Discovering the expenses associated with an alternator replacement doesn’t have to be a mystery. The cost of a new alternator can vary widely based on several factors, but with the right information, you can navigate this expense effectively. At HOW.EDU.VN, we connect you with leading experts who can provide clarity and guidance on understanding alternator costs and ensuring you get the best value for your vehicle’s needs. Connect with our Doctors for detailed consultation and explore optimal solutions tailored to your needs, ensuring peace of mind and informed decision-making.
1. What Factors Influence the Cost of an Alternator?
The price of an alternator isn’t just a random number; it’s determined by several key aspects of the part and your vehicle. Understanding these factors can help you anticipate and manage the expense effectively.
1.1. Vehicle Specifications
The year, make, model, and engine size of your car are primary determinants of the alternator’s price. A specific alternator is designed to meet the exact electrical demands of your vehicle.
1.2. Amperage Output
The amperage of the alternator, indicating its electrical output capacity, affects the cost. Higher amperage alternators, necessary for vehicles with many electrical accessories, generally have higher material costs, such as more copper in the windings.
1.3. Mounting Style
The alternator must fit perfectly within your vehicle’s engine compartment. Due to these fitment requirements, you can’t just choose a low-cost alternator intended for a different car. It simply won’t work.
1.4. Electrical Connections
The type of electrical connections (e.g., 1-wire vs. 3-wire) can influence the price. Older cars that are considered 1-wire alternators often are lower priced, while 3-wire alternators tend to be more expensive.
1.5. Warranty Coverage
The length and scope of the warranty significantly impact the price. A new part with a 1-year warranty will be less expensive than a similar part with a lifetime warranty.
1.6. Core Availability
Alternators are often remanufactured, and the availability of cores (used alternators for rebuilding) affects the price. Rarer vehicles and options produce rarer alternators, which means there’s less cores coming back to rebuild, which means higher costs.
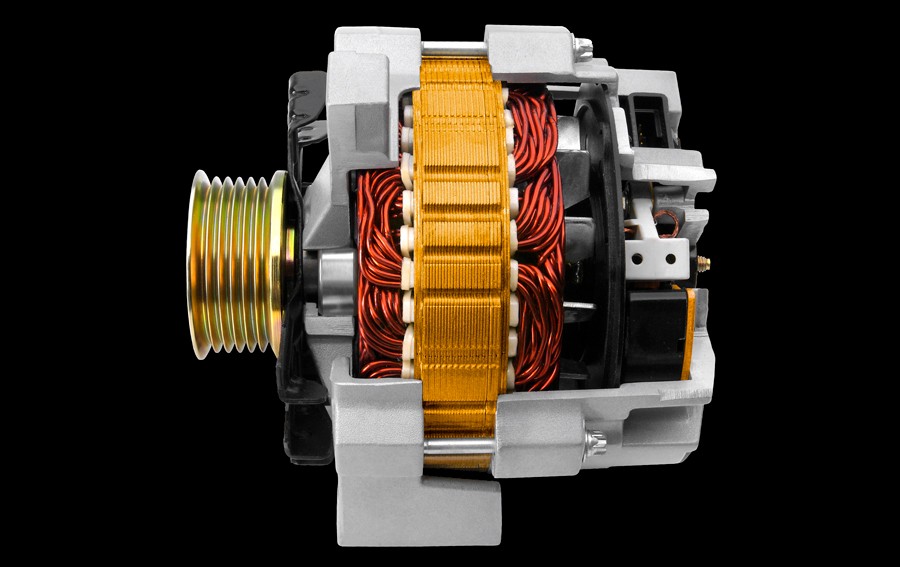 alternator cutaway
alternator cutaway
2. What Is the Role of the Alternator in a Vehicle?
To truly understand the value and necessity of a properly functioning alternator, it’s essential to know its role in your vehicle’s electrical system.
2.1. Power Supply
Cars today require a surprising amount of power. Not only are there obvious systems that need power like the radio, power windows, door locks, sunroof, and heated seats but there are modules and sensors all around as well. As an example, the anti-lock brakes usually have a wheel speed sensor at every wheel, an anti-lock brake control module, an ABS pump, and other related parts that all need constant access to power.
2.2. Battery Charging
The alternator generates enough power to deliver some back to the battery, topping up its charge. The alternator’s magnetic rotor and copper windings create an alternating current (AC), then a set of diodes in the rectifier convert it to direct current (DC), the type of electricity your car’s devices need in order to operate.
2.3. Voltage Regulation
The voltage output is regulated to prevent damage from overcharging as well as issues with too little power.
If the alternator isn’t producing between 13.5 and 14.5 volts, creating noises, or if the wrong type of current is finding its way through the alternator is failing, and it needs to be replaced.
3. What Are the Warning Signs Indicating the Need for a New Alternator?
Recognizing the symptoms of a failing alternator can save you from more extensive and costly repairs down the line.
3.1. Illuminated Battery Light
The battery light on your dashboard often indicates a charging problem. It could be undercharging or undercharging, two conditions that can be caused by a faulty alternator, among other things.
3.2. Burning Smells
A pungent burning rubber smell may be a belt slipping along the alternator pulley if it’s beginning to seize, and a burning electrical smell could be a fault inside the alternator.
3.3. Lighting Issues
You might notice your interior and exterior lights are dimmer than normal or are abnormally bright. There could be flickering as well. This can be from inconsistent voltage from the alternator.
3.4. Unusual Electrical Issues
Odd happenings in your car may not seem related to the alternator, but it’s always a possibility. Low voltage can cause slow power window motors, crackling or fading out from the radio, low fan speed, and a host of other electrical problems.
3.5. Whirring Under the Hood
All else might be working fine, but a whirring or whining noise under the hood can spell disaster for the alternator soon. Worn or corroded alternator bearings can mean a seize-up is impending.
4. Is it Safe to Drive with an Alternator Problem?
Driving with a faulty alternator can be risky. It’s essential to assess the severity of the issue and understand the potential consequences.
4.1. Short Drives
Most of the time, a short drive is fine when the alternator isn’t charging enough. The battery’s reserve power can substitute electricity, such as if you’re driving a few blocks to the repair shop.
4.2. Overcharging Risks
However, if your alternator is overcharging, it could damage computer modules, the battery, and other electronics or wiring even during a short drive.
When you detect an alternator problem, it should be a top priority to have it fixed. If you’re unsure if it’s safe to drive, play it safe and arrange a tow truck to get it to your destination.
5. How Often Should an Alternator Be Replaced?
Unlike your brake pads, tires, or even the serpentine belt, it’s tough to gauge how long an alternator will last. For some cars, it will last for the car’s lifetime while for others, it will require replacement more than once during its course of action.
5.1. Typical Lifespan
Generally speaking, an alternator should last in the range of 7 and 10 years. That may be between 100,000 and 150,000 miles.
5.2. Testing Your Alternator
If you’re questioning whether your alternator is functioning properly or you’d like to arrange to test it, an AutoZoner is an excellent resource to tap into with our free Alternator test service. And if you want to purchase a replacement alternator backed by warranty or get advice on the job, AutoZone can help – or if the job looks to be too big, check out our list of Preferred Shops in your area to help you get back on the road.
Also, if at any time the job appears to be too big, look at our list of local Preferred Shops in your area that can help you tackle the job.
6. What is the Average Cost to Replace an Alternator?
Determining the average cost to replace an alternator involves considering both the part itself and the labor required for installation.
6.1. Parts Cost
The cost of an alternator can vary greatly depending on the vehicle, the quality of the part, and whether it’s new, remanufactured, or used. On average, you might expect to pay anywhere from $100 to $500 or more for the alternator alone.
6.2. Labor Cost
Labor costs can vary widely depending on your location and the complexity of the job. Alternator replacement can range from $50 to $200, depending on the car’s complexity.
6.3. Total Cost
Combining parts and labor, the total cost to replace an alternator typically falls between $200 and $700.
7. New vs. Remanufactured Alternators: Which is Right for You?
When facing an alternator replacement, you’ll likely encounter the option of choosing between a new or a remanufactured unit.
7.1. New Alternators
New alternators are exactly what they sound like: brand new units manufactured by the original equipment manufacturer (OEM) or a third-party aftermarket company.
Pros:
- Reliability: New alternators typically offer the highest level of reliability and performance.
- Warranty: They usually come with a more extended warranty period compared to remanufactured units.
- Longevity: With proper maintenance, a new alternator can last for many years.
Cons:
- Cost: New alternators are generally more expensive than remanufactured options.
- Environmental Impact: Manufacturing new parts consumes resources and energy.
7.2. Remanufactured Alternators
Remanufactured alternators are previously used units that have been disassembled, cleaned, and rebuilt with new or refurbished components.
Pros:
- Cost: Remanufactured alternators are typically more affordable than new ones.
- Environmental Friendliness: Choosing a remanufactured part helps reduce waste and conserve resources.
- Performance: Reputable remanufacturers often replace wear items and test the unit to ensure it meets or exceeds OEM specifications.
Cons:
- Reliability: While generally reliable, remanufactured alternators may not offer the same level of performance or longevity as new ones.
- Warranty: The warranty period may be shorter compared to new units.
- Quality Control: The quality of remanufactured alternators can vary depending on the remanufacturer.
7.3. Making the Right Choice
When deciding between a new or remanufactured alternator, consider the following factors:
- Budget: How much are you willing to spend on the replacement?
- Vehicle Age and Condition: Is your vehicle relatively new or older? What is its overall condition?
- Driving Habits: Do you primarily drive short distances or long distances?
- Warranty Coverage: How important is warranty coverage to you?
If you’re on a tight budget and your vehicle is older, a remanufactured alternator from a reputable supplier may be a suitable option. However, if you prioritize reliability and longevity and are willing to invest more upfront, a new alternator may be the better choice.
8. What Additional Costs Should You Consider When Replacing an Alternator?
When budgeting for an alternator replacement, it’s essential to consider potential additional costs that may arise during the process.
8.1. Battery Replacement
A failing alternator can put additional strain on the battery, potentially shortening its lifespan. It’s a good idea to have your battery tested when replacing the alternator, and if it’s nearing the end of its service life, consider replacing it as well.
8.2. Serpentine Belt Replacement
The serpentine belt drives the alternator, and if it’s worn, cracked, or frayed, it should be replaced simultaneously. A worn serpentine belt can slip, causing the alternator to underperform and potentially leading to premature failure.
8.3. Pulley Replacement
The alternator pulley may need to be replaced if it’s damaged, worn, or corroded. A faulty pulley can cause the serpentine belt to slip or make noise, affecting the alternator’s performance.
8.4. Electrical Connector Repair
In some cases, the electrical connectors that attach to the alternator may be corroded or damaged, requiring repair or replacement. Damaged connectors can cause poor electrical connections, leading to alternator problems.
8.5. Diagnostic Fees
If you’re unsure whether your alternator is the source of your vehicle’s electrical problems, you may need to pay a diagnostic fee to have a mechanic inspect the system and determine the root cause.
8.6. Towing Costs
If your vehicle is not drivable due to a failing alternator, you may need to pay for towing services to get it to a repair shop.
By considering these potential additional costs, you can create a more accurate budget for your alternator replacement and avoid unexpected expenses.
9. Can You Replace an Alternator Yourself or Should You Hire a Professional?
Replacing an alternator can be a DIY project for mechanically inclined individuals, but it’s essential to assess your skills, tools, and knowledge before attempting the job.
9.1. DIY Alternator Replacement
Pros:
- Cost Savings: You can save on labor costs by replacing the alternator yourself.
- Personal Satisfaction: Completing the job yourself can be rewarding.
- Learning Opportunity: You’ll gain a better understanding of your vehicle’s electrical system.
Cons:
- Time Commitment: Replacing an alternator can take several hours, depending on your experience and the vehicle’s complexity.
- Tool Requirements: You’ll need basic tools such as wrenches, sockets, screwdrivers, and a multimeter.
- Safety Concerns: Working with electrical components can be dangerous if proper precautions are not taken.
9.2. Professional Alternator Replacement
Pros:
- Expertise: Professional mechanics have the knowledge, experience, and tools to replace alternators quickly and efficiently.
- Warranty: Reputable repair shops typically offer a warranty on their labor and parts.
- Convenience: You can drop off your vehicle and have the job done while you focus on other tasks.
Cons:
- Cost: Labor costs can add significantly to the total cost of the replacement.
- Finding a Reputable Shop: It’s essential to choose a trustworthy and experienced repair shop.
9.3. Making the Right Decision
When deciding whether to replace the alternator yourself or hire a professional, consider the following factors:
- Mechanical Skills: Are you comfortable working on cars and have experience with electrical systems?
- Tool Availability: Do you have the necessary tools to complete the job safely and effectively?
- Time Constraints: Do you have the time to dedicate to the project?
- Budget: How much are you willing to spend on the replacement?
If you’re confident in your abilities and have the necessary resources, replacing the alternator yourself can be a cost-effective option. However, if you’re unsure or prefer to leave the job to the professionals, hiring a qualified mechanic is the best choice.
10. How Can HOW.EDU.VN Help You With Your Alternator Concerns?
Navigating alternator issues doesn’t have to be a solitary journey. At HOW.EDU.VN, we provide a platform where you can connect with seasoned professionals who offer personalized advice and solutions.
10.1. Expert Consultations
Our team of Doctors are available to provide detailed consultations on alternator-related issues. Whether you’re dealing with a malfunctioning unit, unsure about replacement options, or need a second opinion, our experts can guide you every step of the way.
10.2. Personalized Guidance
Every vehicle and situation is unique. We offer tailored guidance to address your specific needs, ensuring you receive the most relevant and effective advice.
10.3. Trusted Advice
With HOW.EDU.VN, you gain access to a network of trusted professionals who are dedicated to providing accurate and reliable information. Say goodbye to guesswork and hello to clarity.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Alternator Costs
1. What is an alternator and what does it do?
An alternator is a component in your car that charges the battery and powers the electrical system when the engine is running.
2. How much does it cost to replace an alternator?
The cost can vary widely depending on the vehicle, the quality of the part, and labor costs. Expect to pay between $200 and $700.
3. How long does an alternator typically last?
An alternator generally lasts between 7 and 10 years, or about 100,000 to 150,000 miles.
4. What are the signs of a failing alternator?
Signs include a dimming or flickering battery light, dim headlights, slow or malfunctioning electrical components, and difficulty starting the vehicle.
5. Can I drive with a bad alternator?
While you may be able to drive a short distance, it’s not recommended. A failing alternator can lead to a complete loss of power and potentially damage other components.
6. Should I buy a new or remanufactured alternator?
New alternators typically offer the best reliability, while remanufactured units are more affordable. The choice depends on your budget and vehicle needs.
7. Can I replace an alternator myself?
If you have mechanical skills and the right tools, you can replace an alternator yourself. However, it’s often best to have a professional handle the job.
8. What is the warranty on a new alternator?
Warranty periods vary, but new alternators often come with a 1-year or longer warranty.
9. How do I find a reliable mechanic to replace my alternator?
Ask for recommendations, read online reviews, and look for certified mechanics with experience in electrical system repairs.
10. What additional costs should I consider when replacing an alternator?
Additional costs may include battery testing or replacement, serpentine belt replacement, and diagnostic fees.
Don’t let alternator concerns keep you in the dark. Contact the experts at HOW.EDU.VN today for personalized guidance and reliable solutions. Our team of Doctors is here to provide the clarity you need to make informed decisions. Reach out to us at 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States, Whatsapp: +1 (310) 555-1212, or visit our website at how.edu.vn.
