Mountain Dew’s distinctive citrus flavor and electrifying kick make it a popular soda choice, but how much caffeine is actually in Mountain Dew? The caffeine content in Mountain Dew varies depending on the specific flavor and serving size, generally ranging from approximately 55 mg to 135 mg, according to HOW.EDU.VN’s team of expert doctors. Understanding these levels is crucial for managing your caffeine intake. To fully comprehend the impact, you can explore various caffeinated beverages, energy drink alternatives, and sugar content considerations.
1. Breaking Down the Caffeine Content in Mountain Dew Varieties
Mountain Dew offers a range of flavors, each with its unique caffeine level. Knowing the specifics can help you make informed choices about your beverage consumption.
| Flavor | Caffeine Content (per 12 oz can) |
|---|---|
| Original Mountain Dew | 55 mg |
| Diet Mountain Dew | 55 mg |
| Mountain Dew Code Red | 55 mg |
| Mountain Dew Voltage | 69 mg |
| Mountain Dew White Out | 68 mg |
| Mountain Dew Kickstart | 68-92 mg |
| Mountain Dew Game Fuel | 90 mg |
| Mountain Dew Major Melon | 55 mg |
| Mountain Dew Spark | 68 mg |
| Mountain Dew Zero Sugar | 55 mg |

1.1. Comparing Regular and Diet Mountain Dew Caffeine Levels
Both regular and Diet Mountain Dew contain the same amount of caffeine, which is 55 mg per 12 oz can. The primary difference lies in the sugar content. Regular Mountain Dew is high in sugar, whereas Diet Mountain Dew uses artificial sweeteners to reduce sugar content. This makes Diet Mountain Dew an alternative for those looking to reduce their sugar intake while still enjoying the caffeine kick.
1.2. High-Caffeine Mountain Dew Flavors
Certain Mountain Dew flavors pack a more significant caffeine punch. For instance, Mountain Dew Kickstart contains between 68 mg and 92 mg of caffeine, depending on the specific variety. Mountain Dew Game Fuel also has a higher caffeine content at 90 mg per 12 oz can. These flavors are designed to provide an extra energy boost, making them popular choices among gamers and individuals needing extended focus.
1.3. Limited Edition and Regional Mountain Dew Varieties
Limited edition and regional Mountain Dew flavors often have varying caffeine levels. For example, Mountain Dew White Out and Mountain Dew Spark both contain 68 mg of caffeine per 12 oz can. These unique flavors cater to specific taste preferences and offer different caffeine experiences, making them sought after by Mountain Dew enthusiasts.
2. Mountain Dew Caffeine Compared to Other Beverages
Understanding how Mountain Dew’s caffeine content stacks up against other common drinks can provide valuable perspective on your daily caffeine consumption.
2.1. Mountain Dew vs. Coffee
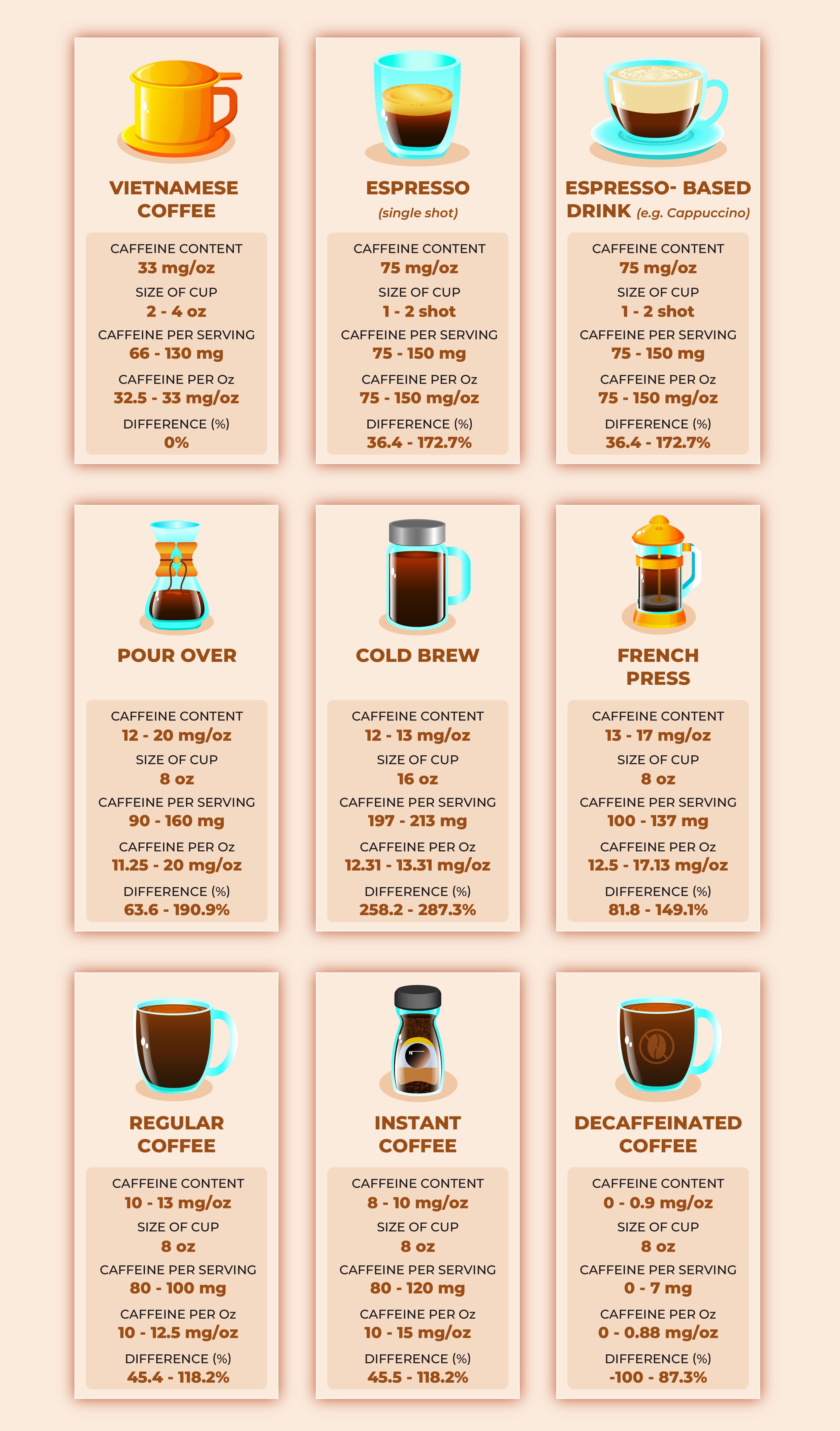
While Mountain Dew is known for its caffeine, coffee generally contains more caffeine per serving. An average 8 oz cup of coffee contains between 80 mg and 100 mg of caffeine, compared to the 55 mg found in a 12 oz can of regular Mountain Dew. However, specialty coffee drinks like lattes or cappuccinos can have significantly higher caffeine levels, depending on the number of espresso shots used.
Caffeine Content of Various Coffee Preparations
2.2. Mountain Dew vs. Other Sodas
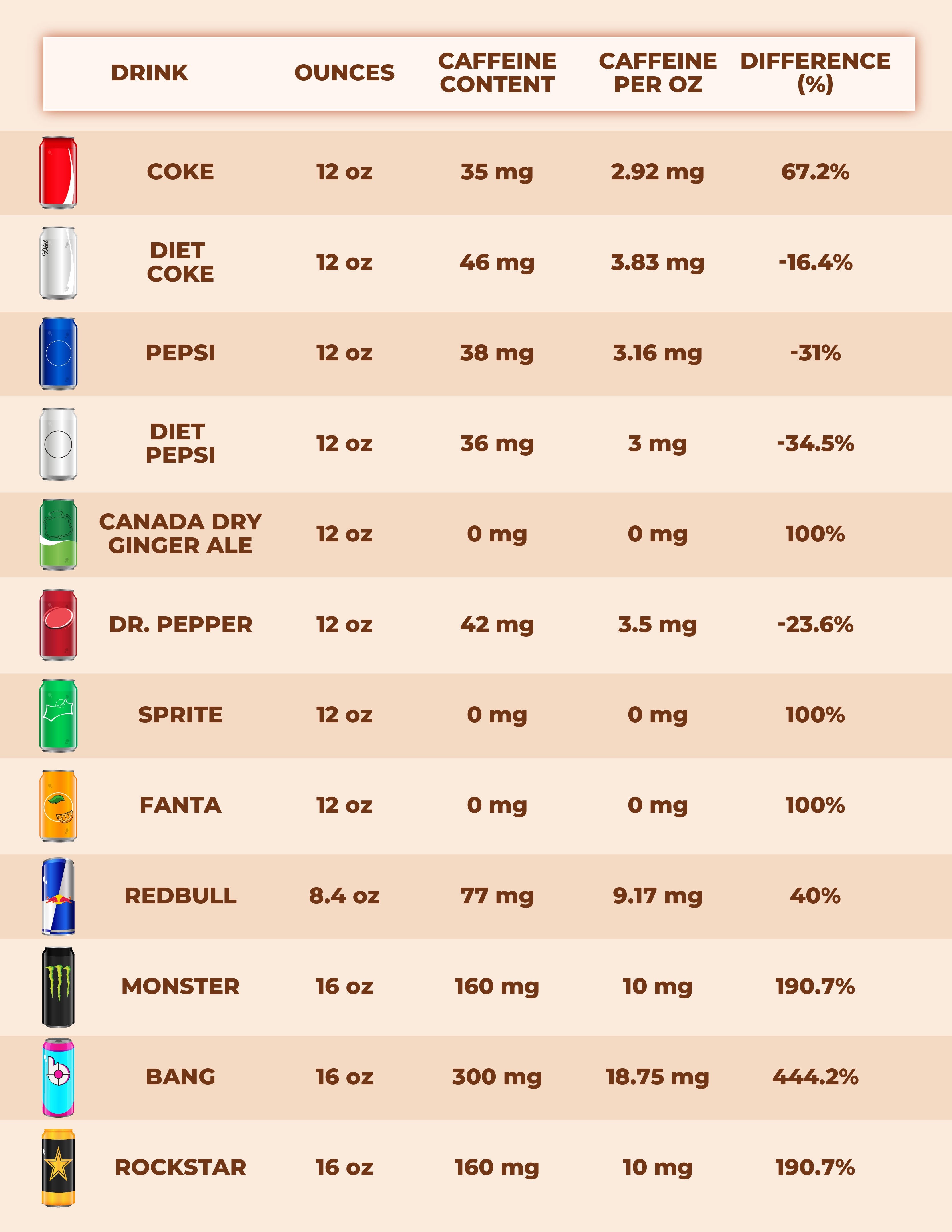
Compared to other sodas, Mountain Dew typically contains a higher caffeine content. Coca-Cola has around 34 mg of caffeine per 12 oz can, while Pepsi contains approximately 38 mg. This makes Mountain Dew a more potent option for those seeking a significant energy boost from their soda.
2.3. Mountain Dew vs. Energy Drinks
Energy drinks are generally formulated to deliver a substantial dose of caffeine. Drinks like Red Bull and Monster can contain anywhere from 80 mg to over 160 mg of caffeine per serving. Mountain Dew, with its 55-90 mg range, falls on the lower end of the energy drink spectrum. However, Mountain Dew’s higher sugar content can also contribute to its perceived energy boost.
Caffeine Content of Common Sodas & Energy Drinks:
3. Factors Affecting Caffeine Levels in Mountain Dew
Several factors can influence the exact caffeine content in Mountain Dew, including variations in production and specific ingredients.
3.1. Production Variations
Minor variations in the production process can lead to slight differences in caffeine levels. While manufacturers strive for consistency, natural variations in ingredients and processing can occur. These variations are typically within an acceptable range and do not significantly impact the overall caffeine content.
3.2. Ingredients and Additives
The specific ingredients and additives used in Mountain Dew can also affect caffeine levels. Some additives may enhance the effects of caffeine, while others could slightly alter the overall caffeine content. Understanding these interactions can provide a more nuanced view of Mountain Dew’s caffeine impact.
3.3. Storage Conditions
Storage conditions, such as temperature and light exposure, can potentially affect the stability of caffeine in Mountain Dew. Extreme conditions might cause a slight degradation of caffeine over time, but this is generally minimal under normal storage conditions.
4. Health Implications of Caffeine in Mountain Dew
While caffeine can offer certain benefits, it’s essential to be aware of the potential health implications associated with caffeine consumption, especially from sources like Mountain Dew.
4.1. Recommended Daily Caffeine Intake
Most healthy adults can safely consume up to 400 milligrams of caffeine daily. This limit helps to avoid potential negative side effects such as insomnia, anxiety, and increased heart rate. However, individual tolerance can vary based on factors like age, weight, and overall health.
4.2. Potential Side Effects of Excessive Caffeine Consumption
Consuming excessive amounts of caffeine can lead to several unpleasant side effects. These include insomnia, anxiety, increased heart rate, upset stomach, headaches, and heart palpitations. In extreme cases, overconsumption of caffeine can result in more severe medical issues such as confusion, hallucinations, and difficulty breathing.
4.3. Long-Term Health Risks
Long-term excessive caffeine consumption has been linked to several health risks, including cardiovascular issues, digestive problems, and mental health disorders. It’s important to moderate caffeine intake and be aware of how it affects your body over time.
5. Mountain Dew and Specific Populations
Certain populations need to exercise extra caution when consuming caffeinated beverages like Mountain Dew.
5.1. Caffeine Consumption During Pregnancy
Pregnant women should limit their daily caffeine intake to under 200 mg. Higher caffeine consumption during pregnancy has been associated with risks such as miscarriage, birth defects, premature labor, and reduced fertility. Mountain Dew also contains high levels of sugar and artificial additives that should be avoided during pregnancy.
5.2. Caffeine and Children
Children are more susceptible to the negative effects of caffeine. Pediatricians generally advise against caffeine consumption for children due to its potential impact on sleep patterns, anxiety levels, and overall development.
5.3. Caffeine and Individuals with Medical Conditions
Individuals with certain medical conditions, such as heart problems, anxiety disorders, or digestive issues, should be particularly cautious about caffeine consumption. Caffeine can exacerbate these conditions and lead to adverse health outcomes.
6. Strategies for Managing Caffeine Intake from Mountain Dew
If you enjoy Mountain Dew but want to manage your caffeine intake, several strategies can help you strike a balance.
6.1. Monitoring Daily Consumption
Keep track of how much Mountain Dew you consume each day to ensure you stay within the recommended caffeine limits. Use a caffeine tracking app or a simple notebook to monitor your intake and make informed decisions about your beverage choices.
6.2. Alternatives to High-Caffeine Mountain Dew Flavors
Opt for lower-caffeine Mountain Dew flavors or caffeine-free alternatives to reduce your caffeine intake. Caffeine-Free Diet Mountain Dew is an excellent option for those looking to limit caffeine consumption.
6.3. Mixing Mountain Dew with Non-Caffeinated Drinks
Dilute Mountain Dew with non-caffeinated beverages like water or herbal tea to reduce the overall caffeine content. This can help you enjoy the taste of Mountain Dew without the full caffeine impact.
7. The Synergistic Effects of Sugar and Caffeine in Mountain Dew
The combination of sugar and caffeine in Mountain Dew can create synergistic effects that amplify the beverage’s impact on your body.
7.1. Impact on Energy Levels
The high sugar content in Mountain Dew provides a quick energy boost, while caffeine enhances alertness and focus. This combination can lead to a rapid increase in energy levels, followed by a subsequent crash as the effects wear off.
7.2. Effects on Mood and Cognitive Function
Both sugar and caffeine can affect mood and cognitive function. While they may initially improve mood and enhance cognitive performance, excessive consumption can lead to mood swings, anxiety, and decreased cognitive function over time.
7.3. Potential for Addiction
The combination of sugar and caffeine can be addictive. Regular consumption can lead to physical dependence and withdrawal symptoms when intake is reduced or stopped.
8. Exploring Caffeine-Free Options
For those looking to avoid caffeine altogether, several caffeine-free alternatives can provide a similar taste experience without the stimulant effects.
8.1. Caffeine-Free Mountain Dew Varieties
Caffeine-Free Diet Mountain Dew is a popular option for those wanting to enjoy the taste of Mountain Dew without the caffeine. However, it’s important to note that Caffeine-Free Diet Mountain Dew is not widely available and can only be found in certain regions.
8.2. Other Caffeine-Free Sodas
Many other caffeine-free sodas are available, including Sprite, 7-Up, and various root beers. These options provide a variety of flavors without the stimulating effects of caffeine.
8.3. Herbal Teas and Naturally Caffeine-Free Beverages
Herbal teas and naturally caffeine-free beverages like fruit juices and flavored water can be excellent alternatives to caffeinated sodas. These options offer hydration and flavor without the potential side effects of caffeine.
9. Understanding Caffeine Withdrawal
If you regularly consume caffeine and suddenly stop, you may experience withdrawal symptoms.
9.1. Common Withdrawal Symptoms
Common caffeine withdrawal symptoms include headaches, fatigue, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and depression. These symptoms can range from mild to severe, depending on your level of caffeine dependence.
9.2. Duration of Withdrawal Symptoms
Caffeine withdrawal symptoms typically last from a few days to a week. The duration and intensity of symptoms vary depending on individual factors such as caffeine intake, metabolism, and overall health.
9.3. Strategies for Minimizing Withdrawal Symptoms
To minimize caffeine withdrawal symptoms, gradually reduce your caffeine intake over time. Stay hydrated, get plenty of rest, and consider using over-the-counter pain relievers to manage headaches.
10. Expert Opinions on Caffeine Consumption
Experts in nutrition and health provide valuable insights into the safe and responsible consumption of caffeine.
10.1. Recommendations from Nutritionists
Nutritionists generally recommend limiting caffeine intake to 400 mg per day for healthy adults. They also advise being mindful of the sources of caffeine and choosing options with lower sugar content.
10.2. Medical Perspectives on Caffeine
Medical professionals emphasize the importance of considering individual health conditions when consuming caffeine. They recommend that individuals with heart problems, anxiety disorders, and other medical issues consult with their healthcare provider about safe caffeine intake levels.
10.3. Scientific Studies on Caffeine Effects
Numerous scientific studies have investigated the effects of caffeine on various aspects of health. These studies provide valuable information about the benefits and risks associated with caffeine consumption, helping individuals make informed decisions about their caffeine intake.
11. Dispelling Common Myths About Caffeine
Several common myths surround caffeine consumption. It’s important to separate fact from fiction to make informed choices about your caffeine intake.
11.1. Myth: Caffeine Is Always Harmful
While excessive caffeine consumption can have negative effects, moderate intake can offer certain benefits. Caffeine can enhance alertness, improve cognitive function, and boost physical performance.
11.2. Myth: Caffeine Is Dehydrating
While caffeine has a mild diuretic effect, it does not cause significant dehydration when consumed in moderation. Staying hydrated is still important, but caffeine intake does not necessarily lead to dehydration.
11.3. Myth: Caffeine Affects Everyone the Same Way
Individual responses to caffeine vary widely. Factors such as age, weight, genetics, and overall health can influence how caffeine affects you.
12. How to Make Informed Choices About Mountain Dew Consumption
Making informed choices about Mountain Dew consumption involves understanding its caffeine content, potential health implications, and your individual needs and preferences.
12.1. Assessing Your Caffeine Sensitivity
Pay attention to how caffeine affects your body and adjust your intake accordingly. If you experience negative side effects such as anxiety, insomnia, or heart palpitations, consider reducing your caffeine consumption.
12.2. Reading Product Labels
Always read product labels to understand the caffeine content of different Mountain Dew flavors. This will help you make informed decisions about which varieties to consume.
12.3. Consulting Healthcare Professionals
If you have any concerns about caffeine consumption, consult with a healthcare professional. They can provide personalized advice based on your individual health needs and conditions.
Navigating the world of caffeinated beverages requires a clear understanding of caffeine levels and their potential effects. By considering factors like recommended daily intake, individual health conditions, and strategies for managing caffeine consumption, you can enjoy Mountain Dew responsibly and make informed choices about your beverage habits.
Are you struggling to manage your caffeine intake or experiencing adverse effects from caffeinated beverages? Do you have questions about how caffeine interacts with your specific health conditions? At HOW.EDU.VN, our team of over 100 distinguished PhDs are available to provide expert guidance and personalized advice. Don’t navigate these concerns alone.
Contact us today for a consultation:
- Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
- Website: HOW.EDU.VN
Let the experts at how.edu.vn help you optimize your health and well-being.
FAQ: Deciphering Caffeine Content in Mountain Dew
Still curious about caffeine levels in Mountain Dew? Here are some frequently asked questions to help you stay informed.
1. Is there caffeine in all Mountain Dew flavors?
No, not all Mountain Dew flavors contain caffeine. Caffeine-Free Diet Mountain Dew is available, offering the same taste without the stimulant. This option is ideal for those looking to avoid caffeine for health reasons or personal preference.
2. How much caffeine is too much in a day?
For most healthy adults, up to 400 milligrams of caffeine per day is considered safe. This is roughly equivalent to four cups of coffee or seven 12-ounce cans of Mountain Dew. However, this amount can vary depending on individual factors such as age, weight, and overall health.
3. Can Mountain Dew affect my sleep?
Yes, consuming Mountain Dew, especially close to bedtime, can disrupt your sleep patterns. Caffeine is a stimulant that can keep you awake and reduce the quality of your sleep. It’s best to avoid caffeinated beverages several hours before going to bed to ensure a restful night’s sleep.
4. What are the signs of caffeine overdose?
Signs of caffeine overdose include anxiety, insomnia, increased heart rate, upset stomach, and headaches. In severe cases, it can lead to more serious symptoms such as confusion, hallucinations, and difficulty breathing. If you experience these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
5. Is Mountain Dew safe for children?
Pediatricians generally advise against caffeine consumption for children. Caffeine can negatively impact their sleep patterns, anxiety levels, and overall development. It’s best to offer children caffeine-free alternatives.
6. Can I become addicted to caffeine from Mountain Dew?
Yes, any drink high in caffeine can potentially lead to caffeine addiction. Because it’s a stimulant, caffeine activates the reward centers in your brain. As a result, regular consumption can lead to physical dependence. Symptoms of caffeine addiction include an inability to reduce or control caffeine consumption and withdrawal symptoms like headaches, depression, and anxiety.
7. What happens if I mix Mountain Dew and alcohol?
Mixing Mountain Dew with alcohol can mask the intoxicating effects of alcohol, leading you to overindulge and increase the risk of alcohol poisoning. Additionally, the combination can contribute to dehydration and cause a more severe hangover.
8. Is diet Mountain Dew a healthier option due to lower sugar content?
While diet Mountain Dew is lower in sugar, it still contains caffeine and artificial additives that can have health implications. It’s important to consider the overall health impact and consume it in moderation.
9. Does caffeine content change if Mountain Dew is stored for a long time?
Under normal storage conditions, caffeine content remains relatively stable. Extreme temperatures and prolonged exposure to light might cause minor degradation, but this is generally minimal.
10. Are there natural sources of caffeine that are healthier than Mountain Dew?
Yes, natural sources of caffeine, such as green tea and yerba mate, offer additional health benefits due to their antioxidant content and other beneficial compounds. These options can provide a more balanced and nutritious way to consume caffeine.
