Community college cost is a critical factor for many students considering higher education. At HOW.EDU.VN, we understand the importance of accessible and affordable education, offering expert guidance to navigate the financial aspects of community college and explore options like tuition assistance and financial planning. Understanding the breakdown of community college expenses, including tuition fees and living expenses, can empower you to make informed decisions about your educational journey, ensuring you’re well-prepared for your academic future and career advancement.
1. What is the Average Cost of Community College Tuition?
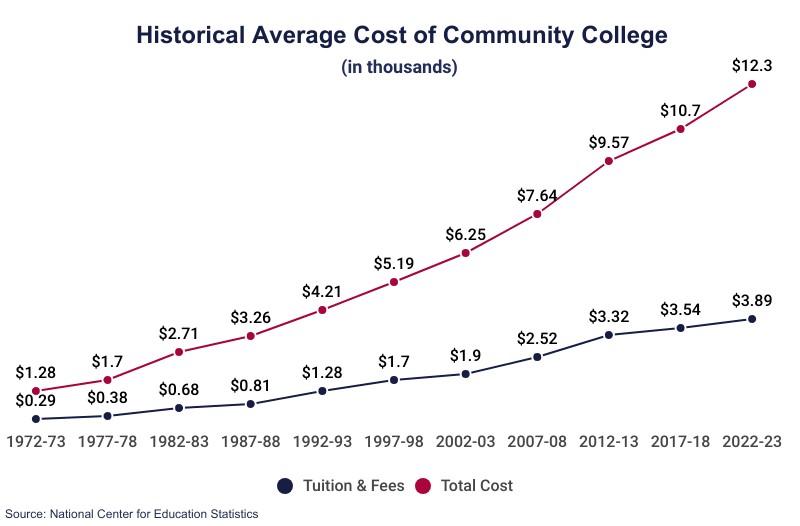
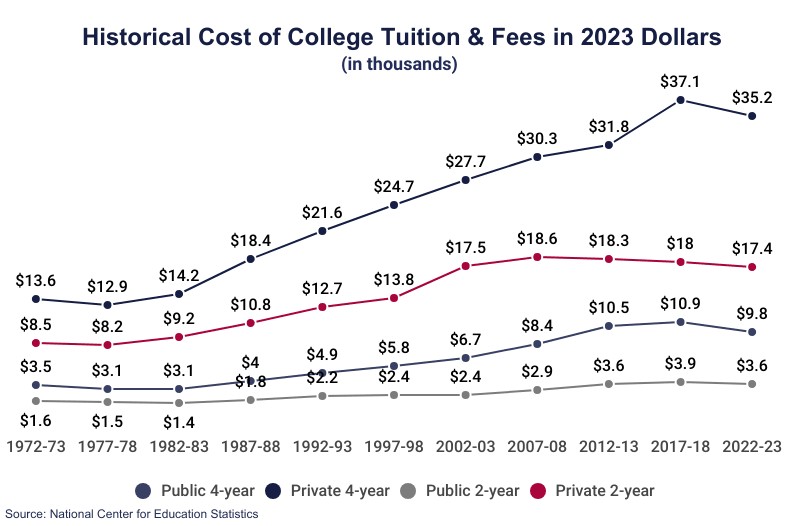
The average cost of community college tuition varies depending on several factors, including whether you’re an in-state or out-of-state student, and the specific institution you choose. On average, tuition alone for in-district community college attendance averages $3,780 per year. This figure can be a starting point for understanding your potential financial commitment, though it’s crucial to delve deeper into the specifics of your chosen college.
- In-State vs. Out-of-State Tuition: One of the most significant factors impacting community college expenses is residency. In-state students typically benefit from significantly lower tuition rates compared to their out-of-state counterparts. According to Education Data Initiative, the average community college tuition for out-of-state students is $8,990, more than double the in-state average. This difference underscores the importance of establishing residency in the state where you plan to attend community college.
- Additional Fees: Beyond tuition, it’s essential to factor in additional fees that can contribute to the overall cost of community college. These fees may include technology fees, activity fees, and other mandatory charges. While these fees may seem small individually, they can add up over time, increasing the total cost of attendance.
- Total Cost of Attendance: The total cost of attendance includes tuition, fees, books, supplies, room and board, and personal expenses. Education Data Initiative estimates the average annual cost to attend any 2-year institution at $12,917. This figure provides a more comprehensive view of the financial commitment involved in pursuing a community college education.
To gain a more accurate understanding of community college expenses, prospective students should research the specific tuition and fees associated with their chosen institutions. College websites typically provide detailed information about tuition rates, fee schedules, and cost of attendance estimates. Tools like the College Board’s Net Price Calculator can also help students estimate their out-of-pocket expenses based on their individual circumstances.
2. How Does Community College Cost Compare to Four-Year Colleges?
Comparing community college cost to that of four-year colleges reveals a significant difference, making community colleges an attractive option for students seeking affordable higher education. Community colleges generally have lower tuition rates and fees compared to four-year colleges, which can result in substantial savings over the course of a degree program.
- Tuition Disparities: One of the most significant cost differences between community colleges and four-year colleges lies in tuition rates. Education Data Initiative reports that in-state tuition at a public four-year institution averages $10,239, nearly three times the average tuition for in-district community college attendance. This disparity highlights the potential for significant savings by starting your education at a community college.
- Living Expenses: Another factor contributing to the overall cost difference is living expenses. While some community college students may choose to live on campus, many opt to live at home or with roommates, which can significantly reduce their housing costs. In contrast, students attending four-year colleges often face higher on-campus living expenses.
- Opportunity Cost: In addition to direct expenses, it’s essential to consider the opportunity cost of attending college. Community colleges often offer more flexible scheduling options, allowing students to work part-time or maintain employment while pursuing their education. This flexibility can help offset the cost of attendance and reduce reliance on student loans.
While community colleges offer significant cost advantages, it’s essential to weigh the benefits of both options carefully. Four-year colleges may provide access to more specialized programs, research opportunities, and extracurricular activities. Ultimately, the best choice depends on your individual goals, preferences, and financial circumstances.
3. What are the Additional Costs Associated with Community College?
Beyond tuition and fees, several additional costs can impact the overall affordability of community college. These expenses may include books, supplies, transportation, and personal expenses.
- Books and Supplies: Textbooks and course materials can represent a significant expense for community college students. The cost of books can vary widely depending on the courses you take and whether you choose to purchase new or used copies. Additionally, certain courses may require specialized supplies, such as art materials or lab equipment.
- Transportation: Transportation costs can also add up, especially for students who commute to campus. Whether you drive, take public transportation, or carpool, it’s essential to factor in the cost of gas, parking, and other transportation-related expenses.
- Personal Expenses: Personal expenses, such as food, clothing, and entertainment, can also impact the overall cost of community college. While these expenses may seem small individually, they can accumulate over time, especially for students living away from home.
To mitigate these additional costs, students can explore several strategies. Renting or buying used textbooks can save money on course materials. Utilizing campus resources, such as the library and computer labs, can reduce the need to purchase additional supplies. Budgeting and tracking expenses can help students manage their personal spending and avoid unnecessary costs.
4. How Does the Cost of Private vs. Public Community Colleges Differ?
The cost of private versus public community colleges can vary significantly, with private institutions generally charging higher tuition rates than their public counterparts. This difference reflects the funding models and resources available to each type of institution.
- Tuition Rates: Private community colleges typically rely on tuition revenue, endowments, and private donations to fund their operations. As a result, they often charge higher tuition rates than public community colleges, which receive funding from state and local governments.
- Financial Aid: While private community colleges may have higher tuition rates, they may also offer more generous financial aid packages. These institutions may have access to additional scholarship funds and grant programs, which can help offset the cost of attendance for eligible students.
- Program Offerings: Private community colleges may offer more specialized programs and smaller class sizes than public institutions. These factors can enhance the learning experience and provide students with personalized attention from instructors.
When considering private versus public community colleges, it’s essential to weigh the cost differences against the potential benefits. While private institutions may offer certain advantages, public community colleges often provide a more affordable option for students seeking quality education.
5. How Much Does Community College Cost Out-Of-State?
The community college cost for out-of-state students is typically significantly higher than for in-state residents. This difference reflects the fact that state governments subsidize public community colleges for the benefit of their residents.
- Higher Tuition Rates: Out-of-state students attending community colleges often pay higher tuition rates than in-state residents. This additional cost can make community college less affordable for students who do not meet residency requirements. According to Education Data Initiative, the average community college tuition for out-of-state students is $8,990.
- Residency Requirements: To qualify for in-state tuition rates, students must typically establish residency in the state where they plan to attend community college. Residency requirements vary by state but may include living in the state for a certain period, obtaining a driver’s license, and registering to vote.
- Cost Savings: Despite the higher tuition rates, community college can still be a cost-effective option for out-of-state students compared to attending a four-year college or university. By completing their general education requirements at a community college, out-of-state students can save money on tuition and fees before transferring to a four-year institution.
For out-of-state students considering community college, it’s essential to research the residency requirements and tuition rates for each institution. Exploring financial aid options, such as scholarships and grants, can also help offset the cost of attendance.
6. What Factors Influence the Cost of Community College?
Several factors can influence the cost of community college, including location, program of study, and enrollment status. Understanding these factors can help students make informed decisions about their education and financial planning.
- Location: The cost of community college can vary significantly depending on the state and region. States with higher costs of living, such as California and New York, may have higher tuition rates than states with lower costs of living.
- Program of Study: Certain programs of study, such as nursing and engineering, may have higher tuition rates due to specialized equipment and resources. Students pursuing these programs should be prepared for potentially higher costs.
- Enrollment Status: The number of credits you take per semester can also impact the cost of community college. Full-time students typically pay a flat tuition rate, while part-time students pay per credit hour. Choosing the right enrollment status can help you manage your costs effectively.
To minimize the cost of community college, students can consider attending institutions in states with lower tuition rates, choosing more affordable programs of study, and enrolling in the appropriate number of credits per semester.
7. What Financial Aid Options Are Available for Community College Students?
A variety of financial aid options are available to help community college students finance their education. These options may include grants, scholarships, loans, and work-study programs.
- Grants: Grants are typically need-based awards that do not need to be repaid. The Federal Pell Grant is one of the most common grants for community college students. Eligibility for Pell Grants is based on financial need and other factors.
- Scholarships: Scholarships are merit-based or need-based awards that do not need to be repaid. Scholarships may be offered by colleges, universities, private organizations, and government agencies.
- Loans: Loans are borrowed funds that must be repaid with interest. Federal student loans are the most common type of student loan for community college students. These loans typically offer lower interest rates and more flexible repayment options than private loans.
- Work-Study Programs: Work-study programs allow students to earn money to help pay for college expenses by working part-time on campus or at approved off-campus locations.
To access these financial aid options, students must typically complete the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA). The FAFSA is used to determine eligibility for federal, state, and institutional financial aid programs.
8. How Can Students Reduce the Cost of Community College?
There are several strategies that students can use to reduce the community college cost and make their education more affordable.
- Attend Community College In-State: As mentioned earlier, attending community college in your home state can save you a significant amount of money on tuition.
- Live at Home: Living at home while attending community college can eliminate room and board expenses, which can be a significant cost for students living away from home.
- Buy Used Textbooks: Buying used textbooks can save you money on course materials. You can often find used textbooks at your college bookstore or online.
- Apply for Scholarships and Grants: Applying for scholarships and grants can help you reduce the amount of money you need to borrow to pay for community college.
- Take Advantage of Tuition Assistance Programs: Some employers offer tuition assistance programs to help employees pay for college. Check with your employer to see if they offer this benefit.
By implementing these strategies, students can significantly reduce the cost of community college and make their education more affordable.
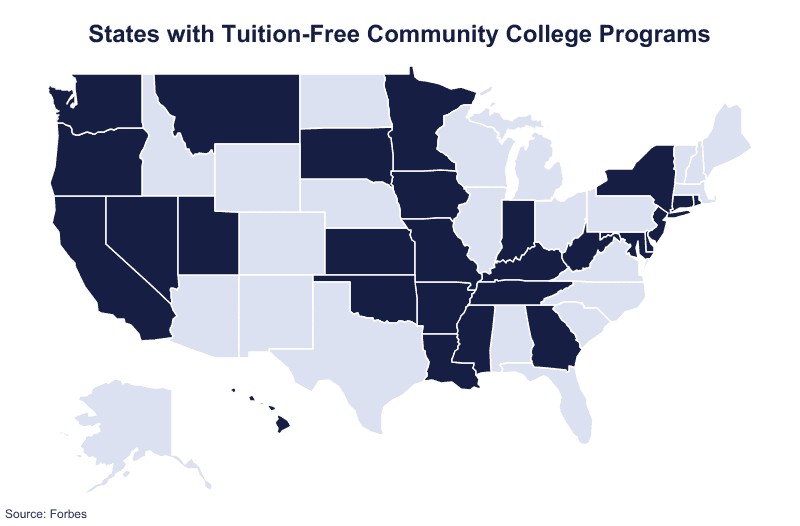
9. What is Tuition-Free Community College and Where is it Available?
Tuition-free community college programs are initiatives designed to make community college more accessible by eliminating tuition costs for eligible students. These programs may be funded by state governments, private organizations, or a combination of both.
- State Initiatives: Several states have implemented tuition-free community college programs to boost enrollment, improve workforce development, and enhance educational attainment. Examples of states with tuition-free community college programs include Delaware, California, Maryland, New York, and Montana.
- Eligibility Requirements: Eligibility requirements for tuition-free community college programs vary by state and institution. Common requirements may include residency, high school diploma or equivalent, enrollment status, and financial need.
- Benefits: Tuition-free community college programs can provide significant benefits for students, including reduced debt, increased access to higher education, and improved career prospects.
Students interested in tuition-free community college should research the programs available in their state and carefully review the eligibility requirements.
10. What are the Long-Term Benefits of Attending Community College?
Attending community college can provide numerous long-term benefits for students, including improved career prospects, increased earning potential, and enhanced personal development.
- Career Advancement: Community colleges offer a variety of career-focused programs designed to prepare students for in-demand jobs. These programs may include associate degrees, certificates, and vocational training.
- Increased Earning Potential: Studies have shown that individuals with associate degrees earn more than those with only a high school diploma. Community college graduates are also more likely to be employed and have access to better job opportunities.
- Personal Development: Community college can provide students with opportunities for personal growth and development. Students can develop critical thinking skills, improve communication skills, and gain a broader understanding of the world around them.
- Pathway to a Bachelor’s Degree: Community college can serve as a pathway to a bachelor’s degree. Students can complete their general education requirements at a community college and then transfer to a four-year college or university to complete their bachelor’s degree.
For students seeking affordable higher education and career advancement opportunities, community college can be an excellent choice.
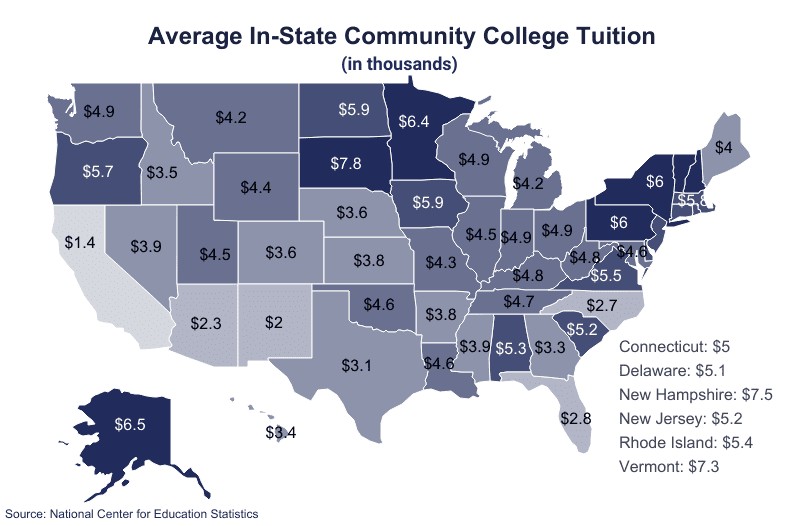
11. Community College Tuition by State
Education costs can dramatically differ from state to state. In some states, the average community college tuition can mirror that of a 4-year institution, whereas, in others, there may be a substantial difference in annual costs. For example, there is a 140% difference in cost between the states with the most and the least expensive community college systems.
| State | In-State Tuition | Out-of-State Tuition |
|---|---|---|
| Alabama | $5,290 | $9,910 |
| Alaska | $6,490 | $6,490 |
| Arizona | $2,270 | $7,820 |
| Arkansas | $3,840 | $5,410 |
| California | $1,350 | $9,810 |
| Colorado | $3,600 | $7,900 |
| Connecticut | $5,000 | $14,890 |
| Delaware | $5,122 | $9,479 |
| Florida | $2,800 | $10,180 |
| Georgia | $3,290 | $8,670 |
| Hawaii | $3,390 | $8,820 |
| Idaho | $3,530 | $8,660 |
| Illinois | $4,460 | $12,280 |
| Indiana | $4,870 | $9,380 |
| Iowa | $5,860 | $7,240 |
| Kansas | $3,830 | $5,070 |
| Kentucky | $4,820 | $16,280 |
| Louisiana | $4,590 | $5,340 |
| Maine | $3,970 | $6,990 |
| Maryland | $4,630 | $10,370 |
| Massachusetts | $5,840 | $11,170 |
| Michigan | $4,160 | $7,870 |
| Minnesota | $6,350 | $7,130 |
| Mississippi | $3,870 | $6,550 |
| Missouri | $4,280 | $8,000 |
| Montana | $4,150 | $10,210 |
| Nebraska | $3,580 | $4,520 |
| Nevada | $3,898 | $12,489 |
| New Hampshire | $7,460 | $16,120 |
| New Jersey | $5,230 | $8,990 |
| New Mexico | $2,020 | $6,940 |
| New York | $6,040 | $9,600 |
| North Carolina | $2,650 | $8,950 |
| North Dakota | $5,890 | $6,980 |
| Ohio | $4,860 | $8,710 |
| Oklahoma | $4,630 | $10,420 |
| Oregon | $5,650 | $9,610 |
| Pennsylvania | $6,000 | $13,840 |
| Rhode Island | $5,350 | $14,230 |
| South Carolina | $5,240 | $11,020 |
| South Dakota | $7,780 | $7,620 |
| Tennessee | $4,660 | $18,120 |
| Texas | $3,080 | $8,260 |
| Utah | $4,470 | $14,390 |
| Vermont | $7,270 | $14,320 |
| Virginia | $5,480 | $12,090 |
| Washington | $4,860 | $8,710 |
| West Virginia | $4,830 | $11,320 |
| Wisconsin | $4,890 | $7,020 |
| Wyoming | $4,400 | $10,490 |
12. Student Financial Aid
Financial aid is readily available to students via government, institutional, and even private organizations. For example, 55% of community college students receive some form of financial aid. It’s important to note that 22% receive student aid from their state government, and 8% receive aid directly from their community college. Also, 17% of federal work-study aid goes to community college students.
Scholarships
For many, scholarships cover the entire cost of the awardee’s education. For example, 36% of community college students receive federal grants, 29% of Pell Grants go to community college students, and 26 states offer scholarships or programs for tuition-free community college.
Student Loans
For the most part, only federal student loan data is available. Unlike students at 4-year institutions, a majority of community college students do not use student loans to pay for school. For example, 15% of community college students receive federal loans, 10% of subsidized federal loans go to community college students, and 4% of unsubsidized federal loans go to community colleges. The average amount borrowed per student at public institutions is $5,483. 61% of community college graduates leave school with no student loan debt, and among those who attended public institutions, 67.2% graduated without debt. Lastly, 79.5% of community college students attend public institutions.
Navigating the complexities of community college cost can be overwhelming. Many individuals face challenges in identifying suitable experts, managing expenses, ensuring data security, and effectively communicating their needs. HOW.EDU.VN connects you with leading experts worldwide, offering personalized guidance and cost-effective solutions.
For expert advice tailored to your unique situation, contact us today:
- Address: 456 Expertise Plaza, Consult City, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 (310) 555-1212
- Website: how.edu.vn
FAQ: Community College Costs
1. How much does community college typically cost per semester?
The cost per semester varies, but on average, tuition alone for in-district community college attendance averages $1,890.
2. Are there any states with free community college tuition?
Yes, 26 states offer a tuition-free community college education, including Delaware, California, Maryland, New York, and Montana.
3. What is the difference in cost between in-state and out-of-state community college tuition?
The average community college tuition for out-of-state students is $8,990, significantly higher than the in-state average of $3,780.
4. What are the most common forms of financial aid available to community college students?
The most common forms of financial aid include federal grants (like Pell Grants), scholarships, federal student loans, and work-study programs.
5. Is it cheaper to attend a community college or a four-year university?
Generally, community colleges are more affordable due to lower tuition rates and fees. The average tuition at a four-year public institution is $10,239, nearly three times the community college average.
6. How can I reduce the cost of attending community college?
You can reduce costs by attending in-state, living at home, buying used textbooks, applying for scholarships and grants, and taking advantage of tuition assistance programs.
7. What are the potential long-term benefits of attending community college?
Long-term benefits include improved career prospects, increased earning potential, personal development, and a pathway to a bachelor’s degree.
8. What factors can influence the overall cost of community college?
Factors that influence the cost include location, program of study, enrollment status, and whether the college is public or private.
9. Are private community colleges generally more expensive than public ones?
Yes, private community colleges typically have higher tuition rates due to their funding models.
10. What is the first step in applying for financial aid for community college?
The first step is to complete the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) to determine eligibility for various federal, state, and institutional aid programs.