. For example, cacao from South America and the Caribbean generally has higher caffeine levels compared to cacao from West Africa. Studies have shown that cacao from Ecuador, Venezuela, and Peru often contains more than twice the caffeine found in cacao from West African countries. These regional variations highlight the importance of considering the origin of cacao when assessing the caffeine content of chocolate products.
7.1. Impact of Weather Conditions
Weather conditions, particularly during the growing season, can also influence caffeine levels in cacao. Research indicates that cacao harvested in the dry season tends to have higher caffeine and theobromine content compared to cacao harvested in the rainy season.
8. Practical Tips for Managing Caffeine Intake from Chocolate
Here are some practical tips to help you manage your caffeine intake from chocolate:
8.1. Keep a Caffeine Diary
Track your caffeine consumption from all sources to get a better understanding of your daily intake. This can help you identify potential sources of excessive caffeine and make informed choices about your consumption habits.
8.2. Space Out Caffeine Consumption
Avoid consuming large amounts of caffeine at once. Instead, space out your caffeine intake throughout the day to maintain a steady level of alertness without experiencing jitters or crashes.
8.3. Combine Chocolate with Other Foods
Eating chocolate with other foods, particularly those high in fiber and protein, can slow down the absorption of caffeine and help mitigate its effects.
8.4. Stay Active
Regular physical activity can help improve energy levels and reduce reliance on caffeine.
8.5. Get Enough Sleep
Prioritize getting enough sleep to reduce feelings of fatigue and the need for caffeine to stay awake.
8.6. Consult a Nutritionist
A nutritionist can provide personalized advice on managing caffeine intake based on individual health needs and preferences. They can help you create a balanced diet that includes chocolate in moderation.
9. Debunking Common Myths About Caffeine in Chocolate
There are several common myths about caffeine in chocolate that are worth debunking:
Myth 1: Chocolate is a Major Source of Caffeine for Most People
While chocolate does contain caffeine, it is not a major source of caffeine for most people compared to coffee, tea, and energy drinks.
Myth 2: All Dark Chocolate Has the Same Amount of Caffeine
The caffeine content in dark chocolate can vary significantly based on the cacao percentage, origin of the beans, and manufacturing practices.
Myth 3: White Chocolate Contains Caffeine
White chocolate does not contain caffeine, as it is made from cocoa butter and lacks cacao solids.
Myth 4: Caffeine in Chocolate is More Harmful Than Caffeine in Coffee
The health effects of caffeine are generally the same regardless of the source. However, the presence of other compounds in chocolate, such as theobromine and antioxidants, may influence the overall experience.
Myth 5: You Can’t Get Addicted to Caffeine from Chocolate
Regular caffeine consumption from any source, including chocolate, can lead to dependence and withdrawal symptoms.
10. Emerging Research on Caffeine and Chocolate
Ongoing research continues to explore the complex relationship between caffeine, chocolate, and health. Some areas of interest include:
10.1. The Effects of Different Cacao Varieties on Caffeine Levels
Researchers are studying how different cacao varieties and growing conditions influence caffeine content.
10.2. The Role of Gut Microbiota in Caffeine Metabolism
The gut microbiota can play a role in how caffeine is metabolized in the body. Research is investigating how different gut bacteria influence caffeine sensitivity.
10.3. The Potential Synergistic Effects of Caffeine and Other Compounds in Chocolate
Studies are exploring how caffeine interacts with other compounds in chocolate, such as flavonoids and theobromine, to produce unique health effects.
10.4. The Impact of Processing Techniques
Emerging research is also examining how different processing techniques, such as fermentation and roasting, affect the caffeine content and overall quality of chocolate.
11. How HOW.EDU.VN Can Help You
At HOW.EDU.VN, we understand the complexities of caffeine consumption and its impact on your health. Our team of expert Ph.D. professionals is dedicated to providing personalized guidance and support to help you make informed choices about your diet and lifestyle.
11.1. Personalized Consultations
Connect directly with our experienced Ph.D. experts for in-depth, personalized consultations. Whether you’re seeking advice on managing caffeine intake, maximizing cognitive benefits, or addressing specific health concerns, our experts are here to help.
11.2. Customized Solutions
We offer customized solutions tailored to your unique needs and preferences. Our experts take the time to understand your individual health profile, lifestyle, and goals to develop strategies that work for you.
11.3. Evidence-Based Advice
Our recommendations are grounded in the latest scientific research and evidence-based practices. You can trust that the information and advice you receive from HOW.EDU.VN is accurate, reliable, and up-to-date.
11.4. Convenient and Accessible Support
Our services are designed to be convenient and accessible. Connect with our experts from anywhere in the world and receive timely, personalized support whenever you need it.
11.5. Addressing Your Challenges
Are you struggling to find reliable expertise, worried about the costs of quality advice, or concerned about the privacy of your consultations? At HOW.EDU.VN, we offer a solution by connecting you directly with top Ph.D. experts worldwide, providing personalized, confidential, and practical advice tailored to your needs.
12. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Caffeine in Chocolate
Here are some frequently asked questions about caffeine in chocolate:
12.1. Is dark chocolate always higher in caffeine than milk chocolate?
Yes, dark chocolate generally has more caffeine than milk chocolate due to its higher cacao content.
12.2. Can white chocolate keep me awake?
White chocolate does not contain caffeine and is unlikely to keep you awake.
12.3. How much caffeine is too much?
Most adults can safely consume up to 400 mg of caffeine per day. However, individual sensitivity varies.
12.4. Does the roasting process affect the caffeine content in chocolate?
The roasting process has minimal impact on the caffeine content in chocolate.
12.5. Is caffeine in chocolate as addictive as caffeine in coffee?
Caffeine from any source, including chocolate, can lead to dependence and withdrawal symptoms.
12.6. Can caffeine in chocolate cause anxiety?
Yes, high doses of caffeine can cause anxiety, particularly in sensitive individuals.
12.7. Is it safe for pregnant women to consume chocolate?
Pregnant women should limit their caffeine intake to no more than 200 mg per day, including caffeine from chocolate.
12.8. Does chocolate affect sleep?
Consuming chocolate close to bedtime can interfere with sleep patterns due to its caffeine content.
12.9. Are there any health benefits to consuming chocolate?
Yes, moderate chocolate consumption, especially dark chocolate, has been linked to potential cardiovascular benefits and antioxidant properties.
12.10. Where can I find reliable information about caffeine content in chocolate?
You can find reliable information on product labels, scientific studies, and reputable sources like HOW.EDU.VN.
13. Conclusion
Understanding the caffeine content in chocolate is essential for making informed choices about your diet and lifestyle. While chocolate offers potential health benefits and can be a delightful treat, it’s important to be mindful of its caffeine content, especially if you are sensitive to stimulants or have specific health concerns. By choosing the right type of chocolate, managing your portion sizes, and paying attention to your body’s responses, you can enjoy chocolate responsibly and reap its potential rewards.
Are you seeking personalized advice and expert guidance on managing your caffeine intake and optimizing your health? Contact us at HOW.EDU.VN today. Our team of experienced Ph.D. professionals is ready to provide you with the support and solutions you need to thrive. Don’t navigate the complexities of health and wellness alone. Let our experts be your trusted partners in achieving your goals.
Contact Information:
Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
Whatsapp: +1 (310) 555-1212
Website: HOW.EDU.VN
Connect with the world’s leading Ph.D. experts at how.edu.vn and unlock your full potential. Your journey to a healthier, more informed you starts here.