COBRA (Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act) insurance can be a financial lifeline when you lose your job-based health insurance. How much does COBRA insurance cost? It’s crucial to understand the costs involved and explore alternative options, which can often be more affordable; that’s where HOW.EDU.VN steps in to guide you. We help you navigate the complexities of healthcare coverage and find solutions that fit your budget and health needs. COBRA premiums, healthcare marketplace, and affordable coverage are key considerations.
1. Understanding COBRA Insurance: What Is It and How Does It Work?
COBRA (Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act) insurance allows you to temporarily continue your employer-sponsored health plan after leaving a job. It ensures continuous health coverage for a limited period. COBRA acts as a bridge between jobs, providing essential coverage during transitions.
1.1. The Basics of COBRA
COBRA insurance provides a temporary extension of your health benefits, typically lasting up to 18 months. This extension applies to the health plan you had while employed. According to the U.S. Department of Labor, COBRA covers group health plans maintained by employers with 20 or more employees in the prior year. COBRA is not free; you must pay the full premium, including what your employer previously covered, plus a 2% administrative fee.
1.2. Who Is Eligible for COBRA?
Eligibility for COBRA requires participation in an employer-sponsored health plan and a qualifying event. Common qualifying events include job loss, reduction in work hours, divorce, or death of a covered employee. The Department of Labor specifies that COBRA rights extend to employees, their spouses, and dependent children. However, eligibility may be lost if you become covered under another group health plan or Medicare.
1.3. How Long Does COBRA Coverage Last?
In most cases, COBRA coverage lasts for 18 months from the date of the qualifying event. Certain situations, such as disability, may extend the coverage to 29 months. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) outline specific conditions for extending COBRA coverage, emphasizing the need for timely notifications and proper documentation.
1.4. When Is the Deadline to Sign Up for COBRA?
You generally have 60 days from the date you receive the COBRA election notice to enroll. The election notice must be sent within 44 days of the qualifying event. Missing this deadline forfeits your right to COBRA coverage. It’s crucial to act promptly to ensure continuous coverage.
2. Decoding the Cost of COBRA Insurance: What to Expect
COBRA insurance costs can be surprisingly high due to the full premium payment plus administrative fees. Understanding these costs helps in evaluating alternatives. Premiums, administrative fees, and cost comparison are essential factors to consider.
2.1. Calculating Your COBRA Premium
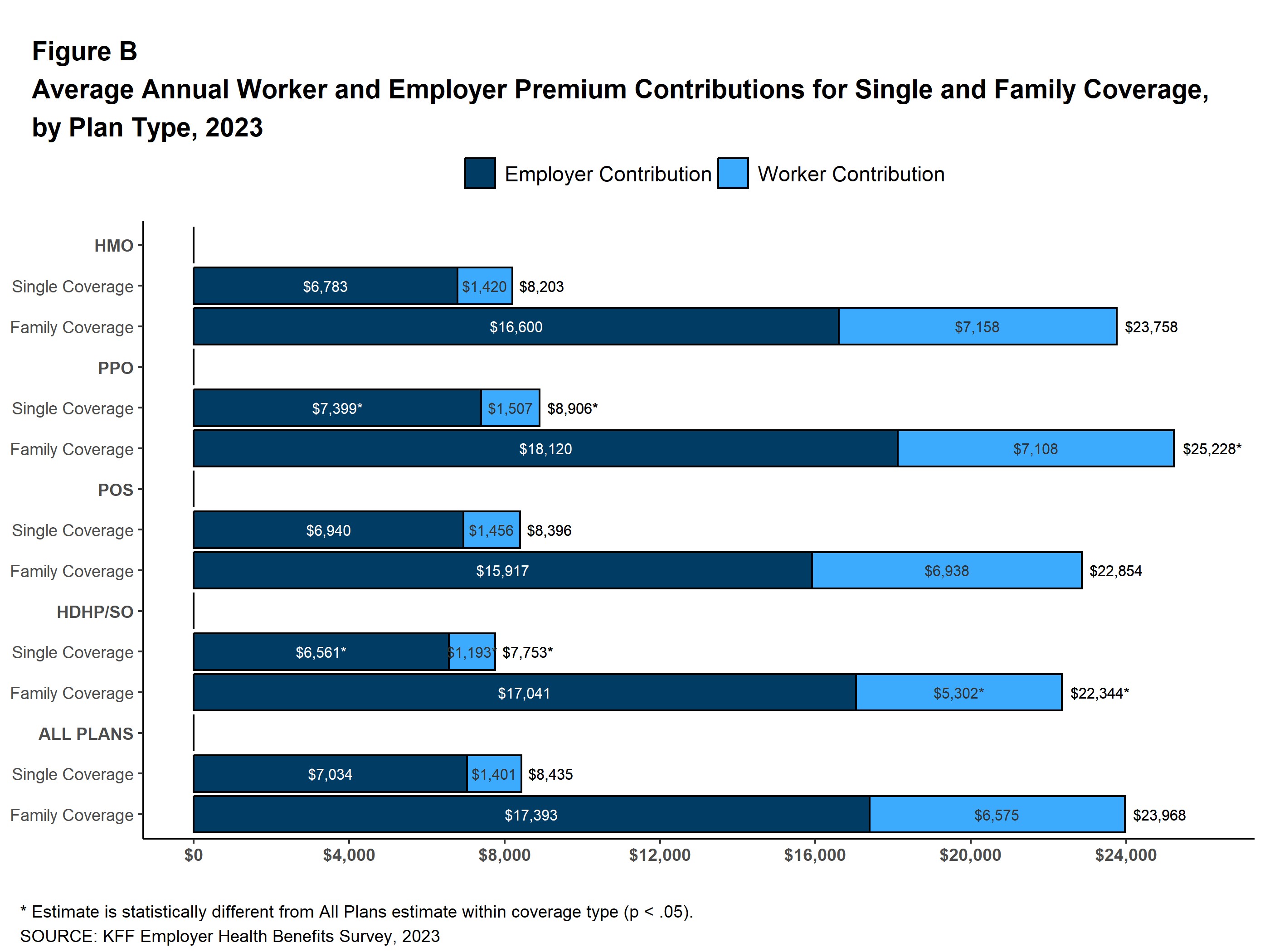
Your COBRA premium includes the total cost of your health insurance plan, which was previously shared with your employer, plus a 2% administrative fee. According to a 2023 Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF) study, the average annual premium for employer-sponsored health insurance was $8,435 for individual coverage and $23,968 for family coverage. With COBRA, you pay the entire amount, making it significantly more expensive.
2.2. Factors Influencing COBRA Costs
Several factors influence the cost of COBRA, including the type of health plan (HMO, PPO, etc.), the scope of coverage, and the number of covered family members. Plans with broader coverage and lower deductibles typically have higher premiums. The geographic location of the plan can also impact costs due to regional healthcare expenses.
2.3. Comparing COBRA to Employer-Sponsored Insurance Costs
The cost difference between COBRA and employer-sponsored insurance is significant because employers typically cover a substantial portion of the premium. For example, employers covered an average of $7,034 of the individuals’ premium and $17,393 for families in 2023, according to KFF. With COBRA, you bear the full financial burden, making it crucial to explore more affordable alternatives.
2.4. Examples of COBRA Cost Scenarios
Individual Coverage:
- Employer-sponsored premium: $8,435 annually ($703 monthly).
- COBRA premium: $703 + 2% administrative fee = approximately $717 monthly.
Family Coverage:
- Employer-sponsored premium: $23,968 annually ($1,997 monthly).
- COBRA premium: $1,997 + 2% administrative fee = approximately $2,037 monthly.
These examples illustrate the substantial cost difference when transitioning to COBRA coverage.
3. Real-World COBRA Cost Examples: Case Studies and Analysis
Analyzing real-world examples provides a clearer understanding of COBRA costs and alternatives. These case studies highlight the financial implications and decision-making process. Case studies, financial analysis, and alternative comparisons provide a thorough overview.
3.1. Case Study 1: John’s Job Loss
John, a 45-year-old marketing manager, lost his job and faced the decision of whether to elect COBRA coverage. His employer-sponsored health plan cost $600 per month, with the employer covering 70% of the premium. Under COBRA, John would have to pay the full $600 plus a 2% administrative fee, totaling $612 per month. John explored marketplace options and found a similar plan for $450 per month with a tax subsidy, making it a more affordable choice.
3.2. Case Study 2: Maria’s Divorce
Maria, a 38-year-old teacher, went through a divorce and lost coverage under her spouse’s health plan. COBRA would cost her $800 per month. After consulting with HOW.EDU.VN, she discovered a health share plan for $350 per month, providing comparable coverage at a significantly lower cost. This option allowed Maria to maintain her health coverage without straining her budget.
3.3. Financial Analysis of COBRA vs. Alternatives
A financial analysis comparing COBRA to alternative options like marketplace plans and health share plans reveals potential cost savings. The table below illustrates the differences:
| Coverage Type | Monthly Premium | Additional Costs |
|---|---|---|
| COBRA | $600 – $800 | 2% admin fee |
| Marketplace Plan | $400 – $600 | Potential subsidy |
| Health Share Plan | $300 – $500 | Membership fees |
3.4. Expert Opinions on COBRA Costs
According to healthcare finance expert Dr. Emily Carter, “COBRA is often a necessary but expensive option. Exploring alternatives like marketplace plans and health share plans can lead to substantial savings while maintaining adequate coverage.” Experts at HOW.EDU.VN emphasize the importance of assessing individual needs and financial situations before making a decision.
 Cobra Cost Analysis
Cobra Cost Analysis
4. Comprehensive Guide to COBRA Insurance Alternatives: Affordable Options
Exploring alternatives to COBRA insurance can lead to more affordable and suitable coverage options. Marketplace plans, spousal coverage, and health share plans are viable alternatives. Marketplace plans, Medicaid, and health share plans offer diverse options.
4.1. Marketplace Health Insurance Plans
Marketplace health insurance plans, available through the Affordable Care Act (ACA) exchanges, often provide more affordable coverage than COBRA. These plans offer subsidies based on income, reducing monthly premiums. The Kaiser Family Foundation provides detailed information on marketplace plan options and eligibility for subsidies.
4.2. Medicaid and CHIP Programs
Medicaid and the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) offer low-cost or free health coverage to eligible individuals and families. Eligibility is based on income and household size. These programs ensure access to essential healthcare services for those who qualify. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) provide resources for determining eligibility and enrolling in these programs.
4.3. Spousal or Family Member Coverage
If your spouse or another family member has employer-sponsored health insurance, you may be able to join their plan. Job loss is typically a qualifying event that allows you to enroll outside the standard open enrollment period. Enrolling in a family member’s plan can provide comprehensive coverage at a lower cost than COBRA.
4.4. Health Share Plans
Health share plans are membership-based organizations where members share healthcare costs. These plans are often more affordable than traditional insurance but may have limitations on covered services. The Health Resources & Services Administration (HRSA) provides information on health share plans and their regulatory status.
4.5. Short-Term Health Insurance
Short-term health insurance plans offer temporary coverage for a limited duration, typically a few months. These plans are useful for bridging gaps in coverage but may not cover pre-existing conditions. The National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) provides guidance on short-term health insurance plans and their limitations.
5. Navigating the COBRA Enrollment Process: Step-by-Step Guide
Enrolling in COBRA involves several steps, from receiving the election notice to making timely payments. Understanding this process ensures a smooth transition. Election notice, enrollment deadlines, and payment schedules are crucial aspects.
5.1. Receiving the COBRA Election Notice
After a qualifying event, your employer must provide you with a COBRA election notice within 44 days. This notice explains your rights and options under COBRA, including the cost of coverage and enrollment deadlines. Review the notice carefully to understand your responsibilities.
5.2. Understanding Enrollment Deadlines
You have 60 days from the date of the election notice to decide whether to enroll in COBRA. Missing this deadline means forfeiting your right to COBRA coverage. It’s essential to act promptly to ensure continuous health coverage.
5.3. Completing the Enrollment Forms
To enroll in COBRA, you must complete and return the enrollment forms provided with the election notice. Ensure all information is accurate and submit the forms before the deadline. Keep a copy of the completed forms for your records.
5.4. Making Your First Payment
Your first COBRA payment is due within 45 days of electing coverage. This payment covers the period from the date your previous coverage ended. Late payments can result in the termination of your COBRA coverage.
5.5. Maintaining Continuous Coverage
To maintain continuous COBRA coverage, you must make timely monthly payments. COBRA coverage can be terminated for non-payment or if you become eligible for other group health insurance or Medicare.
6. Expert Tips for Managing COBRA Costs: Practical Strategies
Managing COBRA costs effectively requires careful planning and informed decision-making. Negotiating premiums, exploring subsidies, and using HSAs can help. Premium negotiation, subsidy eligibility, and HSA utilization are effective strategies.
6.1. Negotiating COBRA Premiums
While negotiating COBRA premiums directly isn’t typically possible, understanding how premiums are calculated can help you anticipate costs. Also, knowing your rights and ensuring the premium calculation is accurate is crucial.
6.2. Checking Eligibility for Premium Subsidies
Explore eligibility for premium subsidies through the ACA marketplace. Subsidies can significantly reduce monthly premiums, making marketplace plans more affordable than COBRA.
6.3. Utilizing Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
If you have a Health Savings Account (HSA), you can use it to pay COBRA premiums. HSAs offer tax advantages for healthcare expenses, including COBRA premiums. The IRS provides guidance on HSA eligibility and usage.
6.4. Seeking Professional Financial Advice
Consulting with a financial advisor can provide personalized strategies for managing healthcare costs. Advisors can help you assess your financial situation and explore cost-effective coverage options.
6.5. Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can reduce healthcare costs by minimizing the need for medical services. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and preventive care can contribute to overall well-being and lower healthcare expenses.
7. Common Mistakes to Avoid with COBRA Insurance: Expert Advice
Avoiding common mistakes ensures you maximize the benefits of COBRA or choose a better alternative. Missing deadlines, neglecting alternatives, and misunderstanding coverage are critical errors. Missed deadlines, neglecting alternatives, and inaccurate information can lead to problems.
7.1. Missing Enrollment Deadlines
Missing the 60-day enrollment deadline is a common mistake that can result in losing your right to COBRA coverage. Always mark the deadline on your calendar and act promptly to ensure continuous coverage.
7.2. Neglecting to Explore Alternative Options
Failing to explore alternative coverage options like marketplace plans, Medicaid, or health share plans can lead to paying unnecessarily high COBRA premiums. Always compare options to find the most affordable and suitable coverage.
7.3. Misunderstanding COBRA Coverage Details
Misunderstanding the details of your COBRA coverage, such as covered services and limitations, can lead to unexpected out-of-pocket costs. Review the COBRA election notice and plan documents carefully to understand your coverage.
7.4. Not Keeping Records of Payments
Not keeping records of COBRA payments can lead to disputes with the insurance provider. Always retain copies of payment confirmations and bank statements to verify your payments.
7.5. Ignoring Changes in Circumstances
Ignoring changes in circumstances, such as becoming eligible for other group health insurance or Medicare, can result in overpaying for COBRA coverage. Notify your COBRA provider of any changes in your eligibility to avoid unnecessary costs.
8. Maximizing Your Healthcare Coverage During Transitions: Strategic Planning
Strategic planning ensures you maintain optimal healthcare coverage during job transitions or other life events. Assessing needs, understanding options, and seeking expert advice are key. Needs assessment, options evaluation, and expert consultation support informed decisions.
8.1. Assessing Your Healthcare Needs
Before making any decisions, assess your healthcare needs and those of your family. Consider factors like chronic conditions, prescription medications, and anticipated medical expenses.
8.2. Understanding Your Coverage Options
Thoroughly understand your coverage options, including COBRA, marketplace plans, Medicaid, and health share plans. Compare the costs, benefits, and limitations of each option to find the best fit for your needs.
8.3. Seeking Expert Advice from HOW.EDU.VN
Consult with experts at HOW.EDU.VN to receive personalized guidance on navigating healthcare coverage during transitions. Our team can help you assess your needs, evaluate your options, and make informed decisions. You can reach us at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States, or via WhatsApp at +1 (310) 555-1212.
8.4. Planning for Future Healthcare Needs
Consider your long-term healthcare needs and plan accordingly. Evaluate the potential for future medical expenses and choose a coverage option that provides adequate protection.
8.5. Regularly Reviewing Your Coverage
Regularly review your healthcare coverage to ensure it continues to meet your needs. Changes in your health, financial situation, or coverage options may warrant adjusting your plan.
9. The Future of COBRA Insurance: Trends and Predictions
Understanding the future trends of COBRA insurance helps in making informed decisions about healthcare coverage. Policy changes, technological advancements, and economic factors play a role. Policy changes, technological advancements, and economic factors are key influences.
9.1. Potential Policy Changes
Changes in healthcare policy could impact the availability and cost of COBRA insurance. Monitor legislative developments and regulatory updates to stay informed about potential changes.
9.2. Impact of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements in healthcare, such as telemedicine and digital health tools, could influence the delivery and cost of healthcare services. Consider how these advancements may affect your coverage needs and options.
9.3. Economic Factors Affecting COBRA Costs
Economic factors like inflation and healthcare costs can impact the premiums for COBRA insurance. Stay informed about economic trends and their potential effects on your coverage costs.
9.4. The Role of Healthcare Reform
Healthcare reform initiatives could reshape the landscape of health insurance coverage, including COBRA. Understand how these initiatives may affect your coverage options and eligibility for subsidies.
9.5. Predictions for COBRA Insurance
Experts predict that COBRA insurance will continue to be a valuable option for those transitioning between jobs, but alternatives like marketplace plans and health share plans will become increasingly popular due to their affordability and flexibility.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About COBRA Insurance Costs
Addressing common questions about COBRA insurance costs provides clarity and empowers informed decision-making. Coverage duration, payment options, and cost factors are frequent inquiries.
10.1. How Long Do I Have to Elect COBRA Coverage?
You have 60 days from the date of the election notice to decide whether to enroll in COBRA.
10.2. When Is My First COBRA Payment Due?
Your first COBRA payment is due within 45 days of electing coverage.
10.3. Can I Pay My COBRA Premiums Monthly?
Yes, you can pay your COBRA premiums monthly to maintain continuous coverage.
10.4. What Happens If I Miss a COBRA Payment?
Missing a COBRA payment can result in the termination of your coverage.
10.5. Is COBRA Coverage Retroactive?
Yes, COBRA coverage is retroactive to the date your previous coverage ended, provided you elect and pay for coverage within the deadlines.
10.6. Can I Cancel COBRA Coverage If I Find Another Plan?
Yes, you can cancel COBRA coverage if you find another health insurance plan.
10.7. Are There Subsidies Available for COBRA Premiums?
There are generally no subsidies available for COBRA premiums, but you may be eligible for subsidies through the ACA marketplace.
10.8. What Are the Alternatives to COBRA Insurance?
Alternatives to COBRA include marketplace plans, Medicaid, health share plans, and spousal coverage.
10.9. How Does COBRA Coverage Compare to Marketplace Plans?
COBRA coverage is often more expensive than marketplace plans, but it provides the same coverage you had under your employer-sponsored plan.
10.10. Where Can I Find More Information About COBRA Insurance?
You can find more information about COBRA insurance on the Department of Labor website or by consulting with experts at HOW.EDU.VN.
Losing health insurance can be stressful, but understanding your options, especially How Much Cobra Insurance Costs, empowers you to make informed decisions. At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with leading experts who can provide personalized advice and support, ensuring you find the best healthcare coverage for your needs. Our team of over 100 renowned PhDs are ready to assist you with any questions or concerns. Don’t navigate this complex landscape alone – contact us today at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States, or via WhatsApp at +1 (310) 555-1212, and let HOW.EDU.VN guide you to the right healthcare solutions. Visit how.edu.vn for more information.