Are you considering pursuing a master’s degree and wondering about the financial implications? The cost of a master’s degree can vary significantly, but HOW.EDU.VN is here to provide expert guidance. This article breaks down the expenses associated with advanced education, offering insights into tuition, fees, and other related costs. Get clarity on financing your future and discover strategies to manage your investment in higher education with expert advice.
1. What Is the Average Cost of a Master’s Degree?
The average cost of a master’s degree typically ranges from $44,640 to $71,140, according to EducationData.org. However, this figure can vary significantly based on factors like the institution (public vs. private), the specific field of study, and the program’s duration. Understanding these variables is crucial for budgeting and financial planning.
The cost of a master’s degree is a significant investment. To make an informed decision, it’s essential to consider:
- Type of Institution: Public universities generally offer lower tuition rates than private institutions, especially for in-state residents.
- Field of Study: Certain fields, such as business or law, often have higher tuition rates due to the specialized resources and faculty involved.
- Program Length: Most master’s programs take one to two years to complete, but accelerated or part-time programs can affect the overall cost.
2. How Much Does a Master’s Degree in Education Cost?
A master’s degree in education typically costs around $44,640, making it one of the more affordable options for graduate studies. This lower cost can be attributed to the high demand for educators and various funding opportunities available to them.
Several factors influence the affordability of a master’s in education:
- Public vs. Private Institutions: Public universities often provide lower tuition rates for education programs.
- Financial Aid and Scholarships: Many scholarships and grants are specifically targeted at educators, reducing the overall cost.
- Loan Forgiveness Programs: Teachers working in public or disadvantaged districts may qualify for federal loan forgiveness programs.
Many universities offer specialized programs that provide financial assistance. According to a report by the American Association of Colleges for Teacher Education (AACTE), targeted financial aid programs significantly reduce the burden of educational debt for teachers, encouraging more individuals to pursue advanced degrees in education.
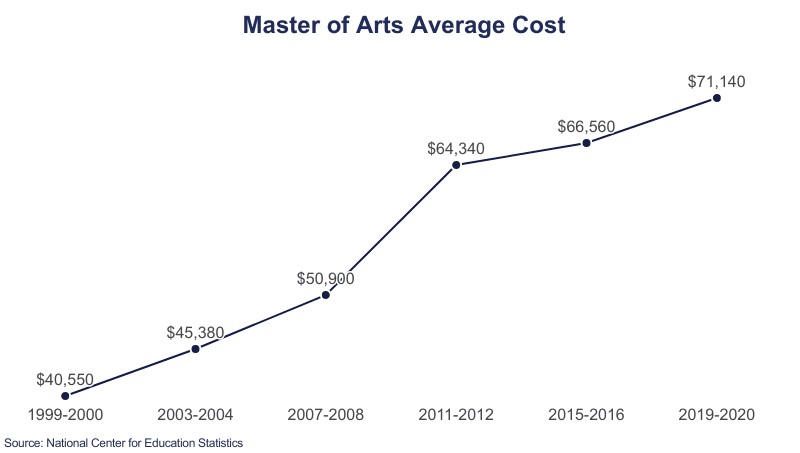
3. What Is the Cost of a Master’s Degree in Arts?
The average cost of a Master’s degree in Arts is generally higher, around $71,140. This reflects the diverse range of disciplines within the arts, including history, literature, and languages, each with its unique resource requirements.
Understanding the costs associated with a Master of Arts involves:
- Program Specifics: Costs can vary widely between different art programs (e.g., creative writing vs. art history).
- Resource Needs: Programs requiring specialized equipment or studio space may have higher fees.
- Financial Aid Availability: The availability of financial aid can vary depending on the specific program and institution.
4. What Are the Expenses for a Master’s Degree in Science?
A Master’s degree in Science typically costs about $61,380. This cost aligns with the resources and facilities needed for STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) programs.
When budgeting for a Master of Science degree, consider these factors:
- Laboratory Fees: Science programs often require laboratory access, which incurs additional fees.
- Technology Requirements: Specific software or equipment may be necessary for coursework or research.
- Career Prospects: STEM graduates often secure high-paying jobs, helping to offset the cost of their education.
5. What is the Cost of an MBA (Master of Business Administration)?
The average cost of a Master of Business Administration (MBA) is approximately $60,410. MBA programs are highly competitive, and the cost can vary significantly depending on the school’s reputation and resources.
To understand MBA costs, consider the following:
- School Reputation: Top-tier business schools often charge higher tuition due to their prestige and networking opportunities.
- Program Length: Full-time MBA programs typically last two years, while part-time or executive programs may have different durations and costs.
- Networking Opportunities: The value of an MBA often lies in the networking opportunities it provides, which can justify the higher cost.
According to a study by the Graduate Management Admission Council (GMAC), MBA graduates often see a significant return on investment (ROI) through higher salaries and career advancement, making the degree a worthwhile investment.
6. What Are the Additional Costs Associated With a Master’s Degree?
Beyond tuition and fees, there are several additional costs to consider when pursuing a master’s degree, including living expenses, books, and transportation. Budgeting for these expenses is essential for a realistic financial plan.
Additional costs can include:
- Living Expenses: Housing, food, and utilities can significantly impact your budget, especially if you are moving to a new city.
- Books and Supplies: Textbooks and other academic materials can be costly.
- Transportation: Commuting to campus or traveling for research can add to your expenses.
7. How Does the Cost of a Master’s Degree Vary Between Public and Private Schools?
The cost of a master’s degree varies significantly between public and private schools. Public schools generally offer lower tuition rates, especially for in-state residents, while private schools tend to have higher tuition costs regardless of residency.
Key differences in cost include:
- Public Schools: Average cost of a master’s degree is around $51,740. These institutions often receive state funding, allowing them to offer lower tuition rates.
- Private Schools: Average cost of a master’s degree is around $62,550. Private schools rely more on tuition revenue and endowments, resulting in higher costs.
- Residency Status: Public schools typically offer lower tuition rates for in-state residents, while private schools usually charge the same tuition for all students.
8. How Can I Finance My Master’s Degree?
Financing a master’s degree requires careful planning and exploring various funding options, including scholarships, grants, loans, and employer sponsorship.
Consider these strategies:
- Scholarships and Grants: Research and apply for scholarships and grants from universities, private organizations, and government agencies.
- Student Loans: Federal and private student loans can help cover tuition and living expenses.
- Employer Sponsorship: Some employers offer tuition reimbursement or sponsorship programs for employees pursuing advanced degrees.
9. What Are the Costs Based on Race to Obtain a Master’s Degree?
The cost of a master’s degree can disproportionately affect different racial groups. Studies have shown that Black graduates are more likely to accrue graduate school debt compared to their White counterparts.
Key findings include:
- Debt Disparities: Black graduate students are roughly 47.8% more likely to acquire graduate school debt.
- Enrollment Trends: From 2004 to 2012, Black enrollment in for-profit colleges increased significantly, often leading to higher debt burdens.
- Borrowing Patterns: Asian students are more likely to borrow from private loan programs or use savings, while Black and Hispanic students rely more on federal loans.
The Brookings Institute and the American Council on Education have conducted studies highlighting these disparities, emphasizing the need for targeted financial support for underrepresented groups.
10. What is the Cost of a Master’s Degree vs. the Potential Salary Increase?
While the cost of a Master’s degree is significant, it’s essential to weigh that against the potential increase in salary and career opportunities that may result. The ROI (return on investment) of a Master’s degree varies by field, but generally, those with advanced degrees earn more over their career.
The salary increase you can expect will be affected by the following:
- Field of Study: Certain fields, such as business and technology, often see a higher salary increase with a Master’s degree.
- Job Market: The demand for specific skills in the job market can influence the salary you can command.
- Experience: Combining a Master’s degree with relevant work experience can significantly boost your earning potential.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, individuals with a Master’s degree typically earn more than those with only a Bachelor’s degree, highlighting the long-term financial benefits of advanced education.
11. What Are Some Master’s Degree Programs with a High ROI?
Some master’s degree programs offer a higher return on investment (ROI) than others due to high demand and earning potential in those fields. These programs often lead to lucrative career paths that can offset the cost of education more quickly.
Here are a few programs with a high ROI:
- Master of Business Administration (MBA): MBA graduates often secure high-paying positions in management and leadership roles.
- Master of Science in Computer Science: With the growing demand for tech professionals, this degree can lead to lucrative careers in software development, data science, and cybersecurity.
- Master of Engineering: Engineering graduates are highly sought after in various industries, offering strong earning potential.
These programs often provide specialized skills and knowledge that are highly valued by employers, leading to increased earning potential.
12. What is the Expected Debt After Getting a Master’s Degree?
The amount of debt graduates hold after obtaining a Master’s degree can vary significantly. Several factors, including the type of program, the cost of living, and the availability of financial aid, influence the total debt burden.
Here are some general statistics regarding debt after a Master’s degree:
- Student Loan Debt: On average, individuals with a Master’s degree hold around $46,798 in student loan debt.
- Credit Card Debt: Master’s degree holders may also carry credit card debt, averaging around $8,115.
- Other Debts: Graduates may have other debts, such as auto loans and mortgages, adding to their overall financial obligations.
Understanding the potential debt burden is crucial for making informed decisions about pursuing a Master’s degree.
13. What kind of financial assistance should I seek for a Master’s Degree?
When pursuing a Master’s degree, several forms of financial assistance can help alleviate the cost burden. Exploring these options can significantly reduce the amount you need to borrow or pay out of pocket.
Some of the key types of financial assistance to consider include:
- Scholarships: Merit-based or need-based awards that do not need to be repaid.
- Grants: Typically need-based awards, often from the government or universities, that do not require repayment.
- Fellowships: Awards often given to graduate students to support research or teaching.
- Student Loans: Federal or private loans that must be repaid with interest.
- Work-Study Programs: Part-time jobs offered through the university to help students earn money for expenses.
14. How Do Online Master’s Degree Programs Compare in Cost to On-Campus Programs?
Online Master’s degree programs can offer a more affordable alternative to traditional on-campus programs. While tuition costs may be similar, online programs often eliminate or reduce expenses related to commuting, housing, and campus fees.
Here’s a comparison of the costs associated with online vs. on-campus programs:
- Tuition: Online programs may have slightly lower tuition rates.
- Fees: Online programs typically have fewer fees, such as campus recreation or transportation fees.
- Living Expenses: Online students can save on housing and commuting costs.
- Flexibility: Online programs offer more flexibility, allowing students to work while studying.
15. What are the tax benefits of pursuing a master’s degree?
Pursuing a Master’s degree may qualify you for various tax benefits, which can help reduce the overall cost of your education. These benefits are designed to support individuals investing in their education.
Some of the key tax benefits to consider include:
- American Opportunity Tax Credit (AOTC): For the first four years of higher education.
- Lifetime Learning Credit (LLC): For all years of higher education.
- Student Loan Interest Deduction: Allows you to deduct the interest paid on student loans.
- Tuition and Fees Deduction: Although this deduction has expired, it may be reinstated in the future.
Consulting a tax professional can help you determine which benefits you are eligible for and how to claim them.
Ready to take the next step in your education but feeling overwhelmed by the costs? At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with top-tier PhDs and experts who can provide personalized advice on funding your master’s degree. From navigating financial aid options to understanding the ROI of different programs, our experts are here to guide you.
Don’t let financial concerns hold you back from achieving your academic goals.
Connect With Our Experts Today:
- Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
- Website: HOW.EDU.VN
Take control of your future and make informed decisions with how.edu.vn. Contact us now to start your journey toward a successful and affordable master’s degree.